Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mental Assessment Status
Uploaded by
Pretty Grace Jumalon AnesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mental Assessment Status
Uploaded by
Pretty Grace Jumalon AnesCopyright:
Available Formats
MENTAL STATUS ASSESSMENT
AREA OF ASSESSMENT A. General Appearance
TYPE OF ASSESSMENT Observations about dress, hygiene, posture, gait and appearance Appearance versus stated age
NORMAL PARAMETERS y y y y y y y y y y Clean Nails trimmed Tidy /neatly dressed hair is combed Dress/ clothing intact appropriate for age, weather and situation Teeth/dentures in good repair No unusual odors No obvious marks or scars Appears as stated age y
y y y y y y
y y y y y y y y y y
ALTERATIONS FROM NORMAL Disheveled (with messed-up hair or clothes) unkempt Untidy Dirty Foul smelling/ unusual odor (urine, alcohol) Inappropriate clothing (explain) Displays either unusual apathy or concern about appearance Malnourished appearance (emaciated) Flushed or pallid skin color Excessive sweating Injury or scarring Dilated or constricted pupils Dental carries or parotid swelling Erosion of nasal or oral mucosa Rope marks on neck Older appearance than stated age Drooling of saliva
IMPLICATIONS y Disinterest in appearance may reflect depression or low self-esteem Poor hygiene and a disheveled appearance may also reflect patients inability to care for himself or herself Worn clothing may indicate financial problems Bright colors or unusual dress are associated with mania Malnourished appearance may indicate eating disorder Flushed or pallid skin color are seen with anxiety Excessive sweating are seen with anxiety Injury or scarring from self injury or past suicide attempts or self mutilation Dilated or constricted pupils are seen with drug abuse Dental carries or parotid swelling are seen with eating disorders Erosion of nasal or oral mucosa maybe secondary
y y
y y y
y Posture Erect/upright Symmetrical extremities Comfortably positioned Slumped Stooped Defensive with hips and knees somewhat flexed and arms bent at the elbows Lordotic Scoliotic Kyphosis (+) spastic movements shuffling unsteady foot dragging limping with wide base of support and short stride length uses an assistive device (crutches)
y y y
y y y y
y y y y
Gait
y y
steady movement is smooth and coordinated
y y y y y y y y y y
to drug use Rope marks on neck seen in children with choking game or patients with history of hanging themselves Older appearance than stated age may be associated with depression Wearing of long sleeves even during warm weather may indicate drug abuse Drooling of saliva may indicate side effects of antipsychotic medication slumped position may indicate fatigue or depression stooped posture may be associated with depression Defensive is associated with paranoia
Gait problems may suggest a musculoskeletal or neurological problem Spastic movements or unsteady gaits maybe seen in patients with cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis Wide base of support and short stride length may have a balance or cerebellar problem
Eye contact
Maintains eye contact
y y
Can not maintain/poor eye contact preoccupied
y Facial expression calm appropriate to words expressed happy Cooperative Calm Attentive Alert Awake Relaxed No unusual movement or behaviors Warm Friendly sad angry facial grimace uncooperative hostile aloof restless agitated irritable aggressive guarded lethargic tremors generalized weakness repeated movements unusual tics or tremors paranoid/suspicious automatism : repeated purposeless behaviors such as drumming of fingers, twisting locks of hair, or tapping the foot psychomotor retardation: overall slowed movements waxy flexibility: maintenance of posture or position over time even when it is awkward or uncomfortable repeated picking at clothes
inability to maintain eye contact may indicate low self esteem or depression pre-occupation may indicate signs of hallucination
B. Behavior /Activity
Observations about patients actions and reactions to health personnels
y y y y y y y y y y y y
y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y
y y y y
y y y y y y
y y
uncooperative is associated with paranoia hostile/aloof are seen with psychosis guarded/aggressive are seen with psychosis unusual tics or tremors or abnormal muscle movement may indicate side effects of antipsychotic medications, drug or alcohol withdrawal agitation maybe seen with dementia or delirium automatism is indicative of anxiety restlessness, tension is associated with anxiety irritability is associated with anxiety suspiciousness are associated with paranoia generalized weakness and tremors are seen with anxiety repeated movements are
y y y y y y y
y y y
increased reflexes hyperactivity rigid catatonic jaw/lip smacking combative apathetic: not taking any interest on anything or not bothering to do anything distant hopeless Echopraxia: repetition or imitation of observed movements Pica :persistent ingestion of nonnutritive substances such as paint, hair, cloth, leaves, sand, clay or soil.
