Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluids Flow Chart
Uploaded by
k.d.buquidOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluids Flow Chart
Uploaded by
k.d.buquidCopyright:
Available Formats
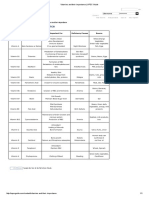
Fluids Flow-Sheet
Dehydration
Isotonic (equal sodium and water loss)
Most common type of dehydration ECF only ECF fluid volume (only) deficit
Overhydration
Isotonic (equal sodium and water gain)
Most common type of overhydration ECF only Only the ECF has excessive fluid and the ICF does not have a fluid imbalance
Hypovolemia
Severe can lead to shock Serum electrolytes WNL VS: orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea Hemoconcentration Causes: hemorrhage; fluid loss from GI tract; diuretics Compensatory mechanisms: Aldosterone (will cause both Na+ and H2O to be reabsorbed from renal tubules) Treatment: isotonic IV fluids (NS, LR); blood (if hemorrhage)
Hypervolemia
Serum electrolytes WNL VS: elevated BP, tachypnea Circulatory overload, pitting edema, oliguria Hemodilution Causes: chronic renal failure, heart disease, overadministration of isotonic IV fluids, Aldosterone Compensatory mechanisms: ANP (will cause H2O and Na+); ADH Treatment: osmotic diuretics and fluid restrictions; dialysis (severe)
Hypertonic (more water lost than sodium)
Second most common type ECF, ICF ICF fluid volume deficit and expansion of ECF
Hypertonic
Water-loss hypernatremia
Serum Na+ VS: Low-grade fever; BP & pulse WNL Causes: large insensible losses; hyperventilation; ketoacidosis; fever; DI; watery diarrhea; tube feedings Compensatory mechanisms: ADH, thirst Treatment: hypotonic IV fluids SLOWLY (D5W, 0.45% NaCl)
(more sodium gained than water) Least common, rare ECF, ICF ECF has fluid overload, and ICF is dehydrated
Sodium-gain hypernatremia
Serum Na+ VS: elevated BP, low-grade fever Circulatory overload, pitting edema Causes: excessive sodium intake; hypertonic saline or sodium bicarbonate; salt-water near-drowning Compensatory mechanisms: ANP Treatment: restrict foods and fluids high in sodium Hypotonic (more water gained than sodium) Second most common type Worst overydration state (all compartments expanded) ECF, ICF Both ECF and ICF have excessive fluid Electrolyte dilution and cellular swelling
Hypotonic
(more sodium lost than water) Least common, rare Most serious depletion of intravascular space ECF, ICF ECF fluid volume deficit and expansion of ICF
Hypovolemia most severe Sodium-loss hyponatremia
Serum Na+, serum K+ Excessive loss of Na+ and K+ from ECF VS: hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea Hemoconcentration Causes: chronic illness, malnutrition, heat stroke Compensatory mechanisms: Aldosterone Treatment: NS (preferred) or hypertonic fluids (with great caution)
Water intoxication Dilutional hyponatremia
Serum Na+ VS: elevated BP Water gain, generalized non-pitting edema. Hemodilution Causes: excessive tap water; SIADH; overadministration of hypotonic IV solutions Compensatory mechanisms: ADH Treatment: restrict fluids, osmotic diuretics
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Acute NeurologiDocument343 pagesThe Acute Neurologizee zeeNo ratings yet
- Interoception-201 March-2019Document38 pagesInteroception-201 March-2019api-526165635No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Aip Summer 2017 PDFDocument116 pagesAip Summer 2017 PDFShibli KushtiaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Gastroenterology PDFDocument2,352 pagesEncyclopedia of Gastroenterology PDFAndor Claudia Florentina100% (1)
- P.E 2nd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesP.E 2nd Quarter ExamCherry Vhim Flores Lanurias100% (3)
- Endocrine Emergencies CompiledDocument102 pagesEndocrine Emergencies CompiledSubhkanish RavindraNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFDocument1 pageVitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFRajesh ManjhiNo ratings yet
- Vetnizah Juniantito's CVDocument3 pagesVetnizah Juniantito's CVjuniantitoNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Kadar Hemoglobin Dan Tercapainya Remisi Pada Anak Penderita Leukemia AkutDocument7 pagesHubungan Kadar Hemoglobin Dan Tercapainya Remisi Pada Anak Penderita Leukemia AkutRezky RahmadayantiNo ratings yet
- Blood Brain BarrierDocument6 pagesBlood Brain BarrierdamonsalvotoreNo ratings yet
- Pathomorphology Final ExamDocument262 pagesPathomorphology Final ExamMann SarwanNo ratings yet
- E147 Full PDFDocument21 pagesE147 Full PDFcahyatiNo ratings yet
- Master List of Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument37 pagesMaster List of Common Medical AbbreviationshealerharishNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportSems AlcozbaryNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument3 pagesMyasthenia GravisfsNo ratings yet
- Paget Disease Causes Excessive Bone Formation and DeformationDocument14 pagesPaget Disease Causes Excessive Bone Formation and DeformationOrson SimonNo ratings yet
- Definition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults - UpToDateDocument16 pagesDefinition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults - UpToDatevara prasadNo ratings yet
- RTO Z6P5CMB Paket1UASGanjil20182019 PDFDocument20 pagesRTO Z6P5CMB Paket1UASGanjil20182019 PDFGlorya ValensiaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Plasma Protein DisordersDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Plasma Protein DisordersJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- TonsillectomyDocument27 pagesTonsillectomyRho Vince Caño MalagueñoNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudySarah McKayNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument43 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundkjjkjkljkjjklNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Document7 pagesGroup 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Crissan Jejomar AbanesNo ratings yet
- Abdominals: Ab Crunch MachineDocument24 pagesAbdominals: Ab Crunch Machinearies_02No ratings yet
- NeuroVas Assessment.2Document2 pagesNeuroVas Assessment.2ROxiie RakiztaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Studies: in The Sleep Laboratory and in The Home: Patient EducationDocument2 pagesSleep Studies: in The Sleep Laboratory and in The Home: Patient EducationALINo ratings yet
- Ed 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFDocument52 pagesEd 4 PHARMACOGNOSY PDFShubham Sabale PatilNo ratings yet
- Synevo Results 5Document3 pagesSynevo Results 5Kenan BagirNo ratings yet
- Understanding CLL: A Guide For Patients Who Want To Take Charge of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument4 pagesUnderstanding CLL: A Guide For Patients Who Want To Take Charge of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaNakul Singh ParkwayIndiaNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive Training HandballDocument23 pagesProprioceptive Training HandballRoginicD100% (1)