Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tense
Uploaded by
manisha_bhavsarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tense
Uploaded by
manisha_bhavsarCopyright:
Available Formats
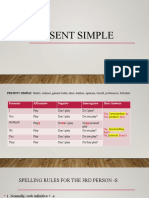
tense
Affirmative/Negative/Question
Use
action in the present taking place once, never or several times facts actions taking place one after another action set by a timetable or schedule action taking place in the moment of speaking action taking place only for a limited period of time action arranged for the future action in the past taking place once, never or several times actions taking place one after another action taking place in the middle of another action action going on at a certain time in the past actions taking place at the same time action in the past that is interrupted by another action putting emphasis on the result action that is still going on action that stopped recently finished action that has an influence on the present action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of speaking
Signal Words
always, every , never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually if sentences type I (If I talk, )
Simple Present
A: He speaks. N: He does not speak. Q: Does he speak?
Present A: He is speaking. Progressive N: He is not speaking. Q: Is he speaking?
at the moment, just, just now, Listen!, Look!, now, right now
Simple Past A: He spoke. N: He did not speak. Q: Did he speak?
yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other day, last Friday if sentence type II (If Italked, )
Past A: He was speaking. Progressive N: He was not speaking. Q: Was he speaking?
when, while, as long as
Present Perfect Simple
A: He has spoken. N: He has not spoken. Q: Has he spoken?
already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
Present A: He has been speaking. Perfect N: He has not been speaking. Progressive Q: Has he been speaking?
putting emphasis on the course or duration(not the result) action that recently stopped or is still going on finished action that influenced the present action taking place before a certain time in the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration) action taking place before a certain time in the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple putting emphasis on the duration or courseof an action action in the future that cannot be influenced spontaneous decision assumption with regard to the future decision made for the future conclusion with regard to the future
all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the whole week
Past Perfect Simple
A: He had spoken. N: He had not spoken. Q: Had he spoken?
already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day if sentence type III (If I had talked, )
Past A: He had been speaking. Perfect N: He had not been speaking. Progressive Q: Had he been speaking?
for, since, the whole day, all day
Future I Simple
A: He will speak. N: He will not speak. Q: Will he speak?
in a year, next , tomorrow If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, shewill help you.) assumption: I think, probably, perhaps in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future I Simple (going to)
A: He is going to speak. N: He is not going to speak. Q: Is he going to speak?
Future I A: He will be speaking. Progressive N: He will not be speaking. Q: Will he be speaking?
action that is going on at a certain time in the future action that is sure to happen in the near future action that will be finished at a certain time in the future
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future II Simple
A: He will have spoken. N: He will not have spoken. Q: Will he have spoken?
by Monday, in a week
Future II A: He will have been speaking. Progressive N: He will not have been speaking. Q: Will he have been speaking? Conditional I Simple A: He would speak. N: He would not speak. Q: Would he speak?
action taking place before a certain time in the future putting emphasis on the course of an action action that might take place
for , the last couple of hours, all day long
if sentences type II (If I were you, I would gohome.)
Conditional A: He would be speaking. I N: He would not be speaking. Progressive Q: Would he be speaking?
action that might take place putting emphasis on the course / duration of the action action that might have taken place in the past if sentences type III (If I had seen that, I would have helped.)
Conditional II Simple
A: He would have spoken. N: He would not have spoken. Q: Would he have spoken?
Conditional A: He would have been speaking. II N: He would not have been Progressive speaking. Q: Would he have been speaking?
action that might have taken place in the past puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
Tenses: forms, signal words and functions:
tenses forms examples signal words
I hope, I expect, I believe soon, in the next few days, in the future, tomorrow, this evening
functions
The "will-future" gives expression to ... ...an action that will take place in the future ...to a spontaneous decision and/or ...to an action that can't be planned (e.g. weather).
will-future
will + infinitive
My friend hopes he'll get a good job.
going tofuture
am, is, are + going to + verb (infinitive) am
He is going to apply for a job as a secretary in a big firm next week.
in the next few days, in the future, this evening, next weekend now, just, at the moment, look !, right now, still
The "going to-future" gives expression to an action that somebody intends / is going to do in the future(planned)
present progressive
is + verb +-ing are
He is writing letters of application now. He is applying for the job at 3 p.m. tommorrow.
