Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Real Reactive Apparent Power
Uploaded by
hafiz_jaaffarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Real Reactive Apparent Power
Uploaded by
hafiz_jaaffarCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Engineering Foundation
Real, Reactive and Apparent Power in AC Circuit
P = V*I
DC Circuit
AC circuit more complex
Phase different between V and I
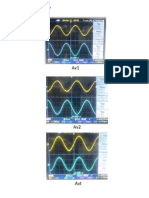
The Instantaneous Power supplied to an AC cct still P = V*I V = Instan. Voltage I = Instan. Current
Average Power supplied to the load will affected by the ( = phase angle between V and I)
I DC Voltage source supplying a load with resistance R
+ -
VDC
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
I AC = I-o + Z =Zo AC Voltage source supplying a load with resistance Z =Zo
VAC = V0o
Inductive Load = +ve Current LAG the voltage by degrees.
o V I Lag V I The voltage applied to this load v(t ) = 2V cos t v(t ) = instant voltage V = Vrms 2V = V peak
Capacitive Load = -ve Current LEAD the voltage by degrees.
I o I Lead V V The voltage applied to this load v(t ) = 2V cos t v(t ) = instant voltage V = Vrms 2V = V peak
The current flowing to this load i (t ) = 2 I cos(t ) I = I rms
The current flowing to this load i (t ) = 2 I cos(t + ) I = I rms
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
Power in AC
From Inductive Load P(t ) = v(t )i (t ) = VI cos t cos t (t ) = VI cos (cos 2t + 1) + VI sin 2t sin where VI cos (cos 2t + 1) > Component 1 VI sin 2t sin > Component 2
The components of power supplied to a single phase load versus time. The first Component represents the power supplied by the component of current in phase with the voltage, while the second term represents the power supplied by the component of current 90o out of phase with the voltage
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation The 1st term of the instantaneous power expression is always +ve, but it produces pulses of power instead of a constant value. The average value of this term is
P = VICos
This is the AVERAGE or REAL POWER (P) supplied to the load. The unit of real power are WATT (W)
1W = 1V * 1 A
The 2nd term of instantaneous power expression is +ve half and ve half so that the average power supplied by this term is zero.
This term represents power that is first transferred from source to the load, and then returned from the load to the source.
It is known as REACTIVE POWER (Q) Reactive Power represents the energy that is first stored and then released in the magnetic field of an inductor or in the electric field of a capacitor.
The Reactive Power of load is given by
Q = VISin
The unit of Reactive Power is volt-amperes reactive (var).
1var = 1V * 1A
is the impedance angle of the load for both cases (Active Power and Reactive Power)
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
Apparent Power (S) is the product of the voltage across the load and the current through
the load whereby the phase angle are ignored.
S = V*I
The unit of Apparent Power is volt-amperes (VA)
1VA = 1V * 1A
S Q P
Relative Forms of the Power Equations
P = VI cos (1) Q = VI sin (2) S = VI (3) if a load = constant V = IZ substituting to (1), (2) and (3) P = I 2 Z cos Q = I 2 Z sin S = I 2Z Z = magnitud of the load impedance Z = R + jX = Z cos + j sin
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
Complex Power (S)
S = P + jQ Complex Power, S supplied to a load can be calculated from the equation below
S = VI* let V = V I = I
(I* = I conjugat)
= (V )( I ) = VI( ) = VI cos( ) + jVI sin( )
=
S = VI cos + jVI sin = P + jQ
The Relationship between Impedance Angle, Current Angle and Power Inductive Load
Has a +ve impedance angle , since the reactance of an inductor is +ve The phase angle of the current flowing through the load will lag the phase angle of the voltage across the load by .
I=
V V0 V = = Z Z Z
Load is said to be consuming both real and reactive power from source.
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation P
I AC = I-o + -
Q Z =Zo
VAC = V0o
Capacitive Load
Has a -ve impedance angle , since the reactance of an inductor is -ve The phase angle of the current flowing through the load will lead the phase angle of the voltage across the load by .
I=
V V0 V = = Z Z Z
Load is said to be consuming real power from the source and supplying reactive power to the source.
I AC = I-o + -
Q Z =Zo
VAC = V0o
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
The Power Triangle
P S Q sin = S Q tan = P
cos =
cos = cos(-), so the power factor produced by an impedance angle of + is exactly same as the power factor produced by and impedance angle of .
