Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MS - M S D S: First Semester Subject Code Subject Name Theory Credits Lab Credits Total Credits
Uploaded by
Raghavendra Kumar ChimalakondaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MS - M S D S: First Semester Subject Code Subject Name Theory Credits Lab Credits Total Credits
Uploaded by
Raghavendra Kumar ChimalakondaCopyright:
Available Formats
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MS MECHANICAL SYSTEM DESIGN SYLLABUS
First Semester Subject Code MSD601 MSD603 MSD605 MSD607 MSD609 MSD611 MSD613 Subject Name Machine Design Finite Element Method Heat Transfer & Computational Fluid Dynamics Solid Mechanics Elective 1 Elective 2 Computer Aided Design Lab Theory Credits 4 4 4 4 4 4 Lab Credits 1 Total Credits 4 4 4 4 4 4 1
TOTAL Second Semester MSD602 MSD604 MSD606 MSD608 MSD610 MSD612 MSD614 Advanced Mechanical Vibrations Mechanism and Robotics Product Design System and Simulation Elective 3 Elective 4 Computer Aided Analysis Lab 4 4 4 4 4 4 1
25
4 4 4 4 4 4 1
TOTAL Third & Fourth Semester Project Work Total Number of Credits to Award Degree -
25
40 90
Elective List Elective 1 MSD609 609.1 Kinematics of Machinery 609.2 Design for Manufacture Elective 2- MSD611 611.1 Turbo Machinery 611.2 Fracture Mechanics Elective 3 MSD610 MSD610.1 Mechatronics and MEMS MSD610.2 Mechanical System Design Elective 4 MSD612 MSD612. 1 Project Management MSD612.2 Advances in Material Sciences
BOS-Jul-09
1 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
Detailed Syllabus MS in Mechanical System Design MSD 601 Machine Design Unit 1 Fatigue consideration in design [16]
Variable load - basic concept; load or stress variations- different patterns Cyclic stressing/straining - materials response and the origin of fatigue failure. Stress life relations; S-N curve-fatigue strength and endurance limit Factors influencing fatigue and endurance strength modification factors Effect of stress concentration and fatigue stress concentration definition Effect of mean stress - Goodman and Soderberg's relations Design approach to fatigue - design for infinite life and finite life Design of members under combined (steady and variable) loading conditions UNIT 2 Design of gear tooth [12]
Law of gearing - conjugate action and gear tooth profile-basics Analysis of forces on spur, helical, bevel and worm gears - determination of bearing reaction forces Bending and contact stress in gear tooth-dynamic loading and wear-Lewis and Buckingham equations for design. Design of fixed ratio gear box-general design procedure UNIT 3 Design of sliding and journal bearings [12]
Types of lubrication-hydro dynamic, hydro static and EHD lubrication. Petroffs equation and the bearing haracteristic number-boundary and film lubrication Pressure distribution-eccentricity and minimum film thickness Heat generation and thermal equilibrium, selection of rolling element bearings. UNIT 4 Design/analysis of Brakes clutches and fly wheels [8]
Plate clutches design for uniform pressure and wear Shoe breakes short and long shoe analysis automotive shoe breake design/analysis Ply wheel design basic concepts. Unit 5: Design using composite materials: Intorduction : Matrix Materials, Fibres, Arrangement and orientation, Fibre Pull Out Laminated Plate Theory. References 1. S.G.Kulkarni, " Machine Design - Solved Problems ", Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing
Company Ltd., 1998. 2. William Orthein, " Machine Component Design (Vol. I & II) ", M/s. Jaico Publishing 1998 - 99. 3. Joseph Edward Shigley and Charles R.Mischke, " Mechanical Engineering Design ",McGraw-Hill International Edition, 1989.
BOS-Jul-09
2 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
4. Gitin M.Maitra and LN Prasad, " Hand Book of Mechanical Design ", Tata McGraw Hill, 1985. 5. V.B.Bhandari, " Design of Machine Elements ", Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd., 1998. 6. T.V.Sundarajamoorthy and N.Shanmugam, " Machine Design ", Khanna Publishers, Delhi-6, 1989.
BOS-Jul-09
3 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD603
Finite Element Method
UNIT 1 [12] Objective of the Course, Basic Steps in FEM Formulation, General Applicability of the Method; Variational Functional, Ritz Method. Variational FEM : Derivation of Elemental Equations, Assembly, Imposition of Boundary Conditions, Solution of the Equations. UNIT 2 [8] 1 -D Elements, Basis Functions and Shape Functions, Convergence Criteria, h and p Approximations. Natural Coordinates, Numerical Integration, Gauss Elimination based Solvers. Computer implementation: Pre-processor, Processor, Post-processor. UNIT 3 [8] Alternate Formulation: Weighted Residual Method, Galerkin Method; Problems with C1 Continuity: Beam Bending, Connectivity and Assembly of C1 Continuity Elements. Variational Functional; 2-D Elements (Triangles and Quadrilaterals) and Shape Functions. UNIT 4 [10] Natural Coordinates, Numerical Integration, Elemental Equations, .Connectivity and Assembly, Imposition of Boundary Conditions. Axisymmetric (Heat Conduction) Problem, Plane Strain and Plane Stress Solid Mechanics Problems. Sub-parametric, Iso-parametric and Super-parametric Elements; Elements with C1 Continuity. UNIT 5 [10] Free Vibration Problems, Formulation of Eigen Value Problem, FEM Formulation. Time-dependent Problems, Combination of Galerkin FEM and FDM (Finite Difference Method), Convergence and Stability of FD Scheme. Problems with Material Nonlinearity, Direct Solution Technique References 1. Reddy J.N. " An Introduction to the Finite Element Method " , Mc Graw Hill, International Edition, 1993. References: 1. Segerlind L.J., " Applied Finite Element Analysis " , John Wiley, 1984. 2. Rao S.S., " Finite Element Method in Engineering " , Pergamon Press, 1989. 3. Chandrupatla & Belagundu , " Finite Elements in Engineering ", Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd., 1997. 4. Cook, Robert Davis et al, " Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis " , Wiley, John & Sons,1999. 5.George R Buchanan, " Schaum's Outline of Finite Element Analysis ", McGraw Hill Company, 1994.
