Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 Sum
Uploaded by
Javeed KassamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Sum
Uploaded by
Javeed KassamCopyright:
Available Formats
The Cell Organelles!
A Brief Summary
•the CELL MEMBRANE controls transport of materials in and out of cell. It
also functions in recognition, communication, and homeostasis. It is
SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE.
•Plant Cells also have a Cell Wall surrounding their cell membrane.
•The NUCLEUS is a large organelle surrounded by a double membrane. It is the control
center or "brain" of cell. Contains the DNA and is site of manufacture of RNA. The DNA
may be bound up tightly in chromosomes, or in the form of chromatin. The nucleus
contains one or more DARK-STAINING structures called NUCLEOLI, which are sites of RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID
(rRNA) SYNTHESIS.
•ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: the ER is a system of MEMBRANOUS TUBULAR CANALS that
begins just outside the nucleus and branches throughout the cytoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum
membranes provide an increase in surface area where chemical reactions can occur.
•if ribosomes are attached to the ER, it is called ROUGH Endoplasmic Reticulum. The function of rough ER is
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS.
•if no ribosomes are attached to the ER, it is called SMOOTH Endoplasmic Reticulum. The function of smooth ER is
synthesis of lipids. Phospholipids and cholesterol, the main components of membranes throughout the cell, are
synthesized in the smooth ER. A second important function of smooth ER is to detoxify drugs and chemicals in the cell.
•RIBOSOMES: Ribosomes are small organelles. The are made of rRNA and protein. The are NOT covered by
membrane. They have two main subunits, which are made in the nucleolus and then sent
out to the cytoplasm. The function of ribosomes is that they are the SITE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS.
• GOLGI APPARATUS (= Golgi Bodies): are stacks of flattened, hollow cavities enclosed by membranes. The
Golgi apparatus functions in modification, assembly, packaging, storage and secretion of substances, like
proteins.
•vesicles from the ER will often merge with the Golgi bodies. The contents of the vesicles will be
modified by enzymes within the Golgi bodies. Then the "finished" proteins etc. will be "pinched
off" the Golgi bodies into new vesicles, which can now be transported to their destination. The
Golgi bodies usually modify and package proteins that are to be used outside the cell.
•VESICLES & VACUOLES: A VESICLE is a small vacuole. vacuoles and vesicles are formed
by: 1) pinching off from the Golgi apparatus 2) endocytosis of the cell membrane 3) extension of the ER membrane (for
example, the large central vacuole of a plant cell). Vesicles are used for transport and storage of materials.
• Plant cells usually have one large Central Vacuole for storing water. It might also store food, wastes, and also helps to support the plant through
"turgor pressure.
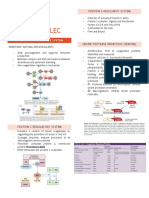
• LYSOSOMES are special vesicles which are formed by the Golgi apparatus. They contain powerful HYDROLYTIC ENZYMES (over 40 kinds).
Lysosomes function in 1) cellular digestion of food 2) autodigestion or breaking down damaged cell components like old mitochondria 3)
occassionally breaking down of a whole cell (by releasing lysosome contents into the cell cytoplasm).
• MITOCHONDRION: large, double-membrane bound organelles that are the SITE OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION. In mitochondria, organic
molecules (especially those formed when glucose is split) are broken down in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. The
RAYCROFT Chapter 3 part 1 — Page 1
waste products of this reaction are water and carbon dioxide. Are sometimes refered to as the "Powerhouses of the Cell." Mitochondria are found
in all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells.
• CHLOROPLASTS: large, double-membrane bound organelles that are found only in PLANT CELLS. They produce food for plant cells.
Specifically, they capture the energy of the sun with a special green pigment called chlorophyll, and then use that energy to combine CO2 and H2O
to form GLUCOSE.
• Animal cells have two cylindrical bodies, called CENTRIOLES, located near the nucleus. The
centrioles appear as sets of triple tubules. Centrioles play a role in cell division. They organize the
spindle apparatus during mitosis. Centrioles are short cylinders with a 9+0 pattern of microtubular
triplets. Centrioles also give rise to basil bodies. . Basal bodies, in turn direct the formation of
CILIA and FLAGELLA.
•CILIA are short, hairlike projections that function in cell
movement (e.g. Paramecium) or to move materials past cells
(e.g. cells of human respiratory tract and oviducts). They
consist of membrane-bound cylinder, with 9+2 arrangement
of microtubules. Cilia are much shorter than flagella, and
beat stiffly back and forth, like oars.