So we cannot know whether a load is inductive or capacitive from the power factor alone.
Then the current leading or lagging have to know whenever a power factor is quoted.
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
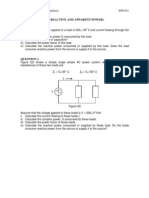
Example
Figure below shows an AC voltage source supplying power to a load with impedance Z = 20-30o . Calculate the current, I supplied to the load, the power factor of the load, and the real, reactive, apparent, and complex power supplied to the load.
I + VAC = 1200o Volt Z =20-30o
By Fuad Latip 2006
Power Engineering Foundation
By Fuad Latip 2006
10
You might also like
- Fundamentals PQ Per Unit 2022Document33 pagesFundamentals PQ Per Unit 2022Shahwar AliaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument34 pagesUntitled Notebookriseupwarrier59No ratings yet
- 02 - Chap 2 - AC Power Analysis - 2021CDocument68 pages02 - Chap 2 - AC Power Analysis - 2021CZhong Kiat TehNo ratings yet
- 1) Electrical Department, Sepuluh Nopember of Institute Technology Surabaya, 60111, IndonesiaDocument45 pages1) Electrical Department, Sepuluh Nopember of Institute Technology Surabaya, 60111, IndonesiadimasfupNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- EPE491 - Power in AC CircuitsDocument12 pagesEPE491 - Power in AC CircuitsNabill HpNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument19 pagesELECTRICITYSiddhant RSNo ratings yet
- Electric Terms DefinitionDocument8 pagesElectric Terms DefinitionGolu kumarNo ratings yet
- Voltage ControlDocument25 pagesVoltage Controlbenson215100% (1)
- 3 Phase Power AnalysisDocument31 pages3 Phase Power AnalysisMeiliana Cendra AsihNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Ac Circuits (Lecture 2) : 1 EPO460 March 2013Document17 pagesFoundation of Ac Circuits (Lecture 2) : 1 EPO460 March 2013Hazizi KhairyNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Research PaperDocument9 pagesA Comprehensive Research PaperInsik Agir ZernaNo ratings yet
- Crest Factor, Power Factor, and Waveform Distortion: An Environmental Potentials White PaperDocument9 pagesCrest Factor, Power Factor, and Waveform Distortion: An Environmental Potentials White PaperChristian MerchanNo ratings yet
- EES (Lec17)Document13 pagesEES (Lec17)Muhammad SagheerNo ratings yet
- L2-BEKG2433-Single Phase Part2 PDFDocument22 pagesL2-BEKG2433-Single Phase Part2 PDFAhmad WahiNo ratings yet
- EEE Module - 2Document48 pagesEEE Module - 2G46Anand P KNo ratings yet
- 2 - 209 - ACPower3PhaseAC Power - 7may2014Document23 pages2 - 209 - ACPower3PhaseAC Power - 7may2014gazpeitia1No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 Parallel RLC CircuitDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 7 Parallel RLC Circuitdoaah hakimNo ratings yet
- Konsep DasarDocument44 pagesKonsep DasarRahmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power Systems PDFDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Power Systems PDFSurender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Manual For Experiment-1Document13 pagesManual For Experiment-1Mrunali BarapatreNo ratings yet
- ESS - Calculation For Capacitive Power Requirement For Achieving Targeted Power FactorDocument3 pagesESS - Calculation For Capacitive Power Requirement For Achieving Targeted Power FactorPrasad GoreNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Improvement in 3 Phase AC Circuits: Experiment No 1Document9 pagesPower Factor Improvement in 3 Phase AC Circuits: Experiment No 1B M SinghNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument23 pagesAtomsAnand KNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Circuit ConceptsDocument31 pagesBasic Electric Circuit ConceptsPiyali BiswasNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument116 pagesElectric Circuit Analysismbuja mbujaNo ratings yet
- Motion in Electric Fields: SACE Stage 2 PhysicsDocument43 pagesMotion in Electric Fields: SACE Stage 2 Physicsrampravesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Power Circuits: Lecture Notes: EEE Instructor: Dr. U D DwivediDocument39 pagesThree-Phase Power Circuits: Lecture Notes: EEE Instructor: Dr. U D Dwivedieche120014No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6merrNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Circuits 1Document25 pages3 Phase Circuits 1JohnLaboguinNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Circuits 1Document25 pages3 Phase Circuits 1ايهاب غزالةNo ratings yet
