Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Autonomic
Uploaded by
api-3757921Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Autonomic
Uploaded by
api-3757921Copyright:
Available Formats
~ ~ ~ AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ~ ~ ~ Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
Dr. Singh D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
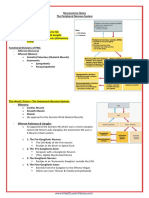
SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
• Afferent Pathway (3 fibers)
○ Where can the afferent sensory fiber go…?
(1) synapses directly to a motor efferent cell body = simple reflex arc (2 fibers)
(2) synapses indirectly to a motor efferent cell body via an interneuron = complex reflex arc (3 fibers)
(3) information is conveyed contralaterally for conscious understanding: SPINAL CORD THALAMUS CORTEX (3 fibers)
• Efferent Pathway (2 fibers)
○ After you perceive the sensory info, muscle commands must be carried out…
(1) Upper motor efferent fiber in the CORTEX contralaterally synapses w/ a Lower motor efferent fiber in the VENTRAL HORN (2 fibers)
(2) Lower motor efferent fiber goes directly out to the PNS w/o stopping at a ganglion to supply SKELETAL MUSCLE
* * * Remember that it takes a chain of 3 somatic neurons to go afferently from the skin to the cortex,
* * * But only 2 somatic neurons to go efferently from the cortex to the skeletal muscle.
SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
• Afferent Pathway (2 fibers)
(1) information is conveyed to the hypothalamus
• Efferent Pathway (3 fibers)
(1) Upper efferent fiber in HYPOTHALAMUS synapses w/ Lower Preganglionic efferent fiber in LATERAL HORN (T1 – L3, some exceptions)
(2) Lower Preganglionic fiber can do any one of the following upon leaving the spinal cord…
- synapse in a ganglion located at the same level where they exited
- travel up or down a few levels before synapsing in a ganglion
- travel all the way up to 3 cervical ganglia = Superior, Middle, Inferior Cervical Ganglia
- travel all the way down to the 1 unpaired Coccygeal Ganglion Impar
- leave the spinal cord w/o synapsing at the paravertebral sympathetic ganglionic chain
(these are the splanchnic nerves… no postganglionic fibers = no grey rami)
(3) Lower PRE-ganglionic fiber (WHITE RAMI) synapses w/ Lower POST-ganglionic fiber (GREY RAMI) in the GANGLIA
(4) Postganglionic motor efferent fiber goes out to supply…
- smooth muscle
- cardiac muscle
- glands, viscera
* * * Somatic * * * Autonomic
afferent pathway = 3 neurons afferent pathway = 2 neurons
efferent pathway = 2 neurons efferent pathway = 3 neurons
ONE lower efferent neuron TWO lower efferent neurons that synapse at a ganglia
lower efferent neuron originates in ventral horn preganglionic efferent neuron originates in lateral horn
no ganglia prior to skeletal muscle innervation yes ganglia prior to smooth muscle / gland innervation
Compiled for you by:
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
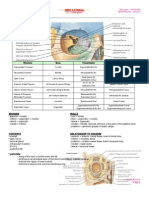
SYMPATHETIC PARASYMPATHETIC
Thoracolumbar Outflow = T1 – L3 lateral horns Craniosacral Outflow = S2, S3, S4 & brainstem
Ganglion = close to the spinal cord Ganglion = close to the target organ
Short preganglionic white fiber Long preganglionic white fiber
Long postganglionic grey fiber Short postganglionic grey fiber
Ganglionic NT = Acetylcholine Ganglionic NT = Acetylcholine
Target NT = Norepinephrine Target NT = Acertylcholine
Response is slow, generalized, long duration Response is fast, localized, short duration
3 cervical ganglia 4 cranial ganglia
• Superior • Ciliary (III)
• Middle • Pterygopalatine (VII)
• Inferior • Submandibular (VII)
• Otic (IX)
Splanchnic Nerves = T5 – T12 Splanchnic Nerves = S2, S3, S4
• Greater Splanchnic Celiac Ganglion • Pelvic Splanchnic
• Lesser Splanchnic Superior Mesenteric Ganglion
• Least Splanchnic Inferior Mesenteric Ganglion
Sympathetic Superior Cervical Ganglion
- preganglionic fibers come from T1, T2
- postganglionic fibers Internal Carotid Nerve
- forms a nerve plexus around the Internal Carotid Artery
- follows the Internal Carotid Artery into the cranial cavity
- supplies ALL cranial structures / viscera requiring sympathetic innervation
- salivary glands / lacrimal glands / palatine, pharyngeal, lingual tonsils
- pupil dilation
Parasympathetic Cranial Ganglia
• Ciliary Ganglion
- located in the Midbrain
- shares w/ CN III – Oculomotor
- preganglionic fibers come from Edinger-Westphal Nucleus
- postganglionic fibers go the eyeball for…
○ pupil constriction
○ accommodation (far → near focusing)
• Pterygopalatine Ganglion
- located in the Pons
- shares w/ CN VII – Facial
