Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atherosclerosis
Uploaded by
Ammar HamzahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atherosclerosis
Uploaded by
Ammar HamzahCopyright:
Available Formats
Atherosclerosis.
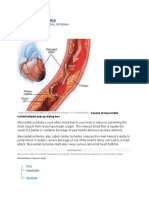
Overview. Atherosclerosis or also known as arteriosclerotic vascular disease (AVSD) is a condition where the artery walls thicken due to the collection of fatty material which collects along the walls of arteries. The fatty material may thicken, hardens and will eventually block the arteries. The fatty materials which can block the arteries are called plaques. It will usually affect large and medium-sized arteries. Atherosclerosis is a very dangerous disease. When the arteries had been blocked, the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the organs and other parts of the body will be limited. This condition can lead to serious problems, including heart attack, stroke, or even death.
Causes of Atherosclerosis The exact cause of atherosclerosis is still yet to be known to mankind. Nevertheless, scientists think that the buildup of plaque starts when the lining of the artery is damaged or injured, but they are not sure why and how the artery becomes damaged in the first place. Atherosclerosis is a slow, complex disease that typically starts in childhood and often progresses when people grew older. Damaged to the lining of the artery may caused by Elevated levels of cholesterols and triglyceride in the blood High blood pressure Tobacco smoke Diabetes
There are also numbers of factors that can increase a persons chance of developing atherosclerosis. They are known as atherosclerosis risk factors, and include: Age (45 or over for men, and 55 or over for women) Being male High cholesterol (Hypercholesterolemia) High blood pressure Diabetes Overweight Not exercising Smoking Having close relatives with heart disease at younger ages. Alcohol Air pollution
Age
As we get older, our arteries naturally begin to harden and get narrower, leading to atherosclerosis. High cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is essential for the functioning of the body. There are two main types of cholesterol:
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is mostly made up of fat, plus a small amount of protein. This type of cholesterol can block the arteries, so it is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol'.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is mostly made up of protein, plus a small amount of fat. This type of cholesterol can help to reduce any blockage in the arteries, so it is often referred to as 'good cholesterol'.
The LDL cholesterol sticks to the artery walls in the form of fatty deposits which, over time, gradually build up, narrowing, or completely blocking, the blood supply. High blood pressure
High blood pressure can cause damage to the lining arteries as it has its own certain pressure. If the pressure exceeded, the artery walls will be damaged. Diabetes
This will only occur with uncontrolled type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The excess glucose in the blood can damaged the wall of artery. Overweight
Those who are overweight have an increased risk of developing high blood pressure, tend to have higher levels of cholesterol, and have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Not exercising
Lack of exercise can increased the risk of being overweight and having a high blood pressure. Smoking
Smoking can damage the walls of the arteries. If the arteries are damaged by smoking, blood cells, known as platelets, will form at the site of the damage to try to repair it. This can cause the arteries to narrow. Smoking also decreases the blood's ability to carry oxygen around the body, which increases the chances of a blood clot occurring.
Alcohol
Drinking an excessive amount of alcohol can cause high blood pressure (hypertension) and raised blood cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of developing atherosclerosis and CVD. Most heavy drinkers also tend to have other unhealthy habits, such as smoking, eating a high-fat diet and not taking enough exercise. Family history
The risk of getting atherosclerosis is twice if there is family history of atherosclerosis. Air pollution
Research that was carried out during 2009 suggested that air pollution, in particular traffic pollution, can cause a slight increase in levels of atherosclerosis. Researchers found that people living within 50 metres of a major road had higher levels of atherosclerosis than would otherwise be expected.
Symptoms . Conditions that are known to be caused by atherosclerosis include: Peripheral arterial disease. It is a condition when there is a blockage in the arteries of the limbs. The most common symptoms is when there is pain in the legs. The pain can be felt like a cramp or sensation of dullness or heaviness. The pain usually comes and goes, and got worse when doing exercise. Angina. It is similar to periphery arterial disease only it is caused by reduced blood supply to heart. The most common symptoms is feeling of pain or discomfort in the chest. The pain can feel tight, dull or heavy and usually passes within a few minutes. Aneurysm. If the atherosclerosis weakens the walls of the blood vessels, it can cause aneurysm which is a bulge in the blood vessels. If it grows too large, there is danger that it will rupture which cause fatal internal bleeding and organ damaged. If an aortic aneurysm ruptures, the person will experience a sudden and severe pain in the middle or side of your abdomen (stomach). Symptoms of a ruptured intracranial aneurysm usually begin with a sudden and severe headache, which has been described as like being hit on the head, resulting in a blinding pain. Heart attack. If one of the plaques of the coronary artery ruptures, it could create a blood clot. If the blood clot blocks the blood supply to the heart, it will cause heart attack. Stroke. Blood clot can also block the blood supply to the brain then causing stroke.