BOS-Jul-09
4 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD 605 HEAT TRANSFER AND COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS Unit 1: Revisiting the Governing Equations of Fluid Mechanics: Models of Flow: Finite control volume and Infinitesimal element approaches. The substantial derivative and divergence of velocity field- its physical meaning. [03] Unit 2: The continuity equation. Derivation for finite volume model, fixed and moving with the fluid. Continuity equation: Derivation for infinitesimal element model, fixed and moving with the fluid. The Conservative and Non-conservative Forms of the above equations. [03] Unit 3: Derivation of the general 3-D Cartesian Momentum Equations in non conservative format and transformation of these into conservative formats..Derivation of the general 3-D Cartesian Energy Equations in non conservative format and transformation of these into conservative format. [03] Unit 4: General Characteristic of the governing equations: The initial and boundary conditions: Dirichlet and Neumann conditions..Mathematical behavior of different classes of partial differential equations: Equilibrium and Marching behavior. [03] Unit 5: The format of the differential equation for the conservation of a general dependent property,. Nature of co-ordinates The independent variables- proper choice of co-ordinates. One-way and two-way co-ordinates. Discretization Process- concept and structure. Methods of deriving the discretised equations. Explicit Tylor series expansion. Simple examples. [03] Unit 6: The Basic Solution Techniques: Steady state conduction heat transfer. Application of explicit finite difference technique..Application of the explicit finite difference technique to one dimensional steady state heat transfer in a rectangular fin.. Implementation of boundary conditions and solution techniques for the above. . Extension of the method to 2-D Conduction through a rectangular slab. [04] Unit 7: Unsteady conduction Heat Transfer. Explicit, Implicit and Crank Nicholson Methods. ADI Methods of solving space and time marching in 2D and 3D problemssimple examples. Consistency and Stability criteria. [03] Unit 8: Discretization using Control Volume technique for 1D Diffusion Problems The Four basic rules in control volume formulation. Dicretization of source terms and linearization of the same. Simple problems on steady diffusion flow problems. Application of control volume technique to two and three dimensional steady diffusion
BOS-Jul-09
5 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
flow problems. Application of control volume technique to 1D unsteady heat transfer problem. [06] Unit 9: Convective flow with diffusion: Numerical methods for steady one-dimensional convective flow with diffusion:- control volume approach.. The CDS, the Upwind, and Exact schemes. properties of discretization schemes: Conservativeness, Boundedness and Transportiveness. Illustrative examples on the above. Numerical false diffusion with physical examples. The direct or the Primitive variable method The need for staggered grid. [06] Unit 10: The SIMPLE algorithms to solve flow problems. Flow chart and discussion. The derivation of the pressure correction equation as Poissons Pressure equation. Implications and implementation. Marker and Cell Explicit Method (MAC) [04] Unit 11: Implementation of Boundary Conditions in CFD. The inlet, exit, outflow and the wall Boundary Conditions. The Constant Pressure, Symmetry as well as Cyclic Boundary Conditions imposition. [02] Unit 12: Turbulence and its modeling: Meaning of turbulence-transition from laminar to turbulent flow. Effect of turbulence on the time averaged N-S equations. Closure problem. The need for turbulence modeling. Characteristics of simple turbulent flow near solid wall.-law of wall. Laminar sub-layer. log law layer and outer layer. Turbulence models: mixing length, - models [08] References: 1. John D Anderson Jr. (1995). Computational Fluid Dynamics- The Basics with Applications. International Edition. McGraw Hill. New York. 2. Suhas V Patankar, (1980).Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. Hemisphere / McGraw Hill. New York. 3. H.K. Versteeg and W. Malalasekera. (1995) An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics.- The Finite Volume Method.-- Longman Scientific & Technical. England 4. K.Muralidhar and T.Sundararajan (2003)Computational Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer, Narosa Publishing House, NewDelhi. 5. Anderson D.A, Tannehill J.C, and Pletcher, R.H. (1997) "Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer- Taylor and Francis Group. New York. 6. Ghoshdastidhar. (1998) Computer Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer Tata- McGraw-Hill Book Company. New Delhi. 7. T.J. Chung. (2003) Computational Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge University Press. South Asia Edition. 8. Fletcher C.A.J., (1988) Computational Techniques for Fluid Dynamics. Vol I and Vol II., Springer- Verlag. Berlin
BOS-Jul-09
6 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD607
Solid Mechanics
MSD 607 Solid Mechanics Unit 1. STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS [9]
Rigid bodies and deformable solids stability, strength, stiffness tension, compression and shear stresses strain, elasticity, Hookes law, limit of proportionately, modules of elasticity, stress-strain curve, lateral strain temperature stresses deformation of simple and compound bars shear modulus, bulk modulus, relationship between elastic constants biaxial state of stress stress at a point stress on inclined plane principal stresses and principal planes Mohrs circle of stresses. Failure Theories Unit 2. ANALYSIS OF PLANE TRUSS, THIN CYLINDERS [7] Stability and equilibrium of plane frames types of trusses analysis of forces in truss members method of joints, method of sections, method of tension coefficients thin cylinders and shells under internal pressure deformation of thin cylinders and shells. Unit 3. TRANSVERSE LOADING ON BEAMS [7] Beams types of supports simple and fixed, types of load concentrated, uniformly distributed, varying distributed load, combination of above loading relationship between bending moment and shear force bending moment, shear force diagram for simply supported, cantilever and over hanging beams Theory of simple bending analysis of stresses load carrying capacity of beams proportioning of sections Unit 4. DEFLECTION OF BEAMS AND SHEAR STRESSES [9]
Deflection of beams double integration method Macaulays method slope and deflection using moment area method, Conjugate Beam method variation of shear stress shear stress distribution in rectangular, I sections, solid circular sections, hollow circular sections, angle and channel sections shear flow shear centre. Unit 5. TORSION AND SPRINGS [8] Stresses and deformation in circular (solid and hollow shafts) stepped shafts shafts fixed at both ends leaf springs stresses in helical springs deflection of springs. Unit 6. STRESS FUNCTIONS [5] Beltrami, Maxwell, Airy Stress Function, Morera, Pandtl Stress functions. References 1. Seely and Smith, "Advanced Mechanics of Materials", John Wiley International Edn, 1952. 2. Rimoahwnko, "Strength of Materials", Van Nostrand. 3. Timoshenko and Goodier, "LTheory of Elasticity", McGraw Hill. 4. Wang, "Applied Elasticity", McGraw Hill.