•FLAGELLA are longer than cilia, but with same basic anatomy as cilia (membrane-bound cylinder, with
9+2 arrangement of microtubules). They beat in a whip-like fashion. They function in cell movement
(e.g. sperm cells, Euglena).
•The CYTOSKELETON is not an organelle, but rather a network of microtubules and
microfilaments within the cell that help it maintain shape, anchor organelles, or help the organelles move as necessary. The
primary constituents of the cytoskeleton are microtubules (which are like tiny hollow tubes) and microfilaments.
RAYCROFT Chapter 3 part 1 — Page 2
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- ATEROESCLEROSISDocument228 pagesATEROESCLEROSISTenazNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Metabolites: An NMR Metabolomics Approach To Investigate Factors A and QualityDocument16 pagesMetabolites: An NMR Metabolomics Approach To Investigate Factors A and QualitykarinaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Meiosis: The Difference Between Meiosis 1 and 2Document4 pagesMeiosis: The Difference Between Meiosis 1 and 2Pako Nicolas MatshabaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument21 pagesCell Growth and Divisionapi-319819727No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- BS1001 LipidsDocument32 pagesBS1001 LipidsLiloyi LupiyaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesThe Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis: Submitted by P. Tejaswi TVM/20-18Document42 pagesPeptidoglycan Biosynthesis: Submitted by P. Tejaswi TVM/20-18Chaitanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Enzymes IntroDocument33 pagesEnzymes IntropragyasimsNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Unit 3 Genetic PolymorphismDocument15 pagesUnit 3 Genetic PolymorphismJyoti SharmaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- GENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestDocument6 pagesGENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestCelsa ChicoNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Cell Organelles DefinitionDocument40 pagesCell Organelles Definitionmuhammad aslam0% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Immunofluorescence Handbook 1601971Document80 pagesImmunofluorescence Handbook 1601971Ray KuoNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- BPT Syllabus PDFDocument99 pagesBPT Syllabus PDFAbhishek NegiNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 21 Natural Scientific Pathways Shown To Stimulate Hair Growth and Prevent Hair Loss 21 Natural ... (PDFDrive)Document36 pages21 Natural Scientific Pathways Shown To Stimulate Hair Growth and Prevent Hair Loss 21 Natural ... (PDFDrive)Mohamed KhaterNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Microarray Technology - A Brief Introduction - : Markus PanhuysenDocument38 pagesMicroarray Technology - A Brief Introduction - : Markus PanhuysenrashmiNo ratings yet
- Bio - Cell Structure and Function QuizDocument2 pagesBio - Cell Structure and Function QuizAditi AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Association Between Genetic Variants in The Coenzyme Q Metabolism and Coenzyme Q Status in HumansDocument7 pagesAssociation Between Genetic Variants in The Coenzyme Q Metabolism and Coenzyme Q Status in HumansLUCIENE CRISTALDO ALBUQUERQUENo ratings yet
- Perspectives: Overcoming Challenges and Dogmas To Understand The Functions of PseudogenesDocument11 pagesPerspectives: Overcoming Challenges and Dogmas To Understand The Functions of Pseudogenesİzem DevecioğluNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of XenobioticsDocument30 pagesMetabolism of XenobioticsCzarina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Clinical PharmacologyDocument2 pagesClinical Pharmacology0921pyNo ratings yet
- Class Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassDocument2 pagesClass Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassYehia Khaled Essam Fawaz ICSBR1No ratings yet
- Vitamin Fat Soluble 2022Document28 pagesVitamin Fat Soluble 2022X x A7md x XNo ratings yet
- Nitro Blue TetrazoliumDocument4 pagesNitro Blue TetrazoliumOsama Bakheet100% (1)
- Bionanotehnologii - Bionanotechnology - PPT - BOGMISDocument10 pagesBionanotehnologii - Bionanotechnology - PPT - BOGMISCristian GondacNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 2.2 Biological Molecules - Proteins QPDocument24 pages2.2 Biological Molecules - Proteins QPsuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- What Is Life? Molecules of Life Cell As Fundamental Unit Cell Membranes and Organelles Cell Metabolism Cells Organized Into Tissues Types of TissuesDocument67 pagesWhat Is Life? Molecules of Life Cell As Fundamental Unit Cell Membranes and Organelles Cell Metabolism Cells Organized Into Tissues Types of TissuestesterNo ratings yet
- CP Biomarker Thyroid 2016 v1001Document11 pagesCP Biomarker Thyroid 2016 v1001karimahihdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 XamideaDocument64 pagesChapter 6 Xamideakeren spamzNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- CBR Biology Cell PDFDocument20 pagesCBR Biology Cell PDFMamandaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)