Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP - Hyperthermia
Uploaded by
edmr12Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP - Hyperthermia
Uploaded by
edmr12Copyright:
Available Formats
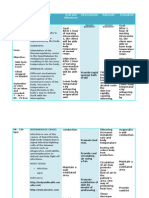
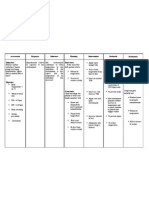
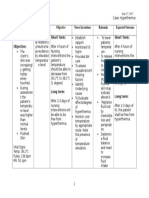
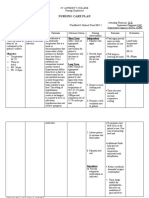
University of San Carlos College of Nursing Cebu City NURSING CARE PLAN Patients health profile: Received patient
lying on bed with ongoing #2 PNSS 1L @ 30 gtts/min, infused @ left arm. Initial Complaint: Fever for 3 weeks, abdominal pain Diagnosis/Impression: Acute Pyelonephritis
Name: M.C.H.
Sex: Male
Age: 57 y.o. Occupation: Farming Date of Admission: 7/31/11 Religion: Roman Catholic Status: Single Needs/Nursing Diagnosis Physiologic need Hyperthermia related to infectious process S: Pag-abot namu dinhi dai pirte naman ana niyang inita hangtud karon wala pa gihapon mahuwasi, as verbalized by the S.O. O: -Increased body temperature above normal range, Temp: 38.1 degree Celsius -Warmth felt when touched -Increased respiration above normal range, Scientific Analysis
Nursing Objectives Interventions After 8 hours of nurse- INDEPENDENT: The most common form of patient interaction, the kidney disease is the patient will be able to: inflammation of the kidney, or commonly called 1. Explain the Assess the clients pyelonephritis. Most possible present health inflammation is caused by causes/contribut status. bacterial infections. That is ing factors of why patient with this kind of elevated body illness manifests elevated temperature body temperature due to using his own the occurrence of the words based on Discussion of the infection in the body his level of possible causes of wherein proteins called understanding. elevated body pyrogens are released due temperature. to the white blood cells that fights the microorganisms 2. Assess the responsible of the illness. patients health Assess clients Increased pyrogen greatly status following body temperature. increases body the actions done temperature. by the nurse. Reference: Fundamentals of nursing by Harry and Perry Check respirations.
Rationale
This would serve as the baseline data for the evaluation of care after the implementation of the planned care. Knowledge about the causes of a particular complication will be a preventive measure.
Body temperature of more than 38.5 degree Celsius may lead to seizures and needs immediate action. Hyperventilation may initially be present, but ventilator effort
Evaluation After 8 hours of nursepatient interaction, the objectives were met. The patient was able to explain possible causes of increased body temperature related to the presence of infection. The client was able to assess the health status of the patient like checking of the body temperature. The client was able to demonstrate behaviors to promote normal body temperature like performing Tepid Sponge Bath as evidenced by reduction of body temperature from 38.1 to 37.0 degree Celsius. The client pays attention to the health teachings provided when she gave adequate fluid intake to her patient.
Own Analysis: The patient is admitted due to acute pyelonephritis. In which there is an infection that happens within the body and the bodys defense is to raise body temperature as a sign that the body is trying to fight the microorganisms responsible for the illness. That is why patient may manifest elevated body temperature. 3. Demonstrate behaviors to manage increased body temperature basing on bodys normal temperature of 36.5-37.5 degree Celsius. Monitor and record all sources of fluid loss.
may be impaired by seizures, shock. Oliguria and or renal failure may occur due to hyperthermia, dehydration and tissue necrosis. Helps reduce elevated body temperature.
Perform Tepid Sponge Bath. Instruct the S.O. not to leave the patient unattended. Discuss importance adequate intake.
4. Pay attention into the health teachings done by the nurse through active participation.
To promote safety and prevent heat injury.
the of fluid
To prevent dehydration.
DEPENDENT: Administer antipyretics, orally/rectally, as ordered. Take note for signs and symptoms indicating need for emergent/further evaluation and follow-up care. Measures to reduce body temperature.
To avoid complications if there are early detections of signs and symptoms.
COLLABORATIVE: Provide caloric diet. high To meet increased metabolic demands. Support circulating volume and tissue perfusion.
Administer replacement fluids and electrolytes.
Nurses pocket guide diagnoses, prioritized interventions and rationalesDoenges et.al., 11th editionF.A Davis companyCopyright 2008- pages 382387.
