Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Aid
Uploaded by
imran_tamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First Aid
Uploaded by
imran_tamCopyright:
Available Formats
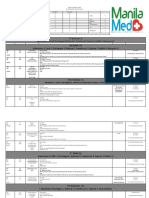
FIRST AID The first assistance or treatment given for a sick or injured person (called casualty) before the
arrival of an ambulance or qualified expert. TIPS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
If unconscious keep the airway clear Make sure the casualty is breathing Stop any bleeding Treat other injuries in the right order Never move the casualty unless there is danger, to avoid further injury Comfort and reassure the casualty Give protection from the cold, exercise heat or wet conditions Dial 999 if unconscious and perform CPR (refer HOW TO PERFORM CPR)
........................................................................ SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTION Common causes are insect bites, foods and medicines. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
9. 10. 11. 12.
Swelling of the affected area, throat, mouth or face Redness of the skin or an itchy rash Breathing difficulty similar to an asthma attack Dizziness, weakness or collapse
1ST AID STEPS
13. 14. 15. 16. 17.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if they have difficulty breathing or if they are very unwell Assist the patient to take any medicine they have been prescribed for severe allergy Put the patient in recovery position if they are unwell or unconscious If they stop breathing, place them on their back and start CPR If the allergy follows exposure to a chemical, wash the contact area thoroughly with water
........................................................................ ASTHMA ATTACK Cause by breathing passages narrow, causing difficulty in breathing. This narrowing can be triggered by pollens, dust, fur, smoke, cold air or exercise. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
18. Breathlessness or difficulty speaking 19. A wheezy noise when breathing 20. Persistent cough
1ST AID STEPS
21. Help the patient to rest in a comfortable position (usually sitting) 22. Assist the patient to take their asthma relieving medicine 23. Call 999 for an ambulance if they are not improving
........................................................................ BURNS Commonly caused by heat. Can also be caused by chemicals, extreme cold and electricity. Burns cause skin loss and tissue damage. 1ST AID STEPS
24. Gently flood the burnt area with any cool clean fluid (e.g. juice, soft drink etc) for 20 minutes. Do not use ice. 25. Call 999 for an ambulance if the patient is badly injured, or the burn is: causing significant pain, or involves the face, hands, joints or genitals, eyes, or is larger than half the patients arm. 26. Remove clothing and jewellery from the burnt area, but do not remove clothing stuck to the skin. 27. Lightly cover the burn with a clean dressing.
........................................................................ DIABETIC EMERGENCIES The most common emergency affecting a patient with diabetes is "low blood sugar". SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
28. 29. 30. 31.
Confusion, slurring of words Falling level of consciousness Sweating Tremor or shakiness
1ST AID STEPS
32. If unconscious put the patient in recovery position 33. Call 999 for an ambulance if they are unconscious
........................................................................ FRACTURED BONES Fractures, particularly of large bones (e.g. thigh bone) are an emergency. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
34. Deformity, swelling and pain 35. Altered sensation (e.g. pins and needles) 36. Inability to move the limb normally
1ST AID STEPS
37. Control any external bleeding using direct pressure over the wound 38. Dial 999 for an ambulance if the patient is in severe pain, or if the bone is sticking through the skin, or if they cannot walk 39. Assist the patient into a comfortable position 40. Support the limb e.g. with a pillow, but do not move the limb unnecessarily
........................................................................ HEAD INJURIES Head injuries involve injury to the brains, skull or face. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
41. 42. 43. 44.
Loss of consciousness or altered state of awareness (groggy) Confusion and memory loss Nausea and vomiting Any bleeding from the head that is more than minor
1ST AID STEPS
45. Dial 999 for an ambulance if they are unconscious or bleeding heavily 46. Assist them to rest in a comfortable position. Place them on their side if they are unconscious. 47. Control external bleeding with direct pressure.
........................................................................ NOSE BLEEDING A nosebleed is usually due to bleeding from inside the front of the nostrils.More serious bleeding may result in considerable blood loss and, if the patient swallows blood, vomiting may result 1ST AID STEPS
48. 49. 50. 51. 52.
Sit the person down. Get them to breathe through their mouth, with their head tilted forward. Firmly pinch the entire soft part of the nose for 10 - 20 minutes. Repeat this if the bleeding does not stop. Dial 999 for an ambulance if the bleeding is very heavy. When the bleeding stops, inform the person not to blow their nose for a few hours, this may restart the bleeding.
