Professional Documents
Culture Documents
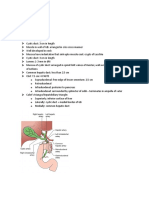
Parietal Cell: Angle of His Angularis Incisura
Uploaded by
URo KkuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parietal Cell: Angle of His Angularis Incisura
Uploaded by
URo KkuCopyright:
Available Formats
Stomach short note by S.
Wichien (SNG KKU)
Anatomy Angle of his -fundus meet lt side GEJ Angularis incisura -lesser curve---beginning antrum Artery 1.Lt gastrric a--largest --celiac trunk -15%--lt hepatic a 2.Rt gastroepiploic a--2nd large--GDA 3.Lt gastroepiploic a--splenic a 4.Rt gastric a--hepatic a 5.short gastric a--splenic a at least 2/4 a may be ligated eso.replace--rt gastric/rt GE Vein -lt/rt gastric--portal v -rt gastroepiploic--SMV -lt gastroepiploic--splenic v Innervation Parasym Ant vagus n -hepatic br -n of Latarjet--crowfoot--terminal br Post vagus n -criminal n of Grassi--post fundus -celiac br Sympathetic -T5-10--celiac gg submu--meissner plexus muscularis--Aurbach plexus/Cajal cell Histology Epithelial cell 1.chief cell (zymogenic cell)--44% -fundus/body -pepsinogen I,II 2.surface mucous epi cell (SEC)--40% -all stomach -bicarbonate/glycoprot--neutral HCL 3.parietal cell (oxyntic cell)--13% -fundus/body -HCL/intrinsic f/bicarbonate 4.G cell/D cell--3% -antrum -G cell--gastrin -D cell--somatostatin 5.ECL cell -fundus/body -H2 secreting Acid secretion -hcl--ingest pathogen -long term PPI--clostri.difficile colitis Parietal cell -+ve=ach/gastrin/H2 --ve=somatostatin -H+/K+ ATPase--proton pump -H pylori--inh D cell Pepsinogen secretion -+ve=ach --ve=somatostatin Intrinsic factor -parietal cell -bind B12--absorb in terminal ileum Mucosal barrier -SEC--mucus barrier/bicarbonate -parietal cell--bicarbonate -Epi barrier :hydrophobic phospholipid :Tight jxn :Restitution-replaced SEC by adja cell -microcircu--back diffuse H+ -mediator--PG,NO,EDGF,peptide Gastrin hormone Gastrin -G cell--antrum Hypergastrinemia -pernicious anemia, acid suppress Gastrinoma,retain antrum follow distal gastrec/billoth2/vagotomy Somatostatin -D cell -inh acid, gastrin, H2 Gastrin releasing peptide--GRP -+ve gastrin/somatostatin -binding G/D cell receptor Leptin -by adipocyte/chief cell -satiety hormone Ghrelin -by stomach -+ve appetite
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
PU -imbalance of acid-mucosa defense -GU : aware cancer -DU : rare cancer Causes 1st--h.pylori 2nd--Nsaid use Other--ZES, G cell hyperfxn/hyperpla trauma, burn, stress Periodicity pain vomit GI bleed appetite diet wt M:f DU GU yes no releif by meal no less more melena hematemesis normal afraid to eat all milk,fish inc dec 2:1 1:1 PU c/p 1.bleeding -3/4--Tx improve 1/4--continue bleed/re-bleed Rockall score (Score 0-11) 0 1 2 3 1age <60 60-79 >80 2shock no PR>100 SBP<100 3comor IHD,HF RF,LF 4EGD mallory PU GI ca dx no lesion 5EGD clean base blood spot clot spurting <3=good prog >8=hi risk motality Blatchford score (Score 0-23) 1SBP :100-109=1 90-99=2 <90=3 2.BUN :6.5-7.9=2 8-9.9=3 10-24.9=4 >25=6 3.Hb men:12-12.9=1 10-11.9=3 <10=6 women:10-11.9=1 <10=6 4.other pulse:>100=1 melena=1 syncope=2 hepatic ds=2 HF=2 2.perforate -free air 80% 3.GOO ->5% of PUD -DU/prepyloric ulcer -acute--inflam swelling chronic--cicatrix (scar)
GU Johnson classification Type1--angularis incisura Txdistal gastrectomy Type2--1+DU TxTV+A, HSV(2nd ) Type3prepyloric Tx-->TV+A, HSV (2nd) Type4--hi lesser curve/near EGJ Txdistal gastrectomy, TV+P or HSV (2nd) Type5--Nsaid induceanywhere Txstop Nsaid (Type 2/3--acid hypersecretion) Nsaid Who need PPI -60yr -Hx of acid/peptic dz -concurrent steroid intake -concurrent anticoag intake -hi-dose Nsaid/ASA EGD ->45 yr + new onset dyspepsia -Alarm symp :wt loss, dysphagia, bleeding, anemia, -hi risk pt :HNPCC, FAP, menetrier, s/p gastrectomy
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
