Professional Documents
Culture Documents
19-Muscle Imbalance Chart of The LQ
Uploaded by
Ashley WhitwellOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
19-Muscle Imbalance Chart of The LQ
Uploaded by
Ashley WhitwellCopyright:
Available Formats
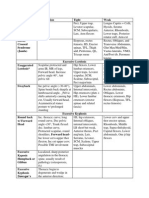
PT 7422 – PT Management of Musculoskeletal Conditions III
Topic: Muscle Imbalance Chart of the Lower Quadrant
Review the list of muscles listed in the left column, and consider their effect on positioning if they are TIGHT (i.e. don’t
focus on what actions the muscles normally create. Rather, focus on what effect they have on positioning if they are TIGHT.)
Use the key listed at the bottom of this page.
Effects of Muscle Length on Lower Extremity Position
Hip hiking (ilial upslip)
Anterior pelvic tilt
Inflare
Sacral rotation left
Hip flexion
Hip extension
Hip abduction
Hip adduction.
Hip lateral rotation.
Knee flexion
Knee extension.
Tibial torsion
elevationPosterior pelvic tilt
Outflare
Hip medial rotation
Muscles Shortened
Rectus abdominis
External oblique
Internal oblique
Erector spinae
Quadratus
Lumborum
Psoas major
Iliacus
TFL/IT band
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus med
(post)
Gluteus med (ant)
Gluteus minimus
Piriformis
Adductor longus,
brevis, gracilis,
pectineus
Adductor magnus
Medial
hamstrings
Lateral
hamstrings
Quadriceps
Gastrocnemius
Peroneals
Anterior and
posterior tibialis
Key: use the following symbols to code your answers
X = use this symbol if generalized tightness causes the positional response
1 = use this symbol if tightness is primarily due to an ipsilateral response
2 = use this symbol if tightness is primarily due to a contralateral response
3 = use this symbol if the anterior fibers are the primarily cause of the tightness
4 = use this symbol if the posterior fibers are the primary cause of the tightness
1
You might also like
- Maps ProgramsDocument1 pageMaps Programssergio viquez50% (4)
- 15 Exercises For Shoulder PainDocument2 pages15 Exercises For Shoulder PainMichael A FarinNo ratings yet
- Toned Thighs & Glutes Workout Calendar - May 2020 PDFDocument1 pageToned Thighs & Glutes Workout Calendar - May 2020 PDFDaniela DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 300 Fitness FREEDocument60 pages300 Fitness FREEBad_ideas_happen100% (3)
- Opleidingen Voor Personal Trainers - Deel 1 OVERLOAD WORLDWIDEDocument27 pagesOpleidingen Voor Personal Trainers - Deel 1 OVERLOAD WORLDWIDEOverload WorldwideNo ratings yet
- PRI Training - Postural Respiration TestDocument8 pagesPRI Training - Postural Respiration TestDenis OsmenajNo ratings yet
- Proc RangeOfMotionDocument4 pagesProc RangeOfMotionSri KuspartianingsihNo ratings yet
- Steroidal Activity in Experimental Animals and ManFrom EverandSteroidal Activity in Experimental Animals and ManRalph I. DorfmanNo ratings yet
- The BIG Routine by Ellington DardenDocument4 pagesThe BIG Routine by Ellington DardenmcsmittyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Stance On Muscle Activation in The SquatDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Stance On Muscle Activation in The Squatapi-320703111100% (1)
- The Acid TestDocument3 pagesThe Acid TestMike AxeNo ratings yet
- A Unified Theory of Fitness ProgrammingDocument5 pagesA Unified Theory of Fitness ProgrammingNikolovskiNikolaKoleNo ratings yet
- Personal Training ExercisesDocument4 pagesPersonal Training Exercisesapi-377252439No ratings yet
- How Much Can You LiftDocument6 pagesHow Much Can You LiftaboubakereldjazairiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot - Ankle and Foot ComplexDocument4 pagesScreenshot - Ankle and Foot Complexno nameNo ratings yet
- 3.2 FHS - Measuring Joint Motion (Goniometer)Document10 pages3.2 FHS - Measuring Joint Motion (Goniometer)Abhishek GirdharNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Frozen ShoulderDocument21 pagesJurnal Frozen ShoulderMega Mulya Dwi FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Knee, Ankle and Foot Joint MobilizationDocument17 pagesKnee, Ankle and Foot Joint MobilizationLokesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Squat Glute Challenge - en PDFDocument1 pageSquat Glute Challenge - en PDFArpit LadoleNo ratings yet
