Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Respiratory Distress
Uploaded by
minaanne100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views2 pagesAfter 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to improve ventilation and have adequate oxygenation. Long term goal After 24 hours the patient will improve respiratory function and will be free from symptoms of respiratory distress. Pulmonary edema is caused by decreased blood flow and fluids in the alveoli.
Original Description:
Original Title
acute respiratory distress
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAfter 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to improve ventilation and have adequate oxygenation. Long term goal After 24 hours the patient will improve respiratory function and will be free from symptoms of respiratory distress. Pulmonary edema is caused by decreased blood flow and fluids in the alveoli.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views2 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress
Uploaded by
minaanneAfter 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to improve ventilation and have adequate oxygenation. Long term goal After 24 hours the patient will improve respiratory function and will be free from symptoms of respiratory distress. Pulmonary edema is caused by decreased blood flow and fluids in the alveoli.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MENDOZA, ANNE MICHELLE D.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome BSN139
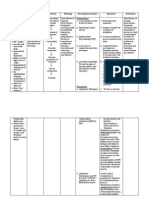
Assessment Nursing Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
diagnosis explanation
Subjective: Impaired gas Short term goal Independent Short term
“Nahihirapan siya exchange related Injury reduces Auscultate breath To determine the presence goal
huminga” as verbalized to alveolar- normal blood flows After 2 hours of sounds. Note of obstruction in airway.
by the wife. capillary to the lungs. nursing adventitious breath Goals met.
membrane Platelets aggregate intervention the sounds (ex.
Objective: changes and release patient will be Wheezes, crackles) After 2 hours
- Restless and secondary to acute histamine, able to improve Assess or monitor of nursing
irritable respiratory serotonin, and ventilation and respiratory rate To identify the presence of intervention the
- Nasal flaring distress syndrome bradykinin have adequate Encourage deep tachypnea. patient was
- Cyanotic skin oxygenation. able to
- Above normal ↓ breathing exercise
or frequent To facilitate maximum improved
respiratory rate Those substances Long term goal position changes expansion of the lungs. ventilation and
– 34 breaths per especially Reinforce need for was able to
minute histamine inflames After 24 hours of adequate rest, have adequate
and damages the nursing while encouraging oxygenation.
alveolocapillary intervention the activity and To decrease dyspnea and As evidenced
membrane, patient will be exercise improve quality of life. by normal
increasing capillary able to improve Emphasize the breaths per
permeability. respiratory importance of minute – 18
Fluids then shift function and will nutrition breaths per
into the interstitial be free from minute.
space symptoms of DEPENDENT To improve stamina and
respiratory reduce the work of Long term
↓ distress.
Administer
supplemental
breathing. goal
As capillary
oxygen, as ordered
permeability Goal met.
increases, proteins Increases alveolar oxygen
and fluids leak out, concentration, which may After 24 hours
increasing Administer correct/reduce tissue of nursing
interstitial osmotic medication as hypoxemia. intervention the
pressure and indicated: patient was
MENDOZA, ANNE MICHELLE D. Acute respiratory distress syndrome BSN139
causing pulmonary Diuretics; e.g., furosemide Reduces alveolar able to
edema (lasix); Bronchodilators; congestion, enhancing gas improved
e.g., aminophylline exchange. Increase oxygen respiratory
↓ delivery by dilating small function and
Decreased blood airways, and exerts mild was able to free
flow and fluids in diuretics effect to aid in from symptoms
the alveoli damages reducing pulmonary of respiratory
surfactant and congestion. distress. As
impair the cells evidenced by
ability to produce absence of
more nasal flaring
and normal
↓ skin color.
