Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Yearly Plan f1
Uploaded by
Nisa Muhd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views8 pagesLEARNING AREA and LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. WHOLE NUMBERS 1. Whole NUMBERS Count, read and write WHOLE NUMBERS Identify place value and value of each digit in WHOLE NUMBERS. Describe the pattern of a given number sequence. Extend number sequences. Complete missing terms in given number sequences.
Original Description:
Original Title
maths yearly plan f1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLEARNING AREA and LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. WHOLE NUMBERS 1. Whole NUMBERS Count, read and write WHOLE NUMBERS Identify place value and value of each digit in WHOLE NUMBERS. Describe the pattern of a given number sequence. Extend number sequences. Complete missing terms in given number sequences.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views8 pagesMaths Yearly Plan f1
Uploaded by
Nisa MuhdLEARNING AREA and LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. WHOLE NUMBERS 1. Whole NUMBERS Count, read and write WHOLE NUMBERS Identify place value and value of each digit in WHOLE NUMBERS. Describe the pattern of a given number sequence. Extend number sequences. Complete missing terms in given number sequences.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
LEARNING AREA &
WEEK / DATE LEARNING LEARNING OUTCOMES CCTS VALUES
OBJECTIVES
• Count, read and write whole numbers
1. WHOLE NUMBERS • Identify place value and value of each digit in whole
1
1.1 Whole numbers numbers
• Round whole numbers
• Add whole numbers
1.2 Addition and • Solve problems involving addition of whole numbers
2
subtraction • Subtract whole numbers
• Solve problems involving subtractions of whole numbers
Working out mentally
• Multiply two or more whole numbers Making inferences
1.3 Multiplication and • Solve problems involving multiplication of whole numbers Translating
3
division • Divide a whole number by a smaller whole number
• Solve problems involving division of whole number
• Perform computations involving any combinations of
addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole
numbers including the use of bracket.
1.4 Combined Operations
• Solve problems involving any combinations of addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers
including the use of bracket.
2. NUMBER • Describe the pattern of a given number sequence. Making generalizations
PATTERNS AND Looking for patterns
• Extend number sequences.
4 SEQUENCES Classifying
2.1 Number patterns and • Complete missing terms in given number sequences. Identifying relations
sequences • Construct number sequences based on given patterns. Working out mentally
2.2 Odd and even • Identify and describe odd and even numbers. Finding all possible
solutions
numbers • Make general statements about odd and even numbers.
• Identify the characteristics of prime numbers.
2.3 Prime numbers • Determine whether a given number is a prime number..
• Determine all the prime numbers less than 100.
5 2.4 Multiples • List factors of whole numbers.
• Determine whether a number is a factor of another whole
number.
• Identify prime factors from a list of factors.
2.5 Common multiples
and Lowest common • Find prime factor(s) of whole numbers.
multiples • Determine whether a number is a prime factor of another
whole number.
• List the multiples of whole numbers.
2.6 Factors • Determine whether a number is the multiple of another
number.
• Find the common multiples of two or three whole numbers.
6 2.7 Prime Factors • Determine whether a number is the common multiple of two
or three given numbers.
• Determine the LCM of two or three given numbers.
• Find common factors of two or three whole numbers.
2.8 Common factors and
Highest Common Factors • Determine whether a number is a common factor of two or
(HCF) three given whole numbers.
• Determine the HCF of two or three given numbers.
• Read fractions. Identifying relations
• Describe fractions as parts of a whole. Drawing diagrams
3. FRACTIONS
7 Interpreting
3.1 Fractions • Represent fractions with diagrams. Finding all possible
• Write fractions for given diagrams. solutions
• Find equivalent fractions for a given fraction. Comparing and
differentiating
• Determine whether two given fractions are equivalent. Looking for patterns
8 3.2 Equivalent fractions • Compare the values of two given fractions. Arranging sequentially
• Arrange fractions in order. Classifying
• Simplify fractions to the lowest terms. Working out mentally
• Recognise mixed numbers. Translating
• Represent mixed numbers with diagrams.
