Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Road Safety Risk Assessment Toolkit
Uploaded by
Damian R. RamesarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Road Safety Risk Assessment Toolkit
Uploaded by
Damian R. RamesarCopyright:
Available Formats
Road Safety Risk Assessment
1.0 Risk Assessment Process
The HSE Team at Daleem General Contracting Ltd. team has developed the risk
assessment process described here.
The methodology is a structured approach to the accepted risk assessment process of:
Identifying Hazards;
Determining Impacts;
Assessing Risk;
Identifying Controls; and
Producing Actions to further mitigate identified risks.
1.1 Key steps
Define Projects processes for assessment.
Develop a list of road safety related risks based on Projects processes.
Assign values for the impact and the probability of the event.
Assign values for the manageability of the risk creating an Overall Risk value that
is used for prioritisation
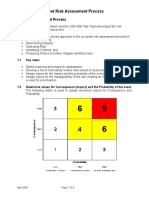
1.2 Determine values for Consequence (impact) and the Probability of the
event
The following matrix is used to assign numerical values for Consequence and
Probability.
High 3 6 9
Consequence
Med 2 4 6
Low 1 2 3
Probability
Low Med High
1 event over > 5 years 1 event every 5 years 1 or more events per Project
April 2011 Page 1 of 4
Road Safety Risk Assessment
1.3 Definitions
The following definitions are commonly in use through DGCL Projects. If not
appropriate, a Project could develop its own definitions.
Consequence of Projects Impact
Category People Property Process Environment
Potential
Severity
High*1 Fatalities >TTD 500,000 Major fire, exposure, >1000 litres
Risk to reputation
Multiple Serious Theft/Fraud Project Interruption:
Injuries >TTD 100,000 >TTD 500,000
Potential Commercial
Loss: >TTD 200,000
Medium DAFWC / >TTD 10,000 to Project Interruption: 100 – 1000
Restricted Work TTD 500,000 >TTD 10,000 to litres
Injuries TTD 500,000
Theft/Fraud Potential Commercial
Medical Treatment >TTD 10,000 to Loss: >TTD 10,000
TTD 100,000 to TTD 500,000
Low First Aid < TTD 10,000 <YYD 10,000 <100 litres
Subject to locality/circumstances/potential
Probability of an event
High
One or more events per Project/ year are likely.
Medium
One event per every 5 Projects/ years.
Low
One event in more than every 5 Projects years.
The assessment is looking for events, which are likely to happen in the
comparable industry and environment.
[Note: Event frequencies can be modified to fit PROJECT requirements.]
April 2011 Page 2 of 4
Road Safety Risk Assessment
Manageability of the risk
High
If the company has direct operational control of the process
Medium
If the company has indirect control of a process, or can only influence
Low
If social, political, cultural or technical issues are the reason for risks
The manageability should provide an overall view, if certain risks are fully under
the control of management. This could be of course a judgement only if it raises
healthy discussions on how far management is able or feels itself empowered to
control or influence HSE matters. The result should be used to tackle the high
manageable items first for quick implementation results only. It does not mean
that low manageable issues should not have actions identified.
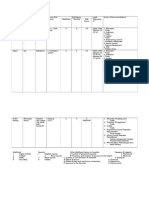
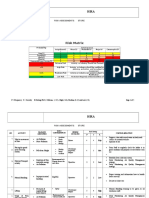
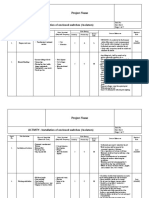
2.0 Risk Assessment Template
The Risk Assessment spreadsheets (attached Excel Workbook at the end of this
document) are used to document the identification of PROJECT Activities, Hazards, and
the values assigned for Consequence, Probability, Manageability and Risk.
It is suggested that a separate Sheet be used for each specific area of Activity.
Individual work site locations can be used as well.
For clarity, a completed example is included in the Excel Workbook.
Number
To be completed once the ‘Process, Sub-process and Hazard’ columns are filled in.
In the first column, record number of main activities within a Process.
In the second column, record the number of activities within sub-processes.
In the third column, record the number of actual risks/Hazards connected to
Process/sub-process
Process
Each individual Process is to be listed in the first instance
Sub-process
Each individual Process is then to be split in meaningful, not too detailed, sub-
processes, if any.
April 2011 Page 3 of 4
Road Safety Risk Assessment
Hazard
Processes and sub-processes are then to be ‘brain stormed’.
Consequence
Determined using the Risk Matrix described in section 1.2.
Probability
Determined using the Risk Matrix.
Risk
Multiply the value for consequence times the value Probability to get Risk.
Manageability
Critically review DGCL’s level of Control to determine levels of Manageability.
Classify Manageability as:
High: If the company has direct operational control of the process.
