Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AHP Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AHP Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosCopyright:
Available Formats
L e s s o n
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
2
InthisExercise
Constructhierarchicalrepresentationofaproblem.
ConstructPairwiseMatrices.
NormalizethePairwiseMatrices.
CalculatePriorityVectors.
SynthesizeWeightsandcalculateoverallrankingsofAlternatives.
UsespecializedsoftwareDecisionMaker.
Duration:100minutes
TheProblem
Inthefirst exerciseabout AHPmethod,asimplemulticriteriadecisionmaking problemis examined
andsolvedstepbystep.Theproblemtobesolvedistheselectionofthecellphonethatbestcovers
theneedsofAlexandros,astudentofInternationalHellenicUniversity.
Alexandrossomeweeksnowisthinkingtobuyanewcellphone.Afteranextensivemarketresearch
hehasfinallyconcludedinthreedifferentmodelsthatmoreorlessfulfillhisneeds.Itisdifficultfor
himthoughttomakethefinaldecisionasallofthemaretopmodels,sohedecidestocometoyou
andaskyourhelp.Heknowsyouareanexpertindecisionmakingasrecentlyyouhavelearnedthat
AHPmethod.Nowyouwillhavetoapplyyourknowledgeandguideyourfriendtothebestdecision.
PartA
Doingallthecalculations
Thesolution
1. An important part of the AHP methodology is to model the problem correctly. So you asked
Alexandrostotellyousomemoredetailsabouthispreferences.Themostimportantfeaturefor
AlexandrosistheCamera.Helikestotakepicturessothereisaneednotjustforhighresolution
(8megapixelsandbeyond),butalsothereisdemandforthesameimageprocessingcapabilities
foundincurrentdigitalstillandvideocameras.Anotherimportantaspectisthebatterytiming,
as it is essential for a busy guy like him. Charging of the cell phone device is a liability and he
cannotperformthisjoboften.Attheendhetoldyouhowmuchfascinatedheisbytouchscreen
cellphones.Touchscreencellphoneshaveusuallylargescreenwithhighresolution,andgivea
wonderful feeling that you are able to connect to the world literally at a touch of a finger.
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
Alexandrosalsotoldyouthathehasconcludedamongthree differentmodels,thatallofthem
havethosefeaturesmoreorless.
Now that you know a little bit more things about the problem you can start applying the AHP
methodology to solve it. First step as mentioned above is to model the problem into a
hierarchicalstructure.Quicklyyouconstructthefollowinghierarchy thatshowsclearly,whatis
theGoal,theCriteriaandtheAlternativesofAlexandrosproblem.
Picture 1: The AHP hierarchy for Alexandros buying decision. The Goal is blue, the Criteria are
yellow and the Alternatives are green. All the Alternatives three different models of cell phones
areshownbelowthelowestlevelofeachcriterion.
2. The second step in AHP is to define the relative importance of the Criteria. This is done by
comparing each possible pair of Criteria and ranking them on the following scale : Comparing
CriterionIandCriterionj,giveavaluea
ij
withthefollowingmeaning:
a
|j
Description
1 Element and i ]areequallyimportant
3 Element isweaklymoreimportantthan i ]
5 Element isstronglymoreimportantthan i ]
7 Element isverystronglymoreimportantthan i ]
9 Elementiisabsolutelymoreimportantthan]
Table1:Pairwisecomparisonvalues.
2 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
iisassumedtobeatleastasimportantas],ando
]
issetto1,andifo
]
ism,theno
]
=
1
m
.
NowitistimetoaskAlexandrostocompareinpairsandratealltheCriteriawithrespecttothe
Goal of the problem. Alexandros after some thinking, comes up with some ratings that you
organizedinthefollowingmatrix:
B
a
t
t
e
r
y
C
a
m
e
r
a
T
o
u
c
h
s
c
r
e
e
n
Battery 1 1/4 3
Camera 4 1 7
Touchscreen 1/3 1/7 1
Table2:PreferencesoftheAlternatives
infavorofnodeBuyanewcellphone.
Next due to AHP method you will have to make some calculations to determine the overall
weight that Alexandros is assgnining to each Criterion. There are two methods to do that. The
first one is to find the Normalized Ratings Matrix and the other one a little bit more time
consuming is to find the eigenvector. Here we will work with the first method so we will
calculatetheNormalizedRatingsMatrix.