PU sx 1.highly selective vagotomy -HSV -parietal cell vagotomy -proximal gastric vagotomy--2/3 -all parietal cell located -preserve vagal to antrum,pylorus -dec acid secretion 70% -hi recurrence than vago/antrectomy -gastric emptying time solid : normal liquid : normal -not well perform for typeII/III 2.vagotomy and drainage : V+D -s/e=dumpling,diarrhea,recurrence 1.truncal vagotomy+pyloroplasty :post bleeding DU :limit or focal scarring in pylorus 2.truncal vagotomy+gastrojejunos :GOO, severe ds prox duodenum :s/e=marginal ulceration Pyloroplasty a.Heineke Mikulicz :close longitu transpyloric incision in transverse fashion b.Finney pyloroplasty :inverted U incision :pylorus-duodenotomy c.Jaboulay pyloroplasty :pylorus-duodenotomy 3.vagotomy and antrectomy -V+A -low ulcer recurrence -higher morbidity -avoid in unstable pt Anastomosis 1.Billoth 1 gastroduodenotomy 2.Billoth 2 loop-gastrojejunostomy 3.Roux en Y gastrojejunostomy -keep duodenum out of stomach/eso -avoid in gastric remnant 60-70% -large gastric remnant--marginal ulcer 4.distal gastrectomy -without vagotomy -usually 50%gastrectomy include ulcer -procedure of choice for type1 GU -Billoth 1/2 -type 2,3 GU--add truncal vagotomy PU Sx option operation of choice in low risk shock 1.Bleeding PU IC for sx -massive hmg unrxn endo.control -recurrent hmg after endo attempt -PRC>4-6/day -lack of endoscopist -repeat hospitalize for bleeding ulcer -perforate/obstruct Early operation -hi risk lesion :post DU (GDA) :lesser curve (lt gastric a) ->60 yr -ulcer >2cm DU 1.overesew 2.oversew,V+D 3.V+A 2.Perforation DU 1.patch 2.patch,HSV 3.patch,V+D 3.Obstruction DU 1.HSV+GJ 2.V+A GU oversew,bx oversew,bx,V+D distal gastrec GU bx,patch wedge resect,V+D distal gastrec GU bx,HSV+GJ distal gastrec
4.Intractable,nonhealing DDx Ca--gastric,pancreatic,duodenum Persistent H.pylori--false-ve Non-compliance ZES DU 1.HSV 2.V+D 3.V+A GU HSV,wedge distal gastrec
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Gastrectomy complication 1.dumping syndrome -5-10% after sx Early -15-30 min after meal -abrupt delivery of hyperosmolar load into small bowel -neuroendocrine rxn -periphera/splanchnic vasodilate -diaphoretic,weak,light-head, tachycardia -imp by lay down,saline infusion Late -2-3 hr after meal -hyperinsulinemia -post pandrial hypoglycemia -imp by sugar Tx -avoid liquid during meal -avoid hyperosmolar liquid -add dietary fiber -if dietary fail,octreotide 100 mcg sc twice daily,can inc up to 500 mcg -alpha glucosidase inh(acarbose) may helpful in late synd 2.diarrhea -result of truncal vagotomy,dumping, fat malabsorption 3.Gastric stasis -gastric motility abnormality -obstruction a.mechanical:anastomosis stricture, eff limb kink,prox small bowel obstr b.functional:retrograde peristalsis in roux limb 4.bile reflux gastritis 5.Roux synd 6.gall stone 7.wt loss 8.anemia -iron def: absorp primary in prox GI -B12,folate def -parietal cell=intrinsic f.=absorb B12 9.bone disease -disturbed ca,vit D metaolism -ca absorp in duodenum -fat malabsorb=vit D def H.pylori -urease enz -urea --> ammonia + bicarbonate Mechanism that damage mucosa Local effect -toxin : vac A,cag A Immune rxn -elaboration cytokine--IL-8 -recruitment inflam cell -release inflam mediator -production of Ig Acid secretion -inc gastrin--hypergastrinemia -dec somatostatin Duodenal bicarbonate secretion -dec duodenal bicarbonate H.pylori test histo exam of antral bx=gold std 1.serologic test -non invasive -sense 80%,spec 90% -not confirm eradication,because sero scar remain after cure 2.urea breath test -std test to confirm cure of infection -sense/spec 90-99% (ingest urea--urease--CO2+ammonia) 3.histologic test -sense 85-100%,spec >95% -hematoxylin-eosin and Diff-Quik stain -Genta stain 4.rapid urease test -simplest method -one bx specimen -sense 80-95%,spec 95-100% 5.culture -when repeated failure of ATB tx Tx Tripple tx -PPI+clarithro+amoxy/metro 14d Fail -PPI+amoxy+levoflox 10d -PPI+bismuth 525mg qid+ metro+tetracycline 10-14d
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Bezoars -young women -undigestible accumulate in stomach -trichobezoar=hair -phytobezoar=vegetable -asso gastroparesis,GOO Rx -enzyme therapy -endoscopic remove,sx remove Mallory weiss syn -longitudinal tear in mucosa--GEJ -forceful vomiting -alcoholic -UGIB -90% stop spontaneous Tx -endoscopic confirm dx and Tx -balloon tamponade -angiographic embolization -vasopressin -Sx--overesewing through gastrotomy Vascular ectasia Watermelon stomach -gastric antral vascular ectasia -parallel red strip atop mucosal fold -distal stomach -elderly women -chronic Gi bl loss -resemble portal HTgastropathy :but PHG -- proximal stomach Histo -dilate mucosal blood vv -often contain thrombi in lamina p. -mucosal fibromascular hyperplasia Tx -estrogen/progesterone -endoscopic--Nd:YAG/ argon plasma -antrectomy--require to control bl loss Menetrier ds -hypertrophic gastropathy -large rugal fold in prox.stomach :spare antrum -overexpress of TGF alpha :+ve EGFR,TKR :surface mucus secreting cell -Bx--diffuse