Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mobile Phone Battery Charger
Uploaded by
Asad AbbasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mobile Phone Battery Charger
Uploaded by
Asad AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
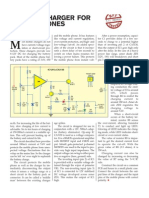
CIRCUIT IDEAS
MOBILE PHONE I THE
O
configuration and the positive DC supply
is directly connected to the charger’s out-
BATTERY CHARGER SAN
put contact, while the negative terminal
is connected through current limiting re-
sistor R2.
T.K. HAREENDRAN LED2 works as a power indicator with
resistor R1 serving as the current limiter
M
obile phone chargers available in 7.2 volts, such as Nokia 6110/6150. and LED3 indicates the charging status.
the market are quite expensive. The 220-240V AC mains supply is During the charging period, about 3 volts
The circuit presented here comes downconverted to 9V AC by transformer drop occurs across resistor R2, which turns
as a low-cost alternative to charge mobile X1. The transformer output is rectified by on LED3 through resistor R3.
telephones/battery packs with a rating of diodes D1 through D4 wired in bridge An external DC supply source (for in-
stance, from a vehicle battery) can also be
used to energise the charger, where resis-
tor R4, after polarity protection diode D5,
limits the input current to a safe value.
The 3-terminal positive voltage regulator
LM7806 (IC1) provides a constant voltage
output of 7.8V DC since LED1 connected
between the common terminal (pin 2) and
ground rail of IC1 raises the output volt-
age to 7.8V DC. LED1 also serves as a
power indicator for the external DC sup-
ply.
After constructing the circuit on a
veroboard, enclose it in a suitable cabinet.
A small heat sink is recommended for IC1.
ELECTRONICS FOR YOU JANUARY 2002
You might also like
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Small and Portable UnitDocument2 pagesSmall and Portable Unittahera aqeelNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedDocument3 pagesCircuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedMashood NasirNo ratings yet
- Mobile ChargerDocument1 pageMobile ChargerVaz Patrick100% (1)
- Qa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitShayan FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Most Mobile Chargers Do Not Have CurrentDocument3 pagesMost Mobile Chargers Do Not Have CurrentRajashri BodduNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasDocument1 pageMobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasKuntaweeNo ratings yet
- Charger For Mobile PhonesDocument2 pagesCharger For Mobile PhonessivaganeshanNo ratings yet
- Constructing a 12V DC Power SupplyDocument7 pagesConstructing a 12V DC Power SupplyOgunyemi VictorNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument4 pagesDC Power SupplyAnti CrazyNo ratings yet
- Qa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitShivam JainNo ratings yet
- Mobile Cellphone Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesMobile Cellphone Battery ChargerWahyu NovendiNo ratings yet
- 12V Battery Charger-cum-Variable Power SupplyDocument11 pages12V Battery Charger-cum-Variable Power SupplyLOLO ISMUNASIBNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationDocument23 pagesWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8No ratings yet
- Vishwa Physics Project New (1) (Repaired) - Vishwa SundarDocument21 pagesVishwa Physics Project New (1) (Repaired) - Vishwa Sundarcoolharini18102006No ratings yet
- Oscillator: How To Build An InverterDocument7 pagesOscillator: How To Build An InverterGopal Prasad BansalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimDocument14 pagesExperiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimStar LordNo ratings yet
- Constant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasDocument54 pagesConstant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasKliffy Fernandes100% (1)
- Circuit DiagramDocument3 pagesCircuit DiagramEarl Jhoy EstreraNo ratings yet
- DC To DC Mobile Charging Using DDocument12 pagesDC To DC Mobile Charging Using DanmolNo ratings yet
- Simple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierDocument2 pagesSimple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierMahum JamilNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConverterDocument4 pagesHigh Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConvertersanilNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 0 30V 0 2ADocument3 pagesPower Supply 0 30V 0 2ARahul DevaNo ratings yet
- Cee-Ehm 468-Part 2Document26 pagesCee-Ehm 468-Part 2goshfukdNo ratings yet