y y
y y
y y
associated with compulsive disorders psychomotor retardation/hypoactivity are associated with depression, catatonic states or drug induced stupor excessive body movements are associated with mania, anxiety or stimulant abuse repeated picking at clothes maybe associated with hallucinations, delirium or toxic conditions increased reflexes may be associated with anxiety hyperactivity is associated with anxiety, mania, or stimulant abuse rigidity may be a sign of NMS akathisia (restlessness) may be seen with extrapyramidal adverse effect from antipsychotic medications catatonia may be seen with schizophrenia unusual movements such as jaw/lip smacking may be associated with tardive dyskinesia, an adverse effect of antipsychotic medications
y y y
suspicious/combative are seen with paranoia apathetic are seen with depression warm/friendly/distant are seen with personality disorders hopeless are seen with depression
C. Speech
Observations of patients speech quantity and quality
y y y y y y
Humor Soft Appropriate Modulated voice/ tone audible Clear Fluent
y y y y y y y y y y y y
Frightened Hesitant Slurred Loud Superior Very soft/ not audible Garbled Mumbling Hesitant Mute Latency of response Poverty of speech
y y
y y
The patients vocabulary and sentence structure offer clues to her or his educational level Changes in voice quality may indicate neurological problem. Slurred speech may indicate drug and alcohol abuse Mumbling are seen with Huntingtons chorea Poor fluency ( mute/hesitation/latency of response)less likely to talk with depression Hesitation is seen with mistrust or paranoia Commonly seen in long term patients in the hospital suspiciousness is associated with paranoia choice of words reflect
Style and vocabulary covey
y y y
Formal Humor Appropriate
y y y
Arrogance Coyness: shy /reserved Fear
y y
No exaggeration
Stream of Talk
y y y
Spontaneous Normal pace Pleasant tone
y y y y y y y y y y
Organization of Talk
y y
Relevant Appropriate response
y y y
y y
Secrecy Superiority Suspiciousness exaggerated Deliberate: carefully thought out and done intentionally Pressured Slow Fast Stuttering Lisping: speech difficulty in which the sounds s and z are pronounced as th Thought blocking: stopping abruptly in the middle of a sentence or train of thought; sometimes unable to continue the idea Irrelevant Disorganized Circumstantiality: patient gives much unnecessary detail that delays meeting a goal or point Clang Association: use of rhyming words Echolalia: parrot like repetition of another persons phrases or words Flight of Ideas: over productivity of talk characterized by verbal skipping from one idea to another composed of fragmented and unrelated
socio-economic status
y y
y y y
y y
Pressured speech, inappropriate responses, and illogical or incoherent speech may be indicative of psychiatric disorders Pressured, hurried speech may also be seen in patients with hyperthyroidism Pressured speech are seen in mania Slow speech and soft tone is associated with depression may be indicative of psychiatric disorders Disorganized speech are seen with schizophrenia Loose Association is associated with schizophrenia Flight of Ideas are associated with mania Perseveration is associated with brain damage and psychotic disorders
y y
ideas Incoherent: unable to express feelings clearly or logically Loose Association: disorganized thinking that jumps from one idea to another with little or no evident relation between the thoughts Neologism: invented words that have meaning only for the client Perseveration: tendency to stuck in one topic and unable to move to another idea Tangentiality: wandering off the topic and never providing information requested Word salad: flow of unconnected words that convey no meaning to the listener Derailment: off track Verbigeration: meaningless repetition of words of phrases Depressed Euphoric Labile : mood swings from depressed to crying (rapidly changing) Sad Anxious Worried y y y y Sad is associated with depression Anxious is seen with anxiety Worried /Angry are seen with personality disorders Mixed : anxious and depressed are seen with
D. Mood
Observation and y assessment to the y clients pervasive and enduring emotional y state
Happy Normal The nurse may ask the client to rate his or her mood on a scale of 1-10. If the client reports being depressed, the nurse might ask, On a scale of 1-10 with 1 being
y y y
y y y
least depressed and 10 being most depressed, where would you place yourself right now?
