Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cine Ole
Uploaded by
Kovidendra KaushikOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cine Ole
Uploaded by
Kovidendra KaushikCopyright:
Available Formats
Cineole
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5.0
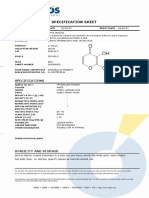
CINEOLE Cineolum
C10H18O DEFINITION 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane.
01/2005:1973 Reference solution (a). To 2.0 ml of test solution (a) add 20.0 ml of the internal standard solution and dilute to 100.0 ml with heptane R. Reference solution (b). Dissolve 50 mg of 1,4-cineole R and 50 mg of the substance to be examined in heptane R and dilute to 50.0 ml with the same solvent. Column : size : l = 30 m, = 0.25 mm, stationary phase : macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness 0.25 m). Carrier gas : helium for chromatography R. Mr 154.3 Linear velocity : 45 cm/s. Split-ratio : 1:70. Temperature :
Time (min) Column 0 - 10 10 - 35 35 - 45 45 - 55 Temperature (C) 50 50 100 100 200 200 220 250
CHARACTERS Appearance : clear colourless liquid. Solubility : practically insoluble in water, miscible with alcohol and with methylene chloride. It solidifies at about 0.5 C. IDENTIFICATION A. It complies with the test for refractive index (see Tests). B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Test solution. Dilute 1 ml of solution S (see Tests) to 25 ml with alcohol R. Reference solution. Mix 80 mg of cineole CRS with alcohol R and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent. Plate : TLC silica gel plate R. Mobile phase : ethyl acetate R, toluene R (10:90 V/V). Application : 2 l. Development : over 2/3 of the plate. Drying : in a current of cold air. Detection : spray with anisaldehyde solution R, heat at 100-105 C for 5 min. Results : the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution. C. To 0.1 ml add 4 ml of sulphuric acid R. An orange-red colour develops. Add 0.2 ml of formaldehyde solution R. The colour changes to deep brown. TESTS Solution S. Dilute 2.00 g to 10.0 ml with alcohol R. Appearance of solution. Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method I). Chiral impurities. The optical rotation (2.2.7) of solution S is 0.10 to + 0.10. Refractive index (2.2.6) : 1.456 to 1.460. Related substances. Gas chromatography (2.2.28). Internal standard solution. Dissolve 1.0 g of camphor R in heptane R and dilute to 200 ml with the same solvent. Test solution (a). Dissolve 2.5 g of the substance to be examined in heptane R and dilute to 25.0 ml with the same solvent. Test solution (b). Dissolve 2.5 g of the substance to be examined in heptane R, add 5.0 ml of the internal standard solution and dilute to 25.0 ml with heptane R. 1294
Injection port Detector
Detection : flame ionisation. Injection : 1 l. System suitability : reference solution (b) : resolution : minimum 10 between the peaks due to impurity A and to cineole. Limits : total : calculate the ratio (R) of the area of the peak due to cineole to the area of the peak due to the internal standard from the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) ; from the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b), calculate the ratio of the sum of the areas of any peaks, apart from the principal peak and the peak due to the internal standard, to the area of the peak due to internal standard : this ratio is not greater than R (2 per cent), disregard limit : 0.025 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent). Residue on evaporation : maximum 0.1 per cent. To 2.0 g add 5 ml of water R, evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and dry at 100-105 C for 1 h. The residue weighs a maximum of 2 mg. STORAGE In an airtight container, protected from light. IMPURITIES