3.3 Mixed number
• Write mixed numbers based on given diagrams.
• Compare and order mixed numbers on number lines.
9 3.4 Proper fractions and • Recognise proper and improper fractions from given
improper fractions fractions.
• Change mixed numbers into improper fractions.
• Change improper fractions into mixed numbers.
• Perform addition involving:
a) Fractions with common denominators.
b) Fractions with different denominators.
c) Whole numbers and fractions.
d) Fractions and mixed numbers.
e) Mixed numbers.
3.5 Addition and • Perform subtraction involving:
subtraction of fractions a) Fractions with common denominators.
b) Fractions with different denominators.
c) Whole numbers and fractions.
d) Fractions and mixed numbers.
e) Mixed numbers.
• Solve problems involving combined operations of addition
and subtraction of fractions.
• Multiply:
a) A whole number by a fraction or mixed number.
b) A fraction by a whole number.
c) A fraction by a fraction (include mixed numbers).
10
3.6 Multiplication and
• Solve problems involving multiplication of fractions.
11
division of fractions • Divide:
12 a) A fraction by a whole number.
b) A fraction by a fraction.
c) A whole number by a fraction.
d) A mixed number by a mixed number.
• Solve problems involving division of fractions.
3.7 Combined operations • Perform computations involving combined operations of
of fractions addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of fractions,
including the use of brackets.
• Solve problems involving combined operations of addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division of fractions,
including the use of brackets.
1 1
• Represent fractions and as decimals and vice-
10 100
4. DECIMALS versa.
4.1 Relationship between • Represent fractions with denominators 10,100 and 1000 as
decimals and fractions decimals.
• Read and write decimals to thousandths. Drawing diagrams
• Change fractions to decimals and vice-versa. Interpreting
• State the place value and value of each digit in decimals. Working out mentally
Looking for patterns
4.2 Place value and the • Compare the values of two given decimals. Comparing and
value of digit in decimals. • Arrange decimals in order. differentiating
• Round decimals to the nearest whole number or up to three Arranging sequentially
decimal places. Making inferences
• Add decimals. Translating
4.3 Addition and • Solve problems involving addition of decimals.
subtraction of decimals. • Subtract decimals.
• Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals.
• Multiply two or more decimals.
• Solve problems involving multiplications of decimals
4.4 Multiplication and • Divide:
division of decimals a) A decimal by a whole number.
b) A decimal by a decimal.
c) A decimal by a fraction.
• Solve problems involving division of decimals.
• Perform computations involving combined operations of
addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals,
4.5 Combined operations including the use of brackets.
of decimals. • Solve problems involving combined operations of addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals,
including the use of brackets.
5. PERCENTAGES • Express percentages as the number of parts in every 100. Working out mentally
5.1 Percentages Identifying relations
• Change fractions and decimals to percentages and vice-versa.
• Find the percentage of a quantity. Making inferences
Comparing and
• Find the percentage one number is of another. differentiating
5.2 Problem solving • Find a number given the percentage. Working backwards
• Find the percentage of increase or decrease. Solve problems Translating
involving percentages.
• Read and write integers.
• Represent integers on number lines.
6. INTEGERS • Compare the values of two integers. Classifying
6.1 Integers • Arrange integers in order. Comparing and
• Write positive or negative numbers to represent word differentiating
descriptions. Arranging sequentially
Translating
• Add integers.
Looking for patterns
6.2 Addition and • Solve problems involving addition of integers. Working out mentally
subtraction of integers • Subtract integers.
• Solve problems involving subtraction of integers.
7. ALGEBRAIC
• Use letters to represent unknown numbers.
EXPRESSIONS
7.1 Unknowns • Identify unknowns in given situations.
• Identify algebraic terms with one unknown.
Interpreting
• Identify coefficients in given algebraic terms with one Working out mentally
7.2 Algebraic terms unknown. Comparing and
• Identify like and unlike algebraic terms with one unknown. differentiating
• State like terms for a given term. Identifying relations
• Recognise algebraic expressions.