hyperplasia of SEC -inc risk of gastric ca Clinical -middle age men -epigastric pain,wt loss,diarrhea -hypoproteinemia Asso 1.protein losing gastropathy 2.hypochlorhydria Tx -EGFR blocking monoclonal ab :cetuximab -gastric resection in :bleeding, severe hypoproteinemia Dieulafoy lesion -congen AVM -large tortous submucosa a. -if a.erode=bleeding -middle aged/elderly men -endoscopic can miss lesion if not active bleeding--normal mucosa Tx -endoscopic hemostatic therapy -angio embolization -sx--oversew/resect Isolate GV -T1--fundus T2--distal to fundus -asso portal HT/ splenic v thrombosis -no I/C for prophylaxis Tx -octreotide -sengstaken blakemore tube--T1 -endo.Tx--sclerotherapy/EVL :less success than EV -splenic v thrombosis--splenectomy -liver transplant--cirrhotic pt
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Diverticula -usually solitary -congen--true diverterticula -acquired--pulsion -most--post cardia or fundus -most asymptomatic :can inflam--pain,bleed Tx -symtomatic pt :should be removed--laparoscopic Volvulus -asso large hiatal hernia 1.organoaxial volvulus -typical -twisted along long axis 2.mesenteroaxial volvulus -twisted around transverse axis Clinical 1.asymptomatic -no sx -rare strangulation 2.symptom -pain -pressure effect :lungs--dyspnea :pericardium--palpitation :eso--dysphagia -gastric infarction=sx emer Borchardt triads 1.severe abdo pain 2.upper abdo distension 3.can not pass NG/vomit Tx -elective sx :reduction of stomach and repair hernia c/co gastroplexy Gastroparesis -delay gastric emptying time -n/v,bloating,early satiety,abdo pain -80% = women -should r/o mecha GOO,gut obs -upper GI study:slow gastric emptying Dx -upper GI--slow gastric emptying -EGD--bezoars, normal -gastric emptying scintigraphy--DGE Etiology Idiopathic Endocrine/metabolic DM/thyroid/CKD After sx resection/vagotomy CNS BS lesion/parkinson Peripheral nm ds -duchenne m dystrophy -myotonia dystrophica CNT scleroderma/PM,DM Infiltrative lymphoma/amyloidosis Medication Elyte k,ca,mg Diffuse GI motility ds Miscellaneous infection,viral paraneoplastic,ischemia,GU Rx 1.medication 1. metroclopramide (plasil) - dopamine agonist 2.erythromycin -motilin agonist 3.neostigmine/bethanecal -Ach agonist 2.sx 2.1 severe diabetic gastroparesis -pancreas transplantation -if can't gastrostomy (decompress) + feeding jejunostomy 2.2 others -Implant gastric pacemaker -1 gastroparesi--gastric resection
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Lymphoma -4% of gastric ca -most common of 1GI lymphoma -95% = NHL (1/2 of NHL involve GI tract) -most are B cell type--in MALT -usually also H.pylori infection Low grade MALT lymphoma -arise from chronic gastritis -asso H.pylori -if eradicate H.pylori :low gr lymphoma--often disappear Tx -not sx lesion--careful f/u is necessary -persist after tx H.pylori :stage1=RT :stage2,3=CMT+RT Hi grade gastric lymphoma -require aggressive onco tx -systemic symptom :fever,wt loss,night sweats -lymphadenopathy/organomegaly -Dx=endoscope+bx 1lympho : nodular c enlarged fold 2lympho : diffuse infiltrative -EUS,CT chest-abdomen,BM Tx -Limit to stomach+region LN :radical subtotal D2 gastrectomy -CMT,RTX Japanese numeric classification 1-rt paracardia 2-lt paracardia 3-lesser curvature 4a-greater curvature,upper 4b-greater curvature,lower 5-suprapyloric 6-infrapyloric 7-lt gastric 8-common hepatic a. 9-celiac a 10-splenic hilum 11-splenic a 12-hepatoduodenal lig 13-post pancreatioduodenal 14-SMA 15-middle colic a 16-paraaortic 17-ant pancreatioduodenal 18-inf margin of pancreas 19-infradiaphragmatic 20-eso hiatus D1=3-6 D2=1,2,7,8,11 D3=9,10,12
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Carcinoid Tumor -rare -1% of carcinoid -ECL cell -malignant potential Type1 -most common--75% -chronic hypergastrinemia -2 to pernicious a.,atrophic gastritis -women -often multiple, small -malignant potential <5% Type2 -asso MEN1, ZES -malignant potential 10% Type3 -Sporadic -solitary >2cm -men -most--metas at dx time Dx -endoscope+bx -EUS in size,dept -plasma chromogrannin A -CT -octreotide scan Tx 1.small lesion (T1,2) confine mucosa,<5lesion -EMR -careful follw up 2.larger lesion -D1/D2 gastrectomy 3.metastatic dz -somatostatin -sx debulking GIST -interstitial cell of Cajal--ICC -2/3 occur in stomach -epithelial cell stromal GIST :most common cell type -GIST--CD117 (c-KIT), CD34 -smooth m tumor--desmin -hematogenous (liver,lungs) -most--body of stomach -almost solitary -prognosis=size,mitotic count,metas Clinical -submucosa tumor--slow growing -large lesion--wt loss,abdo pain, fullness,bleeding,abdo mass Tx -wedge resection c clear margin -invade adjacent organ--en bloc R Imatinib -block tyrosine kinase (product of c-kit) -metas/unresect pt Benign tumor 1.polyps -most common benign tumor 5 type 1.Adenomatous 2.Hyperplastic (regenerative) :most common--75% 1,2 -- malignant potential 3.Hamartomatous 4.Inflammatory 5.Heterotopic (ectopic pancrease) 3,4,5 -- negligible malignant potential Tx -symptomatic ->2cm,adenomatous :endoscopic snare polypectomy 2.Leiomyoma -submucosa -if ulcerate--umbilicated appearance -<2cm--asymp/benign >2cm--greater malignant :should remove by wedge resect :often possible lap 3.Lipoma -found incidentally
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Ca stomach -adenoca 95%,lymphoma 4% GIST1%,carcinoid,angiosarcoma,SCC -metastasic (melanoma,breast) -direct invasion:ca colon,pancrease Adenocarcinoma -elderly -male:female = 2:1 -low economic status -black > white Factor Increase risk -fam hx -bl gr.A -pernicious anemia -hi fat,salt,nitrate diet -FAP(10x) -gastric adenoma -hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal ca -H.pylori (3x) :atrophic gastritis-->intes.metaplasia -previous gastrec/gastrojeju >10yr -tobacco Premalignant lesion 1.Polyps--5 type 1.inflam 2.harmartomatous 3.heterotopic no malignant potential 4.hyperplastic 5.adenoma, FAP(10x) 2.Atrophic gastritis -most common precursor for ca -intestinal type 3.Intestinal metaplasia 4.Benign gastric ulcer 5.Gastric remnant cancer -s/p distal gastrec in PUD >10yr Pathology Classification Bormann 1.polypoid/fungating 2.ulcerative 3.ulcerative+infiltration 4.scirrhous (linitis plastica) :poor prog :need margin 10 cmtotal gastrectomy 5.can not 1-4 Lauren 1.intestinal type 2.diffuse type 3.unclassified Dysplasia -mild dysplasia : f/u bx -severe dysplasia :multifocal=gastric resection :localized=EMR Early gastric ca (Adenoca limited to mucosa/submu) Type1:exophytic Type2:superficial variant 2a:elevate lesion 2b:flat lesion 2c:depressed lesion Type3:excavated lesion EMR criteria 1.tumor < 2 cm 2.T1 3.EUSnode ve 4.no ulceration 5.well & mod diff
-EBV -menetrier dz
Decrease risk -aspirin -vegetable/fruit diet -vit c,e Genetic factor -p53 and COX-2 gene :deletion or suppression of p53 :overexpression of COX-2
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Clinical manifestation -wt loss -dec food intake:anorexia,satiety -abdo pain -n/v -bloating -acute GI bleeding : 5% -chronic occult bl loss : iron def -dysphagia if involve cardia -metas pleural effusion -krukenberg tumor -sister joseph node -rectal shelf/drop metastasis -paraneoplastic syn 1.trousseau sign = thrombophlebitis 2.acanthosis nigrican 3.peripheral neuropathy Dx 1.endoscope -- gold std -if suspicion for ca is hi and bx=neg :re endoscope and aggressive bx 2.CT abdo,pelvic CT--preoperative staging 3.EUS -tumor dept/can FNA LN -distinguished early ca vs advance 4.PETs scanning -evaluate distant metastasis 5.Staging laparo+peritoneal cytology -evaluate peritoneal/liver metas Ca stomach staging T1a-lamina propia/mm T1b-submucosa T2-muscularis propia T3-subserosa T4a-serosa T4b-adjacent organadjacent organs N1-1-2 LN N2-3-6 LN N3a-7-15 LN N3b->=16 LN Ca stomach Sx -Sx is only curative tx Curative Sx goal -resect all tumor,free margin (R0) -adequate lymphadenectomy -grossly -ve margin at least 5 cm Extent of gastrectomy -std sx=radical subtotal gastrectomy -remove 75% stomach :include pylorus, 2cm doudenum -greater/lesser omentum -all asso lymphatic tissue -Billroth-2 gastrojejunostomy :if remnant <20% : Roux-en-Y -Total gastrectomy c Roux-en-Y esophagojejunostomy :prox.gastric ca Procedure Distal gastrectomy Hemigastrectomy Subtotal gastrectomy Near total gastrectomy Total gastrectomy resection 40% 50% 75% 95% 100%
Extent of lymphadenectomy -D1:station 3-6 D2:station 1,2,7,8,11 D3:station 9,10,12 USA :D1 resection Asia :D2 gastrectomy :resect peritoneal over panc, ant mesocolon :hi M&M CMT,RTX -adjuvant tx c CMT (5FU,LV) and RTX benefit in resected pt c stage II,III -no indication for RTX alone :can be effective in bleeding or pain Screening -FAP,adenoma,intes meta/dysplasia HNPCC,Menetrier ds,remote gastrec