- preganglionic fibers come from Superior Salivitory Nucleus
- postganglionic fibers go to…
○ lacrimal gland
○ palatine gland
○ nasopharynx
○ maxillary sinus
• Submandibular Ganglion
- located in the Pons
- shares w/ CN VII – Facial
- preganglionic fibers come from Superior Salivitory Nucleus
- postganglionic fibers go to…
○ submandibular salivary gland
○ sublingual salivary gland
• Otic Ganglion
- located in the Medulla
- shares w/ CN IX – Glossopharyngeal
- preganglionic fibers come from Inferior Salivitory Nucelus
- postganglionic fibers go to…
○ parotid salivary gland
• Vagus Nerve has NO GANGLION!
- located in the Medulla
- shares w/ CN X – Vagus
- preganglionic fibers come from Dorsal Motor Nucleus Compiled for you by:
- postganglionic fibers go to thoracoabdominal viscera
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
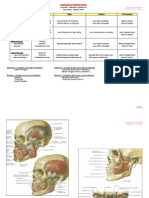
CILIARY GANGLION PTERYGOPALATINE GANGLION OTIC GANGLION
SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
You might also like
- Autonomic Nervous System A. Structure/function of ANSDocument5 pagesAutonomic Nervous System A. Structure/function of ANSXiao Kui LirioNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-1Document46 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-1a-tldNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System: Functions and DivisionsDocument50 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System: Functions and DivisionsTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Pharma - Neurotransmission Ans and SnsDocument10 pagesPharma - Neurotransmission Ans and SnsksescletoNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About the Trigeminal NerveDocument61 pagesEverything You Need to Know About the Trigeminal NerveTanu ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systembasgsr100% (1)
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- Spinal CordDocument48 pagesSpinal CordDr.Saber - Ar - Raffi100% (1)
- Riverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01 Module 4 Lesson 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesRiverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01 Module 4 Lesson 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemNeonil Dequina CaceresNo ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Lecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'Document57 pagesLecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'CHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Preganglionic Neuron (CNS) Preganglionic AxonDocument4 pagesPreganglionic Neuron (CNS) Preganglionic AxonDeja JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Innervation of Abdomen and PelvisDocument6 pagesAutonomic Innervation of Abdomen and PelvisTahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordMai GaberNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFDocument60 pagesLecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFdwataNo ratings yet
- 2 AnsDocument29 pages2 AnsSara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- ANS - PPT NewDocument50 pagesANS - PPT NewBezawit TsigeNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsDocument77 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsHarees ShabirNo ratings yet
- GBSDocument33 pagesGBSbungadielaNo ratings yet
- 083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & FunctionDocument6 pages083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- Sap - Spinal Cord, PNS, AnsDocument6 pagesSap - Spinal Cord, PNS, Ansajminon16No ratings yet
- Student ANS Dr.a QDocument79 pagesStudent ANS Dr.a QJaafar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A&P - 8. The Peripheral Nervous System (12p)Document12 pagesA&P - 8. The Peripheral Nervous System (12p)Gabriel StratulatNo ratings yet
- 11 - Intro To The ANS and Nerves Inside The Thoracic CavityDocument84 pages11 - Intro To The ANS and Nerves Inside The Thoracic CavityYeet JeekiesNo ratings yet
- Sap - Spinal Cord, PNS, AnsDocument6 pagesSap - Spinal Cord, PNS, Ansajminon16No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAbdo HaiderNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Ganglia of Head & Neck 27-05-2020Document52 pagesSeminar - Ganglia of Head & Neck 27-05-2020Chandra dimpleNo ratings yet
- O Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusDocument11 pagesO Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusMaxinefgc BaculoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System ExplainedDocument28 pagesThe Nervous System ExplainedCaim ZNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord NS2.1 Final ArtDocument11 pagesSpinal Cord NS2.1 Final Artdedhomosapien2No ratings yet