7.3 Algebraic expression
• Determine the number of terms in given algebraic
expressions.
• Simplify algebraic expressions by combining the like terms.
• Measure the length of objects. Identifying relations
8. BASIC • Convert one metric unit to another. (mm, cm, m and km) Interpreting
MEASUREMENTS Drawing diagrams
8.1 Length • Estimate lengths of objects in appropriate units. Estimating
• Use the four operations to solve problems involving length. Working out mentally
8.2 Mass • Measure the mass of objects. Translating
• Convert one metric unit to another. (mg, g, kg, tonne).
• Estimate masses of objects in appropriate units.
• Use the four operations to solve problems involving mass.
• Determine the appropriate measurement of time for certain
events.
8.3 Time • Convert measurement of time in different units (seconds,
minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years).
• Estimate the time intervals of events.
Making inferences
• Use the four operations to solve problems involving time.
• Read and write times in twelve-hour system.
• Read and write times in twenty-four hour system.
8.4 Twelve-hour and • Convert time in twelve-hour system to twenty-four hour
twenty-four-hour system system and vice-versa.
• Determine the interval between two given times.
• Solve problems involving time.
• Recognise angles. Drawing diagrams
• Denote and label angles. Finding all possible
• Measure angles using protractors. solutions
• Draw angles using protractors. Interpreting
9. LINES AND Classifying
ANGLES • Recognise, compare and classify angles as acute, right, Identifying relations
9.1 Angles obtuse and reflex.
• Draw acute, right, obtuse and reflex angles using protractors.
• Determine angles on straight lines equal 180°.
• Determine one whole turn is 360°.
• Determine parallel lines.
9.2 Parallel and
• Determine perpendicular lines.
perpendicular lines
• State that the angles formed by perpendicular lines is 90°.
9.3 Intersecting lines • Identify intersecting lines.
• Determine the properties of vertical, complementary and
supplementary angles.
• Determine the value of an angle on a line, given the adjacent
angle.
• Solve problems involving angles formed by intersecting
lines.
• Recognise polygons.
• Name polygons (triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon,
10. POLYGONS heptagon and octagon).
10.1 Polygons • Determine the number of sides, vertices and diagonals of
given polygons.
• Sketch polygons.
• Determine and draw the line(s) of symmetry of shapes.
10.2 Symmetry • Complete shapes given part of the shapes and the line of
symmetry.
• Draw designs using the concept of symmetry.
• Determine and draw symmetry line(s) of given triangles. Classifying
Making generalizations
• Draw triangles using protractors and rulers. Drawing diagrams
10.3 Triangles • State the geometric properties of the different types of Interpreting
triangles and name the triangles. Identifying relations
• Determine that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°.
• Solve problems involving triangles.
• Determine and draw symmetry line(s) of given
quadrilaterals.
• Draw a quadrilateral using protractor and ruler.
10.4 Quadrilaterals • State the geometric properties of the different types of
quadrilaterals and name quadrilaterals.
• Determine that the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is
360°.
• Solve problems involving quadrilaterals.
11. PERIMETER AND • Identify the perimeter of a region. Drawing diagrams
AREA • Find the perimeter of a region enclosed by straight lines. Identifying relations
11.1 Perimeter Translating
• Solve problems involving perimeters.
Making generalizations
11.2 Area of rectangles • Estimate the area of a shape. Estimating
• Find the area of a rectangle.
• Solve problems involving areas.
• Identify the heights and bases of triangles, parallelograms
and trapeziums.
11.3 Area of triangles, • Find the areas of triangles, parallelograms and trapeziums.
parallelograms and • Find the areas of figures made up of triangles, rectangles, Interpreting
trapeziums. parallelograms or trapeziums.
• Solve problems involving the areas of triangles, rectangles,
parallelograms and trapeziums.
• Identify geometric solids.
• State the geometric properties of cubes and cuboids.