Rating = 1
Medium: If the company has indirect operational control of the process, or
can only influence.
Rating = 2
Low: If social, political, cultural or technical issues are the main reason
for the risks.
Rating = 3
3.0 Action Plans
Once all risks have been identified, rated and prioritised, action plans can be agreed.
4.0 Risk Assessment Tool
"Road Safety RAT
(Quant).xls"
April 2011 Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- 4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessDocument4 pages4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessHaymanAHMEDNo ratings yet
- PPO TMP RR ProjectRiskRegisterDocument12 pagesPPO TMP RR ProjectRiskRegisterSwadhin PalaiNo ratings yet
- Example Risk Assessment For A WarehouseDocument3 pagesExample Risk Assessment For A Warehousekhalid najjarNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Saad C.V Storekeeper, "Manufacture - Supply Chain"Document5 pagesIbrahim Saad C.V Storekeeper, "Manufacture - Supply Chain"Ibrahim Mohamed Saad Ibrahim67% (3)
- Health and Safety Risk Assessment: Activity Hazard Risk Rating (0 Low, 5 High) SolutionDocument2 pagesHealth and Safety Risk Assessment: Activity Hazard Risk Rating (0 Low, 5 High) SolutionBarry TuriNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesssment-Vinyl & Tile Floor InstallationDocument2 pagesRisk Assesssment-Vinyl & Tile Floor InstallationMunaku TafadzwaNo ratings yet
- Inherent V Residual RiskDocument2 pagesInherent V Residual RiskAlephNo ratings yet
- Example Risk Assessment FormDocument2 pagesExample Risk Assessment FormAzhar ArisNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: General Business Activity N/ADocument5 pagesRisk Assessment: General Business Activity N/AMOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- CONST-PK-HSE FRM-38 Environmental Risk Assessment and Control FormDocument6 pagesCONST-PK-HSE FRM-38 Environmental Risk Assessment and Control FormPerwez21No ratings yet
- Risk Assessments - StoreDocument5 pagesRisk Assessments - Storederwaishjee1100% (1)
- Safety DetailsDocument3 pagesSafety DetailsNauman TajNo ratings yet
- Sample of JHADocument5 pagesSample of JHAfarizaziz77No ratings yet
- Safety Health Emergency Response ProcedureDocument2 pagesSafety Health Emergency Response Procedurearjuna rahmat100% (1)
- HIRAC - Work - at - Height - Template PDFDocument8 pagesHIRAC - Work - at - Height - Template PDFRohma Desi ThirtasariNo ratings yet
- Loading & Unloading of Fire Fighting Foam 2V-7261 PDFDocument8 pagesLoading & Unloading of Fire Fighting Foam 2V-7261 PDFSanil ThomasNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Project Manager Project Engineer HSE Officer/engineer First AiderDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment: Project Manager Project Engineer HSE Officer/engineer First AiderOvais FarooqNo ratings yet
- Hazard Risk Assessment of Jack HammerDocument14 pagesHazard Risk Assessment of Jack HammerAkhtar BahramNo ratings yet
- Hydro Static Test: Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesHydro Static Test: Risk Assessmentmohammed a hseNo ratings yet
- AsdssssDocument1 pageAsdssssAviects Avie JaroNo ratings yet
- Black Spot Contamination in PelletDocument13 pagesBlack Spot Contamination in PelletkhuelvNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Near Miss ReportingDocument22 pagesHazard Identification and Near Miss ReportingAnandababuNo ratings yet
- Safety Hazard and Risk Assessment Form - DrillingDocument1 pageSafety Hazard and Risk Assessment Form - DrillingWan Aiman Wan Kamarul AzwanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Treatment ProcessDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment and Treatment ProcessManojNo ratings yet
- HIRAC - Work at Height TemplateDocument8 pagesHIRAC - Work at Height Templateputra2azanNo ratings yet
- Sample Swms Heights Mobile ScaffoldDocument7 pagesSample Swms Heights Mobile Scaffoldmani narayananNo ratings yet
- FactoryDocument8 pagesFactoryJonathan D'limaNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmntDocument5 pagesRisk Assessmntapi-456358200No ratings yet
- QuestionnairesDocument3 pagesQuestionnairesindirasiswantoNo ratings yet
- Al Majal QMS - 2018Document19 pagesAl Majal QMS - 2018Adam DeviatteyNo ratings yet
- Final Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesFinal Risk Assessmentapi-514194726No ratings yet
- GEN-005 Low Pressure Turbine and Generator Coupling and Decoupling Alignment CheckDocument3 pagesGEN-005 Low Pressure Turbine and Generator Coupling and Decoupling Alignment Checkacanbasri1980No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment (Park Bench)Document2 pagesRisk Assessment (Park Bench)BaileyNo ratings yet