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Postgastrectomy syndrome 1.dumping syndrome -abrupt delivery of hyperOsm load -most common = B2 Mech 1.bypass pylorus 2.accelerate emptying of liquid--HSV Early dumping -15-30 m after meal -sweating,light-head -relief--NSS Late dumping -2-3 hr after meal -relief--sugar -hypoGlycemia -hyperinsulinemia Tx -diet mx :avoid liquid during meal :not hyperosm liquid :dietary fiber -octreotide -acarbose--late dumping Sx--rare -pylori recons -take down GJ -converse billoth2-->1 -converse to Roux en Y--sx of choice :large gastric remnant--marginal U -interposition 10cm reverse intes :between stomach/duodenum :rarely use 2.diarrhea cause 1.truncal vagotomy -intes dysmotility -accelerated transit Tx--cholestyramine,loperamide Sx--10cm reverse jejunal interposition 2.dumping 3.fat malabsorption 3.gastric stasis 1.Mechanical -anastomosis stricture -efferent loop kink -prox SB obstruct Sx -re-operation 2.Fxn -retrograde peristalsis in Roux limb -should r/o mechanical Tx -Medical tx/diet mx Sx procedure After V+D -subtotal gastrectomy -Billoth2 anas c braun enteroenteros After subtotal gastrectomy -near total gastrectomy/total gastrec c Roux en Y reconstruction 4.bile reflux gastritis -s/p resect pylorus -develop mo-yr -billoth 2 gastrec (most common), GJ DDx -aff/eff loop obstruct -gastric stasis -SMB obstruct Sx -Roux eu Y GJ (best) :Roux limb at least 45 cm -Billoth2 c braun enteroenteros -interposition 40 cm isoperistatic jejunal loop between gastric--duo (Henley loop) 1bile reflux--no previous sx--rare Tx -duodenal switch operation :have marginal ulcer :combined w HSV
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Postgastrectomy syndrome (cont) 5.Roux synd -s/p Roux en Y (long limb) -DGE, no mech obstruct -vomiting/epi pain/wt loss Med -prokinetic drugs Sx -subtotal gastrctomy -resected Roux limb--if dilate/flaccid -Billoth2 c braun enteroenteros or Henley loop 6.gall stone -vagal denervation--GB dysmotility -stasis of GB Prophylactic cholecystectomy -not justified in most case -but appear abnormal GB--yes or GS/sludge 7.wt loss 8.anemia -iron def--absorb in prox GI -B12--no intrinsic f TxB12 iv 1-2 times/year -folate def 9.bone disease -ca--absorb in duodenum -vit D--fat malabsorpt Gastrostomy -alimentation or decompression methods 1.Percu--PEG 2.Open -Stamm--most common -Witzel -Janeway--create permanent stroma 3.laparoscopic C/P -infection -dislodgement -aspirate pneumonia DDx of hypergastrinemia 1.With excessive gastric acid (ulcerogenic) -Zollinger Ellison syn -GOO -retained gastric antrum (after BillrothII reconstruction ) -G-cell hyperplasia 2.Without excessive gastric acid (nonulcerogenic) -pernicious anemia -atrophic gastritis -renal failure -post-vagotomy -short gut syn
Stomach short note by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)
Zollinger Ellison synd--ZES -uncontrol secrete of abnormal gastrin by duodenal or pancreatic NE tumor -80%=sporadic--solitary-->90% cure -80% in gastrinoma triangle (cystic d--jxn 2/3 duo--jxn neck/body) 20%=inherited--MEN1--multiple -50%=malignant 2clinical syndrome by epi hyperplasia & giant gastric fold 1.ZES 2.Menetrier disease 3.lymphoma Symptom -epigastric p. -GERD -diarrhea -PU=90% of pt Typical ulcer=proximal duodenum Atyp ulcer=distal duo,jejunum,multi DDx -recurrent PU -secrete diarrhea -gastric rugal hypertrophy -esophagitis c stricture -bleeding or perforate ulcer -familial ulcer -ulcer w hyperca -gastric carcinoid Dx -gastrin level (false+ve=antisecrete) -BAO>15mEq/h, >5mEq/h (PU sx) -secretin stimulation test :confirm test :iv bolus of secretin (2u/kg) :gastrin level before/after injection :inc serum gastrin of 200 pg/ml -serum ca,parathyroid level r/o men1 Imaging 1.u/s--not very sensitive 2.CT--detect lesion>2cm 3.MRI 4.EUS -more sensitive -may miss smaller lesion -confuse normal LN 5.Somatostatin R.Scintigraphy--SRS -octreotide scan -imaging of choice -gastrinoma cell--type2 somato R 6.Dx angiography and transhepatic selective venous sampling of portal s. -a.catheter--gastroduodenal,splenic -v.catheter--hepatic v -inject secretin--gastrin in hepatic v -signi elevate in hepatic v gastrin indicate tumor is supplied by inject a. *most important locate tumor is intraop exploration Rx 1.sporadic (nonfamilial) gastrinoma -usually solitary -intra op u/s -should sx resection--possible cure -explor gastrinoma triangle+pancreas -other site :liver,stomach,SMB,mesen,pelvis -if can't locate, should consider :longitudinal duodenotomy 2.MEN1 -rarely cure by operation -multiple lesion -HSV in unresectable gastrinoma