Treatments. Prevention is better than cure. Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, are often the first line of defence in treating atherosclerosis. But sometimes, medical or surgical procedures may be recommended as well. Various drugs can be used: Cholesterol medications. Aggressively lowering the LDL cholesterol can slow or even reverse the build up of fatty deposits in the arteries. Boosting the HDL will help too. Example of drugs known as statins and fibrates. Anti-platelets medications. Examples given as aspirin, to reduce the risk of platelets that will clump at the narrow arteries, form a blood clot and causing blockage. Anticoagulants. Example as heparin or warfarin can help thin the blood to prevent blood from clotting. Blood pressure medications. Medications to control blood pressure such as beta blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and calcium channel blockers. It can help to slow down the progression of atherosclerosis.
Sometimes more aggressive treatment is needed. Angioplasty. In this procedure, the doctor will inserts a long, thin tube (catheter) into the blocked artery. A wire with deflated balloon is passed through the catheter to the narrowed area. The balloon will then inflated, compressing the deposits against the artery walls. A mesh tube is usually left in the artery to help keep the artery open. Angioplasty may also be done with laser technology. Endarterectomy. In some cases, fatty deposits must be surgically removed from the walls of a narrowed artery. Thrombolytic therapy. A clot-dissolving drug may be introduced to a patient with an artery blocked by blood clot in order to break the blood clot. Bypass surgery. A graft bypass may be created by using a vessel from another part of the body. This allows blood to flow around the blocked or narrowed artery.
Healthy lifestyle. Healthy lifestyle may ensure a life of free atherosclerosis. Smoking. Smoking may damage the arteries. By quitting smoking, the progression of atherosclerosis may be slow or even been halted down and reduce the risk of complications. Exercise. Physical activity can also improve circulation and promote development of new blood vessels that form a natural bypass around obstruction. Ideally, we must exercise 30-60 minutes most day of the week. Diet. A heart-healthy diet based on fruits, vegetables and whole grains and low in saturated fat, cholesterol and sodium can help to control not only weight but also blood pressure and cholesterol level. Stress. Stress must be managed. Reduce stress as much as possible.
You might also like
- Edexcel As Level Biology Revision Powerpoint Unit 1Document43 pagesEdexcel As Level Biology Revision Powerpoint Unit 1Roslyn Taylor100% (1)
- Case Study Sa Nutrition-1Document7 pagesCase Study Sa Nutrition-1Hazel Sumulong GumapacNo ratings yet
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: UMMC, 2010Document10 pagesAtherosclerosis: UMMC, 2010egyseptiansyahNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument8 pagesCase Study For Coronary Artery DiseaseGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- What is Acute Myocardial Infarction? Risks, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument6 pagesWhat is Acute Myocardial Infarction? Risks, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentNovianty GliceriaNo ratings yet
- Arteriosclerosis: Bio 3360-01:biogerontology Jennie Young Dr. LloydDocument12 pagesArteriosclerosis: Bio 3360-01:biogerontology Jennie Young Dr. LloydJennie MarcellisNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Arterial ThrombosisDocument4 pagesArterial ThrombosisFaraida Jilzani ArsadNo ratings yet
- Risks and Treatments of AtherosclerosisDocument6 pagesRisks and Treatments of AtherosclerosisRoland EmersonNo ratings yet
- Written Report Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesWritten Report Coronary Heart DiseaseJade WushuNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)Document4 pagesHeart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)Mack Javier VenturaNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute Myocardial Infarction?: Heart AttackDocument4 pagesWhat Is Acute Myocardial Infarction?: Heart AttackMavic DerainNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument6 pagesAtherosclerosisNader Smadi100% (1)
- AtherosclerosisDocument1 pageAtherosclerosisroci74No ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Heart Disease CDDocument28 pagesCoronary Artery Heart Disease CDchristinaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension & Stroke: Prepared By: Sharinah Ainee S. Pasandalan BSN-III, Group 4Document56 pagesHypertension & Stroke: Prepared By: Sharinah Ainee S. Pasandalan BSN-III, Group 4Sharinah Ainee Sabalburo PasandalanNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument27 pagesPrevention of Cardiovascular DiseaseskennfenwNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument28 pagesReportHazel KingNo ratings yet