- Components of Electric Power SystemsDocument21 pagesComponents of Electric Power SystemskpchakralaNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument29 pagesUntitled Notebookriseupwarrier59No ratings yet
- Review of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerDocument9 pagesReview of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerNormanSulimaNo ratings yet
- Chap31 PHYDocument19 pagesChap31 PHYAnand KNo ratings yet
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureDocument52 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureSreenath MNo ratings yet
- EE311 Notes+tutorialsDocument1,216 pagesEE311 Notes+tutorialslpl bobalobNo ratings yet
- On Solar CellDocument17 pagesOn Solar CellMab Sharma100% (2)
- Active, Reactive, Apparent and Complex PowerDocument26 pagesActive, Reactive, Apparent and Complex Powers.n.alzaabiNo ratings yet
- 7LABO Ganago Student Lab8Document37 pages7LABO Ganago Student Lab8Rocio Deidamia Puppi HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 1Document29 pagesChapter 1 - 1Nour Ziad Ibrahim AlkurdiNo ratings yet
- Control of Voltage and Reactive PowerDocument47 pagesControl of Voltage and Reactive Powerbluegreen02100% (2)
- Chapter-2 Electric PotentialDocument29 pagesChapter-2 Electric PotentialKpNo ratings yet
- The Operational Amplifier in CommutationDocument6 pagesThe Operational Amplifier in CommutationJugurthaHadjarNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power RequirementDocument3 pagesReactive Power RequirementPrasad GoreNo ratings yet
- Section 2: Power System Mathematics and Physics, Three-Phase, Power FactorDocument65 pagesSection 2: Power System Mathematics and Physics, Three-Phase, Power FactorKhuram TabassomNo ratings yet
- Quantities of Electrical EngineeringDocument12 pagesQuantities of Electrical EngineeringLarios, Miguel Angelo S. -CEANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Ac Power AnalysisDocument40 pagesChapter 3: Ac Power AnalysisSemifallenNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC P.E and ELECTRIC POTENTIALDocument43 pagesELECTRIC P.E and ELECTRIC POTENTIALJodi AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Single and Three - 2Document28 pagesSingle and Three - 2Rafiq_HasanNo ratings yet
- Complex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three PhaseDocument31 pagesComplex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three Phaseahmah2009No ratings yet
- ppt5 - Operational Amplifiers - ApplicationsDocument45 pagesppt5 - Operational Amplifiers - ApplicationsMichael Angelo BerjaNo ratings yet
- 17 - Electric FieldsDocument32 pages17 - Electric FieldsBONGLAV JemasonNo ratings yet
- BEE Module1 Chapter 1 Lec1-3Document70 pagesBEE Module1 Chapter 1 Lec1-3kali hembramNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory I - LecDocument137 pagesCircuit Theory I - LecAsaad MusaabNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance: UNIT-II: Chapter-02Document19 pagesElectrostatic Potential and Capacitance: UNIT-II: Chapter-02Teju tejasNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Transformers: 3.1 The Ideal TransformerDocument16 pages3.0 Transformers: 3.1 The Ideal Transformerhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1hafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line ModelsDocument5 pagesTransmission Line Modelshafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- The Per Unit SystemDocument9 pagesThe Per Unit Systemhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Background Theory: Power Engineering OverviewDocument8 pagesBackground Theory: Power Engineering Overviewhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine: Generator MotorDocument14 pagesSynchronous Machine: Generator Motorhafiz_jaaffar100% (1)