12. SOLID • Draw cubes and cuboids on:
GEOMETRY a) Square grids. Classifying
12.1 Geometric properties b) Blank papers. Making generalizations
of cubes and cuboids Drawing diagrams
c) Make models of cubes and cuboids by: Interpreting
Combining given faces. Identifying relations
Folding given layouts of solids. Translating
• Estimate the volume of cuboids.
12.2 Volumes of a
• Find the volume of cuboids.
cuboids
• Solve problems involving volume of cuboids.
You might also like
- Year 5 Multiplication and Division BookletDocument40 pagesYear 5 Multiplication and Division BookletKadek Adi Wibawa100% (2)
- Spreader BeamDocument7 pagesSpreader BeamAnonymous sfkedkymNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document70 pagesChapter 1rdscleaners100% (1)
- SASMO 2020 Grade 6 + SolutionDocument24 pagesSASMO 2020 Grade 6 + SolutionBentley Leopold Halim94% (18)
- IGCSE Math Revision ChecklistDocument22 pagesIGCSE Math Revision ChecklistKay SinghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Core Extended Cambridge IgcseDocument12 pagesMathematics: Core Extended Cambridge IgcsefoddgdNo ratings yet
- Open Die ForgingDocument7 pagesOpen Die ForgingCharanjeet Singh0% (1)
- Year 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsDocument4 pagesYear 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Cryogenic Engineering 37) Takayuki Kishi, Mizuo Kudo, Hiromasa Iisaka (Auth.), R. W. Fast (Eds.) - Advances in Cryogenic Engineering-Springer US (1991)Document729 pages(Advances in Cryogenic Engineering 37) Takayuki Kishi, Mizuo Kudo, Hiromasa Iisaka (Auth.), R. W. Fast (Eds.) - Advances in Cryogenic Engineering-Springer US (1991)ksvvijNo ratings yet
- Text Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBDocument129 pagesText Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBEnglish Buzz100% (1)
- RPT Form 1 Maths DLPDocument38 pagesRPT Form 1 Maths DLPdaharizuraida0% (1)
- RPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017Document9 pagesRPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017sitihajar88No ratings yet
- Foundation 20 Maths 20 GCSE20 ChecklistDocument19 pagesFoundation 20 Maths 20 GCSE20 ChecklistsmunroNo ratings yet
- MELC With BOW Grade VIIDocument8 pagesMELC With BOW Grade VIIera resusNo ratings yet
- Essential Math Competencies Budget for Grade 7Document36 pagesEssential Math Competencies Budget for Grade 7Park NimfaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument37 pagesBudget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesMadelyn PaitanNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument37 pagesBudget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesNyliram CariagaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument36 pagesBudget of Works For The Most Essential Learning CompetenciesRiz Edward MontenegroNo ratings yet
- New Mathematics Scheme 2019Document10 pagesNew Mathematics Scheme 2019api-451254697No ratings yet
- Bow Mathematics 7-10...Document37 pagesBow Mathematics 7-10...era resusNo ratings yet
- Bow Mathematics 7 10Document28 pagesBow Mathematics 7 10Rowena BenigaNo ratings yet
- RPT 2013 Form 1 Math Yearly PlanDocument9 pagesRPT 2013 Form 1 Math Yearly PlanNorliza SapatanohNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentDocument8 pagesPaper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentUmmul BaneenNo ratings yet
- O Level Math Syllabus Matching GridDocument6 pagesO Level Math Syllabus Matching GridKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 - Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths Aligned With The New BooksDocument5 pagesYear 7 - Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths Aligned With The New BooksMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalDocument15 pagesRevision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalHussain TafazzulNo ratings yet
- OIPM 6 SoWDocument16 pagesOIPM 6 SoWkarthika.rvNo ratings yet
- c01 Se m01 t01 l04Document12 pagesc01 Se m01 t01 l04api-261894355No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of AlgebraDocument46 pagesBasic Concepts of AlgebraKit AlbertNo ratings yet
