Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aldehyde-Ketone Tests
Uploaded by
Prabu HafizhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aldehyde-Ketone Tests
Uploaded by
Prabu HafizhCopyright:
Available Formats
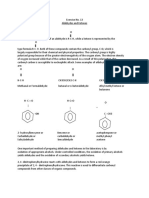
Aldehyde and Ketone Identification
Series of classification tests
Aldehydes and Ketones
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (we did not do this)
Aldehyde Methyl Ketone Compounds w/ enol content
Chromic Acid Iodoform Test Ferric Chloride Test
Tollens Reagent (we did not do this)
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (Handle with care, dispose of in appropriate waste)
Reacts with ketones and aldehydes. (we did not do this test)
O2N O2N
R R
H H+ H
O H2N N NO2 N N NO2 H2O
R R
Form precipitate with aldehydes and ketones
Color of precipitate may provide info about compound:
• unconjugated = yellow
• conjugated = orange to red
• occasionally strongly acidic, strongly basic compounds, and some allylic alcohols.
Procedure
• Place 1 drop of unknown in a tube.
• Add 1ml of phenylhydrazine solution
• Shake vigorously
• If unknown is a solid, dissolve 10mg in 95% ethanol
• Most aldehydes/ketones give yellow to red precipitate.
It may take 15 minutes or gentle heating to achieve color change
Chromic Acid Test (Handle with care, dispose of in appropriate waste)
Reacts with aldehydes.
H+
2CrO3 + 2H2O 2H2Cr2O7 + H2O
3RCHO + H2Cr2O7 + 3H2SO4 3RCOOH + Cr2(SO4)3 + 4H2O
orange green
Works because of ready oxidation of aldehydes
Primary and secondary alcohols may also be oxidized as well giving false positive.
• Dissolve 1 drop or 10mg of unknown in 1ml reagent grade acetone
• Add several drops of chromic acid, w/ shaking
• Green precipitate and loss of orange color indicates presence of an aldehyde
• w/ aliphatic aldehydes – turns cloudy in 5 sec. and forms precipitate w/in 30 sec.
• If solution remains orange bur precipitate forms = negative result.
Tollens Test (Handle with care, rinse glassware and acidify waste with 5% HCL,
dispose of in appropriate waste)
Reacts with aldehydes.
R-CHO + 2Ag(NH3)2OH 2Ag + RCO2-NH4+ +H2O + NH3
Should only be used if the compound has been determined to either be a ketone or an
aldehyde.
• Combine 1ml Tollens A and 1ml Tollens B
• Add dilute ammonia dropwise to dissolve prcpt.
• Divide solution evenly between three test tubes.
• Add 1 drop of aldehyde or solid aldehyde in bis(2ethoxyethyl)ether to tollens reagent.
• Precipitation of silver (mirror formed) indicates presence of aldehyde (it may be
necessary to warm the reaction
• Reagents cannot be stored—dispose of them after they are used
Iodoform Test
Methyl ketone
O O O
I2 OH-
R CH3 R CI3 R O- + HCI3
NaOH
Iodoform is a yellow precipitate
• Use a water bath between 60-70°C
• 6 drops of unknown or 0.06g in 2ml 1,2 dimethoxyethane
• Add 2ml of 10% NaOH
• Place in water bath
• Add 4ml of iodine-potassium iodide solution (in 1ml portions)
• Cork test tube and shake
• Heat in water bath ~5min.
• Dark color should be discharged
• If not, add more 10% NaOH
• Once color has disappeared, add water to within 2cm of lip
• cork and shake vigorously
• Let stand 15 minutes.
• Pale yellow precipitate (iodoform) indicates presence of methyl ketone
• Other ketones will discharge color, but will not form iodoform precipitate
Ferric Chloride Test
(we did not do this)
Phenols and compounds with high enolate content
Color is the result of enolate complexation with Fe(III) ion
• Add several drops of 2.5% aqueous soln of ferric chloride to 1ml of dilute ketone in
aqueous solution.
• If solid not soluble in water, 20mg dissolved in CHCl3 can be used.
• Add 1 drop of pyridine and 3-5 drops of 1% ferric chloride
• Formation of color (red, blue, purple, or green) indicates the presence of a compound
with high enol content. Colors are short lived.