3. Normalizetheprioritymatrixbydividingeachelementbythesumofthecolumnitappearsin.
Forinstanceo
11
entrywouldendupas:
1
1 + 4 + u.SSS
= u.187
Theotherentriesbecome:
B
a
t
t
e
r
y
C
a
m
e
r
a
T
o
u
c
h
s
c
r
e
e
n
A
v
e
r
a
g
e
Battery 0.188 0.179 0.273
0.213
Camera 0.750 0.718 0.636
0.701
Touchscreen 0.063 0.103 0.091
0.085
Sum=1
3 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
Table3:WeightsonCriteria.
Thatmeansthat70%oftheCriterionweightisonCamera,about20%isonBatteryand8%ison
Touchscreen.ItisclearlythatAlexandrospreferstheCameraovertheBatterytimingandtouch
screen.
4. The next step is to evaluate all the cell phone models on each of the cell phones features. For
exampleAlexandrostoldyouthattheBatteryefficiencyofModelAismuchbiggerthanthatof
Model B and the Battery of Model C is slightly bigger than Model B. You value those
characteristicswiththefollowingmatrix:
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
ModelA 1 4 3
ModelB 1/4 1 1/2
ModelC 1/3 2 1
Table4:Batteryscoresfromeachmodel.
Again you normalize the scoring table dividing each element by the sums of the columns, and
average across rows to get the relative weights of each model regards to Battery. You end up
withthefollowingtable:
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
A
v
e
r
a
g
e
ModelA 0.632 0.571 0.667
0.623
ModelB 0.158 0.143 0.111
0.137
ModelC 0.210 0.286 0.222
0.239
Sum=1
Table5:RelativeBatteryscoresfromeachmodel.
ThismeansthatModelAhasthestrongestbatteryastheweightis62%,followedby24%of
ModelCand13%ofModelB.
GoingthroughasimilarprocesswithCameraandTouchscreenwegetthefollowingmatrices:
4 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
ModelA 1 5 3
ModelB 1/5 1 1/4
ModelC 1/3 4 1
Table6:Camerascoresfromeachmodel.
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
A
v
e
r
a
g
e
ModelA 0.652 0.500 0.706
0.619
ModelB 0.130 0.100 0.059
0.096
ModelC 0.217 0.400 0.235
0.284
Sum=1
Table7:RelativeCamerascoresfromeachmodel.
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
ModelA 1 0.333 0.143
ModelB 3.000 1 0.500
ModelC 7.000 2.000 1
Table8:Touchscreenratingsfromeachmodel.
5 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
M
o
d
e
l
A
v
e
r
a
g
e
ModelA 0.091 0.100 0.087
0.093
ModelB 0.273 0.300 0.304
0.292
ModelC 0.636 0.600 0.609
0.615
Sum=1
Table9:RelativeTouchscreenscoresfromeachmodel.
5. Wecannowplacealltheoverallweightsonthehierarchymodelfrompicture1andgetamore
clearpictureofhowmucheachelementinthemodelcountsinthefinaldecision.
6. Wecannowgetafinalvalueforeachcellphonemodel:
ThevalueforModelAis:
(0.623*0.213)+(0.619*0.701)+(0.093*0.085)=0.133+0.434+0.008=0.575
ThevalueforModelBis:
(0.137*0.213)+(0.096*0.701)+(0.292*0.085)=0.029+0.068+0.025=0.122
ThevalueforModelCis:
(0.239*0.213)+(0.284*0.701)+(0.615*0.085)=0.051+0.199+0.052=0.303
6 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
The winner is Model A cell phone, as it fits 57.5% the needs of Alexandros comparing with the
othertwomodels.
7 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
PartB
Usingspecializedsoftware.
InthispartthesolutiontotheproblemSelectanewcellphoneisgivenusingspecializedsoftware
namedDecisionMaker.
1. Runtheprogram(JavaRuntimeEnvironmentneeded).
2. Sincenowyouareopeningtheprogramthetreecanvasareashouldbeempty.Selectthenode
GoalandfromtheleftmenuclickEditnode.ThedialogEditnodewillshow.
3. In the Node name text field type Buy cell phone. If you like type a short description of the
nodeinthefieldNodeDescription,asitisshowninthefollowingcapture:
4. In the following steps we will build
the hierarchy of the problem as
presented in Part A. With the root
node selected click the button
Insert new node on the left menu.
ThedialogAddnewproblemnode
will come up as shown in the
following capture. This dialog allows
toinsertanewnodeintheproblemshierarchy,aswellastosetthepropertiesofthisnewnode
8 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
such as node name, node type (Goal, Criteria, Alternative), and the information type that this
nodewillhold(eitherQualitativeorQuantitativeinformation).
5. InthetextfieldNewnodename,typeBattery.
6. InthefieldNewnodetype,selectCriteria(onlythevalueCriteriaisavailablefornowasitis
forbiddentoinsertanAlternativenodeintherootnode).