- RPT (Ting 1 BM & DLP)Document38 pagesRPT (Ting 1 BM & DLP)Noor Amira RosliNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mathematics Atp Grade 7Document7 pages2022 Mathematics Atp Grade 7Themba NyoniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Coverage Mathematics 2022-23Document3 pagesSyllabus Coverage Mathematics 2022-23Ayyan NomanNo ratings yet
- Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division of FractionsDocument18 pagesAddition Subtraction Multiplication Division of Fractionsrommel legaspi0% (1)
- CH 1 - Parent NewsletterDocument2 pagesCH 1 - Parent NewsletterChandni MehtaNo ratings yet
- 6-Scope-Sequence-Cmp3 1Document14 pages6-Scope-Sequence-Cmp3 1api-262318725No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document70 pagesChapter 1trax eservicesNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 MathDocument8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 MathNAJIB MIRZANo ratings yet
- KSSM Form 1 Yearly Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesKSSM Form 1 Yearly Lesson PlandinNo ratings yet
- MELCDocument11 pagesMELCApril Aquino-RomanNo ratings yet
- Yr 7 4b Adding and Subtracting FractionsDocument20 pagesYr 7 4b Adding and Subtracting Fractionsaa.7911.2000No ratings yet
- JSU Paper 2 - Form 1Document4 pagesJSU Paper 2 - Form 1surayaothmanNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade ReviewDocument21 pages6th Grade ReviewMariah MoranNo ratings yet
- VII Maths Fractions Decimals Mod1Document23 pagesVII Maths Fractions Decimals Mod1natashaNo ratings yet
- CH 2.1Document32 pagesCH 2.1Smpnsatubontang KaltimNo ratings yet
- Hello Partner!Document32 pagesHello Partner!Abegail AguilandoNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Document14 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Karthiga MohanNo ratings yet
- - 6వ తరగతి మాథ్స్ లెసన్ ప్లాన్Document5 pages- 6వ తరగతి మాథ్స్ లెసన్ ప్లాన్Poorvi PatelNo ratings yet
- SOW RPT Template 2019 MathsDocument9 pagesSOW RPT Template 2019 Mathspiliciaa alcontaraNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Maths Linear Exam Topic List - FOUNDATION NumberDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCSE Maths Linear Exam Topic List - FOUNDATION NumbersymNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018Document29 pagesChapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018harshana rajagopalNo ratings yet
- Budget OF Work: Amparo High SchoolDocument12 pagesBudget OF Work: Amparo High SchoolElaine AringNo ratings yet
- Yearly Teaching Plan f1 2011Document8 pagesYearly Teaching Plan f1 2011Nursyaheeda YusofNo ratings yet
- Yearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberDocument8 pagesYearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberMohd Nazmi RahimiNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)Document6 pages1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)graman65No ratings yet
- Yearly Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesYearly Teaching PlanCikgu SyedNo ratings yet
- McDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch02Document68 pagesMcDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch02gsparksNo ratings yet
- Buksis-2.1 Revisi AkhirDocument22 pagesBuksis-2.1 Revisi AkhirF X AGUS SISWANTONo ratings yet
- Y10 Topic ListDocument2 pagesY10 Topic ListNavampreetNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan 1Document2 pagesUnit Plan 1api-381393246No ratings yet
- CURRICULUM SPECIFICATION MATHEMATICS FORM ONEDocument11 pagesCURRICULUM SPECIFICATION MATHEMATICS FORM ONErumputkecilNo ratings yet
- Math Workbook Unit 01Document48 pagesMath Workbook Unit 01spcwtiNo ratings yet
- Extended Learner GuideDocument30 pagesExtended Learner GuideArminda Sofia AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 1ST Quarter First ModuleDocument10 pagesGrade 7 1ST Quarter First ModuleFaith Marie QuintoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Weekly Teaching PlanDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Math Weekly Teaching PlanSnqobileNo ratings yet