........................................................................ POISONING A poison is any substance that can cause damage to the body. Common examples of poisons include medicines (if taken in large amounts), industrial products, household cleaning products and sprays. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
53. Altered level of consciousness (not fully awake) 54. Burns around or in the mouth 55. Stomach or abdominal pain
56. Vomiting
1ST AID STEPS
57. 58. 59. 60. 61.
DO NOT induce vomiting Do not give the patient anything to drink If they are unconscious, place them in the recovery position Call 999 for an ambulance if they are unconscious or if they are very unwell Keep the container of the poison
........................................................................ ELECTRIC SHOCK SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS The patient may:
62. 63. 64. 65.
Still be connected to an electrical cable or appliance Be unconscious Have stopped breathing Have burns where the electrical current entered and exited their body
1st AID STEPS
66. 67. 68. 69. 70.
Ensure safety turn the electricity off. DO NOT approach a patient if they may still be connected to electricity Dial 999 for an ambulance if they are unconscious, injured or unwell If they are unconscious and not breathing, place them on their back and start CPR If they are unconscious and breathing place them in the recovery position If conscious, check for injuries or burns
........................................................................ DROWNING When a patient drowns your safety is paramount. 1ST AID STEPS
71. Remove the patient from the water safely 72. If not breathing, commence CPR 73. Dial 999 and ask for ambulance
........................................................................ EYE INJURY Usually caused by flying particles. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
74. 75. 76. 77.
Pain Watering and redness Bleeding Altered vision
1ST AID STEPS
78. 79. 80. 81.
If you can see the particle, gently try to remove it with water or a clean cloth. Do not persist if it is hard to remove. Prevent the patient from rubbing the eye as this may result in scratching. If symptoms persist or you cannot remove the particle, see a Doctor. Dial 999 for an ambulance if there is severe pain or bleeding.
........................................................................ CARDIAC ARREST People in cardiac arrest need CPR and an ambulance. CPR saves lives by causing blood to flow to the heart and brain while waiting for an ambulance. CPR is needed when the patient is not responding and not breathing normally. 1st AID STEPS
82. Perform CPR
........................................................................ HEAT EXHAUSTION Usually caused by exposure to extreme temperature or not replacing fluid being lost by sweating. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88.
Weakness Loss of appetite Fainting Dizziness Sweating Nausea/vomiting
1ST AID STEPS
89. Rest patient in a cool place 90. Give patient fluid to drink. Most patients will respond well with water, fruit juice, or their soft drink of choice 91. Arrange medical attention, or dial 999 for an ambulance, if the patients condition gets worse or if they are unable to drink fluids
........................................................................ HYPOTHERMIA Results from excessive cooling of the body core. Prevention is the best cure for hypothermia. For outdoor activities, adequate clothing, frequent rests for drinks/snacks are important.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
92. Patient feels cold to touch and may be shivering violently 93. Cold environment 94. Patient feels cold to touch and may be shivering violently 95. Cold environment 96. Tiredness patient may fall behind others in outdoor activities 97. Clumsy, uncoordinated, may fall over and appear drunk 98. Changes in mood with irritability, irrational behaviour 99. Patient may resist help 100. Slow to respond to questions 101. Shivering may decrease and stop 102. Loss of consciousness 103. Pale or blueish skin colour
1st AID STEPS
104. Provide immediate shelter out of the wind, and dry clothing 105. If fully conscious, give warm drinks, sweets, chocolates etc 106. Use body contact to reduce heat loss and slowly warm patient e.g. huddle around the patient in a sleeping bag 107. If hypothermia is mild, and rest, warmth, drinks etc. allow recovery, there is no need for further medical assistance. But monitor the patient and any others in the group 108. If hypothermia has reached the stage where the patient is becoming drowsy, urgent medical assistance is required.
........................................................................ FOOD POISONING Inflammation of the stomach and intestine due to infection from a variety of organisms such as viruses and bacteria. Most often, it is caused by poorly prepared, cooked or preserved food.Prevention is the best philosophy for food poisoning and the following key points provide guidance on how best to prevent suffering from food poisoning: SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
109. In the majority of cases, symptoms first appear within 24 hours of eating contaminated food 110. The patient has abdominal cramps with diarrhoea 111. There may be vomiting and nausea 112. There is usually a loss of appetite 113. There may be fever
1st AID STEPS
114. Ensure the patient rests 115. The patient can suck ice to provide a small amount of cooling fluid 116. Give fluids such as flat lemonade to replace body fluids 117. Medical assistance should be obtained if any of the following occurs: 1. Severe vomiting in a child under 1 year 2. Considerable and constant diarrhoea 3. Persistent vomiting
4.