As a result Alveoli
collapse, impeding
gas exchange and
decreasing lung
compliance
You might also like
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure NCPDocument1 pageRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP For Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNCP For Pleural EffusionLilian Linogao71% (7)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pagePOC Ineffective Breathing PatterncuicuitaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Managing Respiratory Infection with Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesManaging Respiratory Infection with Nursing InterventionsJessa Borre100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaDocument9 pagesLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Document1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Danna Tan50% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- 17Y Patient Pleural Effusion CareDocument4 pages17Y Patient Pleural Effusion CareTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NCP EmphysemaDocument9 pagesNCP Emphysemahermesdave188% (8)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageAsthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceWdy Tanakht Sparrow100% (4)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in SwallowingDocument1 pageDifficulty in SwallowingmawelNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Assessing Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageAssessing Impaired Gas ExchangeRryje Salleva100% (1)
- NCP - CopdDocument3 pagesNCP - CopdhystericoNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For AsthmaDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis For AsthmaTINAIDA33% (3)
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildMarion Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Ards NCPDocument5 pagesArds NCPgopscharanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKyla Carbonel100% (1)
- Assessing and Managing Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Respiratory DistressGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEsther RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingDocument2 pagesD. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Nursing Care Plan for Difficulty BreathingDocument1 pageSt. Anthony's Nursing Care Plan for Difficulty Breathingcen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Iudmc ActivityDocument10 pagesIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentFat NrqzNo ratings yet
- Terminology in Clinical SettingDocument13 pagesTerminology in Clinical SettingCiuss ThamrinNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding, Bottle Feeding, and Non-Nutritive SuckingDocument3 pagesBreastfeeding, Bottle Feeding, and Non-Nutritive SuckingAulia HardiantiNo ratings yet
- Advance Beekeeping Manual Pam GregoryDocument79 pagesAdvance Beekeeping Manual Pam GregoryveverexNo ratings yet
- Anatomic and Physiologic Overview of The BrainDocument5 pagesAnatomic and Physiologic Overview of The BrainIlona Rosabel Bitalac0% (1)
- Character SheetDocument5 pagesCharacter SheetAnonymous M0IX1Q5No ratings yet
- Dwitya To TrityaDocument34 pagesDwitya To TrityaAsh GamejiNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Penelitian TB ParuDocument6 pagesJURNAL Penelitian TB ParuCarseen Jilly Leo EvlistNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infectio Case StudyDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract Infectio Case Studyjunex123No ratings yet
- Mouseheart 2: Hopper's Destiny by Lisa Fiedler (Excerpt)Document63 pagesMouseheart 2: Hopper's Destiny by Lisa Fiedler (Excerpt)Simon and Schuster75% (4)
- Selection 2the Weird and Wonderful Echidna UpdatedDocument15 pagesSelection 2the Weird and Wonderful Echidna UpdatedShaikha TariqNo ratings yet
- 5096 s10 Ms 21Document6 pages5096 s10 Ms 21mstudy123456No ratings yet
- AnhydramnionDocument3 pagesAnhydramnionNi Wayan Ana PsNo ratings yet
- HEGUDocument2 pagesHEGUSee Hing Kok100% (1)
- Multi-Analyte ELISArrayDocument1 pageMulti-Analyte ELISArrayShi Jie PangNo ratings yet
- Talking Stick's Effect on HIV/AIDS Prevention Knowledge and Attitudes in TeenagersDocument7 pagesTalking Stick's Effect on HIV/AIDS Prevention Knowledge and Attitudes in TeenagersbaesootzuNo ratings yet
- Released Test Questions: English-Language ArtsDocument21 pagesReleased Test Questions: English-Language Artsapi-231632840No ratings yet
- Chapter_005 Interdependent Body SystemsDocument46 pagesChapter_005 Interdependent Body SystemsTina VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bites and StingsDocument23 pagesBites and StingsAngela PabloNo ratings yet
- Goats Farming Production Guide Thomson ZuluDocument16 pagesGoats Farming Production Guide Thomson ZuluOpirexNo ratings yet
- Ebook - ENG - PSICOLOGIA The Rorschach Test 1Document10 pagesEbook - ENG - PSICOLOGIA The Rorschach Test 1Carlos Ruiz R.No ratings yet
- Vinod DasDocument1 pageVinod DasAlfaiz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument7 pagesCommunity Acquired PneumoniaJoshuaOng100% (1)
- TB 06Document30 pagesTB 06Maria LumbanrajaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121No ratings yet
- Multiple Alleles Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesMultiple Alleles Detailed Lesson PlanDonna Domingo100% (6)
- Microlife bprm100 Usersmanual PDFDocument66 pagesMicrolife bprm100 Usersmanual PDFanon_188270051No ratings yet
- Effect of Subclinical Mastitis On Milk Composition in The Kenyan Smallholder Dairy HerdsDocument6 pagesEffect of Subclinical Mastitis On Milk Composition in The Kenyan Smallholder Dairy HerdsHenry OgolaNo ratings yet
- Cu31924001176878 DjvuDocument528 pagesCu31924001176878 Djvugaud28No ratings yet
- Retention and RelapseDocument59 pagesRetention and RelapseAshwin ThejaswiNo ratings yet
- Ode of The Jade Dragon Yu Long Fu PDFDocument10 pagesOde of The Jade Dragon Yu Long Fu PDFAikido EurogetNo ratings yet