- 4 Day Full BOdyDocument4 pages4 Day Full BOdyCarla BaraybarNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementDocument10 pagesRehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementSandeep DhimanNo ratings yet
- Hip Application SolutionsDocument3 pagesHip Application SolutionsDNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy After Rotator Cuff RepairDocument19 pagesPhysical Therapy After Rotator Cuff RepairMaria RosmaNo ratings yet
- Cavemanv2 0-English PDFDocument45 pagesCavemanv2 0-English PDFOverload WorldwideNo ratings yet
- Diet vs Training for Muscle Gains - Why Training Matters MoreDocument2 pagesDiet vs Training for Muscle Gains - Why Training Matters MorejapNo ratings yet
- NSCA - Functional Training For SwimmingDocument7 pagesNSCA - Functional Training For SwimmingLuiz Felipe100% (1)
- Shoulder Dislocation Factsheet: Exercises and Recovery TipsDocument2 pagesShoulder Dislocation Factsheet: Exercises and Recovery TipscilengsaiNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Training For Fat LossDocument5 pagesLactic Acid Training For Fat LossTasos ChatzNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Myasthenia Gravis (MG)Document3 pagesExercise and Myasthenia Gravis (MG)sridhar_physioNo ratings yet
- Osgood Schlatter Disease With Exercises ChocDocument4 pagesOsgood Schlatter Disease With Exercises ChocJoni MokodoNo ratings yet
- FR Training Cert Worksheets 080412 2Document8 pagesFR Training Cert Worksheets 080412 2api-30886506No ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary AssessmentDocument8 pagesCardio Pulmonary AssessmentSHAIK SHABEENANo ratings yet
- 5 Senior ExercisesDocument3 pages5 Senior Exercisestamaki55No ratings yet
- The Role of Core StabilityDocument11 pagesThe Role of Core StabilitykevintriyaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ComplexDocument55 pagesShoulder ComplexKim VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Kraemer and Ratamess 2004 PDFDocument16 pagesKraemer and Ratamess 2004 PDFCleiton CorreaNo ratings yet
- ITband Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesITband Exercises PDFShashNo ratings yet
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 pagesThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Protocol 1 Achilles Tendon Repair v5Document2 pagesProtocol 1 Achilles Tendon Repair v5Carlos Martín De RosasNo ratings yet
- Training ExampDocument1 pageTraining ExampsdjuknicNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Shoulder ComplexDocument83 pagesBiomechanics of The Shoulder ComplexpiciliviNo ratings yet
- Upper Cross SyndromeDocument3 pagesUpper Cross Syndromecarrotbutter0% (1)
- Warm-Up Exercise Quadriceps:: Lower-Body 1 Set of 15 Repetitions On EachDocument8 pagesWarm-Up Exercise Quadriceps:: Lower-Body 1 Set of 15 Repetitions On EachRaymanNo ratings yet
- Plantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideDocument8 pagesPlantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideAjmera HarshalNo ratings yet
- Bicep Curl To Shoulder PressDocument5 pagesBicep Curl To Shoulder Presssavvy_as_98-1No ratings yet
- MMT 6-1Document20 pagesMMT 6-1Mughal ZadiiNo ratings yet
- Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles anatomyDocument35 pagesChest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles anatomyOr100% (2)
- Mike ReinoldDocument20 pagesMike ReinoldVikas Kashnia0% (1)
- Power Plate Group Ex Power Basic 1 PDFDocument4 pagesPower Plate Group Ex Power Basic 1 PDFRicardo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Disaster MenegementDocument82 pagesPhysiotherapy in Disaster MenegementAtiKa YuLiantiNo ratings yet
- Proprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionDocument10 pagesProprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionAlejandra VasquezNo ratings yet
- What Is Biceps Tendonitis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Biceps Tendonitis?Nishant RajaNo ratings yet
- Toe Touch ProgressionDocument1 pageToe Touch Progressionses1984205No ratings yet
- PostureDocument2 pagesPostureNader MorrisNo ratings yet
- How Could Periodization Help Enhance MuscleDocument9 pagesHow Could Periodization Help Enhance Musclemehrdad_44No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - RecoveryDocument20 pagesChapter 11 - RecoveryDDVNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Knee During Closed Kinetic Chain and Open Kinetic Chain ExercisesDocument15 pagesBiomechanics of The Knee During Closed Kinetic Chain and Open Kinetic Chain ExercisesAndresLeivaMckendrickNo ratings yet
- 7 Patellar Tracking Exercises For Subluxation & DislocationDocument9 pages7 Patellar Tracking Exercises For Subluxation & DislocationAnh Đức NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Nebraska CoreDocument42 pagesNebraska CoreGreg MarsoNo ratings yet
- Strong Hamstrings: 5 Exercises to Prevent InjuryDocument5 pagesStrong Hamstrings: 5 Exercises to Prevent InjuryTomSusNo ratings yet
- Walking AidsDocument38 pagesWalking AidsMurad KurdiNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury HockeyDocument65 pagesSpinal Injury HockeyTaniaR.BernalNo ratings yet
- Stage 4 - Forced Adaptation: The Quick Guide to Professional Level LiftingFrom EverandStage 4 - Forced Adaptation: The Quick Guide to Professional Level LiftingNo ratings yet
- Exercise Booklet for Ankle and Leg StrengtheningDocument19 pagesExercise Booklet for Ankle and Leg StrengtheningMiss M.No ratings yet
- Somatic Anatomy and Posture: The Postural FluteDocument6 pagesSomatic Anatomy and Posture: The Postural FlutearonolamNo ratings yet
- Excel - All Workout Routines Exercises Reps Sets EtcDocument10 pagesExcel - All Workout Routines Exercises Reps Sets EtcJanus Blacklight100% (1)
- Prelim ReviewerDocument45 pagesPrelim ReviewerMarela VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pe104 Student Fitness Portfolio 2nd Semester 2022-2023Document8 pagesPe104 Student Fitness Portfolio 2nd Semester 2022-2023Jr CañaresNo ratings yet
- PED027 Module 2 ContemplationDocument17 pagesPED027 Module 2 ContemplationAngel MayNo ratings yet
- PEH3 12 - Q4 - Mod5 - Health and Dance Related Career Opportunities - Version2Document12 pagesPEH3 12 - Q4 - Mod5 - Health and Dance Related Career Opportunities - Version2Rohanisah Dansal50% (2)
- First Quarter Test in Pe11Document3 pagesFirst Quarter Test in Pe11Monaliza PawilanNo ratings yet
- CAE 3c Met 5 ListeningDocument6 pagesCAE 3c Met 5 Listeningleo.king.1480.3No ratings yet
- Stuart McRobert - Build Muscle, Lose Fat, Look Great, 2nd Edition (2013, CS Publishing LTD)Document431 pagesStuart McRobert - Build Muscle, Lose Fat, Look Great, 2nd Edition (2013, CS Publishing LTD)Federico BiettiNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting and Principles of TrainingDocument35 pagesGoal Setting and Principles of TraininggabrielleNo ratings yet
- FITT Principles of TrainingDocument3 pagesFITT Principles of TrainingXiscoNo ratings yet
- Effect of PMR and deep breathing after aerobic exercises on essential hypertensionDocument2 pagesEffect of PMR and deep breathing after aerobic exercises on essential hypertensionNetraNo ratings yet
- EMOMdiary EbookDocument54 pagesEMOMdiary EbookjakovvlakicNo ratings yet
- HOPE4 MELC3 Module3noanswerkeyDocument11 pagesHOPE4 MELC3 Module3noanswerkeySai WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Qonnita's Hobbies ExplainedDocument4 pagesQonnita's Hobbies ExplainedQonnita DhiyaNo ratings yet
- Volleyball Research PaperDocument4 pagesVolleyball Research Paperdmkrajulg100% (1)
- 3j17q3bb1ewr p32 - International Physical Activity QuestionnaireDocument1 page3j17q3bb1ewr p32 - International Physical Activity QuestionnaireHappy NeuronsNo ratings yet
- The Health Benefits of Resistance Exercise Beyond.2Document5 pagesThe Health Benefits of Resistance Exercise Beyond.2CamiloAndresRinconYNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Module 9Document20 pagesPathfit 1 Module 9Katherine Lauren MaglayaNo ratings yet
- Soriano - Hiit Workout RoutineDocument2 pagesSoriano - Hiit Workout RoutineNicole SorianoNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based Learning Material: Program and Year LevelDocument20 pagesCompetency-Based Learning Material: Program and Year LevelkielNo ratings yet
- HCF - LCM WorksheetDocument2 pagesHCF - LCM WorksheetFarhad HossainNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - FIDPDocument5 pagesGroup 4 - FIDPRuth Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- APRE For Strength & SizeDocument24 pagesAPRE For Strength & SizePete Puza100% (2)
- Training and BreathingDocument6 pagesTraining and BreathingMIIIBNo ratings yet