You might also like
- The Shadows of TypeDocument232 pagesThe Shadows of TypePhilip 'Don Brewer' Lynott100% (7)
- Pgmee Test Series For Neet & Aiims: WWW - Aim4Aiims - In/Pg +91-7529938911Document16 pagesPgmee Test Series For Neet & Aiims: WWW - Aim4Aiims - In/Pg +91-7529938911SHAKEEL1991No ratings yet
- Review Cram SheetDocument57 pagesReview Cram Sheetjim j100% (1)
- David Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexDocument6 pagesDavid Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexKostyaNo ratings yet
- Clinical UrologyDocument98 pagesClinical Urologythapan87100% (2)
- CLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSFrom EverandCLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSNo ratings yet
- Dupuytren's ContractureDocument273 pagesDupuytren's Contractureslaughteringtheposer100% (1)
- Mental HealthDocument80 pagesMental HealthSingYen QuickNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder & Cystic DuctDocument22 pagesGall Bladder & Cystic Ductsheethal prabhavanNo ratings yet
- MCQs 1Document10 pagesMCQs 1Mostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Prana Calendar 11Document23 pagesPrana Calendar 11tamles77100% (2)
- Absite 21 Answers - StomachDocument2 pagesAbsite 21 Answers - Stomachsiriopa08No ratings yet
- Grief & Loss - pptx-1Document66 pagesGrief & Loss - pptx-1pinkyNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument25 pagesGastric CancerAndreea SubcinschiNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic ETT 6yr Fail IV 2: Primary Survey 1.airway 3.circulationDocument17 pagesProphylactic ETT 6yr Fail IV 2: Primary Survey 1.airway 3.circulationURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Management Gastric CancerDocument76 pagesManagement Gastric Cancerwawan siswokoNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Pancreas DR DilberDocument51 pagesTumors of Pancreas DR Dilberdrdilber100% (1)
- Historical Developments of Community Health Nursing in The WorldDocument75 pagesHistorical Developments of Community Health Nursing in The Worldsoniya naik0% (1)
- Case Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IDocument75 pagesCase Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IpeeconNo ratings yet
- Endopeptidase: Carbo ProteinDocument12 pagesEndopeptidase: Carbo ProteinURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument9 pagesPeptic UlceremiliasammutNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Length: Duodenum 2.submucosaDocument12 pagesAnatomy (Length: Duodenum 2.submucosaURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Incidence SignsDocument4 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Incidence SignsWichien SiriNo ratings yet
- Exocrine PancreasDocument4 pagesExocrine PancreasIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction 2Document46 pagesIntestinal Obstruction 2Lawrence WanderiNo ratings yet
- Sunday, 30 August 2020 1:54 PM: Whitcomb-D-NEJM-2006 PDFDocument2 pagesSunday, 30 August 2020 1:54 PM: Whitcomb-D-NEJM-2006 PDFMichelle De FreitasNo ratings yet
- Gastro GuiaDocument17 pagesGastro GuiaLudy Isa IzaNo ratings yet
- Colonic Cancer. Presentation.. Docdani - PHDocument106 pagesColonic Cancer. Presentation.. Docdani - PHdocdani_phNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis Ppt. DR Dilip S. RajpalDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis Ppt. DR Dilip S. Rajpaldiliprajpal73100% (1)
- CA Stomach OverviewDocument84 pagesCA Stomach OverviewDr Shafiq Ahmad ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Sef de Lucrari DR - Adina PurcareanuDocument24 pagesSef de Lucrari DR - Adina PurcareanuGeorge SimaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: - 4 Glands ( 4 Gland 3%) PhysiologicDocument6 pagesAnatomy: - 4 Glands ( 4 Gland 3%) PhysiologicURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Mortality of A Post Partial Gastrectomy PatientDocument12 pagesMortality of A Post Partial Gastrectomy PatientMohan SamarasingheNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Sequelae of Gastric SurgeryDocument86 pagesPowerpoint: Sequelae of Gastric Surgeryj.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument51 pagesPeptic UlcerSnega RathnakumarNo ratings yet
- By Subramaniyam Sabesan 4 Year Grodno State Medical UniversityDocument80 pagesBy Subramaniyam Sabesan 4 Year Grodno State Medical UniversitySam SabesNo ratings yet