- Production Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesProduction Risk AssessmentEmilyNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Pandemic Risk Assessment (High Medium and Low Risk Employees)Document6 pagesCOVID-19 Pandemic Risk Assessment (High Medium and Low Risk Employees)Zain Ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- TRA Strainer Cleaning 01Document7 pagesTRA Strainer Cleaning 01Ijaz Hussain0% (1)
- Risk Assessment PDFDocument30 pagesRisk Assessment PDFSamboy DionisioNo ratings yet
- Borang Hirarc (Surau)Document4 pagesBorang Hirarc (Surau)NurDoriaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Installation of Enclosed Switches IsolatorsDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment For Installation of Enclosed Switches IsolatorsADIL AL-AQABYNo ratings yet
- Jurong Island Cargo Tec RA Alignment of Cover Belt BC1 & BC2Document3 pagesJurong Island Cargo Tec RA Alignment of Cover Belt BC1 & BC2Anonymous kWfNFb100% (1)
- Risk ProfilingDocument12 pagesRisk ProfilingedmeanNo ratings yet
- TSTI FormDocument2 pagesTSTI FormJinu ThomasNo ratings yet
- HSE AuditingDocument20 pagesHSE AuditingMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Location Risk Assessment Form-Part A: Basic Information &: Hazard ListDocument4 pagesLocation Risk Assessment Form-Part A: Basic Information &: Hazard Listapi-330575448No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Form (RA1) : (Action by Whom and Completion Date - Use Separate Action Plan If Necessary)Document6 pagesRisk Assessment Form (RA1) : (Action by Whom and Completion Date - Use Separate Action Plan If Necessary)michael wakuthii100% (1)
- Hse Plan 3Document14 pagesHse Plan 3YcRij SeYerNo ratings yet
- RA Arc, Welding 150310Document4 pagesRA Arc, Welding 150310Mohd FikryNo ratings yet
- PPE Risk Assessment DocumentDocument5 pagesPPE Risk Assessment DocumentFarzanaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response PlanDocument18 pagesEmergency Response PlanExplosive DepressionNo ratings yet
- ABC - ra.CWSS.19-HIRA-Erection of Precast Columns, BeamsDocument5 pagesABC - ra.CWSS.19-HIRA-Erection of Precast Columns, BeamsShafie ZubierNo ratings yet
- 4 August 2021 ExamDocument5 pages4 August 2021 ExamRafa'eel BickooNo ratings yet
- Use of Stepladders 05Document1 pageUse of Stepladders 05cardyNo ratings yet
- HIRA MatrixDocument4 pagesHIRA MatrixManoj SurveNo ratings yet
- Fse Risk Assessment ExampleDocument11 pagesFse Risk Assessment ExampleRami Fa'our100% (1)
- Crisis ManagementDocument19 pagesCrisis Managementsssr3103No ratings yet
- HiraDocument8 pagesHirarajmohapatraNo ratings yet
- Risk Control Activities Contro L Catego RY Coso Components Control Attributes Control Classification TestingDocument7 pagesRisk Control Activities Contro L Catego RY Coso Components Control Attributes Control Classification TestingCaptain ObviousNo ratings yet
- 4risk ManagementDocument8 pages4risk ManagementSomar SafatlyNo ratings yet
- Guyana Parliament 2020Document13 pagesGuyana Parliament 2020Damian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Liquidity in The Global Gold MarketDocument20 pagesLiquidity in The Global Gold MarketMarco PoloNo ratings yet
- Guyana Parliament 2020Document13 pagesGuyana Parliament 2020Damian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Animal Riddles Copyright English Created Resources WWW The7esl Com PDFDocument12 pagesAnimal Riddles Copyright English Created Resources WWW The7esl Com PDFbabytwelveNo ratings yet
- Florida Vegetable Production HandbookDocument256 pagesFlorida Vegetable Production HandbookDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Creating A Prequalification ProgramDocument1 pageCreating A Prequalification ProgramDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Course Outlines IashepDocument143 pagesCourse Outlines IashepDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Handle GuideDocument46 pagesFuel Handle Guidekrunalb@inNo ratings yet
- 5010A SafeStart WORKER 2004 PDFDocument11 pages5010A SafeStart WORKER 2004 PDFDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Model WatchmanDocument72 pagesModel WatchmanDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Tank Cleaning ProcedureDocument3 pagesTank Cleaning ProcedureAlfredoNo ratings yet
- EDIYA StartersguideDocument18 pagesEDIYA StartersguideDamian R. RamesarNo ratings yet