- Travelling Mobile Charger by C.jeyarajDocument13 pagesTravelling Mobile Charger by C.jeyarajMeghan BrownNo ratings yet
- HOLD Adapter Za VoltmetarDocument1 pageHOLD Adapter Za VoltmetarDražen BorčićNo ratings yet
- SCC3 20A 12V Solar Charge Controller Electronic CircuitDocument2 pagesSCC3 20A 12V Solar Charge Controller Electronic CircuituimNo ratings yet
- Circuit Provides Reverse Battery ProtectionDocument1 pageCircuit Provides Reverse Battery ProtectionJar TesNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument105 pagesChapter Oneadugna abdissaNo ratings yet
- Efy 2009Document8 pagesEfy 2009Vipin Chalakutty CNo ratings yet
- Viper 12s Buck Boost ConverterDocument14 pagesViper 12s Buck Boost ConverterelkillyNo ratings yet
- Constant Current ChargerDocument3 pagesConstant Current ChargerchakralabsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Workshop Project ReportDocument5 pagesElectronic Workshop Project ReportAbubakr AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Security Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1Document30 pagesSecurity Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1DebashishParida100% (1)
- 12v 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB DiagramDocument3 pages12v 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB DiagramRajeeb DasNo ratings yet
- PB Battery ChargerDocument6 pagesPB Battery ChargerarezrthNo ratings yet
- ODD II YR 2 MarksDocument99 pagesODD II YR 2 MarksjesudosssNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power Supply with Short-Circuit DetectionDocument1 pageRegulated Power Supply with Short-Circuit DetectionDiego ManchayNo ratings yet
- IR Remote Controlled Home AppliancesDocument48 pagesIR Remote Controlled Home AppliancesRomeobenet0% (1)
- Mini UPS System PDFDocument1 pageMini UPS System PDFShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- 9 Basic DC To DC Converter CircuitsDocument40 pages9 Basic DC To DC Converter Circuitsuser123phc100% (1)
- Solar FanDocument37 pagesSolar Fantechcare12389% (9)
- 12V Car Battery Charger CircuitDocument2 pages12V Car Battery Charger CircuitJaved hashimNo ratings yet
- ANNEXE - Chademo ProtocoleDocument4 pagesANNEXE - Chademo ProtocoleAmina El AnsariNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 12Document10 pagesPhysics Project Class 12Pratik Punj75% (4)
- Now-A-Days Maintenance Free Lead Acid Batteries Are Common in Vehicles, Inverters, and UPSDocument21 pagesNow-A-Days Maintenance Free Lead Acid Batteries Are Common in Vehicles, Inverters, and UPSAnkit Surya NairNo ratings yet
- Car Battery MonitorDocument39 pagesCar Battery MonitorroopavennelaNo ratings yet
- Low Cost LED Emergency LightDocument2 pagesLow Cost LED Emergency LightAmir AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Final 2222Document18 pagesFinal 2222Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solar Charging Lamp: Department of Electrical &electrical B.V.C. Engg College OdalarevuDocument8 pagesSolar Charging Lamp: Department of Electrical &electrical B.V.C. Engg College OdalarevuRamgopal SripadaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project: The Construction of 9 - 12 Volt DC Power Supply 1.0 ObjectivesDocument8 pagesMini Project: The Construction of 9 - 12 Volt DC Power Supply 1.0 ObjectivesChyNaluri89No ratings yet
- Milli Ohm AdapterDocument6 pagesMilli Ohm Adapteralexandru25No ratings yet
- 94 96 DIY 12V Battery Charger EFY Nov 16Document3 pages94 96 DIY 12V Battery Charger EFY Nov 16Vaz PatrickNo ratings yet
- Switched LanDocument2 pagesSwitched LanUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Cournot Duopoly ModelDocument4 pagesCournot Duopoly ModelUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Wave GuidesDocument44 pagesRectangular Wave GuidesArshadahcNo ratings yet
- Full AdderDocument3 pagesFull AdderUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocument145 pagesSolved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsZoryel Montano33% (3)
- Half SubtractorDocument2 pagesHalf SubtractorUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- The History and Mysteries of the Great Sphinx of GizaDocument11 pagesThe History and Mysteries of the Great Sphinx of GizaUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Half SubtractorDocument2 pagesHalf SubtractorUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Half AdderDocument3 pagesHalf AdderUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument42 pagesWaste Water TreatmentUtkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Utkarsh MishraNo ratings yet