A. 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane (1,4-cineole).
See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Revisin Test - Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesRevisin Test - Chemical KineticsSABIQNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Pyrite Formation by H2S Oxidation of Iron (II) Monosulfide in Aqueous Solution Between 25 and 125 °C The Rate EauqetionDocument20 pagesKinetics of Pyrite Formation by H2S Oxidation of Iron (II) Monosulfide in Aqueous Solution Between 25 and 125 °C The Rate EauqetionSergio ArangoNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Ceramics TESDocument9 pagesYear 8 Ceramics TESZain AliNo ratings yet
- GPC-IR DatasheetDocument2 pagesGPC-IR DatasheetEdwel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 5th International Seminar On Process Hydrometallurgy PDFDocument447 pages5th International Seminar On Process Hydrometallurgy PDFRicardo BertolottoNo ratings yet
- Esssential Water Chemistry I-2Document12 pagesEsssential Water Chemistry I-2Mers AbeNo ratings yet
- Patel J - ULNb Solution For Commodty Grade Structural SteelsDocument8 pagesPatel J - ULNb Solution For Commodty Grade Structural SteelsimetallurgyNo ratings yet
- Texapon SFA (OPP)Document1 pageTexapon SFA (OPP)paromanikNo ratings yet
- Bigdye Terminator V3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit: ProtocolDocument72 pagesBigdye Terminator V3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit: Protocoliis faridahNo ratings yet
- Hypervalent Compounds: G. Sean Mcgrady & Jonathan W. SteedDocument21 pagesHypervalent Compounds: G. Sean Mcgrady & Jonathan W. SteedAndreea DamianNo ratings yet
- Results of First Periodical Test in Science: Name of School: EUGENIO G. SY TAMCO E. SDocument3 pagesResults of First Periodical Test in Science: Name of School: EUGENIO G. SY TAMCO E. SDima JhamboyNo ratings yet
- SPME Injection TechniquesDocument2 pagesSPME Injection TechniqueshtcpetroupoliNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inspection of Piping CircuitDocument14 pagesCorrosion Inspection of Piping CircuitPrasad ChakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry and Thermochemistry ProblemsDocument2 pagesCalorimetry and Thermochemistry ProblemsHakan öztepeNo ratings yet
- HETEROGENEOUSDocument18 pagesHETEROGENEOUSMaan Joy Revelo GallosNo ratings yet
- AMIT PPT Sem 1Document21 pagesAMIT PPT Sem 1Uma VedulaNo ratings yet
- Explore Our Phenomenal World: PhysicsDocument66 pagesExplore Our Phenomenal World: Physicsjsencion977100% (1)
- Oxford Combined Brochure 8.5x11 V3.0-CompressedDocument44 pagesOxford Combined Brochure 8.5x11 V3.0-CompressedRafaelGerardoAgueroZamoraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Expt 2Document4 pagesLab Report Expt 2Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- Space Lattice Basis Crystal StructureDocument6 pagesSpace Lattice Basis Crystal StructureMainzaNo ratings yet
- Voltammetry and PolarographyDocument30 pagesVoltammetry and PolarographyDr Nilesh Patel100% (1)
- Lucar & Connector Plate Plating DetailsDocument2 pagesLucar & Connector Plate Plating DetailsSVAIPLNo ratings yet
- Module 2 HydrocarbonsDocument19 pagesModule 2 HydrocarbonsGabrielle TomoNo ratings yet
- Sweet Caramel Flavoring Spec SheetDocument1 pageSweet Caramel Flavoring Spec SheetMarhun AlcinaNo ratings yet
- AMBERLITE™ HPR1200 Na Ion Exchange Resin: DescriptionDocument4 pagesAMBERLITE™ HPR1200 Na Ion Exchange Resin: DescriptionIGNyomanAnomWijayaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY PROBLEMSAbhishek RavirajNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science MCQ on Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument30 pagesClass 10 Science MCQ on Periodic Classification of ElementsAymen WaelNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesTopic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerCheng Xun LeeNo ratings yet
- Class Xi HHWDocument16 pagesClass Xi HHWDhruv PanditaNo ratings yet
- Coursework E-Submission Cover Sheet: To Be Completed by The StudentDocument50 pagesCoursework E-Submission Cover Sheet: To Be Completed by The Studentniran_udayangaNo ratings yet