BOS-Jul-09
7 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
5. Cas, "Strength of Materials", Edward Arnold, London 1957. 6. Robert D. Cook, Warren C. Young, "Advanced Mechanics of Materials", Mc-millan pub. Co., 1985.
BOS-Jul-09
8 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD609
Elective 1
MSD 609.1 Advanced Kinematics of Machinery Unit 1 [8]
Kinematics and Dynamics, Mechanisms and Machines, Plane and Space Mechanisms, Kinematic Pairs, Kinematic Chains, Kinematic Diagrams, Kinematic Inversion. Four Link Planar Mechanisms and their Inversions Unit 2 [12] Mobility and range of movement - Kutzbach and Grublers criterion, Number Synthesis, Grashofs criterion. Displacement analysis of plane mechanisms graphical and analytical methods. Plane motion of a rigid body, Instantaneous Centre (IC) of Velocity, Velocity analysis using IC Unit 3 [12]
Velocity and Acceleration Diagrams, Sliding Velocity, Velocity and Acceleration Images, Coriolis component of acceleration. Dimensional synthesis of mechanism; motion, path and function generation, precision point approach, Chebyshev spacing. Three position synthesis, graphical approach for four link mechanisms. Unit 4 [8] Advanced synthesis solutions, branch and order defects. Analytical methods, straight line mechanisms. Special Mechanisms - Indicator Diagram Mechanisms, Steering Mechanism, Hookes Joint Unit 5 [8]
Determine of basic dimensions and synthesis of cam profiles, graphical and analytical methods, cams with specified contours. Unit 1: References: 1. P.L.Ballaney (2003) Theory of Machines Khanna Publishers, New Delhi 2. Dr. R.K. Bansal (2004) Theory of Machines Laxmi Publications (p) Ltd. New Delhi. 3. S.S. Rattan (2005) Theory of Machines Tata Mc Graw Hill Publishing Company Ltd. New Delhi.
BOS-Jul-09
9 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
609.2 Design for Manufacture UNIT 1 Introduction [10]
General design principles for manufacturability - strength and mechanical factors, mechanisms selectiion, evaluation method, Process capability - Feature tolerances Geometric tolerances - Assembly limits Datum features - Tolerance stacks. UNIT 2 Factors Influencing Form Design [10] Working principle, Material, Manufacture, Design - Possible solutions - Materials choice - Influence of materials on from design - from design of welded members, forgings and castings. UNIT 3 Component Design-Machining Consideration [12]
Design features to facilitate machining - drills - milling cutters - keyways - Doweling procedures, counter sunk screws - Reduction of machined area - simplification by separation - simplificaation by amalgamation - Design for machinability - Design for economy - Design for clampability - Design for accessibility - Design for assembly. UNIT 4 Component Design - Casting Considerations [8]
Redesign of castings based on parting line considerations - Minimising core requirements, machined holes, redesign of cast members to obviate cores. UNIT 5 Redesign For Manufacture And Case Studies [8]
Identification of uneconomical design - Modifying the design - group technology Computer Applications for DFMA References 1. Harry Peck, "Design for Manufacture", Pittman Publication, 1983. 2. Robert Matousek, "Engineering Design - A systematic approach", Blackie & sons Ltd., 1963. 1. James G. Bralla, "Hand Book of Product Design for Manufacturing", McGraw Hill Co., 1986. 2. Swift K.G., "Knowledge based design for manufacture, Kogan Page Ltd., 1987.
BOS-Jul-09
10 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD611
Elective 2
611.1 Thermal Turbo Machinery Unit 1: Brief Review of compressible flow equations: [8] Continuity and Momentum Equations, Energy equations. SFEE ,Stagnation Properties and Mach No effect on flow. Normal & oblique shocks in fluid flow. Thermodynamics of Turbo Machinery: Total and Static efficiencies of Turbines and Compressors Infinitesimal Polytropic Efficiency of Turbines and Compressors, Finite stage efficiency of Multistage Turbines and Compressors, Reheat factor of a Turbine and Preheat factor of a Compressor Unit 2: General Features of Gas Turbine Engines [8] Different types and arrangements. Major areas of Applications. Ideal cycles-Efficiency and work output of simple cycles with heat exchangers Reheat, intercooling and combinations Cogeneration Plant. Environmental issues. Mechanical losses -Design point performance of simple cycle and series flow cycle Unit 3: Axial Flow Compressors [10] Elementary theory -Degree of reaction -.factors affecting stage pressure rise. Radial equilibrium-free and forced vortex: simple design method for blades Overall and off design performance. Compressor Characteristics Radial Flow Compressors Energy Transfer -Slip & Slip Factor, Radial Blowers and Fans-Performance analysis Unit 4 : Axial flow turbines: [8] h-s diagram. Expression for Energy Transfer. Degree of reaction- Impulse and Reaction type. Factors affecting turbine design Blade speed ratio, velocity ratio and torque & operating temperature, Centrifugal and disc stresses , Compressibility effects, radius ratio of annulus, reaction and swirl Unit 5 : Combustion systems: [14] Operational requirements, Types of combustion systems Combustor designs. combustion intensity, efficiency and pressure loss Gas Turbine cycles for Aircraft propulsion, Intake and Propelling nozzle efficiency. Momentum theorem of fluid mechanics, Simple Turbojet cycle, Classification of propulsion engines Turbofan, Turboprop and Turbo shaft engines. Application .of momentum theorem to propulsion systems -propulsive efficiency and specific Thrust: Thermal and overall efficiency: Static performance at the design point. Flight performance at the design point. thrust augmentation. TEXT BOOKS AND REFERENCES: 1. Gas Turbine Theory, V Edition, HIH Saravanamuttoo, GFC Rogers and H Cohen, Pearson Education 2. A Treatise on Turbo machines- D. Prithviraj and G. Gopalakrishnan- Scitech Publishers,
BOS-Jul-09
11 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
2. Turbomachines, A guide to Design, Selection and Theory, O.E. Balje, John Wiley and Sons, NY,1981
BOS-Jul-09
12 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
611.2 Fracture Mechanics UNIT 1 Stationary Crack Under Static Loading [10] Two dimensional elastic fields-Analytical solutions Yielding near a crack front-Irwins approximation-plastic Zone size-Dugdaale model-J integral and its relation to crack opening displacement UNIT 2 Energy Balance And Crack Growth [10] Griffth analysis-Linear Fracture Mechanics-Crack opening displacement-Dynamic energy balance-crack arrest UNIT 3 Fatigue Crack Growth Curve [10] Empirical relation describing crack growth by Ftaigue-Life calculations for a givenm load amplitude-effects of changing the load spectrum-Effects of Enviroment UNIT 4 Elements Of Applied Fracture Mechanics [10] Examples of crack-growth Analysis for cyclic loading-leak before break- crack initiation under large scale yielding-Thickness as a Design parameter-crack instability in Thermal or Residual-stress fields UNIT 5 Fracture Toughness [8] Behaviour of Crack Griffith Theory, Fracture Resistance. Brittle Fracture, Ductile fracture References 1. David Broek, "Elementary Engineering Fracture Mechanics ", Fifthoff and Noerdhoff International Publisher,1978 2. Kare Hellan, "Introduction to Fracture Mechanics", Mc Graw Hill Book Company,1985. 3. Preshant Kumar,"Elements of Fracture Mechanics", Wheeler Publishing,1999
BOS-Jul-09
13 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD 613 - Computer Aided Design Laboratory
Modeling using Design software: Practice : 1 [24] Introduction, Sketching, Extrude, cut, hole, chamfer, round, shell, rib, draft, revolve, pattern, sweep, blend, Datums Plane, axis, points, Swept blend, variable section sweep, helical sweep, Assembly, Drawing Views, dimensioning, tolerances. Practice : 2 [24]
Sketcher Work Bench - Drawing and constraining sketches, Part modeling - Sketch based features, 3D transformations, Advanced 3D modeling with loft, rib, loft remove, slot features, Surface modeling - Wire frame and surface creations, Editing and modifying the surfaces.