y y y y
E. Affect
Assessment of the outward expression of the clients emotional state or feelings
Appropriate to the situation and feelings verbalized
y y
y y
y y y y y F. Range of Affective Expression y y Consistent Appropriate to the situation and feelings verbalized y y
Angry Unpredictable Fearful Ambivalent : opposing impulses or feelings directed toward the same person or object at the same time Blunt: showing little or slow to respond facial expression Broad : displaying a full range of emotional expression Flat : showing no facial expression Inappropriate affect: displaying a facial expression that is incongruent with mood or situation; often silly or giddy regardless of circumstances Restricted : displaying one type of expression, usually serious or somber Euphoric/Elated: happy and excited Angry Anxious Fearful Labile Labile Anhedonic; having no pleasure or joy in life; losing sense of pleasure from activities formerly enjoyed
depression
y y y
Labile affect may indicate mania Flat incongruent affect may reflect schizophrenia Inappropriate affect is associated with schizophrenia
G. Perception
a. Hallucination Auditory Gustatory Olfactory Tactile Visual b. Delusion Grandeur Persecutory Reference
y y y y y y y y y y
Assesses the way a person experiences reality. Observe the patients statements about his or her environment and the behaviors expressed in association with those statements. Assesses false sensory perceptions or perceptual experiences that do not really exist Hearing voices Tasting unusual tastes not related to food eaten Smelling things Able to feel something not really there Seeing things, people, etc that do not exist Fixed false belief not based in reality False belief of being great or almighty False belief of being persecuted Clients inaccurate interpretation that general events are personally directed to him or her, such as hearing speech on the news and believing the message has personal meaning A delusional belief that others can hear or know what the client is thinking A delusional belief that others are putting ideas or thought into the clients head- that is , the ideas are not those of the client A delusional belief that others are taking the clients thoughts away and the client is powerless to stop it Misperception of a real external stimulus Feeling of having something experienced before, although in fact it is the first time that it has been experienced Altered perception or experience that causes temporary loss of self or personal identity Client senses events are not real when in fact, they are Unconscious imitation of patterning ones mannerisms, behavior and feelings in accordance with those of the other person An irrational feeling, that what is being perceived has never
y y y y y
Associated with schizophrenia
Seen with organic problems, drug abuse, or delirium tremens (DTs) Often organic in nature Associated with psychosis
Thought Broadcasting Thought insertion Thought withdrawal c. Illusion Dj Vu Depersonalization Derealization Identification
y y y y y y y y
Common with dementia, Alzheimers, and schizophrenia
Seen with panic disorder
Jamais Vu
May be seen in some forms of epilepsy and some psychiatric
been seen before H. Thought Content Paranoia Phobias Assessment of what the patient is thinking Assessment of suspiciousness Illogical, intense, persistent fear of a specific object or social situation that causes extreme distress and interferes with normal functioning Thoughts of harming self or others y Are you thinking about killing yourself? y Do you have a plan to kill yourself? y How do you plan to kill yourself? y How would you carry out this plan? y Do you have acces to the means to carry out the plan? y Where would you kill yourself? y When do you plan to kill yourself? y What day or time of day do you plan to kill yourself? y Recurrent, persistent, intrusive, and unwanted thoughts and images or impulses that cause marked anxiety and interfere with interpersonal, social, or occupational function y Primitive form of thinking that something will make it happen y Can not make sense of his or her surroundings or figure things out even if he is oriented y Assessment of patients awareness of date, time, place y What year is it? y What day is today? y What time is it now? y Where are you right now? y In what country do you live? y What is the capital of this province? y Who is sitting in front of you? y What is the name of the nurse? y Assesses immediate y Intact y y y
conditions, Seen in patients with schizophrenia Seen in patient with anxiety disorders
y y
Suicidal/homicidal
Associated with depression, anxiety or schizophrenia
Obsession
Seen in OCD
Magical thinking Confused I. Orientation
y y y Altered orientation may be seen with organic disorders or schizophrenia
Date Time Place
People (Examiner, etc.) J. Memory
Confabulation: giving
Seen with organic,
recall of recent and remote memory
Good
fictitious accounts of past events, believing they are true, in order to cover a gap in the memory
dissociative and conversion disorders Seen with dementia or Korsakoffs syndrome
Recent (24 hrs)
Past (1 week) Remote y Recall of events beyond 2 weeks before assessment
K. Neuro-vegetative Functioning
To test recent memory: y State clearly and slowly the name of three unrelated objects. After you say all three, ask the patient to repeat each. Continue until the patient is successful. Then, later in the assessment ask the patient to repeat the three words again. The patient should be able to identify the three words. y Ask the patient to recall events during the same day (e.g. what was eaten during the breakfast). Validate information with a family member. y Ask the patient about any news or events during the week y Ask patient to recall maiden name of mother, a birthday or a special day in history. It is best to ask open ended questions rather than simple yes or no questions y Normal Sleep
y y y y y y
Early morning awakening Middle night awakening Hyperinsomia Difficulty of falling asleep Interrupted sleep
May be seen in bipolar disorder
L. Elimination Bowel y Once a day y Twice a day
Three times a day y Others Bladder y Once a day y Twice a day y Three times a day Others M. Abstract Thinking Ability y
Enuresis
Enuresis may indicate anxiety
Assesses capacity to think abstractly
y y
Intact Good
y y
Intellectual functioning
The nurse must consider formal education of client
Ask patient to explain common sayings such as: y A stitch in time saves nine. y Dont count the chickens before they are hatched y You cant teach old dogs new tricks. y People who live in glass houses should not throw stones. y Intact y Good y y What is the similar about an apple and an orange? What do newspaper and the television have in common? Good Intact Appropriate
Lacking Concrete thinking :Impaired/unable to abstract: thinks in concrete terms
Seen with psychosis organic brain disorders
Impaired
May indicate level of education of client.
