Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adrenergic Receptors
Uploaded by
rababmohsin110Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adrenergic Receptors
Uploaded by
rababmohsin110Copyright:
Available Formats
ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS:INTRODUCTION:-
The adrenergic receptors (or adrenoceptors) are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of the catecholamine, especially nor adrenaline (nor epinephrine) and adrenaline (epinephrine). Although dopamine is a catecholamine, its receptors are in a different category. Many cells possess these receptors, and the binding of an agonist will generally cause a sympathetic response (e.g. the fight-or-flight response). For instance, the heart rate will increase and the pupils will dilate, energy will be mobilized, and blood flow diverted from other nonessential organs to skeletal muscle. BASIC STRUCTURES:PHENYLETHANOLAMINE:-
PHENYLETHYLAMINE:-
ALPHA1, ALPHA2 BETA1, BETA2, BETA3 AGONIST AND ANTAGONIST DERIVATIVES:-
RECEPTORS
AGONIST POTENCY ORDER
SELECTED ACTION OF AGONIST
AGONISTS
ANTAGONISTS.
1: A, B, D
Nor epinephrine epinephrine isoprenaline
Smooth muscle contraction
(Alpha-1 agonists) Noradrenaline Phenylephrine Methoxamine Cirazoline Xylometazoline
(Alpha-1 blockers) (TCA:s) Amitriptyline Clomipramine Doxepin Trimipramine Phentolamine Prazosin Tamsulosin Terazosin
Alpha-2 blockers) 2: A, B, C Epinephrine Smooth muscle norepinephrine relaxation and >> isoprenaline neurotransmitter inhibition (Alpha-2 agonists)
Lofexidine Xylazine Tizanidine Guanfacine Amitraz Clonidine
Phentolamine Yohimbine Idazoxan Atipamezole
Beta blockers) 1 Isoprenaline > Heart muscle epinephrine = contraction norepinephrine
Noradrenaline Isoprenaline Dobutamine
Metoprolol Atenolol
(Short/long) 2 Isoprenaline > Smooth muscle epinephrine >> relaxation norepinephrine
(Beta blockers)
Salbutamol (Albuterol in USA) Bitolterol mesylate Formoterol Isoprenaline Levalbuterol Metaproterenol Salmeterol Terbutaline Ritodrine
Butoxamine Propranolol
Isoprenaline = Enhance lipolysis norepinephrine > epinephrine
Amibegron Solabegron
SR 59230A
STRUCTURES OF ALPHA 1 AGONIST AND ANTAGONIST:-
NOR-ADRENALINE
PHENYLEPHRINE.
METHOXAMINE.
PHENTOLAMINE.
PRAZOSIN.
AMITRIPTYLINE
STRUCTURES OF ALPH 2 AGONIST AND ANTAGONIST.
CLONIDINE
AMITRAZ
ATIPAMEZOLE.
IDAZOXAN
STRUCTURES OF BETA 1 AGONIST AND ANTAGONIST.
DOBUTAMINE
ISOPRENALINE
ATENOLOL.
STRUCTURES OF BETA2 AGONIST AND ANTAGONISTS
SALBUTAMOL
TERBUTALINE
PROPANOLOL
STRUCTURE OF BETA3 AGONIST AND ANTAGONISTS:-
SOLABEGRON
SR- 59230A
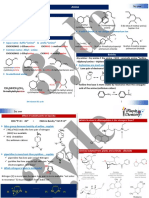
STRUCTURE ACTIVITY RELATION OF PHENYLETHYLAMINE DERIVATIVES:The group of phenethylamine derivatives is referred to as the phenethylamine. Substituted phenethylamine, substituted amphetamines, and substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines (MDxx) are a series of broad and diverse classes of compounds derived from phenethylamine that include stimulants, psychedelics, and entactogens, as well as anorectics, bronchodilators, decongestants, and antidepressants, among others. a phenethylamine core with a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon resulting in amphetamine, along with additional substitutions. Examples of amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone amphetamine and methamphetamine which lack both ring substituents and a side chain hydroxyl, are sufficiently lipophilic to cross the blood brain barrier readily and cause dramatic CNS stimulation. Ephedrine is a substituted amphetamine and a structural methamphetamine analogue. It differs from methamphetamine only by the presence of a hydroxyl (OH). Ephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine. The principal mechanism of its action relies on its indirect stimulation of the adrenergic receptor system, which is part of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), by increasing the neither activity of nor adrenaline at the post-synaptic and -receptors. The presence of direct interactions with -receptors is unlikely, but still controversial. Action upon the central nervous system (CNS) is limited because ephedrine only crosses the blood-brain barrier weakly and not very efficiently.