7. In the field Information type, select the value Qualitative as the Battery criterion holds
Qualitativeinformation.
8. ClickOktoinsertthenode,anddoubleclicktherootnodetoshowthenewinsertednode.
9. Repeat the steps 47 to insert the nodes Camera and Touch screen in the root node. Now
thehierarchystructureshouldlookliketheoneinthefollowingcapture.Takeamomenttosee
thecommentsinthatcaptureandwhatthedifferencesintheappearanceofthenodesmean.
10. NowitistimetoinsertinthehierarchytheAlternativenodesasshowninPartAofthisexercise.
SelectaleafnodefromthehierarchythenclickthebuttonInsertnewnodeplacedontheleft
side of the window. The familiar dialog Insert new node appears. Type Model A for the
name of the node select Alternative for the type and for the information type leave as is the
valueParentnodetype
11. Click Ok. You just entered in your hierarchy, the first Alternative node with the name Model
A. Note that Alternative nodes are colored with orange, and they also have slightly different
graphic.
12. Repeat the previous step to insert the Alternative nodes Model B and Model C. Your tree
hierarchyshouldnowlookliketheoneinthefollowingcapture.
9 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
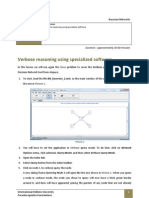
13. Click the button Next, located almost at the top of the window. It will open the interface for
thepairwisecomparisonsoftheCriterianodesasshowninthefollowingpicture.
ClicktheNextbuttontotakeyouin
step2ofthesolutionprocess.
14. Remember what Alexandros told you about his preferences and make the correct ratings as
showninthefollowingcapture:
Youcannoticethatwhilemakingtheselectionsforthepairwisecomparisons,twonumbersare
changingatthetopoftheselectiontool.ThosearetwoindicesnamedConsistencyIndexand
10 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
Consistency Ratio. We will talk about those two indices in the next exercise. Now keep in
mind that if those indices are colored red then you should rethink your ratings as they are
inconsistent.
15. When finished with the selections click on the Show Calculations button at the left of the
window.ThedialogAHPCalculationswillopenshowingtoyouallthecalculationsthatyoudid
inthefirstpartoftheexercisewhenthepairwisecomparisonsweremade.Checktoseeifyou
arecorrect!
16. Close the dialog AHP Calculations and click again on Next button. The necessary tools to
makethepairwisecomparisonsfortheAlternativenodesareshown.
17. Rate the Alternatives as you did in the first part of the exercise. When done with the ratings
yourscreenshouldlooklikethefollowingcapture:
11 InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
TheAnalyticHierarchyProcess(AHP)
InternationalHellenicUniversity
ParaskevopoulosKonstantinos
18. CheckthecalculationsifyouwantbyclickingonthebuttonShowCalculationsontheleftside
ofthewindow.
19. When done with the ratings of the
Alternatives click Next button once
more. Next step screen will show as
youcanseeinthefollowingcapture.
20. Here are the final rankings of the
Alternatives. Model A is the winner.
You can see also the score of each
Alternative in respect to its last
Criterion.
21. You can click also if you want at the
Show Graphs button and see
graphic representation of your
ratingsasshowninthepicture.