N. Judgment
Ability to interpret ones environment and situation correctly and to adapt ones behavior and decisions accordingly
y y y
y y y y
Poor Impaired Impulsive Risky behavior
y y
To test: y If you were walking down the street and saw a smoke coming
poor judgment is seen in psychosis poor impulse control is seen with OCD, psychosis, mania
O. Insight
Judgment requires a comparison and evaluation of facts and ideas to understand their relationships and to form appropriate conclusions. Attempts to measure patients logical ability to make logical decisions Awareness of the nature of illness/situation and accept some personal responsibility for that situation
out from a window of a home, what would you do? What would you do if somebody suddenly becomes ill at home?
y y
Good Intact
y y y
Partial Poor Impaired
poor insight is seen in psychosis
P. Ability to concentrate
y y y
Focused Attentive Receptive
To test: y Spell the word BIRD backwards y Begin with the number 100, subtract 7, and subtract 7 again, and so on. This is called the SERIAL SEVENS. y Repeat the days of the week backward. y Perform a three-part task, such as Take a piece of paper in your right
It is my wifes fault that I drink and gets into fight. The problem is my medication. As soon as the doctor gets the medication right, Ill be just fine. y impaired y Distracted y Preoccupied y Poor y Short attention span
Inability to maintain attention is associated with schizophrenia and depression Preoccupation is seen with patients experiencing hallucination
Q. Self concept
The way one views oneself in terms of personal worth and dignity
hand, fold it in half, put it on the floor. (The nurse should give the instructions one at a time.) Good
Poor
R. Roles and Relationships
To test y Ask the client to describe herself or himself and what characteristics he or she would like to change Assesses how a y Can manage roles and sustain person function in the relationships community (mother, wife, son, daughter, teacher, secretary) y Do you feel close to your family? y Do you have or want a relationship with a significant other? y Are your relationships meeting your needs for companionship or intimacy? y Can you meet your sexual needs satisfactorily? y Have you been involved in any abusive relationships?
Poor self concept is common to depressed patients
y y
Can not maintain satisfying relationship Has difficulty managing her roles and functions
Inability to sustain satisfying relationships can result from mental health problems or can contribute to the worsening of some problems.