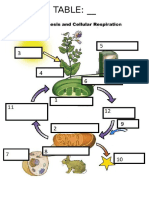
- Exercise Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageExercise Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisNisa MuhdNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment: The Bunsen BurnerDocument4 pagesLab Equipment: The Bunsen BurnerNisa MuhdNo ratings yet
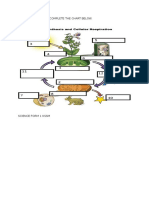
- Chapter 2 Exercise. Complete The Chart BelowDocument1 pageChapter 2 Exercise. Complete The Chart BelowNisa MuhdNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Are Complement To Each OtherDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Are Complement To Each OtherNisa Muhd100% (1)
- Science Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2 NotesDocument6 pagesScience Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2 NotesNisa Muhd0% (2)
- Science Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Document3 pagesScience Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Nisa MuhdNo ratings yet
- Armando Anaya Guenter y Zender - Sak Tz'iDocument14 pagesArmando Anaya Guenter y Zender - Sak Tz'iAngel Sanchez GamboaNo ratings yet
- Command Line Basics - Everything CurlDocument2 pagesCommand Line Basics - Everything Curlnot hereNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsDocument6 pagesAdiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsBibartan DasNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Ceramics and PolymersDocument41 pagesDeformation of Ceramics and PolymersJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Manual Fx2n 485 BDDocument8 pagesManual Fx2n 485 BDaxo_vfrNo ratings yet
- Academic Performance of Face-to-Face and Online Students in An Introductory Economics Course and Determinants of Final Course GradesDocument13 pagesAcademic Performance of Face-to-Face and Online Students in An Introductory Economics Course and Determinants of Final Course GradesLou BaldomarNo ratings yet
- MediaanditsterilzationDocument15 pagesMediaanditsterilzationAyushi MauryaNo ratings yet
- Materials Refractive Index and Extinction CoefficientDocument276 pagesMaterials Refractive Index and Extinction CoefficientDr-Mandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- in 01 en KATALOGDocument50 pagesin 01 en KATALOGSigma Ragam ManunggalNo ratings yet
- Swat Luu: User ManualDocument13 pagesSwat Luu: User ManualgjferreiraNo ratings yet
- AtmegaDocument22 pagesAtmegaMUKILANNo ratings yet
- Section 1Document28 pagesSection 1Sonia KaurNo ratings yet
- Libro de FLOTACIÓN-101-150 PDFDocument50 pagesLibro de FLOTACIÓN-101-150 PDFIsaias Viscarra HuizaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Explained: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates Explained: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesJhayce Christian S. CapanayanNo ratings yet
- Bandura Et Al.Document16 pagesBandura Et Al.Siddhant JhawarNo ratings yet
- 925E II 24 PG A4 Broch - 12 - 2020 - DCECDocument13 pages925E II 24 PG A4 Broch - 12 - 2020 - DCECekkyagungNo ratings yet
- Ecen 326 - Lab 2 ReportDocument7 pagesEcen 326 - Lab 2 Reportapi-241454978No ratings yet
- Xy6112 EtcDocument4 pagesXy6112 EtcJalal AsadianNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Reasoning: Factors, HCF & LCM, FactorialsDocument2 pagesQuantitative Reasoning: Factors, HCF & LCM, FactorialsNaman JainNo ratings yet
- Active FilterDocument16 pagesActive FilterRam SankarNo ratings yet
- CS610 Final Term Past Papers Mega FileDocument35 pagesCS610 Final Term Past Papers Mega Filehowtoplaygames38No ratings yet
- The Road Beyond 5G: A Vision and Insight of The Key TechnologiesDocument7 pagesThe Road Beyond 5G: A Vision and Insight of The Key TechnologiesSaurav SarkarNo ratings yet
- Player PrefsDocument1 pagePlayer PrefsHafiz AbdulwahabNo ratings yet
- Detailed Geotechnical ReportDocument29 pagesDetailed Geotechnical Reportathar abbasNo ratings yet
- PI ControllerDocument5 pagesPI Controllerdanuega1No ratings yet