Signs of dehydration dry mouth, skin and thirst
........................................................................ HOW TO PERFORM CPR
118. Dial 999 for an ambulance 119. Lie the person on their back 120. Push on the chest hard and fast 30 times at a rate of approximately twice a second. Keep your arms straight and push in the middle of the chest. 121. Tilt the head back, pinch the nose and blow twice in the mouth 122. Continue to alternate 30 pushes on the chest with 2 blows in the mouth until an ambulance arrives 123. Any CPR is better than no CPR. If you do not want to do the breaths, just continue with the chest pushes
*Extracted from various sources. Should there be any disagreement, feel free to edit it.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Nami Understanding Psychosis BookletDocument59 pagesNami Understanding Psychosis BookletSalma KarimahNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by KisnerDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by Kisnera33085258962% (13)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Viral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocument200 pagesViral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinKarla Jane100% (1)
- What is migraine and how can it be managedDocument6 pagesWhat is migraine and how can it be managedEliza SitinjakNo ratings yet
- Human Induced HazardDocument56 pagesHuman Induced HazardMaria Flor Pabelonia100% (3)
- Couser Signifying Bodies - ExtractDocument79 pagesCouser Signifying Bodies - ExtractMarceloNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Dummy ReportDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Dummy ReportVirat DaineNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Nurses To Disaster ManagementDocument10 pagesPreparation of Nurses To Disaster Managementai nisa hasnasariNo ratings yet
- A Concise Review On Nerium Oleander L.Document5 pagesA Concise Review On Nerium Oleander L.tatralor100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goal/Objective Intervention Rational EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goal/Objective Intervention Rational EvaluationmalindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Health Management Information SystemDocument14 pagesLecture 12 Health Management Information SystemKamran SheikhNo ratings yet
- NAIOMT C-516 Cervical Spine I (v2014)Document4 pagesNAIOMT C-516 Cervical Spine I (v2014)bmj123No ratings yet
- Biochem 2 Chapter 1Document19 pagesBiochem 2 Chapter 1Suzaila's SyfaNo ratings yet
- United Home Whitfield's OintmentDocument5 pagesUnited Home Whitfield's OintmentWalidur Rahman MridulNo ratings yet
- Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 - Your Income Vs Your Peers'Document8 pagesMedscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 - Your Income Vs Your Peers'David J ShinNo ratings yet
- 10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemDocument7 pages10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemrynNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsDocument61 pagesLecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Joint Mobilization EnhancesDocument12 pagesJoint Mobilization EnhancesDavid BrunoNo ratings yet
- Hendra - EKGDocument34 pagesHendra - EKGRINANo ratings yet
- 13 Levels of AssessmentDocument11 pages13 Levels of AssessmentCatherine Cayda dela Cruz-BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Golden Berry Bioautography Reveals Antibacterial CompoundsDocument11 pagesGolden Berry Bioautography Reveals Antibacterial CompoundsGeraldineMoletaGabutinNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Module #3 - Oxygenation (Oxygen Therapy)Document28 pagesFar Eastern University: Module #3 - Oxygenation (Oxygen Therapy)aaaaaNo ratings yet
- Diane Pills Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiane Pills Drug StudyDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- CDC - Rabies Around The World - RabiesDocument1 pageCDC - Rabies Around The World - RabieskaminiNo ratings yet
- TRIUMPHANT COLLEGE COVID-19 TRAINING NewDocument26 pagesTRIUMPHANT COLLEGE COVID-19 TRAINING NewDaniellaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Questions:: Analysis of SalivaDocument2 pagesAnswers To Questions:: Analysis of Salivaerisseval14No ratings yet
- Atopic Eczema in Adulthood and Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Population-Based Cohort StudyDocument26 pagesAtopic Eczema in Adulthood and Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Population-Based Cohort Studyyenny handayani sihiteNo ratings yet
- Census August 8 - August 9, 2020Document6 pagesCensus August 8 - August 9, 2020Patrick JohnNo ratings yet
- SwatiDocument97 pagesSwatiswati malikNo ratings yet
- Oman New Health Application FormDocument3 pagesOman New Health Application FormAravind AlavantharNo ratings yet