Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Financial System
Uploaded by
Rahul AgarwalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Financial System
Uploaded by
Rahul AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
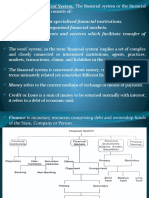
Financial System: The economic development of a nation is reflected by the progress of the various economic units, broadly classified
d into corporate sector government and Household sector.
While performing their activities these units will be placed in a surplus/deficit/balanced budgetary situations. Means - There are areas or people with surplus funds and there are those with a deficit. A financial system or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates the flow of funds from the areas of surplus to the areas of deficit. A Financial System is a composition of various institutions, markets, regulations and laws, practices, money manager, analysts, transactions and claims and liabilities. It plays a vital role in growth of the economy of a country by mobilizing the scarce resources of a country and allocating them to required use It is a complex, well-integrated set of subsystems of financial institutions, markets, instruments, services which facilitates the transfer and allocation of funds efficiently and effectively
Financial system is characterized by the co-existence of the Formal and informal financial sectors commonly referred to as Financial Dualism o Formal Financial System well organized, institutional and regulated system catering to the modern spheres of economy o Informal Financial System unorganized, un-institutional and non-regulated system developed due to financial repressions and certain deprived sections of the society from accessing funds Characterized by the Flexibility of operations, depending on the relationships between the lender and seeker, exploitation
Indian Financial System: Broadly classified into formal and informal financial system Informal System Mainly Consists of o Individual money lenders (friends, landlords, neighbors, traders etc) o Group of persons operating as funds or association o Partnership firms consisting of local brokers and NBFCs like investment companies, chit fund companies etc. Formal System o Comes under the purview of Ministry of Finance, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and other regulatory bodies like IRDA, AMFI etc o Mainly composed of Financial Institutions These are intermediaries that affects generation of savings, mobilizes these savings and facilitates the allocation of funds in an efficient manner Can be classified as Banking and Non Banking Banking institutions creates and supplies the credit whereas the non banking only supplies the credit The main Non-Banking institutions are DFIs (Development Financial Institutions), NBFCc (Non-Banking Financial Institutions), HFCs (Housing Finance Institutions) They can be specialized finance institutions such as SIDBI, NABARD, IDBI, ICICI They can be investment institutions like LIC, GIC, UTI etc They can be state level or national level Financial Markets Imaginary marketplace bringing the seeker and supplier of funds together and provides a platform to deal in financial claims Also provide the facility to set the price (interest rate) for such claims Of two types o Capital Market dealing in long- term instruments and financial claims ( more than one year) o Money Market dealing in short -term instruments (less than one year) Can be classified into o Primary deals with new issues (first time issued securities IPOs) o Secondary deals in outstanding securities Financial Instruments Are the outstanding financial claims against a person or institution for payment at a future date of a sum of money eg shares, bonds, debentures, notes Enable channelizing funds from surplus units to deficit units They are freely marketable in the organized markets and thus reduces the risk of investors They are negotiable and tradable and hence they ensure the financial liquidity Are of two types
Primary Instruments Also called as direct securities. These securities are directly issues by the ultimate borrowers to the ultimate lenders/savers. Eg IPOs, FPOs o Secondary Instruments - these are indirect securities as they are issued by the intermediaries to the ultimate savers. Eg. Bank deposits, Mutual Funds, insurance policies, shares Financial Services These are those services that help in borrowing and funding, lending and investing, buying, selling, enabling and making payments and managing risk exposures in financial market. They also bridge the gap between the lack of knowledge on the part of investor and increasing complex instruments They enable quick, safe and convenient transfer of funds and settlements of transactions. Various financial services are merchant banking, leasing, hire-purchase, credit rating, bill discounting, venture capital etc Are of two types o Fund based Asset based. Services that involves lending money o Fee Based - Advisory services. Services that involves advice/non fund activities
Financial System
Formal
Informal
Financial Market
Financial Intermediaries
Financial Instruments
Financial Services
Primary Market
Secondary Market
Banking
Non Banking (NBFC's)
Primary Instruments
Secondary Instruments
Fund BAsed
Fee Based
Capital Market
Money Market
Long Term
Short Term
Sec. Secu.
Financial Markets Financial Intermediaries
Pri. Secu.
Ultimate Lenders
Pri. Secu.
Pri. Secu.