- 1-NEU-Histology Lecture CNS (1, 2, 3, 4 & 5) 2021-2022Document16 pages1-NEU-Histology Lecture CNS (1, 2, 3, 4 & 5) 2021-2022Mohamed AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of Spinal Cord: Dr. Normaizatul Afizah Ismail Normaizatul@unishams - Edu.myDocument48 pagesGross Anatomy of Spinal Cord: Dr. Normaizatul Afizah Ismail Normaizatul@unishams - Edu.mykalppena naiduNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument79 pagesSpinal CordNona NadimNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemBarneybabybopbjbtwo FdrgyNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Abdomen, Pelvis & Lower Limb ReviewDocument112 pagesAbdomen, Pelvis & Lower Limb ReviewLester Cintron-PerezNo ratings yet
- The Spinal Cord: DR - SatyaDocument61 pagesThe Spinal Cord: DR - SatyacheckmateNo ratings yet
- TractologyDocument28 pagesTractologysamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Extra HelpDocument41 pagesExam 4 Extra HelpJayNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument50 pagesSpinal CordReem 10No ratings yet
- 7 - AnsDocument15 pages7 - AnsAliNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neuroscience Review Session 2: Ivan Luu Sahar G. Hari Sainath TJ Akram Rishi AdaDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Neuroscience Review Session 2: Ivan Luu Sahar G. Hari Sainath TJ Akram Rishi AdajonathanNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2009Document181 pagesNeuro 2009mcie22dwestNo ratings yet
- Pons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy LectureDocument47 pagesPons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy LecturePlutokidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology (10th Ed.) - NewDocument7 pagesEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology (10th Ed.) - NewNicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesNervous SystemGwynth Mrgrtt GnzlsNo ratings yet
- Tutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BDocument92 pagesTutor 16.2 GRACE NASYA (18-091) 4BGrace HerlisNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: MR Christopher Simon BSC (Neuroscience / Cognitive Psychology) MSC (Human Anatomy)Document66 pagesCranial Nerves: MR Christopher Simon BSC (Neuroscience / Cognitive Psychology) MSC (Human Anatomy)checkmateNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam Notes CNSPDFDocument60 pagesAnatomy Exam Notes CNSPDFBerk SonmezNo ratings yet
- PL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesPL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemFoong Zhen HinNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves I-VI: NeuroanatomyDocument36 pagesCranial Nerves I-VI: NeuroanatomyGolden TamonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanKharisulNo ratings yet
- PARASYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN HEAD AND NECKDocument53 pagesPARASYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN HEAD AND NECKDEEP SABNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves NeuroanatomyDocument57 pagesCranial Nerves NeuroanatomyArvin TanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesPeripheral Nervous Systemapi-26762768100% (4)
- Somatosensory System and PainDocument40 pagesSomatosensory System and PainAhaisibwe GordonNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika33% (3)
- 5 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1Document291 pages5 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1api-3757921No ratings yet
- 4 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1Document266 pages4 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1api-3757921No ratings yet
- 3 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1Document273 pages3 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1api-3757921No ratings yet
- 14-Nasal & SinusesDocument1 page14-Nasal & Sinusesapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 2 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1Document210 pages2 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1api-3757921No ratings yet
- 1 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1Document362 pages1 - 2009 CFA Notes - Level 1api-3757921No ratings yet
- 13-Orbit & EyeDocument12 pages13-Orbit & Eyeapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 2004Document5 pages2004api-3757921No ratings yet