- Medications Various Drugs Can Slow - or Even Reverse - The Effects of Atherosclerosis. Here AreDocument8 pagesMedications Various Drugs Can Slow - or Even Reverse - The Effects of Atherosclerosis. Here Areluis fernando santos narvaezNo ratings yet
- Physiological Monitoring and Arterial DiseasesDocument100 pagesPhysiological Monitoring and Arterial DiseasesZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Health Service of The Republic of Belarus Vitebsk State Medical UniversityDocument7 pagesMinistry of Health Service of The Republic of Belarus Vitebsk State Medical UniversityTalal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Triglycerides Function and Impact on Heart HealthDocument5 pagesTriglycerides Function and Impact on Heart Healthrosidin_551390No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular & Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular & Circulatory SystemkilomikmikNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation on Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument18 pagesCase Presentation on Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseMaria Vanessa Lopez - BSN Level 3 A100% (1)
- Hap Proj!Document15 pagesHap Proj!Darla Louise MituNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) : Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) - A Partial Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)Document4 pagesHeart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) : Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) - A Partial Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)mbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Disease Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument7 pagesDisease Congenital Heart DiseaseMahesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack Risk Factors and Symptoms ExplainedDocument12 pagesHeart Attack Risk Factors and Symptoms ExplainedHazwan AkmalNo ratings yet
- AsthersclorsisDocument3 pagesAsthersclorsismazenali7473No ratings yet
- Strokes: Abdominal Aortic AneurismDocument5 pagesStrokes: Abdominal Aortic AneurismMaja LucasNo ratings yet
- ArteriosclerosisDocument8 pagesArteriosclerosisRhea Liza Comendador-TjernmoenNo ratings yet
- Activity BS 1.3Document5 pagesActivity BS 1.3Camba TracyNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument29 pagesNotesujala khanNo ratings yet
- Paper Work of High Cholesterol: English AssignmentDocument10 pagesPaper Work of High Cholesterol: English AssignmentVyeren VestalNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensiveDocument7 pagesAntihypertensiveAKASH BISWASNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology ProjectFelicia Charles0% (1)
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument11 pagesCoronary Heart DiseaseZaryna TohNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack Symptoms, Causes & Treatment GuideDocument4 pagesHeart Attack Symptoms, Causes & Treatment GuideMirella Lereleré100% (1)
- What Is Acute Myocardial Infarction?Document6 pagesWhat Is Acute Myocardial Infarction?Md Sherajul HaqueNo ratings yet
- What Is Coronary Artery Disease?: AtherosclerosisDocument69 pagesWhat Is Coronary Artery Disease?: AtherosclerosisAyhan AdsizNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument12 pagesCoronary Heart DiseaseAji Prima Putra100% (2)
- Aging Changes in The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesAging Changes in The Heart and Blood VesselsTotalenesya Reforrent SutiknoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Cronary Heart Diseas (CHD)Document7 pagesBiology Project Cronary Heart Diseas (CHD)احمد المغربي50% (2)
- What Is A Heart AttackDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Heart AttackAlia MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Science Project About HeartDocument20 pagesScience Project About Heartmaryamakram5076No ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument4 pagesCauses and Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseFadhilah DhilahNo ratings yet
- Cardio Changes 2Document14 pagesCardio Changes 2BSN 1H- TUAZON,SARAH MAE T.No ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument4 pagesHYPERTENSIONmariaestercampos22No ratings yet
- CoronaDocument7 pagesCoronaUDDE-E MARISABELNo ratings yet
- Types of Heart DiseasesDocument9 pagesTypes of Heart DiseasesJesslyn LimNo ratings yet