- 3 Phase SystemDocument12 pages3 Phase SystemAuji ZaharudinNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis (Short-Circuit Analysis) Definition of FaultDocument4 pagesFault Analysis (Short-Circuit Analysis) Definition of Faulthafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors: The Concept of Rotor SlipDocument12 pagesInduction Motors: The Concept of Rotor Sliphafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- DC Motors: RLB EDocument6 pagesDC Motors: RLB Ehafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- The Voltage Gain WaveformDocument1 pageThe Voltage Gain Waveformhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- 05442777Document4 pages05442777hafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Power AmplifierDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Power Amplifierhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Pspice LabDocument2 pagesPspice Labhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- ELE413Document6 pagesELE413hafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- Lab Am DetectorDocument2 pagesLab Am Detectorhafiz_jaaffarNo ratings yet
- KDM Elecricity SOP 1Document4 pagesKDM Elecricity SOP 1Reagan MkiramweniNo ratings yet
- Ounding and Shielding For Sound and Video PDFDocument37 pagesOunding and Shielding For Sound and Video PDFMoyGar2014No ratings yet
- Technical Manual: ATS115-ATS115PlusDocument103 pagesTechnical Manual: ATS115-ATS115PlusSeitec AssistenciaNo ratings yet
- Protection Theory of Power SystemDocument319 pagesProtection Theory of Power Systemdb04110100% (2)
- Lightning Protection For Equipment On MV FeedersDocument19 pagesLightning Protection For Equipment On MV FeedersArshad SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Royer Back Light CCFLDocument12 pagesRoyer Back Light CCFLPeter MossNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Current and Voltage TransformersDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Current and Voltage TransformersMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- 2nd PUC PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS - 2 PDFDocument6 pages2nd PUC PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS - 2 PDFRamya. R0% (1)
- Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College: Code No.Document4 pagesSree Vidyanikethan Engineering College: Code No.Nmg KumarNo ratings yet
- Testing of SEL-411L Relay PDFDocument42 pagesTesting of SEL-411L Relay PDFJavier Valencia Murillo100% (3)
- Budner 1970Document10 pagesBudner 1970Joyce SouzaNo ratings yet
- Altivar Machine ATV320 ATV320U15N4C DocumentDocument11 pagesAltivar Machine ATV320 ATV320U15N4C DocumentPhaniNo ratings yet
- And You: AC DC Shunts Can Believe Their Specs?Document6 pagesAnd You: AC DC Shunts Can Believe Their Specs?termmmNo ratings yet
- Catalogue en 31-01-2018Document125 pagesCatalogue en 31-01-2018LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Protection and Control Strategies For Blackout AvoidanceDocument22 pagesPower Plant Protection and Control Strategies For Blackout Avoidance北科大-林立No ratings yet
- 1MRK504113-UEN C en Technical Reference Manual RET670 1.2Document1,104 pages1MRK504113-UEN C en Technical Reference Manual RET670 1.2kaushikray06No ratings yet
- Laboratory Session 3 Single-Phase Transformers: Milwaukee School of Engineering EE-340Document10 pagesLaboratory Session 3 Single-Phase Transformers: Milwaukee School of Engineering EE-340Isabell GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Earthing Body Voltage 2005Document20 pagesEarthing Body Voltage 2005TorentSpy100% (1)
- ECE 451 Automated Microwave Measurements Laboratory Experiment No. 9 (Part A) Port Extension Method and TRL CalibratationDocument5 pagesECE 451 Automated Microwave Measurements Laboratory Experiment No. 9 (Part A) Port Extension Method and TRL CalibratationShiva MohammadzadehNo ratings yet
- EET308 Chapter 4 Lecture 1 - Updated 13 March 2016 - 0Document30 pagesEET308 Chapter 4 Lecture 1 - Updated 13 March 2016 - 0Mustafa AlfahadNo ratings yet
- Ut60e ManualDocument5 pagesUt60e Manualfacu0014No ratings yet
- Busbar ProtectionDocument16 pagesBusbar ProtectionDEADMANNo ratings yet
- Maxim Trimless Vco DesignDocument6 pagesMaxim Trimless Vco DesignVedran Ibrahimovic100% (2)
- Relay - Setting - P443 REV.3Document29 pagesRelay - Setting - P443 REV.3Noptana Tummasit100% (2)
- Tuned OscillatorDocument15 pagesTuned OscillatorPn Linda Mohd KasimNo ratings yet
- R5582E RELAY Selection GuideDocument14 pagesR5582E RELAY Selection GuideChandra Hamidi KautsarNo ratings yet
- Clamp Meter - Mastering The Art of Measurement - EN.r00Document65 pagesClamp Meter - Mastering The Art of Measurement - EN.r00Carl SundbergNo ratings yet
- Ac CircuitsDocument6 pagesAc CircuitsMurugeswariNo ratings yet
- 193 Sample-Chapter PDFDocument82 pages193 Sample-Chapter PDFAjwad Haziq100% (1)
- Transistors TutorialDocument3 pagesTransistors Tutorialarness22No ratings yet