The presence of an N-methyl group decreases binding affinities at -receptors, compared with nor ephedrine. On the other hand ephedrine binds better than N-methyl ephedrine, which has an additional methyl group at the N-atom. Also the steric orientation of the hydroxyl group is important for receptor binding and functional activity
Both ephedrine and pseudoephedrine act as a bronchodilator
AMPHETAMINE
EPHEDRINE
METHAMPHETAMINE
STRUCTURE ACTIVITY RELATION OF PHENYLETHANOLAMINE DERIVATIVES:1. Primary or Secondary Amine, charged at physiological pH 2. Hydroxyl at Beta carbon in the R configuration for maximum effect 3. R1, R2, R3 control selectivity and Metabolism
BASIC STRUCTURE
Disruption of the Catechol inhibits COMT Metabolism Monoamine Oxidase
o
Agonist SAR Substitutions Metabolism
R1 substitutions
Isopropyl slow, but do not block Tertiary Butyl blocks
R2 substitutions
Methyl slow
Ethyl block
R1 - larger than a methyl R1 - Larger than isopropyl generally target Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptors R2 - Methyl or larger R3
o o o
Beta Receptor Selectivity SAR Substitutions
If only one hydroxyl, must be 4' If two hydroxyls, many combination of 3,4,5 are possible Can be as large a formyl, but must be able to hydrogen bond
All have hydroxyl at beta carbon, except Dobutamine which is special
Alpha Receptor Selectivity SAR Substitutions
R1 Guanidine Alpha
o
and Imidazoline
are selective for
Guanidine, for exam purposes, is almost always alpha-2 selective
R1 - Methyl or smaller R2 - S (-) Enantiomer R2 - must be no larger than methyl R3 - Lone hydroxyl at 3' is selective for Alpha-1 Adrenergic Receptors (Phenylephrine) R3 - 2,5 dimethoxy alpha selective
R3 - lipophilic (halide) ortho substitutions promote alpha-2 selectivity.
Oxymetazoline Isoproterenol Bitolterol Colterol Isoetharine Terbutaline Labetalol Sotalol Dobutamine
Drugs Following the Phenyl ethanolamine SAR
REFERENCES:-
http://drtedwilliams.net/kb/index.php?pagename=Phenylethanolamine%20SAR http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ephedrine http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methamphetamine http://www.ei-resource.org/articles/mental-and-emotional-problem-articles/hormonal-treatment-ofdepression-with-phenylethylamine-(pea)/ BOOK:Foyes principles of medicinal chemistry.
You might also like
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument7 pagesAdrenergic AgentsMuhamed ArsalanNo ratings yet
- PHARM4515 8 (Antihistamines)Document45 pagesPHARM4515 8 (Antihistamines)Street Pasutri RolferNo ratings yet
- Hist AntihisDocument20 pagesHist AntihisSusanti AsmiNo ratings yet
- Antihistamines: Student Learning GoalsDocument45 pagesAntihistamines: Student Learning GoalsDaniel WangNo ratings yet
- Direct-Acting Sympathomimetics Structure-Activity RelationshipsDocument9 pagesDirect-Acting Sympathomimetics Structure-Activity RelationshipsMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- Prodrug Design PDFDocument29 pagesProdrug Design PDFmehulpatel100% (1)
- Synthesis of AcetaminophenDocument8 pagesSynthesis of Acetaminophenapi-383568092No ratings yet
- Antiseizures DrugsDocument27 pagesAntiseizures DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNo ratings yet
- By Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra RanchiDocument31 pagesBy Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra Ranchiexcel pro100% (1)
- Receptor and Dose Response CurveDocument27 pagesReceptor and Dose Response Curveadnankhalid100% (2)
- (PTSM-I) : Pharmacological & Toxicological Screening Methods-IDocument44 pages(PTSM-I) : Pharmacological & Toxicological Screening Methods-INeha RoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacognosyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To PharmacognosyReyes MesshaelNo ratings yet
- Autocoids and Their AntagonistsDocument19 pagesAutocoids and Their AntagonistsHossein Sehati100% (1)
- Antipsychotics and Their SarsDocument3 pagesAntipsychotics and Their SarsJarein Mae CirunayNo ratings yet
- Drug Target and Drug Receptor InteractionDocument42 pagesDrug Target and Drug Receptor InteractionAceng Nunu NNo ratings yet
- N-Demethylation of Alkaloids: A Key Transformation in Drug SynthesisDocument13 pagesN-Demethylation of Alkaloids: A Key Transformation in Drug SynthesisPhuongNo ratings yet