- 15 PharynxDocument9 pages15 Pharynxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 12-Cranial CavityDocument3 pages12-Cranial Cavityapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 10 InfratemporalDocument8 pages10 Infratemporalapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 4 SkullDocument1 page4 Skullapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8 NeckDocument1 page8 Neckapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 9 FaceDocument6 pages9 Faceapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 20-Lymphatics ChartDocument1 page20-Lymphatics Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8-Neck Muscles ChartDocument1 page8-Neck Muscles Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 6-Spinal CordDocument4 pages6-Spinal Cordapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 1-Back Shoulder ArmsDocument6 pages1-Back Shoulder Armsapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 5 JointsDocument2 pages5 Jointsapi-3757921100% (2)
- 2 ThoraxDocument7 pages2 Thoraxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 3 AbdomenDocument7 pages3 Abdomenapi-3757921100% (1)
- Manhattan Sentence CorrectionDocument125 pagesManhattan Sentence Correctionapi-3736636100% (8)
- Pembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFDocument15 pagesPembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFArdi Ansyah YusufNo ratings yet
- 1F4 Catalog0808Document12 pages1F4 Catalog0808Edwin Ng0% (1)
- Vernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratDocument12 pagesVernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratArjun GuptaNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareDocument14 pagesUser Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareComputershastriNoproblem0% (1)
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocument39 pagesAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Component 2 Learner Statement Y2Document6 pagesComponent 2 Learner Statement Y2api-426152133No ratings yet
- Karate Writing AssessmentDocument2 pagesKarate Writing AssessmentLeeann RandallNo ratings yet
- Case Briefing and Case SynthesisDocument3 pagesCase Briefing and Case SynthesisKai RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Accounting Students' Attitude Towads AccountingDocument29 pagesAccounting Students' Attitude Towads AccountingSham Salonga Pascual50% (2)
- All Types of Switch CommandsDocument11 pagesAll Types of Switch CommandsKunal SahooNo ratings yet
- Inclusive E-Service or Risk of Digital Divide The Case of National ICT Policy 2018 of BangladeshDocument11 pagesInclusive E-Service or Risk of Digital Divide The Case of National ICT Policy 2018 of BangladeshInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- CH 22 Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesCH 22 Solutions Manuallmbrn0415No ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument4 pagesLaboratory SafetyLey DoydoraNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadAnonymous ffje1rpaNo ratings yet
- MATH6113 - PPT5 - W5 - R0 - Applications of IntegralsDocument58 pagesMATH6113 - PPT5 - W5 - R0 - Applications of IntegralsYudho KusumoNo ratings yet
- 4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFDocument32 pages4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Adapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumDocument3 pagesAdapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumVini PezzinNo ratings yet
- Clinical behavior analysis and RFT: Conceptualizing psychopathology and its treatmentDocument28 pagesClinical behavior analysis and RFT: Conceptualizing psychopathology and its treatmentAnne de AndradeNo ratings yet
- FD-BF-001 Foxboro FieldDevices 010715 LowRes PDFDocument24 pagesFD-BF-001 Foxboro FieldDevices 010715 LowRes PDFThiago FernandesNo ratings yet
- Anki Very Useful ManualDocument5 pagesAnki Very Useful ManualSoundaryaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019Document4 pagesQuantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019SANAMGI BHAVYANo ratings yet
- Bhajan Songs PDFDocument36 pagesBhajan Songs PDFsilphansi67% (6)
- Math 2 Curriculum GuideDocument19 pagesMath 2 Curriculum GuideMichelle Villanueva Jalando-onNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent: Ghaiath M. A. HusseinDocument26 pagesInformed Consent: Ghaiath M. A. HusseinDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxides Semiconductor CeramicsDocument14 pagesMetal Oxides Semiconductor Ceramicsumarasad1100% (1)
- ccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookDocument30 pagesccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookJeremy HamptonNo ratings yet
- Event ReportDocument2 pagesEvent Reportakshitdaharwal997No ratings yet
- WP1019 CharterDocument5 pagesWP1019 CharternocnexNo ratings yet
- Ukraine and Russia E IRDocument287 pagesUkraine and Russia E IRtatgirNo ratings yet
- Clinnic Panel Penag 2014Document8 pagesClinnic Panel Penag 2014Cikgu Mohd NoorNo ratings yet