- Surgicalshuntversus Tipsfortreatmentof Varicealhemorrhagein Thecurrenteraofliver Andmultivisceral TransplantationDocument15 pagesSurgicalshuntversus Tipsfortreatmentof Varicealhemorrhagein Thecurrenteraofliver Andmultivisceral TransplantationHưng Nguyễn KiềuNo ratings yet
- 10 StomachDocument10 pages10 StomachApabrita KarmakarNo ratings yet
- AscitesDocument71 pagesAscitessohilaw210No ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ProceduresDocument4 pagesCommon Laboratory ProceduresrahafNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument28 pagesPancreatitisFrench Pastolero-ManaloNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder IIDocument22 pagesGallbladder IIAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- GI Radiography: Astro Ntestinal EquenceDocument7 pagesGI Radiography: Astro Ntestinal EquenceKath CacatianNo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Ácido-PépticaDocument10 pagesEnfermedad Ácido-PépticaDoris Santiago FloresNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder and Bile DuctDocument18 pagesGall Bladder and Bile DuctClint MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionDocument10 pagesBowel Obstructionenke.nwekeNo ratings yet
- Step Up To Medicine Chapter 03Document868 pagesStep Up To Medicine Chapter 03yanks1120No ratings yet
- s13304 011 0131 2 PDFDocument3 pagess13304 011 0131 2 PDFRoderick Núñez JNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Stasis in Rabbits and Rodents - WSAVA2010 - VINDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal Stasis in Rabbits and Rodents - WSAVA2010 - VINAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Imaging of StomachDocument92 pagesImaging of StomachKN SharmaNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument5 pagesAcute AppendicitisSHINMEN TAKEZONo ratings yet
- Tropical Medicine AssignmenDocument7 pagesTropical Medicine AssignmenMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- TMP 15Document38 pagesTMP 15FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Git DisordersDocument16 pagesDrugs For Git DisordersmardawinNo ratings yet
- GI+hemato Past YearDocument9 pagesGI+hemato Past YearThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- -renalเ -adrenalเ -aortaเ: FeverDocument4 pages-renalเ -adrenalเ -aortaเ: FeverWipaporn ChaengsriNo ratings yet
- Dr. S.P. Hewawasam (MD) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Senior Lecturer in PhysiologyDocument33 pagesDr. S.P. Hewawasam (MD) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Senior Lecturer in PhysiologyAjung SatriadiNo ratings yet
- Barrett's, PVSDocument16 pagesBarrett's, PVSNurulasyikin MAANo ratings yet
- Surgery of The Bovine Large IntestineDocument18 pagesSurgery of The Bovine Large IntestineJhon Bustamante CanoNo ratings yet
- Anast Bleed MMDocument17 pagesAnast Bleed MMsgod34No ratings yet
- Dr. Pankaj Tejasvi: Dept. of Surgery MGMMC & MYH IndoreDocument76 pagesDr. Pankaj Tejasvi: Dept. of Surgery MGMMC & MYH IndoreDang HungNo ratings yet
- 12-Liver Cirrhosis 2012Document73 pages12-Liver Cirrhosis 2012nadiaNo ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument17 pagesGastroenterologykhanNo ratings yet
- Pancreas - Enzyme and FunctionDocument18 pagesPancreas - Enzyme and FunctionLisa PalabaoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction: By: Dr. Wasfi M SalaytaDocument16 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: By: Dr. Wasfi M SalaytayayaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pancreatitis: NOTE Most Pancreatic Enzyme Preparations Are Enteric-Coated To Protect TheDocument17 pagesChronic Pancreatitis: NOTE Most Pancreatic Enzyme Preparations Are Enteric-Coated To Protect TheSampanna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryFrom EverandCurrent and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Urologic Imaging For Externist PDFDocument55 pagesUrologic Imaging For Externist PDFURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Ruptured DiverticulitisDocument18 pagesRuptured DiverticulitisURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument76 pagesAbdominal PainURo KkuNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด Essay 4.1Document1 pageแบบฝึกหัด Essay 4.1URo KkuNo ratings yet