BOS-Jul-09
14 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
Second Semester MSD602 Advanced Mechanical Vibrations Unit 1:Introduction: Importance, causes and elimination of vibration, vibration measuring parameters and their values, natural & operating frequency values. [02] Unit 2:Vibration fundamentals: Single degree freedom systems-longitudinal, lateral and torsional vibration, damping, free and forced vibration, force transmissibility, vibration isolation, design of isolators, two degree freedom systems-dynamic vibration absorber, multi-degree freedom system, geared systems, whirling of shaft. [13] Unit 3:Continuous systems: Longitudinal vibration of bars, lateral vibration of beams, transverse vibration of a string, torsional vibration of a shaft. [03] Unit 4:Finite element method: Standard and nonstandard eigen value problem, mass & stiffness matrix, Cholesky factorization, concept of iteration, successive iteration, simultaneous iteration, subspace iteration, Lanczos method, Rayleigh damping. [10] Unit 5:Nonlinear vibration: Exact method, approximate analytical methods, subharminic & superharmonic oscillations, graphical methods, stability of equilibrium states, limit cycles andchaos, Perturbation method, Duffings system, VanderPols systems. [06]
Unit 6:Random vibration: Random variables & random processes, probability distribution, joint probability distribution of several random variables, correlations functions of a random process, stationary random process, Gaussian random process, Fourier analysis, power spectral density, wide band and narrow band processes, response of a single degree of freedom system. [04] Unit 7:Vibration instruments: Transducers-variable resistance, piezoelectric, electrodynamic and linear variable differential transformer transducers; Vibration pickups-vibrometer, accelerometer, velometer, phase distortion; Frequency measuring instruments, Exciters-mechanical exciters, electrodynamic shaker. [04]
BOS-Jul-09
15 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
Unit 8:Signal analysis: Techniques-time & frequency domain analysis, amplitude & power spectra, coherence, auto & cross correlations, amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, spectrum analysers, bandpass filter, constant percent bandwidth & constant bandwidth analysers; dynamic testing of machines and structures, Experimental modal analysis- analysis of random signals, determination of modal data, measurement of mode shapes; Machine condition monitoring and diagnosis. [06]
References: Singiresu S. Rao (2004) Mechanical Vibrations 4/e, Pearson Education Inc. Ramamurti V. (2000) Mechanical Vibration Practice with Basic Theory Narosa Publishing House, Chennai Rao J. S. and Gupta K. (1999) Theory and Practice of Mechanical Vibrations New Age International Publishers Rao J. S. ( 1992) Advanced Theory of Vibrations Wiley Eastern Limited, Bangalore Balakumar Balachandran and Edward B. Magrab (2004) Vibrations Thomson Brooks/Cole
BOS-Jul-09
16 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD604 Robotics Unit 1: Introduction [9] Brief History, Types of robots, uses of robots, Present status and future trends in robotics, Overview of robot subsystems. Issues in designing and controlling robots: resolution, repeatability and accuracy, transmission, Robot configurations and concept of workspace, Mechanisms and transmission. Unit 2: Robot Anatomy [9] Different types of grippers, vacuum and other methods of gripping. Pneumatic, hydraulic and electric actuators. Internal and external sensors, position, velocity and acceleration sensors, proximity sensors, force sensors, laser range finder, camera. Micro-controllers, DSP, centralized controllers, real time operating systems. Unit 3: Task specification [4] Point to point and continuous motion specifications for typical applications, joint interpolation, task space interpolation, executing user specified tasks Unit 4: Robot analysis & Control [12] Position and orientation of rigid bodies, spatial mechanism description, DenavitHartenberg notation, homogenous transformation. Forward and inverse position analysis, velocity mapping, static force analysis, singularities, acceleration mapping. Independent joint control, PD and PID feedback, actuator models, nonlinearity of manipulator models, issues in nonlinear control, force feedback, hybrid control Unit 5: Motion planning [6] Obstacle avoidance, configuration space, road map methods, graph search algorithms, potential field methods. Camera model and perspective transformation, image processing fundamentals for robotic applications, image acquisition and preprocessing. Unit 6: Robot vision [8]
Segmentation and region characterization, object recognition by image matching and based on features, Problem of bin-picking. Micro-robotics and MEMS (Micro electro mechanical systems), Fabrication technology for micro-robotics, stability issues in legged robots, under-actuated manipulators References 1. Fu K.S., Gonzalez R.C.., and Lee C.S.G., " Robotics control, sensing, vision, and intelligence McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1987. 2. Klafter R.D., Chmielewski T.A. and Negin M., " Robot Engineering An Intergrated approach ", Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 1994.