You might also like
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument6 pagesNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNaidin Catherine De Guzman-AlcalaNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaAnn Wincel NoblezaNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument6 pagesHyperthermiaBerlyn FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Hyperthermiasamanthabox50% (2)
- Definition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverSherwin B. CaytapNo ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument2 pagesNCP FeverMary Joyce LimoicoNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMarla NavarroNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaBracel GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fever NCPDocument3 pagesFever NCPBruno MercuryNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPatricia Trinidad100% (1)
- NCP FeverDocument2 pagesNCP FeverRic Velasco100% (2)
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMeljonesDaanNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPSian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Doenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Document3 pagesDoenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Theresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post Op CSDocument3 pagesNCP Pain Post Op CSKersey Adricula Ricalde100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Patty NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesPatty NCP HyperthermiaPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPJayr DiazNo ratings yet
- Problem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationDocument3 pagesProblem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationgrazheNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 pageDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureVanessa AbboudNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverDominises Jade Corpuz82% (17)
- NCP - FeverDocument2 pagesNCP - FeverJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- NCP For HeadacheDocument1 pageNCP For HeadacheJohn MajanNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaMiguelMartinNo ratings yet
- NCP Loss of AppetiteDocument5 pagesNCP Loss of AppetiteStenneli Gumban Trojillo50% (2)
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument1 pageHyperthermia NCPMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain NCPRyan PanNo ratings yet
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPDocument2 pagesTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael Baccol100% (1)
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument1 pageHyperthermia NCPRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young50% (2)
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJ. ishtelleNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanLegendX100% (1)
- VI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesVI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- "Nilalagnat Anak Ko. Kagabi Pa Po Siya Mainit" As: Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 page"Nilalagnat Anak Ko. Kagabi Pa Po Siya Mainit" As: Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMiguel LeybaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJachel Kathleen LaguioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceDarkCeades83% (6)
- Management of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument7 pagesManagement of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverjoycevillamorNo ratings yet
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDocument19 pages5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology - Febrile SeizureDocument17 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology - Febrile SeizureSundaraBharathi75% (4)
- Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesSeizure NCPFlashbomb Paras92% (12)
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP DengueJanna Carrel Isabedra Rodio100% (2)
- Rosilla, Leandro AGE: 5 Yrs Old Diagnosis: DHF IiiDocument4 pagesRosilla, Leandro AGE: 5 Yrs Old Diagnosis: DHF IiiAlexander Rodriguez OlipasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale SubjectiveDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjectivemacloy21No ratings yet
- Safety Guidelines PDFDocument15 pagesSafety Guidelines PDFDayanand SharmaNo ratings yet
- RA-for Glass Installation 30-04-2022Document6 pagesRA-for Glass Installation 30-04-2022Muideen Oyedele100% (2)
- Measuring Heat Stress in Industry: Research SummaryDocument12 pagesMeasuring Heat Stress in Industry: Research SummaryIr Moise MatabaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of at Risk/ High Risk/ Sick ClientDocument256 pagesNursing Care of at Risk/ High Risk/ Sick ClientAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- A.sahaya Pratheesh Fero 1Document29 pagesA.sahaya Pratheesh Fero 1Arun Godson57% (7)
- Ide 20.3 Prelim ReviewerDocument14 pagesIde 20.3 Prelim ReviewerEla Mae CoNo ratings yet
- HOPE-11 1st Semester Assessment ToolDocument8 pagesHOPE-11 1st Semester Assessment ToolAldrin BagasinaNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress Management Plan Rev - 1Document31 pagesHeat Stress Management Plan Rev - 1Ahmad Assad mrednNo ratings yet
- Personal Safety Protocol During MVPADocument4 pagesPersonal Safety Protocol During MVPAKatrina Ella Joy CaraangNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress Poster 2 - 260520153053Document2 pagesHeat Stress Poster 2 - 260520153053TomNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument9 pagesMAPEHZayn SturnioloNo ratings yet
- Night FeverDocument5 pagesNight FeverdewioktaNo ratings yet
- DPJV - Heat Stress AwarenessDocument41 pagesDPJV - Heat Stress AwarenessibrahimNo ratings yet
- PE 12, (HOPE3) Q2, Module 2, Lesson 5 by LeviDocument22 pagesPE 12, (HOPE3) Q2, Module 2, Lesson 5 by LeviRegie CarinoNo ratings yet
- ETG7 - Heat Stress at WorkDocument3 pagesETG7 - Heat Stress at WorkRahul RamachandranNo ratings yet
- CMP Final Draft FuelDocument33 pagesCMP Final Draft Fuelapi-594648232No ratings yet
- 1 New Hand Out Detect Pharmaceutical Health&hazards levelIIDocument21 pages1 New Hand Out Detect Pharmaceutical Health&hazards levelIISamuel Merga100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young50% (2)
- RA - Ducting WorksDocument6 pagesRA - Ducting WorksResearcherNo ratings yet
- Heat StrokeDocument27 pagesHeat StrokeAkash NirveNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Cover Sheet: Wayame 150kV ProjectDocument42 pagesRisk Assessment Cover Sheet: Wayame 150kV ProjectBaso Firdaus PannecceNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Occupational Heat Related Illnesses.25Document8 pagesPrevention of Occupational Heat Related Illnesses.25Santi YuliandariNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaDhonabelleVanessaFetalinoAdona100% (1)
- Prepared By: Dan SawallDocument13 pagesPrepared By: Dan SawallTonyNo ratings yet
- DEFTAC 103 Topic 1 - Intro To First AidDocument3 pagesDEFTAC 103 Topic 1 - Intro To First AidArhakir AlpaparaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Pallavi WakodeDocument49 pagesErgonomics: Pallavi WakodeAkshay BangadNo ratings yet
- Beware of DehydrationDocument2 pagesBeware of DehydrationFavour ChukwuelesieNo ratings yet
- ThermoregulationDocument34 pagesThermoregulationAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid, DCPQSDocument44 pagesBasic First Aid, DCPQSDelando CoriahNo ratings yet
- Recognizing Hazard ChecklistDocument2 pagesRecognizing Hazard ChecklistDwi Agung AriyonoNo ratings yet