- Exercise Prescription & ProgrammingDocument34 pagesExercise Prescription & ProgrammingSmiley Jhen Garcia SabinianoNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis - Michigan MedicineDocument3 pagesAtherosclerosis - Michigan MedicineJohn SammutNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease Term PaperDocument7 pagesCoronary Heart Disease Term Paperafmabhxbudpljr100% (1)
- HYPERTENSION, Also Known As High Blood Pressure Affects MillionsDocument7 pagesHYPERTENSION, Also Known As High Blood Pressure Affects MillionsPrince KarikariNo ratings yet
- High Blood PressureDocument4 pagesHigh Blood PressureMacalalad, Charles JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System DiseasesDocument4 pagesCirculatory System DiseasesLudwigJayBarayugaNo ratings yet
- Another BookletDocument8 pagesAnother BookletMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- TherosclerosisDocument6 pagesTherosclerosismeaad kahtanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PROJECT (Class 12)Document21 pagesBIOLOGY PROJECT (Class 12)Manoghna MaheshNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors of CHDDocument2 pagesRisk Factors of CHDspooferbarnabasNo ratings yet
- Flash Pulmonary EdemaDocument11 pagesFlash Pulmonary EdemaEda SopNo ratings yet
- How nitric oxide benefits your heart, lungs, brain and moreDocument4 pagesHow nitric oxide benefits your heart, lungs, brain and moreAtiqah Liyana15No ratings yet
- Circulatory System LessonDocument13 pagesCirculatory System LessonNan Houm SianNo ratings yet
- A Morphological Study of Anatomical Variations in 96 Circles of Willis An Autopsic Evaluation and Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesA Morphological Study of Anatomical Variations in 96 Circles of Willis An Autopsic Evaluation and Literature ReviewRoxana RoxNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Cardiology Secrets 6Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Cardiology Secrets 6Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfjohn.eastman290100% (20)
- TOFDocument17 pagesTOFMaryel PascualNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical care for hypertension patients to improve quality of lifeDocument55 pagesPharmaceutical care for hypertension patients to improve quality of lifeREYNER AURELINUS MAXIMUS 2018No ratings yet
- Ascites in PoultryDocument37 pagesAscites in Poultryamamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesScience 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemMaricel PenaNo ratings yet
- Roger Hainsworth (Auth.), Marek Malik (Eds.) - Clinical Guide To Cardiac Autonomic Tests-Springer Netherlands (1998)Document425 pagesRoger Hainsworth (Auth.), Marek Malik (Eds.) - Clinical Guide To Cardiac Autonomic Tests-Springer Netherlands (1998)Victor LauneNo ratings yet
- HCM Case Study in Young AthleteDocument1 pageHCM Case Study in Young AthleteLADY JOWAHER ALLASNo ratings yet
- Dr.T.Venkatachalam Professor of Anaesthesiology Madras Medical College, ChennaiDocument35 pagesDr.T.Venkatachalam Professor of Anaesthesiology Madras Medical College, ChennaiNailahRahmahNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Embryology and Developmental Biology 6th Edition CarlsonDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Human Embryology and Developmental Biology 6th Edition Carlsonmelanieboniface7n9100% (1)
- Atherosclerosis: A Disease of ArteriesDocument35 pagesAtherosclerosis: A Disease of ArteriesSevda MemetNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert PDF Full Chapteradrianblackiadxetkrqm100% (14)
- Practice Exams - CardiovascularDocument19 pagesPractice Exams - CardiovascularpadialmichelleNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in PregnancyDocument56 pagesHeart Disease in PregnancyyandraNo ratings yet
- Heli FX Ordering InformationDocument2 pagesHeli FX Ordering Information子麟楊No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesZyryll VegaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Peripheral Vascular SystemDocument91 pagesAssessment of The Peripheral Vascular SystemKeid Reuma100% (1)
- Cardiorespiratory Endurance: in This Chapter Student Web ResourcesDocument9 pagesCardiorespiratory Endurance: in This Chapter Student Web ResourcesFRANCO PANUGALINGNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cardiology + RomanaDocument120 pagesJournal of Cardiology + RomanaMiss Oana100% (1)
- Pengaruh Autogenik3Document5 pagesPengaruh Autogenik3Ruslan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- Ala 3Document30 pagesAla 3Alaz NellyNo ratings yet
- Cardio Q&aDocument147 pagesCardio Q&aHoney Lyn AlebioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Cvs BdsDocument142 pagesCvs BdsDr Dhiren Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 11Document5 pagesBio Lab 11Sarah JaglalNo ratings yet