Ultimate Borrowers
Financial Instruments/Claims Financial System
Capital Formation
Economic Growth
Functions of Financial System: To link savers and seekers of fund and thus help in mobilizing and allocating the savings efficiently and effectively It not only fund the projects but also monitors the performance of the investment through corporate monitoring and control Provides for payment mechanism for the exchange of goods and services in a safe, quick and timely manner Transfer economic resources across time, place and parties and thereby enable financial transactions Helps in pooling and trading the risk involved in mobilizing savings and aims at limiting risk at acceptable limits. This is done by o Laying down the rules and regulations governing the operation of system o By holding diversified portfolios and screening of borrowers o By providing protection from unexpected losses Makes available the price-related and other financial information to those who need to make financial decision regarding investment, divestment, re-investment. It also make sure that this information is available on unbiased and non-preferential basis so that some should not take advantage of such information over others. It also reduces the cost of such gathering and analyzing such information. It provides a ready market for securities to buy/sell wide variety of financial assets in a cheap, quick and reliable way and thereby enhancing the liquidity of the portfolio Helps in reducing the cost of financial transaction by providing a structure that enables such transactions in a cheap, faster, effective and efficient way Helps in
o o
financial deepening refers to the increase in financial assets as the percentage of GDP Financial Broadening refers to building increasing number of participants and variety of instruments
You might also like
- Instructions: Put Your Notes Below The Unit of Your Portion. and Also Try Type/copy and Paste Your Part Instead of Pictures or Screenshots Unit-1Document76 pagesInstructions: Put Your Notes Below The Unit of Your Portion. and Also Try Type/copy and Paste Your Part Instead of Pictures or Screenshots Unit-1Diya MNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution & Markets - Short NotesDocument41 pagesFinancial Institution & Markets - Short NotesGovind RathiNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution & Markets - Short NotesDocument43 pagesFinancial Institution & Markets - Short NotesSanya Gupta100% (1)
- Components of IFS NotesDocument6 pagesComponents of IFS NotesPrasad IngoleNo ratings yet
- The Financial SystemDocument82 pagesThe Financial SystemGaurav007100% (1)
- The Financial System Provides The Intermediation Between Savers and Investors and Promoters Faster Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesThe Financial System Provides The Intermediation Between Savers and Investors and Promoters Faster Economic DevelopmentsanskritiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - OverviewDocument6 pagesFinancial Markets - OverviewCharmaine Klaire Agan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Financial SystemDocument7 pagesThe Philippine Financial SystemKhyell PayasNo ratings yet
- Structure of Financial SystemDocument72 pagesStructure of Financial Systemsaha apurvaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 ReportDocument7 pagesGroup 5 ReportSonam Peldon (Business) [Cohort2020 RTC]No ratings yet
- Gabriel Adegite BUAD 811 Individual AssignmentDocument5 pagesGabriel Adegite BUAD 811 Individual AssignmentSheila OdorNo ratings yet
- Financial System 1.zeroDocument86 pagesFinancial System 1.zerokhalifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial SystemsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Financial SystemsVinay ArtwaniNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediationDocument41 pagesFinancial IntermediationRphdd100% (4)
- Unit 1 MBS FIMDocument16 pagesUnit 1 MBS FIMSarun ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesFinancial MarketsArham JainNo ratings yet
- INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWDocument28 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM OVERVIEWRajEev ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Features of The Financial System of DevelpoedDocument35 pagesFeatures of The Financial System of DevelpoedChahat PartapNo ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial MARKETSDocument46 pagesOverview of Indian Financial MARKETSGaurav Rathaur100% (2)
- Financial Markets AND Services: Vi SemesterDocument84 pagesFinancial Markets AND Services: Vi SemesterSamuel AnthrayoseNo ratings yet
- Fim 4Document33 pagesFim 4akshat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Financial SystemDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Indian Financial SystemManoher Reddy100% (2)
- CH1@FI&M Final EditedDocument7 pagesCH1@FI&M Final Editedtamiratg24No ratings yet