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 12Document6 pages12NathaLie Sta ElenaNo ratings yet
- Idk PDFDocument25 pagesIdk PDFNael NomanNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDocument44 pagesPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- Detection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesDetection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsKiran PatroNo ratings yet
- REDOX TitrationsDocument132 pagesREDOX TitrationsAnis SayyedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical TipsDocument18 pagesChemistry Practical TipsK K Chamath Aachinthya64% (11)
- CHY 32.1 Alcohols and PhenolsDocument37 pagesCHY 32.1 Alcohols and PhenolsMA. NECOLE JEREMIAH GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Expt 10Document4 pagesLab Report Expt 10Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- 2 5352688982180245339Document11 pages2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- POCtheoryDocument7 pagesPOCtheoryPreetesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- The Properties of Alcohols I.: C H OH H R C R' OH H R C R' OH R'' RDocument10 pagesThe Properties of Alcohols I.: C H OH H R C R' OH H R C R' OH R'' RWimbo TrionoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestDocument4 pagesQualitative TestSwati KaushalNo ratings yet
- 1 - RedOx MethodsDocument55 pages1 - RedOx MethodsMarian Isabel YuNo ratings yet
- Identification of AlcoholsDocument26 pagesIdentification of Alcoholspupu_wowNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl UnknownDocument8 pagesCarbonyl UnknownYocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetoneDocument19 pagesAldehyde and KetoneEra MelaniaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- Screenshot 2023-11-21 at 2.33.44 PMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-21 at 2.33.44 PMsalmafmohamed444No ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17Document28 pagesReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17angeline medallo100% (1)
- Acrolein TestDocument6 pagesAcrolein TestJesserene Ramos75% (4)
- Praktikum#5 Dan 6Document34 pagesPraktikum#5 Dan 6Nur BillahNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument38 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersMike Daven LaderaNo ratings yet
- Chem-No.-13 2Document5 pagesChem-No.-13 2ho laNo ratings yet
- FInal Chemistry Sessional ReportDocument11 pagesFInal Chemistry Sessional ReportSyed M IslamNo ratings yet
- A Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in BleachDocument5 pagesA Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in Bleachskrim240No ratings yet
- Lipids TestsDocument12 pagesLipids TestsNikki Nina Arabe BarcinasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Tests For UnknownsDocument5 pagesChemical Tests For UnknownsKogulan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- CHEM 102 Experiment 8 Aldehyde Ketone Version Covid19Document3 pagesCHEM 102 Experiment 8 Aldehyde Ketone Version Covid19Azizah MunitaNo ratings yet
- E3alcohol PDFDocument9 pagesE3alcohol PDFWinonaNo ratings yet
- Diazotization Titration or Nitrite TitrationDocument5 pagesDiazotization Titration or Nitrite TitrationDeep NNo ratings yet
- InChO1999 PracDocument2 pagesInChO1999 PracCorneliaNo ratings yet
- Limit Tests of Chloride Sulphate Heavy Mattel PDFDocument6 pagesLimit Tests of Chloride Sulphate Heavy Mattel PDFBrajesh Suman100% (2)
- Name: Muhmmad Asif Roll # 115 Class: B.S Chemistry Semester: 5Document22 pagesName: Muhmmad Asif Roll # 115 Class: B.S Chemistry Semester: 5MUhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- FM7 Labreport 2Document12 pagesFM7 Labreport 2Jei y’allNo ratings yet
- Alcohols NotesDocument4 pagesAlcohols Notesjohn mNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1Document93 pagesAldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- 21 - Appendix II PDFDocument11 pages21 - Appendix II PDFSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Tests For Unknowns PDFDocument5 pagesChemical Tests For Unknowns PDFAnonymous otayTyJANo ratings yet
- Distinguish TestDocument1 pageDistinguish TestAnsia MeenazNo ratings yet
- WJEC CH4 Compound TestsDocument2 pagesWJEC CH4 Compound TestsBhavesh TailorNo ratings yet
- Limit TestsDocument20 pagesLimit TestsBMohdIshaqNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Elements Organic LabDocument6 pagesQualitative Analysis of Elements Organic LabSophia ManzanoNo ratings yet
- 2.1.4 Acids: Bases and AlkalisDocument4 pages2.1.4 Acids: Bases and AlkalisAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown ObjectiveDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown Objectivebabywenn100% (6)
- Rashid Kanetsa - Organic PracDocument4 pagesRashid Kanetsa - Organic PracRashid KanetsaNo ratings yet
- 6 Alcohols and Phenols PDFDocument7 pages6 Alcohols and Phenols PDFKristine Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- 46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Document3 pages46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Khaled KayaliNo ratings yet
- Classification and Identification of AldehydesDocument9 pagesClassification and Identification of AldehydesMeh Neff100% (1)
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Diazotization, KF TitrationsDocument15 pagesDiazotization, KF Titrationsiasnit100% (2)
- Lab Manual MSc. ChemistryDocument21 pagesLab Manual MSc. ChemistryGovardhan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Review: - OxidationDocument10 pagesSynthesis Review: - OxidationAmna YousafNo ratings yet
- Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and KetonesDocument3 pagesTest Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and KetonesMj WeakNo ratings yet
- Non Aqueous Titration: Madhuri PoulkarDocument15 pagesNon Aqueous Titration: Madhuri PoulkarMadhuri poulkarNo ratings yet
- 6.1.135.ephedrine Hydrochloride (Ephedrini Hydrochloridum)Document2 pages6.1.135.ephedrine Hydrochloride (Ephedrini Hydrochloridum)Kevin DonalNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet