Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Core Revision
Uploaded by
Maasa AliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Core Revision
Uploaded by
Maasa AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Core 1 - Maths Revision.
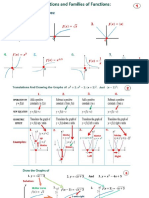
Indices. A to the power of x times a to the power of y is equal to a to the power of (x+y). A to the power of half is equal to the square root of A. A to the power of 0 is equal to 1. A to the power of minus 1 is equal to (1 over a to the power of one). Square root of 4 times square root of 3 equals square root of 12 or 2 root 3. Discriminate. The discriminate is b squared 4ac. If the discriminate is less than 0 there are no real roots. If the discriminante is more than 0 then there are two real roots. If the discriminate equals 0 there are equal roots. What is the quadratic formula? The quadratic formula is minus b plus or minus the discriminate divided by 2 times a. Equations and inequalities. There are 2 methods of solving simultaneous equations: substitution and elimination. When you multiply or divide an inequality by a negative number, you need to change the inequality sign to its opposite. Sketching curves. Transformations of graphs: If the change to the equation is inside the bracket it affects the x co-ordinates in the opposite way to what you would expect. If it is outside the bracket then the transformation of the graph is to the y co-ordinates and as you would expect. F(x + a) is a translation of a in the x direction. F(x) + a is a translation of +a in the y direction.. F (ax) is a stretch of 1 divided by a in the x direction (multiply x co-ordinates by 1 divided by a). af (x) is a stretch of a in the y direction ( multiply y co-ordinates by a). Quadratic graphs The general equation for a quadratic graph is a times x squared plus b times x plus c. For the general equation c is the y intercept. If the a times x squared is negative then the parabola is upside down.
The factorised form of a quadratic gives the x intercepts. The completed square form gives the minimum point. The quadratic equation form gives the y intercept. Co-ordinate geometry in the x, y plane. The general form of a straight line is y = mx +c. For this equation c is the intercept of the y axis and m is the gradient. The gradient of a straight line is: the change in y divided by the change in x. To find the equation of a line using the gradient and one point you use: Y Y1 = M times (X-X1). If a line has gradient of m then the perpendicular gradient is 1 divided by m. Differentiation. Differentiation the equation of a curve gives you the gradient function. To differentiate you: Multiply by the power and then subtract one from the power. The notation for differentiation is d y by d x and f dash x. Integration. When you integrate you have to remember to add C, and in nearly every exam there will be a questions where you have to find C using the given x and y co-ordinates. To integrate you: Add one to the power and then divide by the new power.
You might also like
- Capstone Project MarketingDocument9 pagesCapstone Project MarketingKawalpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Exam Study NotesDocument6 pagesGrade 9 Math Exam Study Notescynthia_88No ratings yet
- Formal and InformalDocument8 pagesFormal and Informalapi-246444495No ratings yet
- Session 9 FunctionDocument7 pagesSession 9 Functionzlmulaudzi42No ratings yet
- Try To Graph and Name The Following EquationsDocument46 pagesTry To Graph and Name The Following EquationsStephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Linear Graphs and Equations: Y1 M (x-x1) When The Gradient and The Co-Ordinates (x1, Y1) of A Single Point That The LineDocument6 pagesLinear Graphs and Equations: Y1 M (x-x1) When The Gradient and The Co-Ordinates (x1, Y1) of A Single Point That The LineSchoolSlackerNo ratings yet
- Common CurvesDocument9 pagesCommon CurvesTagore uNo ratings yet
- 478 PDFDocument166 pages478 PDFdkrirayNo ratings yet
- System of Linear Equation and ApplicationDocument32 pagesSystem of Linear Equation and Applicationihsaanbava0% (1)
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation and Quadratic EquationDocument30 pagesLinear Equation and Quadratic EquationAmz AlburoNo ratings yet