- Indian Financial System ComponentsDocument8 pagesIndian Financial System ComponentsSteffin JosephNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument52 pagesFinancial Marketsdaksha pathakNo ratings yet
- Overview of Financial System: Photo: Suomen PankkiDocument32 pagesOverview of Financial System: Photo: Suomen PankkiCarla Mae PasiaNo ratings yet
- Hide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditDocument21 pagesHide 1 Financial Controls and Monitoring 2 Financial Services 3 See Also 4 References EditPankaj GautamNo ratings yet
- MPCB Module 1 Intro To Financial MarketDocument6 pagesMPCB Module 1 Intro To Financial MarketAlfe PinongpongNo ratings yet
- Cifa Financial Institutions and Markets PDFDocument104 pagesCifa Financial Institutions and Markets PDFMswakubaffNo ratings yet
- Components of the Financial System ExplainedDocument3 pagesComponents of the Financial System ExplainedRekha SoniNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument31 pagesFinancial MarketsCheesca Macabanti - 12 Euclid-Digital ModularNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Financial Systems and Financial MarketsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Financial Systems and Financial MarketsWill De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Ifss Mod-1Document24 pagesIfss Mod-1ŚŰBHÁM řájNo ratings yet
- ABIYDocument9 pagesABIYEyob HaylemariamNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument4 pagesIndian Financial SystemDivya BhadriNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument7 pagesIndian Financial SystemNaveen DevarajNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1Document16 pagesAn Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1bhavyaNo ratings yet
- FM 2nd Unit NotesDocument86 pagesFM 2nd Unit NotesrachitcreativeNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Systems in Economic GrowthDocument7 pagesRole of Financial Systems in Economic GrowthRVNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument4 pagesFinancial InstitutionsTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- Financial System Scope and FunctionDocument2 pagesFinancial System Scope and FunctionvivekNo ratings yet
- INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEMDocument36 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEMMony RrrNo ratings yet
- A Brief On Indian Financial SystemDocument9 pagesA Brief On Indian Financial Systemjai_tri007No ratings yet
- Unit 1: - Investment Environment in India - Overview of Indian Financial System - Investment AlternativesDocument35 pagesUnit 1: - Investment Environment in India - Overview of Indian Financial System - Investment AlternativesSatya KumarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionSagar100% (1)
- Nature and Importance of Financial SystemsDocument11 pagesNature and Importance of Financial SystemsAuie Eugene Frae SalameraNo ratings yet
- IFS PRITAM SIR NOTESDocument100 pagesIFS PRITAM SIR NOTES3017 Antara Mudi Cse AiNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- NBFC Full NoteDocument119 pagesNBFC Full NoteRashmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Financial System and Its ComponenetsDocument54 pagesUnit 2 Financial System and Its Componenetsaishwarya raikar100% (1)
- Introduction to Financial MarketsDocument53 pagesIntroduction to Financial MarketsAddy Khan100% (1)
- Module IDocument36 pagesModule IKrishna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument36 pagesLecture NotesAmritNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Financial SystemDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Financial SystemSimran JainNo ratings yet
- IfsDocument23 pagesIfsRahul Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- Index Executive Summary of Capital Markets Chapter 1 Investment BasicsDocument23 pagesIndex Executive Summary of Capital Markets Chapter 1 Investment Basicsswapnil_bNo ratings yet
- Impact of Financial Sector Reforms On Ec PDFDocument46 pagesImpact of Financial Sector Reforms On Ec PDFSourabh YadavNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument19 pagesFinancial MarketAshishNo ratings yet
- Given Below Are The Features of The Indian Financial SystemDocument3 pagesGiven Below Are The Features of The Indian Financial SystemALLIED AGENCIES0% (1)
- The Finace Master: What you Need to Know to Achieve Lasting Financial FreedomFrom EverandThe Finace Master: What you Need to Know to Achieve Lasting Financial FreedomNo ratings yet