BOS-Jul-09
17 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
3. Deb S.R., " Robotics Technology and Flexible Automation ", Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., Ltd., 1994. 4. Craig J.J., " Introduction to Robotics Mechanics and Control ", Addison-Wesley, 1999. 5. Groover M.P., " Industrial robotics Technology, programming and applications ", McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1995.
BOS-Jul-09
18 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD606 Product Design UNIT 1 Introduction [10] Need for IPPD-Strategic importance of Product development - integration of customer, designer, material supplier and process planner, Competitor and customer - behaviour analysis. Understanding customer-promoting customer understanding-involve customer in development and managing requirements - Organization process management and improvement - Plan and establish product specifications UNIT 2 Concept Generation And Selection [10] Task - Structured approaches - clarification - search-externally and internally-explore systematically - reflect on the solutions and processes - concept selection methodology - benefits. UNIT 3 Product Architecture [12] Implications - Product change - variety - component standardization - product performance - manufacturability - product development management - establishing the architecture - creation - clustering - geometric layout development - fundamental and incidental interactions - related system level design issues - secondary systems architecture of the chunks - creating detailed interface specifications. UNIT 4 Industrial Design [8] Integrate process design - Managing costs - Robust design - Integrating CAE, CAD, CAM tools Simulating product performance and manufacturing processes electronically - Need for industrial design-impact design process - investigation of customer needs - conceptualization - refinement - management of the industrial design process - technology driven products - user - driven products - assessing the quality of industrial design. UNIT 5 Design For Manufacturing And Product Development [8] Definition - Estimation of Manufacturing cost-reducing the component costs and assembly costs Minimize system complexity - Prototype basics - principles of prototyping - planning for prototypes - Economic Analysis - Understanding and representing tasks-baseline project planning - accelerating the project-project execution.
1. Jones J.C., "Design Methods", interscience, 1970. 2. Buhl, H.R., "Creative Engineering Design", Iowa State University Press, 1960. 3. Dieter, G.E., "Engineering Design", McGraw Hill, 1983. 4. Robert Matouseek, "Engineering Design", Blackie & Sons Ltd., 1963. 5. Niebel, B.W. & Draper, A.B., "Product Design and Process Engineering, McGraw Hill, 1974. 6. Harry Peck, "Designing for Manufacturing", Sir Issac Pitman and Sons Ltd., 1973. 7. Gladman, C.A., "Manual for Geometric Analysis of Engineering Designs", Austrlian Trade Publications Ltd., 8. Wade, Or., "Tolerance Control in Design and Manufacture", Industrial Press, Inc.
BOS-Jul-09
19 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD608 Systems and Simulation UNIT 1 Introduction To Systems And Simulation [8] Basic concepts of systems, General systems, Elements of systems, theory, concept of simulation-Simulation as a decision making tool-types of simulation-System modeling and types of modeling-desk and bench mark simulation. UNIT 2 Random Number [10]
Probability and statistical concepts of simulation-Pseudo random numbers-Methods of generating random variables-Discrete and continuous distributions-Testing of random numbers-Sampling-simple random and simulated. UNIT 3 Design Of Simulation Experiments [12]
Problem formulation-Data collection and reduction time flow mechanism-Key variablesLogic flowchart starting condition-Run size-Experimental design consideration-Output analysis and interpretation, validation-Application of simulation in Industries, Engineering and scientific organizations. UNIT 4 Simulation Language [8]
Use of digital computer in simulated sampling -Comparison and selection of simulated languages-Analysis-Study of any simulation language-Modification of simulation models using simulation language. UNIT 5 Case Studies/Mini Project [10]
Development of simulation models using the simulation language studied for systems like Queuing systems Production Systems-Inventory systems-Maintenance and replacement systems-Investment analysis and network. References 1. JERRY BANKS and JOHN S.CARSON," Discret event system simulation ", Prentice Hall,1984. 2. R.E.SHANNON," Systems simulation ,the art and science ", Prentice Hall,1975. 3. JOE H. MIZE AND J. GRADY COX," Essentials of simulation ", Prentice Hall Inc.1968. 4. JEFFREY L. WHITTEN,LONNIE D.BENTLEY AND VICTOR M.BARICE, " System analysis and design methods ", Calgotia Publications Pvt Ltd.,1991 5. THOMAS J. SCHRIBER, " Simulation using GPSS ", John Wiley,1974.
BOS-Jul-09
20 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD 610.1 MECHATRONICS AND MEMS
Unit 1: Introduction: Definition, basic concepts and elements of mechatronic systems, needs and benefits of mechatronics in manufacturing. [03] Unit 12: Sensors and Transducers: Position sensors - Linear and rotary potentiometers, incremental and absolute encoders. Velocity sensors - Tachometers, pyroelectric sensor. Proximity and Range sensors Eddy current sensor, ultrasonic sensor, laser interferometer transducer, Hall Effect sensor, inductive proximity switch. Light sensors Photodiodes, phototransistors, Flow sensors Ultrasonic sensor, laser Doppler anemometer, Tactile sensors PVDF tactile sensor, microswitch and reed switch.Piezoelectric sensors, vision sensor. [09] Unit 3: Drives and Actuators, Data acquisition and translation: Solenoids, relays, diodes, thyristors, triacs. AC & DC servomotors, stepper motors, Hydraulic & Pneumatic devices Power supplies, valves, cylinder sequencing. Signal conditioning Operational amplifiers, inverting amplifier, differential amplifier, comparator, filters, counters, decoders, ADC, DAC. [12] Unit 4: Controllers and Algorithms: Microcontrollers, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Fuzzy controls, Neuro-Fuzzy controls. [08] Unit 5 Applications: NC/CNC machines, robots, automatic camera, temperature monitoring system, engine management system, washing machine. [04] Unit 6: MEMS: Fundamentals and limitations of photolithography, Pattern transfer with etching techniques, Pattern transfer with other physical and chemical techniques, Bulk micromachining, Surface micromachining, Packaging techniques, Micro scaling considerations, Applications in automotive industry. [12] References: 1. D.A. Bradley and others Mechatronics Chapman & Hall. 2. W. Bolten (1999) Mechatronics, Addison Wesley Longman Ltd, 3. Devdas Shetty & Richard Kolk Mechatronics System Design, PWS Publishing. 4. Dan Nesculescu (2002) Mechatronics, Pearson Education Pte. Ltd. 5. Alciatore David G & Histand Michael B (2003) Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement systems, Tata McGraw Hill. 6. Mechatronics HMT, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, 1998. 7. Aditya P. Mathur (1989) Introduction to Microprocessors, Tata Mcgraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd., 8. C.R. Venkataramana (2001) Mechatronics, Sapna Book house, Bangalore
BOS-Jul-09
21 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD610.2 Mechanical System Design Unit 1 Introduction [6]
Review of fundamentals of kinematics--Mobility analysis --Formation of one D.O.F. multiloop kinematics chains, Network formula - Gross motion concepts. Unit 2 Kinematic Analysis [10]
Position analysis -Vectorloop equations for four bar, slider crank, inverted slider crank - Geared five bar and six bar linkages. Analytical method for velociy and acceleration analysis - Four bar linkage jerk analysis - Plane complex mechanism Unit 3 Path Curvature Theory [8]
Fixed and Moving centrodes, inflection points and inflection circle. Euler Savary equation, Graphical constructions - Cubic of stationary curvature. Unit 4 Synthesis Of Mechanisms [10]
Type synthesis - Number sythesis - Assosiated linkage concept. Dimensional systhesis - Function generation , path generation, motion generation. Graphical methods. Cognate linkage - Coupler curve synthesis, design of six bar mechanisms .Algebraic methods. Application of instant centre in linkage design. Cam mechanism Determination of optimum size of Cams. Unit 5 Dynamics Of Mechanisms [8]
Static force analysis with friction - Inertia force analysis - combined static and inertia force analysis.shaking force, Kinetostactic analysis. Introduction to force and moment balancing of linkages.