- Implicitly Defined Curves and Their TangentsDocument5 pagesImplicitly Defined Curves and Their TangentsRaphael Sevilla0% (1)
- If God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotesDocument9 pagesIf God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotescallumkhangNo ratings yet
- Unit1 SummaryDocument1 pageUnit1 SummaryknoxmathsNo ratings yet
- As MathematicsDocument17 pagesAs Mathematicsjupe01No ratings yet
- Yyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyyDocument4 pagesYyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyycambreayaNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphDocument27 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Asymptotes: Name: Mehak Roll No: s-2021-08-020 BSC 1 YearDocument15 pagesAsymptotes: Name: Mehak Roll No: s-2021-08-020 BSC 1 YearMehak waliaNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocument5 pagesAP Calculus BC Study GuideJohn MoonNo ratings yet
- Maths GCSE Revision 9 - 1 2022Document5 pagesMaths GCSE Revision 9 - 1 2022jsa4ye99teNo ratings yet
- Maths Study - GRAPHS Year 10Document2 pagesMaths Study - GRAPHS Year 10JosephNo ratings yet
- Mate VocabDocument1 pageMate VocabRiccardo LopezNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument21 pagesFinal Revisionsprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- Lecture, OnDocument14 pagesLecture, OntempNo ratings yet
- C1 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesC1 Revision Notesxxtrim100% (1)
- Mathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraDocument10 pagesMathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraJAY BHAVIN SHETH (B14EE014)No ratings yet
- MHF4U Unit 1Document9 pagesMHF4U Unit 1Daniswara HafidzNo ratings yet
- Exploring Fractional IndicesDocument15 pagesExploring Fractional IndicesLuly G.No ratings yet
- Cu 3Document39 pagesCu 3omgitsjediNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Function Investigation - Maria AncutaDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Function Investigation - Maria Ancutaapi-515654558No ratings yet
- Curve TracingDocument4 pagesCurve Tracingsurekha surekha0% (1)
- Linear EquationDocument8 pagesLinear EquationkleyrgNo ratings yet
- 11MMCAS 2021 NotesDocument189 pages11MMCAS 2021 NotesJinang ShahNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Project 1) Quadratic Equations in One Variable: Algebra Latin Square EquationDocument2 pagesMathematics Project 1) Quadratic Equations in One Variable: Algebra Latin Square Equationsachin DesardaNo ratings yet
- In The Coordinate Plane Graphing AlgerbaDocument3 pagesIn The Coordinate Plane Graphing AlgerbaAnthony CottomNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Relation and FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Difference Between Relation and Functionbjkhaw75No ratings yet
- Linear Equations and GraphsDocument25 pagesLinear Equations and GraphsSonu JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes PDFDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Notes PDFCharles GribbenNo ratings yet
- Maths - 1Document10 pagesMaths - 1Sohid BacusNo ratings yet
- Pair of Linear Equations in 2 VariablesDocument36 pagesPair of Linear Equations in 2 VariablesshaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Arithmetic Sequences and SeriesDocument18 pagesDefinition of Arithmetic Sequences and Seriesroyce59No ratings yet
- Pre Calculus PrimerDocument17 pagesPre Calculus PrimeracsimsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Linear EquationsJami MendozaNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Explanatorynotes - WES PDFDocument166 pagesAlgebra - Explanatorynotes - WES PDFSaikiran RoyalNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations and GraphsDocument25 pagesLinear Equations and GraphsDexter CarpioNo ratings yet
- Dania - 22 - 12363 - 1-Lecture 2 Coordinate System-Fall 2015Document34 pagesDania - 22 - 12363 - 1-Lecture 2 Coordinate System-Fall 2015erwin100% (1)
- STEM 1 Assignment 1.odtDocument3 pagesSTEM 1 Assignment 1.odtCassy BulataoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- Linear EquationsDocument4 pagesLinear Equations4ma3x100% (1)
- Precalculus I: Quadratic FunctionsDocument28 pagesPrecalculus I: Quadratic FunctionsSONITANo ratings yet