- Perirenal HematomaDocument23 pagesPerirenal HematomaURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Mesenteric AdenitisDocument28 pagesMesenteric AdenitisURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Stab Injury L Frank CHFDocument27 pagesCase Discussion: Stab Injury L Frank CHFURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Malignant Renal TumorDocument17 pagesMalignant Renal TumorURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Histology: GIST Short Note by by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)Document3 pagesHistology: GIST Short Note by by S.Wichien (SNG KKU)URo KkuNo ratings yet
- Hepatoblastoma ReseachDocument32 pagesHepatoblastoma ReseachURo KkuNo ratings yet
- LRP PresentationDocument21 pagesLRP PresentationURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Renal Trauma BluntDocument40 pagesRenal Trauma BluntURo KkuNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด Essay 3Document1 pageแบบฝึกหัด Essay 3URo KkuNo ratings yet
- GEP NETsDocument3 pagesGEP NETsURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Possible Sign of Superfi V.abnor: 2 Primary FXNDocument7 pagesPossible Sign of Superfi V.abnor: 2 Primary FXNURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Reflec in SXDocument2 pagesReflec in SXURo KkuNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด Essay 3Document1 pageแบบฝึกหัด Essay 3URo KkuNo ratings yet
- Reflec in SXDocument2 pagesReflec in SXURo KkuNo ratings yet
- UrologyDocument10 pagesUrologyURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: - 4 Glands ( 4 Gland 3%) PhysiologicDocument6 pagesAnatomy: - 4 Glands ( 4 Gland 3%) PhysiologicURo KkuNo ratings yet
- ColorectalDocument26 pagesColorectalURo KkuNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument13 pagesLiverURo KkuNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument13 pagesBreastURo KkuNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument5 pagesHerniaURo KkuNo ratings yet
- SpleenDocument3 pagesSpleenURo KkuNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument36 pagesAcute PancreatitisURo KkuNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritic: Activity of N-Butanol Fraction From Telosma Pallida (Roxb) Craib LeafDocument7 pagesIn-Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritic: Activity of N-Butanol Fraction From Telosma Pallida (Roxb) Craib LeafPunitNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument14 pages1 SMRosalina Pertiwi GultomNo ratings yet
- Decalogue For Front LinersDocument2 pagesDecalogue For Front LinersWilson EjercitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Test Skeletal SystemDocument49 pagesChapter 6 Test Skeletal SystemAlexandra CampeanuNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Feb23Document47 pagesPricelist Feb23Farmasi RstciremaiNo ratings yet
- Kings UK Uni Pathways Alumni 2015 16Document18 pagesKings UK Uni Pathways Alumni 2015 16Joins 세계유학No ratings yet
- AK Vegan Animals Lifescape 2008 (May) 74-6Document3 pagesAK Vegan Animals Lifescape 2008 (May) 74-6Pepa GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Britannia Industry LTD in India: Eat Healthy Think BetterDocument12 pagesBritannia Industry LTD in India: Eat Healthy Think BetterMayank ParasharNo ratings yet
- Your Electricity BillDocument8 pagesYour Electricity BillE EeNo ratings yet
- S.No Emp - No Emp - Name Designation Department DOJ Current - Location Mobile NoDocument16 pagesS.No Emp - No Emp - Name Designation Department DOJ Current - Location Mobile Noabreddy2003No ratings yet
- Revised BizTown PPDocument16 pagesRevised BizTown PPRene BrathwaiteNo ratings yet
- Topic 13Document23 pagesTopic 13hasvinNo ratings yet
- Nov Art IsDocument6 pagesNov Art IsSaran KuttyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsDocument10 pagesImpact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Johnson's Baby OilDocument10 pagesJohnson's Baby OilVictor SolipasNo ratings yet
- P9 Lecture Child Abuse PDFDocument53 pagesP9 Lecture Child Abuse PDFVira PebrianaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test 2 Eco Class-12Document4 pagesPeriodic Test 2 Eco Class-12amandeep malikNo ratings yet
- Wiri 08 - Zambia Trip Application FormDocument11 pagesWiri 08 - Zambia Trip Application Forminfo@zcfcanada.orgNo ratings yet
- CCMA Consent Form - BlankDocument2 pagesCCMA Consent Form - BlankChristina Blignault50% (2)
- New Patient Medical Form: in One SentenceDocument1 pageNew Patient Medical Form: in One SentenceAzra BarliNo ratings yet
- MAPEH NasDocument7 pagesMAPEH Nasnoronisa talusobNo ratings yet
- Mod DescriptionsDocument9 pagesMod DescriptionsGuilherme CoutinhoNo ratings yet