The "present progressive" gives expression to an action that is going on at the moment The "present progressive" gives expression to an action that is planned to happen at a certain date in the future The "simple present" gives expression to ... - a repeated action that often, sometimes ... happens, but notto an action that is happening at the moment (see "present progressive"). - to a list of facts.
at 3 p.m. tomorrow
He always reads the vacancies in the newspapers. he
every day, always, often, normally, usually, regularly, sometimes, occasionally, seldom, on Sundays, at weekends First... then.. afterwards
simple present
she + verb +-s it
First he reads the vacancies in the newspapers, then he does his work. The moon goes round the earth and the earthgoes round the sun.
- to an "eternal truth". this week, this month, this year, today, since, for.., ...ever...? ...yet? not... yet. already, just, recently, lately yesterday, last week, The "present perfect" gives expression to an action that started in the past and goes on in the present.
present perfect
have, has + -ed or + 3 rd form
He has been unemployed for half a year.
past
verb + - ed 2nd
or
He worked as a lorry driver.
The "simple past" gives expression to an action that started in the past and finished in the past
form
last month, last .... Before(conj.).... While father was doing the washing up Mum was phoning Granny. at ten o'clock last night when while up to that time in the past. "married" to a clause in "simple past" After (conj.)... The "past progressive" gives expression to apparently continuous uninterrupted actions in the past (perhaps suddenly interrupted by an action in "simple past") The "past perfect" gives expression to an action which started in the past and ended before another action in the past started
past progressive
was / were + ing
past perfect
After he had survived an accident he gave up this job. had + - ed or + 3rd form He had survived an accident before he gave up this job
You might also like
- Learning and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesLearning and Developmentmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesTraining and Developmentmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Pragmatics GeneralDocument16 pagesPragmatics Generalaraosina12No ratings yet
- BOT GRAPHS REVEAL SYSTEMIC BEHAVIOR PATTERNSDocument8 pagesBOT GRAPHS REVEAL SYSTEMIC BEHAVIOR PATTERNSmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Kaushik Basu - Understanding and Controlling InflationDocument56 pagesKaushik Basu - Understanding and Controlling Inflationlniyer55No ratings yet
- List of NounsDocument6 pagesList of NounsamitoraryanNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses ExplainedDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Explainedmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing: A Curriculum For Secondary Students...Document104 pagesCreative Writing: A Curriculum For Secondary Students...Chandra Friend Montoya100% (2)
- List of Regular VerbsDocument5 pagesList of Regular Verbssiiimpaaticaa79% (34)
- Truth-Conditional Content and Conversational ImplicatureDocument36 pagesTruth-Conditional Content and Conversational Implicaturemanisha_bhavsar100% (2)
- Business Letter FormatDocument2 pagesBusiness Letter Formatmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Methi Aloo ParathaDocument1 pageMethi Aloo Parathamanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Word ListDocument12 pagesGrade 6 Word Listmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Fiures of Speech Lesson PlanDocument1 pageFiures of Speech Lesson Planmanisha_bhavsar80% (5)
- Volleyball SkillsDocument12 pagesVolleyball Skillsmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Passive Voice Voz Pasiva: Structure ExampleDocument3 pagesPassive Voice Voz Pasiva: Structure Examplewalquiria cabezaNo ratings yet