- 1 Risk ManagementDocument28 pages1 Risk ManagementRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1 OB IntroductionDocument19 pages1 OB IntroductionRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PlatformificationDocument8 pagesPlatformificationRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 02 Cultural EnvironmentDocument36 pages02 Cultural EnvironmentRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1 OB IntroductionDocument19 pages1 OB IntroductionRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1 HRM - IntroductionDocument31 pages1 HRM - IntroductionRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policies IndiaDocument52 pagesIndustrial Policies IndiaUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Compensation ConceptsDocument59 pagesCompensation ConceptsRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Work EnvironmentDocument37 pagesWork EnvironmentRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Brain StillingDocument11 pagesBrain StillingRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 1 Financial SystemDocument5 pages1 Financial SystemRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 6 Media Planning and PromotionDocument46 pages6 Media Planning and PromotionRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Corporate GovernanceDocument14 pagesCorporate GovernanceRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Red Orchid - Best PracticesDocument80 pagesRed Orchid - Best PracticeslabiaernestoNo ratings yet
- BI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014Document1 pageBI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014scribdNo ratings yet
- MM-18 - Bilge Separator - OPERATION MANUALDocument24 pagesMM-18 - Bilge Separator - OPERATION MANUALKyaw Swar Latt100% (2)
- Architectural PlateDocument3 pagesArchitectural PlateRiza CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W3Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W3AnatasukiNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Wildlife and Cultural TourDocument9 pagesSri Lanka Wildlife and Cultural TourRosa PaglioneNo ratings yet
- Poetry Recitation Competition ReportDocument7 pagesPoetry Recitation Competition ReportmohammadNo ratings yet
- Advanced VLSI Architecture Design For Emerging Digital SystemsDocument78 pagesAdvanced VLSI Architecture Design For Emerging Digital Systemsgangavinodc123No ratings yet
- UG022510 International GCSE in Business Studies 4BS0 For WebDocument57 pagesUG022510 International GCSE in Business Studies 4BS0 For WebAnonymous 8aj9gk7GCLNo ratings yet
- LLB 1st Year 2019-20Document37 pagesLLB 1st Year 2019-20Pratibha ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 2C Syllable Division: Candid Can/dDocument32 pages2C Syllable Division: Candid Can/dRawats002No ratings yet
- Ethiopian Civil Service University UmmpDocument76 pagesEthiopian Civil Service University UmmpsemabayNo ratings yet
- Skin Yale University Protein: Where Does Collagen Come From?Document2 pagesSkin Yale University Protein: Where Does Collagen Come From?Ellaine Pearl AlmillaNo ratings yet
- CP ON PUD (1) ADocument20 pagesCP ON PUD (1) ADeekshitha DanthuluriNo ratings yet
- 00.arkana ValveDocument40 pages00.arkana ValveTrần ThànhNo ratings yet
- IB Theatre: The Ilussion of InclusionDocument15 pagesIB Theatre: The Ilussion of InclusionLazar LukacNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Basico Del Metodo AJAX Con PHP y MySQLDocument14 pagesTutorial Basico Del Metodo AJAX Con PHP y MySQLJeese Bahena GarciaNo ratings yet
- Contract Costing and Operating CostingDocument13 pagesContract Costing and Operating CostingGaurav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Conflicts and PeacekeepingDocument2 pagesEthnic Conflicts and PeacekeepingAmna KhanNo ratings yet
- Neligence: Allows Standards of Acceptable Behavior To Be Set For SocietyDocument3 pagesNeligence: Allows Standards of Acceptable Behavior To Be Set For SocietyransomNo ratings yet
- Toolkit:ALLCLEAR - SKYbrary Aviation SafetyDocument3 pagesToolkit:ALLCLEAR - SKYbrary Aviation Safetybhartisingh0812No ratings yet
- 2010 Economics Syllabus For SHSDocument133 pages2010 Economics Syllabus For SHSfrimpongbenardghNo ratings yet
- Note-Taking StrategiesDocument16 pagesNote-Taking Strategiesapi-548854218No ratings yet
- Bandwidth and File Size - Year 8Document2 pagesBandwidth and File Size - Year 8Orlan LumanogNo ratings yet
- ROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEDocument9 pagesROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEfrola5100% (2)
- Developments in ESP: A Multi-Disciplinary ApproachDocument12 pagesDevelopments in ESP: A Multi-Disciplinary ApproachDragana Lorelai JankovicNo ratings yet
- IJAKADI: A Stage Play About Spiritual WarfareDocument9 pagesIJAKADI: A Stage Play About Spiritual Warfareobiji marvelous ChibuzoNo ratings yet
- List of Parts For Diy Dremel CNC by Nikodem Bartnik: Part Name Quantity BanggoodDocument6 pagesList of Parts For Diy Dremel CNC by Nikodem Bartnik: Part Name Quantity Banggoodyogesh parmarNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ReportDocument135 pagesSummer Internship Reportsonal chandra0% (1)
- Popular Painters & Other Visionaries. Museo Del BarrioDocument18 pagesPopular Painters & Other Visionaries. Museo Del BarrioRenato MenezesNo ratings yet