Unit 6 Spatial Mechanism And Robotics [6] Kinematic analysis of spatial RSSR mechanism - Denavit - Hartenberg parameters. Forward and inverse Kinematics of robotic manipulators
References 1. Sandor G.N. and Erdman A.G., "Advanced Mechanism Design Analysis and Synthesis", Prentice Hall,1984. 2. Shigley, J.E., and Uicker, J.J., "Theory of Machines and Mechanisms", McGraw Hill, 1995. 3. Amitabha Ghosh and Ashok Kumar Mallik, "Theory of Mechanism and Machines", EWLP, Delhi, 1999. 4. Nortron R.L., "Design of Machinery", McGraw Hill, 1999. 5. Kenneth J. Waldron, Gary L. Kinzel, "Kinematics, Dynamics and Design of Machinery", John Wiley-sons, 1999.
BOS-Jul-09
22 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
Elective 4 MSD612 MSD612. 1 Engineering Project Managenment Unit 1: Basics of Project Management [6] Introduction, Definition, The Project Life-cycle, Project Management Processes Why do Projects Fail, Project Lifecycle and Process Flows, Project PlanningScoping, Planning Tools, Planning- Estimation, PERT Analysis, Estimation Approaches, Estimation Tools, Risk Management , Project Monitoring and Control Progress Control, Project Statues Reports, Change Control, Change Management Process, Project Closure Unit 2: Project Management Essentials [6] Introduction, Project Mindset, Macro-Issues of Project Mindset, Partnering Decision Making, Knowledge (K) Factor, Conflict Management, Communication Requirements and Capabilities , Quality Management, Project Management Information System (PMIS) Unit 3: Basic Management Issues In Project Management [8] Introduction, Improving Project Performance through the PMO, Project Manager Teams, Human Resource Management & Professional Responsibility, Team Work & Interpersonal Behavior, Traits of successful teams, Personal Productivity , The Project Development Process Cycle, Modern Trends in Project Management Perception, Recent revolutions in project management Unit 4: Organizational Issues in Project Management [6] Introduction, Organizational Change, Traits of the professional manager in changing scenario, Projectized Technology-based Organizations in the Century of Changes and Challenges, Project & Programme Management ( P2M ) for Enterprise Innovation, Guidelines for Development of High Technology Unit 5: Guide to Systematic Scientific Project Management [6] Introduction, New Horizons In Project Management Nine Steps, Stages in a Project Management Cycle DMAIS, The Role of Effective Data Management in the Success of Project Management ,Measuring and Managing Success, Tips and tricks for successfully implementing a metrics program Unit 6: Project Management Process [8] Introduction, Project Management Review Process Guide for Corporate and Major Information Systems, Project Management Review Process Schedule and Timeline, Review Templates, Post-Review Activities, Planning for Project Surprises - Coping with Risk, Risk Management Process
BOS-Jul-09
23 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
Unit 7: Project Management Application Software, Plan, Global Delivery Model, Case studies [8] Introduction, Odette Documentation System Specifications, ARIS Web Publisher, Microsoft Project 2002, Writing a Winning Business Plan, The ARROW Project, FEDORA, VITAL, PILIN Project Management Plan - Xyz Project, Global Delivery Model
References 1.Project Management by S. Choudhury (Hardcover - 2004) 2.Project Management by Phil Baguley (Paperback - 07-2009) 3.Project Management: 24 Lessons To Help You Master Any Project (mhpe Series) by Gary Heerkens (Paperback - 2005) 4.Project Management, 1e by Patel (Paperback - 2000) 5.Project Management 3e by Nicholas J M (2008)
BOS-Jul-09
24 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD612.2 Advances in Material Sciences Unit 1 : Introduction to Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials [8] Historical perspective of Materials Science. Atomic Structure, Interatomic Bonding and Structure of Crystalline Solids, Imperfections in Solids, Mechanical Properties of Metals Diffusion, Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms, Phase Diagrams Unit 2: Failure [10] Fracture. Ductile and brittle fracture. Fracture mechanics. Impact fracture. Ductile brittle transition. Fatigue. Crack initiation and propagation. Crack propagation rate. Creep. Generalized creep behavior. Stress and temperature effects Applications and Processing of Metals and Alloys Types of metals and alloys. Fabrication of metals. Thermal processing of metals. Heat treatment. Precipitation hardening. Unit 3: Applications and Processing of Ceramics & Polymers , composites [10] Types and applications of ceramics. Fabrication and processing of ceramics. Mechanical behavior of polymers. Mechanisms of deformation and strengthening of polymers. Crystallization, melting and glass transition. Polymer types. Polymer synthesis and processing. Particle reinforced composites. Fiber reinforced composites. Structural composites. Corrosion of metals. Corrosion of ceramics. Degradation of polymers Unit 4: Electrical, Thermal, Magnetic Properties [12]
Electrical conduction. Semi conductivity. Super conductivity. Electrical conduction in ionic ceramics and in polymers. Dielectric behavior. Ferroelectricity. Piezoelectricity Heat capacity. Thermal expansion. Thermal conductivity. Thermal stresses, Diamagnetism and paramagnetism. Ferromagnetism.Antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism. Influence of temperature on magnetic behavior. Domains and Hysteresis Unit 5: Optical Properties [4] Basic concepts. Optical properties of metals. Optical properties of nonmetals. Application of optical phenomena. Unit 6: Economic, Environmental and Social Issues of Material Usage [4] Economic considerations. Environmental and societal considerations. Recycling issues. Life cycle analysis and its use in design.