- Actividades Libro InglesDocument7 pagesActividades Libro InglesPaola Ivett CorreaNo ratings yet
- Learning modal verbs and grammarDocument7 pagesLearning modal verbs and grammarRosanna BellaubiNo ratings yet
- Argument Structure in The Verb Phrase (VP) : Reach), EtcDocument8 pagesArgument Structure in The Verb Phrase (VP) : Reach), EtcPavelNo ratings yet
- English I Mid Term Exam 3 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesEnglish I Mid Term Exam 3 Answer KeyEgoo BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Here are the first 12 words from the lesson:1. car2. taxi 3. bus4. underground5. plane6. bike7. go8. walk9. drive10. ride 11. fly12. take Check the verbs from the lessonDocument42 pagesHere are the first 12 words from the lesson:1. car2. taxi 3. bus4. underground5. plane6. bike7. go8. walk9. drive10. ride 11. fly12. take Check the verbs from the lessonARMANDO JRNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 02 - Extra - Grammar - Exercises RESUELTADocument3 pagesUNIT - 02 - Extra - Grammar - Exercises RESUELTAguadalupe sangabriel ruizNo ratings yet
- Verbs, Nouns and Adjectives for Idiomatic Expressions and Sentence Completion ExerciseDocument6 pagesVerbs, Nouns and Adjectives for Idiomatic Expressions and Sentence Completion ExerciseZheel JainNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of Degree PDFDocument2 pagesAdverbs of Degree PDFVũ Công Bình88% (8)
- Pronoun UnitDocument5 pagesPronoun UnitMaryJoy Abulencia FerrerNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives ExplainedDocument28 pagesGerunds and Infinitives Explainedconlatdat1784No ratings yet
- Go Billy Korean Episode 88Document4 pagesGo Billy Korean Episode 88Luke PittsNo ratings yet
- Ingles Priscila Mat Casa 13 06 2023Document4 pagesIngles Priscila Mat Casa 13 06 2023Geane FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Future Passive Presentation SlideDocument7 pagesFuture Passive Presentation SlideTony HalimNo ratings yet
- What Is A Phrase?: "After Dinner" "Waiting For The Rain To Stop"Document3 pagesWhat Is A Phrase?: "After Dinner" "Waiting For The Rain To Stop"Johnlloyd NageraNo ratings yet
- 10th English F.A - IIIDocument1 page10th English F.A - IIIAskani Kurumaiah100% (1)
- Inflectional Vs Word-FormationDocument19 pagesInflectional Vs Word-FormationMaria.Fer79No ratings yet
- The Word Formation GameDocument2 pagesThe Word Formation GameSzabó KrisztinaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT SIMPLE AND CONTINUOUS LESSONDocument15 pagesPRESENT SIMPLE AND CONTINUOUS LESSONGiulia TortiNo ratings yet
- Rpt-Sow Form 3 2023 - 2024 SMKMDocument7 pagesRpt-Sow Form 3 2023 - 2024 SMKMmaznah abdullahNo ratings yet
- LP AdjectiveDocument5 pagesLP AdjectiveJerico MarcosNo ratings yet
- Plani I Orëve Të Konsultimeve Për Provimet e Lirimit Të Klasave Të NëntaDocument3 pagesPlani I Orëve Të Konsultimeve Për Provimet e Lirimit Të Klasave Të NëntaAlesiaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice-April 2020Document5 pagesPassive Voice-April 2020Daniela LozadaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Items with Less and Not As...AsDocument3 pagesComparing Items with Less and Not As...Ascamila ruiz0% (1)
- Past Continuous actions and eventsDocument1 pagePast Continuous actions and eventsBilly RamliNo ratings yet
- 6 3 Myself/yourself/themselves Etc.: o o o o o o oDocument2 pages6 3 Myself/yourself/themselves Etc.: o o o o o o oJosé Manuel Henríquez Galán100% (1)
- Adverbial Clauses and SubjectDocument14 pagesAdverbial Clauses and Subjectokka haznanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Lingua House Lingua HouseDocument4 pagesConjunctions: Lingua House Lingua HouseTika VirginiyaNo ratings yet
- Negative-Interrogative and Affirmative SentencesDocument6 pagesNegative-Interrogative and Affirmative SentencesLiliana NederitaNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument8 pagesPresent SimpleSARANo ratings yet