You might also like
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20Document47 pagesNursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20nidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExamDocument44 pagesMental Status ExamHershey Cordero Briones100% (1)
- IV TherapyDocument34 pagesIV Therapyfairwoods100% (2)
- Health Assessment TAKE HOME ASSIGNMENT CH 4 The Complete Health History Name - Section - DateDocument5 pagesHealth Assessment TAKE HOME ASSIGNMENT CH 4 The Complete Health History Name - Section - DateAndy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Complete Head To Toe AssessmentDocument13 pagesComplete Head To Toe AssessmentJoanne Bernadette AguilarNo ratings yet
- HCA Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesHCA Job DescriptionAnonymous 8sBh71wrHNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Health Care PlanDocument14 pagesBehavioral Health Care Planapi-472030023100% (1)
- Fdar Psyche 3Document1 pageFdar Psyche 3Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing (Personality Disorders)Document9 pagesPsychiatric Nursing (Personality Disorders)Magbanua Airene MarielNo ratings yet
- Assignment GERIATRIC ASSESSMENTDocument6 pagesAssignment GERIATRIC ASSESSMENTNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Mental State Examination (MSE)Document3 pagesMental State Examination (MSE)austin worksNo ratings yet
- Most Question That The "Psychiatrist" Would Ask?Document1 pageMost Question That The "Psychiatrist" Would Ask?Chayantorn NimmanwathanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover Letterapi-441650865No ratings yet
- Patient History and PhysicalDocument6 pagesPatient History and PhysicalDavid DengNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "Extended Care"Document29 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Extended Care"jhonroks100% (3)
- ChartingDocument1 pageChartingberhanubedassa100% (2)
- Anti Social Personality HandoutDocument4 pagesAnti Social Personality HandoutErfana ThasnemNo ratings yet
- Stages of Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesStages of Growth and DevelopmentJaney Cunanan100% (6)
- KleptomaniaDocument3 pagesKleptomaniaaditiNo ratings yet
- Summary Complete Mental Health NursingDocument20 pagesSummary Complete Mental Health Nursingraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Process Recording Doument 1Document2 pagesProcess Recording Doument 1Susan Bloomquist DavisNo ratings yet
- Real Resume Family Nurse Practitioner Resume Phoenix ArizonaDocument1 pageReal Resume Family Nurse Practitioner Resume Phoenix ArizonaRick WhitleyNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart PresentationDocument38 pagesCrash Cart PresentationElsubaiNo ratings yet
- Psych - Nursing InterventionsDocument23 pagesPsych - Nursing Interventionsmarie100% (19)
- Insulin Administration)Document1 pageInsulin Administration)DanielleNo ratings yet
- Diet TherapyDocument78 pagesDiet TherapyVianne Arcenio100% (1)
- Mental Status Examination: April 04, 2019 Sablan, BenguetDocument73 pagesMental Status Examination: April 04, 2019 Sablan, BenguetChristi MilanNo ratings yet
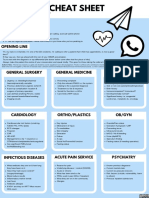
- Referral Cheat Sheet: Before You CallDocument2 pagesReferral Cheat Sheet: Before You CallXyz100% (2)
- Mental Status AssessmentDocument16 pagesMental Status Assessmentnokolip100% (1)
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument5 pagesTherapeutic CommunicationShielah de Paul Enriquez100% (2)
- Mental Health E3 QuizletDocument2 pagesMental Health E3 QuizletTodd ColeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument12 pagesNursing Leadership and ManagementEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia PDFDocument32 pagesSchizophrenia PDFJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Tele MedicineDocument9 pagesTele MedicinekevinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ProjectDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan ProjectMj WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Insulin Comparison ChartDocument1 pageInsulin Comparison Chartmaend87No ratings yet
- SOAP NoteDocument26 pagesSOAP Noteapi-376765485% (13)
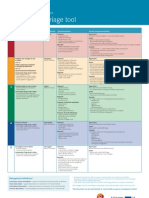
- Mental Health Triage Tool 2006Document1 pageMental Health Triage Tool 2006MelbourneFXNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient InteractionDocument15 pagesNurse Patient Interactionglynn_i_pasigonNo ratings yet
- The Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFDocument29 pagesThe Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFMiguel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Progress NotesDocument13 pagesProgress Notesdnarita100% (1)
- Psychiatric Phenomenology From First Principles for Medical Students, Psychiatric Residents, and PractitionersFrom EverandPsychiatric Phenomenology From First Principles for Medical Students, Psychiatric Residents, and PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Outline of A Mental Status AssessmentDocument7 pagesOutline of A Mental Status AssessmentAnnalisa TellesNo ratings yet
- Terminologies Use in PsychiatryDocument35 pagesTerminologies Use in PsychiatryKing IvyNo ratings yet
- M S eDocument87 pagesM S eabhishek agarwalNo ratings yet
- MSE1Document8 pagesMSE1Granty GarcesNo ratings yet
- The Mental Status ExamDocument7 pagesThe Mental Status ExamAnonymous ewPKlLWtfhNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument33 pagesAbnormal PsychologyChristie SabgaNo ratings yet