References
1. Thomas H.Courtney, " Mechanical Behaviour of Materials ", (2nd Edition), McGrawHill, 2000.
BOS-Jul-09
25 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
2. Charles J.A., Crane, F.A.A and Furness, J.A.G., " Selection and use of Engineering Materials (3rd Edition ), Butterworth-Heiremann, 1977. 3. Flinn, R.A. and Trojan, P.K., " Engineering Materials and their Applications ", (4th Edition), Jaico, 1999. 4. George E.Dieter, " Mechanical Metallurgy ", McGraw Hill, 1988. 5. Metals Hand Book, Vol.10, " Failure Analysis and Prevention ", (10th Edition), 1994.
BOS-Jul-09
26 of 27
MS MSD(Syllabus)
MSD 614 Computer Aided Analysis Laboratory Introduction to Different Element types: Introduction to FEA , Exercises on link, beam, plane stress/strain, shell and solid elements. Accuracy and error estimation. [12] Example Problems: Static structural analysis of Leaf connections, Gear teeth in mesh. Introduction to Analysis types: Thermal Analysis Steady state, transient, Modal Analysis, Harmonic analysis, Buckling Analysis, CFD analysis, Thermo-mechanical analysis, Fluid-structure interaction. [18] Applications: Optimization of structures, Composite structure analysis, Fracture Mechanics, Non-linear analysis. [8] spring, Threaded fasteners, Bolted [10]
BOS-Jul-09
27 of 27
You might also like
- UploadedFile 129816616088888750Document35 pagesUploadedFile 129816616088888750Jeyaram KumarNo ratings yet
- Mech AutoDocument36 pagesMech Autoapi-236544093No ratings yet
- ME Engineering Design-2013 Syllabus Anna UnivDocument28 pagesME Engineering Design-2013 Syllabus Anna Univshibumankulath4727No ratings yet
- FEM SyllabusDocument2 pagesFEM SyllabuscodieNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and SyllabiDocument38 pagesCurriculum and SyllabiVelmurugan ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Open ElectiveDocument7 pagesOpen ElectivevibhaNo ratings yet
- Fea BookDocument155 pagesFea BookLakhan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL CivilZone review of rock mechanics methodsDocument19 pagesNUMERICAL CivilZone review of rock mechanics methodsRui BarreirosNo ratings yet
- BTech - 5th - 6th - Sem MEDocument9 pagesBTech - 5th - 6th - Sem MEN KumarNo ratings yet
- M.E. CAD/CAM CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS AT ANNA UNIVERSITYDocument27 pagesM.E. CAD/CAM CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS AT ANNA UNIVERSITYBhuvanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ManufacturingDocument35 pagesManufacturingMichael EnglishNo ratings yet
- M Tech. Design Mnnit2010Document6 pagesM Tech. Design Mnnit2010ambujsharma08No ratings yet
- Fem CoDocument5 pagesFem Comuralict2009No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg Classes at Jyothis AcademyDocument14 pagesMechanical Engg Classes at Jyothis AcademyRAMA RAJU PYDINo ratings yet
- SPH BasicsDocument27 pagesSPH BasicsSubash Gerrard DhakalNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pagesFinite Element MethodsJames SudhakarNo ratings yet
- M-TECH Machine Design Kerala University SYLLABUSDocument71 pagesM-TECH Machine Design Kerala University SYLLABUSMathew JohnNo ratings yet
- Analyze Residual Stresses in Welded Joints with ANSYSDocument39 pagesAnalyze Residual Stresses in Welded Joints with ANSYSDvasSrikanthKingNo ratings yet
- B.tech (Hons) Mechanical Course OutlineDocument16 pagesB.tech (Hons) Mechanical Course OutlineTableegi TehreekNo ratings yet
- Third Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueDocument8 pagesThird Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueSudeep GamerNo ratings yet
- FEM - Cont. & Chapt-1 - Slide PresentationDocument10 pagesFEM - Cont. & Chapt-1 - Slide PresentationMohammed B TuseNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 5th Sem MechanicalDocument10 pagesB.Tech 5th Sem MechanicalRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Gate-Me-2024, V-IiDocument401 pagesGate-Me-2024, V-Iiyash guptaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Rock MechanicsDocument24 pagesNumerical Methods in Rock Mechanicsali100% (2)
- Design, Simulate Then ValidateDocument5 pagesDesign, Simulate Then ValidateLowrence SenNo ratings yet
- Mahmaya Techanical University, Noida (U. P) : M. Tech (Regular Programme)Document31 pagesMahmaya Techanical University, Noida (U. P) : M. Tech (Regular Programme)durgeshrsharmaNo ratings yet
- M.tech Machine SyllabusDocument41 pagesM.tech Machine SyllabusSyed Faiz Quadri0% (1)
- Engineering Design and Fluid Mechanics Qualifying Exam GuideDocument15 pagesEngineering Design and Fluid Mechanics Qualifying Exam GuideAnastasiya DobrovaNo ratings yet
- 7th SEM - SYLLABUS OF INSTITUTE ELECTIVE PDFDocument71 pages7th SEM - SYLLABUS OF INSTITUTE ELECTIVE PDFVinay RajuNo ratings yet
- AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSDocument8 pagesAERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING SYLLABUSaeroromeosNo ratings yet
- Ae6601 Finite Element Methods L T P C 3 1 0 4Document2 pagesAe6601 Finite Element Methods L T P C 3 1 0 4Minu.j.jNo ratings yet
- 7TH Semester SyllabusDocument9 pages7TH Semester SyllabusShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- I Semester 15ae01 Computational Mathematics 2 2 0 3Document22 pagesI Semester 15ae01 Computational Mathematics 2 2 0 3sagarNo ratings yet
- Defect Analysis in Hot RollingDocument11 pagesDefect Analysis in Hot RollingVashishth KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Semister 2Document6 pagesSemister 2Anand JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Review of Subdomain Modeling Techniques in Electrical Machines Performances and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA Review of Subdomain Modeling Techniques in Electrical Machines Performances and ApplicationsFaiza OuiddirNo ratings yet