- MC Bus Slope 2009 1Document2 pagesMC Bus Slope 2009 1redzuan.hajaraNo ratings yet
- Modul Mengenalpasti Bentuk GrafDocument10 pagesModul Mengenalpasti Bentuk GrafhafabaNo ratings yet
- Kms 1 Task: Pattimura University 2014Document8 pagesKms 1 Task: Pattimura University 2014AlfredOhman100% (1)
- Graph of PolynomialDocument12 pagesGraph of PolynomialLastCardHolderNo ratings yet
- MidtermreviewprojectpptxDocument37 pagesMidtermreviewprojectpptxapi-553954607No ratings yet
- CurvesDocument12 pagesCurveskandarpNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasAmir MustakimNo ratings yet
- AsymptotesDocument17 pagesAsymptotesPriyanka HaldarNo ratings yet
- Proportionality (Mathematics)Document4 pagesProportionality (Mathematics)OmarGarciaNo ratings yet
- Souvenir As Tourism ProductDocument13 pagesSouvenir As Tourism ProductThree Dimensional Product DesignNo ratings yet
- Topic: Atoms and Molecules Sub-Topic: Mole: Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTopic: Atoms and Molecules Sub-Topic: Mole: Lesson PlanPushpa Kumari67% (3)
- Designation Order SicDocument3 pagesDesignation Order SicMerafe Ebreo AluanNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle Management Comprehensive Solutions - 0Document4 pagesRevenue Cycle Management Comprehensive Solutions - 0avinashn1984No ratings yet
- Antiphon - Caritas - Habundat - in - Omnia - Hildegard Von BingenDocument3 pagesAntiphon - Caritas - Habundat - in - Omnia - Hildegard Von BingenGStarkNo ratings yet
- RFP For Bikaner City Circle DFDocument325 pagesRFP For Bikaner City Circle DFSougata MitraNo ratings yet
- Alter NadorDocument10 pagesAlter NadorJOSE0% (2)
- EnglishDocument44 pagesEnglishP DasNo ratings yet
- Blast Injury ManagementDocument16 pagesBlast Injury Managementheart wisdomNo ratings yet
- Prevalencia Geofagia - 2014Document108 pagesPrevalencia Geofagia - 2014Farmaceutico RaulNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ShakerDocument2 pagesLaboratory ShakeradhgachaswNo ratings yet
- Key Professional DispositionsDocument3 pagesKey Professional DispositionsEmily SneedNo ratings yet
- Professionalism in The Dental Office, Part One: I Chairside Conscience IDocument3 pagesProfessionalism in The Dental Office, Part One: I Chairside Conscience IKingjokerNo ratings yet
- Raman SpectraDocument22 pagesRaman SpectraAnanda SelvamNo ratings yet
- Constitutions and ConstitutionalismDocument10 pagesConstitutions and ConstitutionalismmylovebhuNo ratings yet
- STS Reviewer 1Document9 pagesSTS Reviewer 1Kyle SeseNo ratings yet
- X Ray DiffractionDocument12 pagesX Ray DiffractionSiddraKhalidNo ratings yet
- Understanding Advertising and Consumer Behaviour: Pankaj KumarDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Advertising and Consumer Behaviour: Pankaj KumarAlfredo ValeraNo ratings yet
- Surf Excel ND AirelDocument13 pagesSurf Excel ND AirelPratibha Chandil100% (1)
- Study On Causes & Control of Cracks in A Structure: Mulla FayazDocument4 pagesStudy On Causes & Control of Cracks in A Structure: Mulla FayazShubham ThakurNo ratings yet
- CSPL v1.2.0 Install-Eng Memo1Document3 pagesCSPL v1.2.0 Install-Eng Memo1rammirisNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Observation and Assessment of Child DevelopmentDocument3 pagesSelf-Assessment Observation and Assessment of Child Developmentapi-508676940No ratings yet
- 3.2 Server Maintenance Administration PlanDocument30 pages3.2 Server Maintenance Administration PlanAG Network ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Indra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043Document28 pagesIndra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043AnhTuấnPhanNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior TestDocument22 pagesHuman Behavior TestEsmani BraineNo ratings yet
- WordDocument48 pagesWordenkelene.zulfajNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesChapter-Ii Review of LiteratureANU GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Reheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionDocument9 pagesReheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionSourav GopeNo ratings yet
- Geometri Unsur StrukturDocument10 pagesGeometri Unsur StrukturNirmaya WulandariNo ratings yet