- Emotional Disturbance & Speech and Language ImpairmentDocument9 pagesEmotional Disturbance & Speech and Language ImpairmentJai SabusabNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease: By: Nalla Sheena Daffodil C. ArizaDocument18 pagesHeart Disease: By: Nalla Sheena Daffodil C. ArizaCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument9 pagesCognitive Disordersgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- DysarthriaDocument2 pagesDysarthriaBanjo VergaraNo ratings yet
- Health Reporting Mind IllnessesDocument8 pagesHealth Reporting Mind IllnessesChristian Kyle Talledo BaclayNo ratings yet
- O Inappropriate Seasonal Dress: Violence and AbuseDocument10 pagesO Inappropriate Seasonal Dress: Violence and AbuseJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hyperacusis, (Hypersensitivity to Sound) diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hyperacusis, (Hypersensitivity to Sound) diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Acute Laryngotracheobronchitis LTB (Croup)Document61 pagesAcute Laryngotracheobronchitis LTB (Croup)Gem DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument10 pagesMental Status ExaminationAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- You're Not Triggered, You're Dysregulated: Managing The Nervous System & Regulating EmotionsFrom EverandYou're Not Triggered, You're Dysregulated: Managing The Nervous System & Regulating EmotionsNo ratings yet
- Electro Convulsive TherapyDocument19 pagesElectro Convulsive TherapyDeepshikha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument79 pagesElectroconvulsive TherapyMariam IftikharNo ratings yet
- Catatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Document13 pagesCatatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Wen Silver100% (1)
- Mood Disorders DR Jean-Claude YazbekDocument167 pagesMood Disorders DR Jean-Claude YazbekDaniel GhosseinNo ratings yet
- SET 2 Oct 27 TRUE KEY ANSWERDocument16 pagesSET 2 Oct 27 TRUE KEY ANSWERJayrald CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4Document21 pagesEmergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4CetVital100% (1)
- The Impact of ECT On The Mean Duration of Hospitalisation of Patients in The Psychiatric Unit, Kath, Kumasi, GhanaDocument7 pagesThe Impact of ECT On The Mean Duration of Hospitalisation of Patients in The Psychiatric Unit, Kath, Kumasi, GhanaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument46 pagesSchizophreniaEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- Focus On Psychosis Gaebel Zielasek (2015)Document10 pagesFocus On Psychosis Gaebel Zielasek (2015)rap 2treyNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument10 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Plus Psychiatry MCQ Book DranilkakunjeDocument141 pages1000 Plus Psychiatry MCQ Book Dranilkakunjethelegend 20220% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument30 pagesLesson Plan On Psychiatric EmergenciesRajani AshwinNo ratings yet
- CatatoniaDocument14 pagesCatatoniaRENJULAL100% (1)
- Typical Signs and Symptoms of Psychiatric IllnessesDocument52 pagesTypical Signs and Symptoms of Psychiatric IllnessesmejammbatoonNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument10 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesUdaya Sree100% (2)
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDocument14 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disordereyesheild100% (1)
- Brief Psychotic DisorderDocument56 pagesBrief Psychotic DisorderJohanna ConnollyNo ratings yet
- Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating ScaleDocument31 pagesBush-Francis Catatonia Rating ScaletamaraNo ratings yet
- DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders: George F. Parker, MDDocument9 pagesDSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders: George F. Parker, MDMonika LangngagNo ratings yet
- Get Through MRCPsych Paper A1 MockDocument570 pagesGet Through MRCPsych Paper A1 MockFirdaus RafiNo ratings yet
- Catatonic Disorders: 5% - 9 % of All Psychiatric Inpatients According To Dsm-IvDocument10 pagesCatatonic Disorders: 5% - 9 % of All Psychiatric Inpatients According To Dsm-IvNikole CrastaNo ratings yet
- Anti N Methyl D Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis A Review of P - 2020 - Brain ReDocument10 pagesAnti N Methyl D Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis A Review of P - 2020 - Brain RejikaperluonlineNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesPsychopathology of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaMarlonReyes2011100% (2)
- Seminar: Sameer Jauhar, Mandy Johnstone, Peter J MckennaDocument14 pagesSeminar: Sameer Jauhar, Mandy Johnstone, Peter J MckennaMagdalena Zepeda MarambioNo ratings yet
- ECT Trust Wide Medical Protocol UPDATEDocument98 pagesECT Trust Wide Medical Protocol UPDATEguptaamritNo ratings yet
- November 2016Document19 pagesNovember 2016Luis Javier Rivera LealNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument10 pagesMental Status ExaminationAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- E C T Document PDFDocument17 pagesE C T Document PDFDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- 2016 - Psychiatric SymptomsDocument164 pages2016 - Psychiatric SymptomsCristina100% (1)
- Neeraj AhujaDocument13 pagesNeeraj Ahujaclinicweecare100% (1)