- Elective - IDocument33 pagesElective - IMohit RanaNo ratings yet
- CIM Techniques and ApplicationsDocument39 pagesCIM Techniques and ApplicationsAnilNo ratings yet
- An Optimization-Based Computational Method For Surface Fitting To Update The Geometric Information of An Existing B-Rep CAD ModelDocument8 pagesAn Optimization-Based Computational Method For Surface Fitting To Update The Geometric Information of An Existing B-Rep CAD ModelAguz JmjNo ratings yet
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocument22 pagesAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderNo ratings yet
- B TECH New BatchDocument11 pagesB TECH New Batchhidowi4609No ratings yet
- MS Mechanical Engineering Course Plan and SyllabusDocument12 pagesMS Mechanical Engineering Course Plan and SyllabusEngr Nayyer Nayyab Malik100% (1)
- P Seshu BookDocument32 pagesP Seshu BookShridhar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- MECH Syllabus 2010-11Document55 pagesMECH Syllabus 2010-11Srinivasa Reddy NallimilliNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014: Syllabus of Me (Gate)Document8 pagesGATE 2014: Syllabus of Me (Gate)Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- SE Production SandwichDocument43 pagesSE Production SandwichRohittitansinghNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignDocument11 pagesFinite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignroscillaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Machine DesignDocument2 pagesAdvanced Machine Designsamir0% (1)
- CZM Formulation and ABAQUSDocument44 pagesCZM Formulation and ABAQUSaravind kumarNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Simulation STR 18Document12 pagesProcess Plant Simulation STR 18Sandeep SureshNo ratings yet
- Karanataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Document35 pagesKaranataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)nav1278No ratings yet
- PR2351 Finite Element Analysis in Manufacturing Engineering 3 0Document2 pagesPR2351 Finite Element Analysis in Manufacturing Engineering 3 0Anonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg RM PET SyllabusDocument5 pagesMechanical Engg RM PET SyllabusAnil MagareNo ratings yet
- Mech 6th Sem SyllabusDocument14 pagesMech 6th Sem SyllabusArun ManoNo ratings yet
- Fea Module 1Document56 pagesFea Module 1NAVADE SATISHNo ratings yet
- BEBI2 CurriculumDocument14 pagesBEBI2 CurriculumRagnar RagnarsonNo ratings yet
- LPile 2015 Technical ManualDocument238 pagesLPile 2015 Technical ManualMahesh HanmawaleNo ratings yet
- PrestressedTendonElongations-MIDAS V1Document4 pagesPrestressedTendonElongations-MIDAS V1sanusi69No ratings yet
- ME-EM 5210 Advanced Fluid Engineering: Course Goals, Policies Textbooks GradesDocument16 pagesME-EM 5210 Advanced Fluid Engineering: Course Goals, Policies Textbooks GradesashNo ratings yet
- FEM-quiz Bank-Mid-2Document2 pagesFEM-quiz Bank-Mid-2DarbhalaPavanKumarNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Negative Gravitational Propulsion.Document33 pagesAn Investigation of Negative Gravitational Propulsion.Armando Milak Pérez100% (1)
- Witt 2018Document19 pagesWitt 2018pesek.llukasNo ratings yet
- Se 2015Document267 pagesSe 2015BeastNo ratings yet
- Basic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Document2 pagesBasic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Muhammad Noman Mughal0% (1)
- Navier-Stokes Equation (An Overview and The Simplification) : July 2020Document10 pagesNavier-Stokes Equation (An Overview and The Simplification) : July 2020JuniorNo ratings yet
- Proposed Macro-Model For The Analysis of Infilled Frame StructuresDocument12 pagesProposed Macro-Model For The Analysis of Infilled Frame StructuresAngga AriefNo ratings yet
- Fracture ToughnessDocument31 pagesFracture ToughnessX800XLNo ratings yet
- Vertical Stress Distribution in SoilDocument59 pagesVertical Stress Distribution in SoilAagneya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Constitutive Models of ConcreteDocument37 pagesConstitutive Models of ConcreteRamon Gutierrez100% (1)
- JSR PH Q 18Document16 pagesJSR PH Q 18JYOTISMAT RAULNo ratings yet
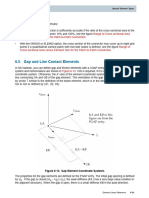
- Gap ElementDocument6 pagesGap ElementEman HassanNo ratings yet
- CAE Mechatronic Systems IDocument14 pagesCAE Mechatronic Systems IAdarsh SamratNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Measurements and VectorsDocument15 pagesMCQs on Measurements and VectorsZahid Iftikhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mixed Mode Crack Propagation in ConcreteDocument45 pagesMixed Mode Crack Propagation in ConcreteAdolfo Gálvez VillacortaNo ratings yet
- FEM1001 Anglais PDFDocument312 pagesFEM1001 Anglais PDFandredurvalandradeNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet: Test Job Member Design For SB2Document2 pagesCalculation Sheet: Test Job Member Design For SB2bungykitNo ratings yet
- Trejectory Ofr Fin Artillery RocketDocument14 pagesTrejectory Ofr Fin Artillery RocketasifkkNo ratings yet
- Midterm Practice1 Sc3Document11 pagesMidterm Practice1 Sc3Toni TonesNo ratings yet
- MonorailDocument14 pagesMonorailZain AndabloNo ratings yet
- Solutions - HW 3, 4Document5 pagesSolutions - HW 3, 4batuhany90No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document28 pagesLecture 8noorrhamadddNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Quiz 1: First Nam e Last Nam eDocument9 pagesUltrasound Quiz 1: First Nam e Last Nam emanojit goswamiNo ratings yet
- Final-Problems BPO5 ENGDocument3 pagesFinal-Problems BPO5 ENGPool Giancarlo Pujay GasparNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 22975Document7 pagesS Announcement 22975patricia piliNo ratings yet
- BlastingDocument18 pagesBlastingZig BlankNo ratings yet
- ARC Additional Problems MWFDocument5 pagesARC Additional Problems MWFonly. starNo ratings yet