- Antihistaminic Agents and Their ClassificationDocument8 pagesAntihistaminic Agents and Their ClassificationGopal Krishna PadhyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodyanamics-Model Questions & AnswersDocument6 pagesPharmacodyanamics-Model Questions & AnswersDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Introduction and History of Medicinal ChemistryDocument16 pagesIntroduction and History of Medicinal Chemistryrubal guptaNo ratings yet
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocument36 pagesTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- MCU-MEDICINE BATCH 2018 PHARMACOLOGYDocument5 pagesMCU-MEDICINE BATCH 2018 PHARMACOLOGYMica CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Receptors 2006Document31 pagesNuclear Receptors 2006lsintaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Lab Report AcetaminophenDocument5 pagesLab Report Acetaminophenapi-487596846No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting BioavailabilityDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting BioavailabilityMalvinder SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch30MR The Organic Chemistry of DrugsDocument33 pagesCh30MR The Organic Chemistry of DrugsAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- SAR of Benzodizepines by Dr.P.B. MohiteDocument20 pagesSAR of Benzodizepines by Dr.P.B. MohitePRITAM ACHARJYANo ratings yet
- Notes-Unit 3 - Instrumental Methods of AnalysisDocument40 pagesNotes-Unit 3 - Instrumental Methods of AnalysisAlexis UthaNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument25 pagesAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Document166 pagesPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Adimera TsehayeNo ratings yet
- Reverse PharmacolgoyDocument55 pagesReverse Pharmacolgoyعبدالله الجزارNo ratings yet
- JuvabioneDocument13 pagesJuvabionePreeti Yadav100% (1)
- Major Alkaloids: Sources, Classes and ExamplesDocument3 pagesMajor Alkaloids: Sources, Classes and ExamplesKristine Lei RiveraNo ratings yet
- ANTI INFLAMMATORY Screening MethodsDocument7 pagesANTI INFLAMMATORY Screening MethodsBrajesh Thankamony67% (3)
- Medicinal ChemistryDocument24 pagesMedicinal ChemistrymeeraanushaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Drug DesignDocument2 pagesSummary of Drug DesignRahima Akter RakhiNo ratings yet
- CNS ReceptorsDocument28 pagesCNS ReceptorsSpaynkter100% (6)
- Research in Organic ChemistryDocument38 pagesResearch in Organic ChemistryAkindele O AdigunNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessDocument40 pagesAntidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument8 pagesHPLCAdi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsDocument52 pagesOrganic Synthesis Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsVirginia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Acetylcholine Stimulates Muscle Contraction in Guinea Pig Ileum and Atropine Diminishes The Extent of ContractionDocument2 pagesAcetylcholine Stimulates Muscle Contraction in Guinea Pig Ileum and Atropine Diminishes The Extent of Contractionleh.mo931580% (5)
- Pharmacology Practical Manual - Student Copy2Document11 pagesPharmacology Practical Manual - Student Copy2NareshNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Ergot AlkaloidsDocument143 pagesPharmacology of Ergot AlkaloidsParveen Hullon100% (1)
- Drugs: Drug - Target InteractionDocument10 pagesDrugs: Drug - Target InteractionAnil Choudhary100% (1)
- Cholinergic and AnticholinergicDocument77 pagesCholinergic and Anticholinergicsweta sumanNo ratings yet
- Revellionz'19 - Second Year Question BankDocument114 pagesRevellionz'19 - Second Year Question BankRamNo ratings yet
- Organ Bath ReportDocument13 pagesOrgan Bath ReportYusri Yusoff100% (1)
- Lecture 18-21 - Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesLecture 18-21 - Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemJedoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectros PDFDocument54 pagesAtomic Spectros PDFTukai KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsDocument48 pagesAntiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsNofa PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Insulin Analogues: Pharmacology and Clinical UsesDocument53 pagesInsulin and Insulin Analogues: Pharmacology and Clinical UsesNathanNo ratings yet
- Autacoid PharmacologyDocument38 pagesAutacoid PharmacologyAakkkNo ratings yet
- BioassayDocument4 pagesBioassayAddictedto Nonsense50% (2)
- Anxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Document38 pagesAnxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Peter Harris100% (1)
- 13-Opioids Lecture 1Document41 pages13-Opioids Lecture 1api-343631539100% (1)
- BIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFDocument7 pagesBIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFTammy StephanieNo ratings yet
- Receptors As Drug Targets PDFDocument66 pagesReceptors As Drug Targets PDFAubreyNo ratings yet
- Lectins - Function Structure Biological Properties andDocument22 pagesLectins - Function Structure Biological Properties andOrlando Pérez DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Cns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Document39 pagesCns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Mirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Program I KetoFastDocument33 pagesProgram I KetoFastAndre OhyNo ratings yet
- Pharma For StudentsDocument23 pagesPharma For StudentsDominic Reambonanza0% (1)
- Daftar 60 Item Produk Generik Kenaikan Hna 2019Document14 pagesDaftar 60 Item Produk Generik Kenaikan Hna 2019Nurul HeriaNo ratings yet
- Adult Critical Care IV Medication Infusion Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesAdult Critical Care IV Medication Infusion Sheet PDFihtisham1No ratings yet
- Drug ListDocument3 pagesDrug ListluciNo ratings yet
- Stok Per TGL: DIV SUB Kode Produk Nama Produk SAT HNA Value Principal Kode PCPDocument2 pagesStok Per TGL: DIV SUB Kode Produk Nama Produk SAT HNA Value Principal Kode PCPOriza SafriniNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantsDocument8 pagesMuscle RelaxantsFemi AustinNo ratings yet
- Data Obat Emesys New UpdateDocument14 pagesData Obat Emesys New UpdateDhifa Mutia KiraniNo ratings yet
- Buy 4mmc Mephedrone Miaow Miaow Meow Meow Mkat Mcat BubblesDocument3 pagesBuy 4mmc Mephedrone Miaow Miaow Meow Meow Mkat Mcat Bubbleschemicals_uk201033% (3)
- Daftar Obat Obat IGD 1Document4 pagesDaftar Obat Obat IGD 1Novi YuliantiNo ratings yet
- 5.so RF Mei 22Document48 pages5.so RF Mei 22shalmaNo ratings yet
- PT Axelor Ultima Management 1Document72 pagesPT Axelor Ultima Management 1titin gusmayantuNo ratings yet
- 344 drugs banned by Indian Ministry of HealthDocument10 pages344 drugs banned by Indian Ministry of Healthfreelancer800100% (1)
- Obat High AlertDocument5 pagesObat High AlertChia GracellaNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Tagihan Detail PortraitDocument8 pagesRekapitulasi Tagihan Detail Portraitanon_495464522No ratings yet
- Nama Disc C Harga COD @barang Baru Nama Disc C Harga COD Aventis/Hoech/R.PoelencDocument43 pagesNama Disc C Harga COD @barang Baru Nama Disc C Harga COD Aventis/Hoech/R.PoelencIntanRatnadii Ni PutuNo ratings yet
- Leprosy Summary of MedsDocument1 pageLeprosy Summary of MedsNikki LegaspiNo ratings yet
- CatinoneDocument32 pagesCatinoneanon_703837948100% (1)
- Psychotropic Substances List Update - 2018Document1 pagePsychotropic Substances List Update - 2018Ivan BaleticNo ratings yet
- SKU SKU Name Qty Satuan Jual Sales PriceDocument39 pagesSKU SKU Name Qty Satuan Jual Sales PricePhani SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Patient medication scheduleDocument19 pagesPatient medication schedulefarmasi rsud cilincingNo ratings yet
- Daftar Formularium Obat di UPT Puskesmas RandulawangDocument7 pagesDaftar Formularium Obat di UPT Puskesmas RandulawangutamiNo ratings yet
- Cafer's: Mood Stabilizers and AntiepilepticsDocument67 pagesCafer's: Mood Stabilizers and Antiepilepticskaw gdNo ratings yet
- Amine classification and nomenclatureDocument2 pagesAmine classification and nomenclaturehaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Klinik Hadeli SariDocument13 pagesDaftar Obat Klinik Hadeli Sariardykuncoro.oNo ratings yet
- To Place An Order Call - 0800 919 312 Retail Price ListDocument9 pagesTo Place An Order Call - 0800 919 312 Retail Price ListKhongorzul MendbayarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Narkotika: NO Nama SatuanDocument5 pagesDaftar Obat Narkotika: NO Nama Satuanhernandi denkgNo ratings yet
- Rencana Distribusi Obat PuskesmasDocument58 pagesRencana Distribusi Obat PuskesmasLita Rahma YulitaNo ratings yet
- 68922Document40 pages68922arnidaNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines ToxicityDocument19 pagesBenzodiazepines ToxicityNagendra NayakNo ratings yet