22. SavetheprobleminafilenamedExercise_2.xml.
12
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Μοντελοποίηση Αρχαίας Ελληνικής Κατοικίας (Google SketchUp) - Ελληνικό Κολλέγιο Θεσσαλονίκης - Παρουσίαση - Ancient Greek HouseDocument22 pagesΜοντελοποίηση Αρχαίας Ελληνικής Κατοικίας (Google SketchUp) - Ελληνικό Κολλέγιο Θεσσαλονίκης - Παρουσίαση - Ancient Greek HouseKonstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees Exercise 4Document5 pagesDecision Trees Exercise 4Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees Exercise 3Document6 pagesDecision Trees Exercise 3Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Under Uncertainty Exercise 2Document3 pagesDecision Under Uncertainty Exercise 2Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees Exercise 1Document8 pagesDecision Trees Exercise 1Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Under Uncertainty Exercise 1Document6 pagesDecision Under Uncertainty Exercise 1Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees Exercise 2Document7 pagesDecision Trees Exercise 2Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- AHP Lesson 1Document5 pagesAHP Lesson 1Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Networks Exercise 3Document9 pagesBayesian Networks Exercise 3Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Networks Exercise 4Document7 pagesBayesian Networks Exercise 4Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Networks Exercise 2Document6 pagesBayesian Networks Exercise 2Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Networks Exercise 1Document8 pagesBayesian Networks Exercise 1Konstantinos ParaskevopoulosNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Cell Barring (RAN15.0 02)Document51 pagesCell Barring (RAN15.0 02)hekriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Deep Learning: Technical Seminar by Md. Abul Fazl (14261A05A0) CSE DeptDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Deep Learning: Technical Seminar by Md. Abul Fazl (14261A05A0) CSE DeptpavansfdsfNo ratings yet
- Edward Malek's MBA Engineering ResumeDocument1 pageEdward Malek's MBA Engineering ResumeEdward Nicklaus MalekNo ratings yet
- ICT158 Workshop 7Document2 pagesICT158 Workshop 7Jaya MathiNo ratings yet
- Ssp393 - Audi A5 - Convenience Electronics and Driver Assist SystemsDocument56 pagesSsp393 - Audi A5 - Convenience Electronics and Driver Assist SystemsCyberemuleNo ratings yet
- Brksec-3005 (2017)Document100 pagesBrksec-3005 (2017)Paul ZetoNo ratings yet
- Sample Data Protection Policy TemplateDocument8 pagesSample Data Protection Policy TemplateMarcelo Partes de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT Karta Bhumi Nusantara - 2023Document22 pagesCompany Profile PT Karta Bhumi Nusantara - 2023Syarifuddin IshakNo ratings yet
- Pinouts ICRDocument38 pagesPinouts ICRAdal Vera100% (1)
- Amber Krieg ResumeDocument1 pageAmber Krieg Resumeapi-376941376No ratings yet
- Solucionario Econometría Jeffrey M. WooldridgeDocument4 pagesSolucionario Econometría Jeffrey M. WooldridgeHéctor F Bonilla3% (30)
- UntitledDocument1,903 pagesUntitledTu Vieja A casa peteNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math - Quarter 1 Exam (11-HUMS-ALS)Document3 pagesGen. Math - Quarter 1 Exam (11-HUMS-ALS)JerryNo ratings yet
- Q4M2 Giving Technical and Operational Def.2.0Document60 pagesQ4M2 Giving Technical and Operational Def.2.0Shadow Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Fidelityfx Cas: Lou Kramer, Developer Technology Engineer, AmdDocument92 pagesFidelityfx Cas: Lou Kramer, Developer Technology Engineer, AmdJohn K SmithNo ratings yet
- Popis RozhraníDocument36 pagesPopis RozhraníMarek DužíNo ratings yet
- Ups MotherboardDocument5 pagesUps MotherboardMustapha El MaouzouniNo ratings yet
- Labs: Introductio N To Spring 5 and Spring Mvc/Rest (Eclipse/Tom Cat)Document34 pagesLabs: Introductio N To Spring 5 and Spring Mvc/Rest (Eclipse/Tom Cat)darwinvargas2011No ratings yet
- Maths Bds Contpeda9 10Document7 pagesMaths Bds Contpeda9 10AhmedNo ratings yet
- QRQC / 8D Form: D 1. Description of The ProblemDocument5 pagesQRQC / 8D Form: D 1. Description of The ProblemDearRed FrankNo ratings yet
- Big Data Simplified: Book DescriptionDocument14 pagesBig Data Simplified: Book DescriptionN C NAGESH PRASAD KOTINo ratings yet
- Easychair Preprint: Adnene Noughreche, Sabri Boulouma and Mohammed BenbaghdadDocument8 pagesEasychair Preprint: Adnene Noughreche, Sabri Boulouma and Mohammed BenbaghdadTran Quang Thai B1708908No ratings yet
- SAP SRM 7.0 Strategic SourcingDocument90 pagesSAP SRM 7.0 Strategic SourcingSergio Martinez PerezNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Learning PlanDocument11 pagesMath 10 Learning PlanmichaelNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 5Document22 pages11 - Chapter 5Parth MundhwaNo ratings yet
- FLS DemonstrationDocument30 pagesFLS DemonstrationLeah UljerNo ratings yet
- Stock Coal and Limestone Feed Systems: Powering Industry ForwardDocument12 pagesStock Coal and Limestone Feed Systems: Powering Industry ForwardAchmad Nidzar AlifNo ratings yet
- Performance: Lenovo Legion 5 Pro 16ACH6HDocument5 pagesPerformance: Lenovo Legion 5 Pro 16ACH6HsonyNo ratings yet
- CEA201 CH11-DigitalLogicDocument24 pagesCEA201 CH11-DigitalLogicTTNo ratings yet
- Brochure en Knick PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure en Knick PDFbango7886No ratings yet