- Complete Quality Manual Vol 2 Rev. 2010Document277 pagesComplete Quality Manual Vol 2 Rev. 2010Percy Ruiz Feril100% (1)
- I. You'll Hear A Conversation Between Two People. Listen and Fill in The Blanks (10 PTS) This Is The VOA Special English Agriculture ReportDocument7 pagesI. You'll Hear A Conversation Between Two People. Listen and Fill in The Blanks (10 PTS) This Is The VOA Special English Agriculture ReportTHỌ NGUYỄN VĂNNo ratings yet
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Intraday Trading On Nifty (2nd September, 2021) 8 Lakhs Profit Shreyas Bandi Trade Ideas Live (DownSub - Com)Document41 pages(English (Auto-Generated) ) Intraday Trading On Nifty (2nd September, 2021) 8 Lakhs Profit Shreyas Bandi Trade Ideas Live (DownSub - Com)YaaroNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Electronics - Book - CircuitLabDocument3 pagesUltimate Electronics - Book - CircuitLabEldon50% (2)
- Himachal Pradesh Staff Selection Commission Hamirpur - 177001Document2 pagesHimachal Pradesh Staff Selection Commission Hamirpur - 177001Verma JagdeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SBLDocument4 pagesChapter 6 SBLbrave manNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm SymbolsDocument6 pagesFire Alarm Symbolscarlos vasquezNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 9-A - Module 6 - Tumacder, DHMLDocument6 pagesProf Ed 9-A - Module 6 - Tumacder, DHMLDanica Hannah Mae TumacderNo ratings yet
- Sem06 Gca InsoDocument2 pagesSem06 Gca InsoBogdan PistolNo ratings yet
- P&G Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesP&G Interview Questionssupu100% (3)
- Casio AT 1 Service ManualDocument28 pagesCasio AT 1 Service ManualMario Gabriel MoralliNo ratings yet
- FINAL ReportDocument48 pagesFINAL ReportMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Solved Consider Again The Demand Function For Corn in Formula 1Document1 pageSolved Consider Again The Demand Function For Corn in Formula 1M Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- 02.certificate of Compliance FM UkDocument10 pages02.certificate of Compliance FM Ukmyatthura870No ratings yet
- Beamforming For 4.9G/5G Networks: Exploiting Massive MIMO and Active Antenna TechnologiesDocument12 pagesBeamforming For 4.9G/5G Networks: Exploiting Massive MIMO and Active Antenna TechnologiesAymen Ben zinebNo ratings yet
- ICorr CED CT01 InspectionAndTestingOfCoatings Issue1-2Document13 pagesICorr CED CT01 InspectionAndTestingOfCoatings Issue1-2AlineMeirelesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To EFTDocument24 pagesAn Introduction To EFTkunjammuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Fundamental and Derived QuantitiesDocument7 pagesChapter 01 Fundamental and Derived QuantitiesAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Robots Part Two, The Illusion of Life (Week Three)Document34 pagesRobots Part Two, The Illusion of Life (Week Three)Vitor MacedoNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0009 Thermodynamic Lecture MRCDocument1 pageIMG - 0009 Thermodynamic Lecture MRCBugoy2023No ratings yet
- 3-Storeyed 31-3-2015-Schedule PDFDocument1 page3-Storeyed 31-3-2015-Schedule PDFSi Thu AungNo ratings yet
- MiningDocument3 pagesMiningDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Revised Research ZoomDocument51 pagesRevised Research ZoomAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Parking SpaceDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Parking Spacefvgy6fn3100% (1)
- INT PL 2020 Web 01-20 PDFDocument320 pagesINT PL 2020 Web 01-20 PDFAndriana Vilijencova100% (1)
- St. Louis College of Bulanao: Title/Topic Technical English I Introduction To Police Report WritingDocument41 pagesSt. Louis College of Bulanao: Title/Topic Technical English I Introduction To Police Report WritingNovelyn LumboyNo ratings yet
- Permeability Estimation PDFDocument10 pagesPermeability Estimation PDFEdison Javier Acevedo ArismendiNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Problem 2Document3 pagesOlympiad Problem 2Đạt Nguyễn BáNo ratings yet
- Cusps: Ramesh 04-Jun-1976 12:30:00 PM Krishnagiri 78:14:0 E, 12:32:0 N Tzone: 5.5 KP (Original) Ayanamsha 23:26:2Document1 pageCusps: Ramesh 04-Jun-1976 12:30:00 PM Krishnagiri 78:14:0 E, 12:32:0 N Tzone: 5.5 KP (Original) Ayanamsha 23:26:2Suresh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- SOL-Logarithm, Surds and IndicesDocument12 pagesSOL-Logarithm, Surds and Indicesdevli falduNo ratings yet
- Compressor-Less: Historical ApplicationsDocument70 pagesCompressor-Less: Historical Applicationssuryakantshrotriya100% (1)