Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iso27k Iso Iec 27002 Outline
Uploaded by
vishnukesarwaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iso27k Iso Iec 27002 Outline
Uploaded by
vishnukesarwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Information security
e and reporting is defined as
responsibilities the preservation
necessary of confidentiality,
to manage, integrity
control and direct and availability
information security of information ?
fLayoutInCell1fIsButton1fLayoutInCell1
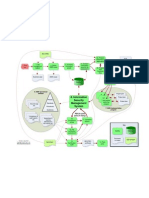
Outline of ISO/IEC 27002:2005
Prepared for the international community of
ISO27k implementers at ISO27001security.com
Version 1 28th November 2007
0 INTRODUCTION 6 ORGANIZATION OF INFORMATION SECURITY
0.1 WHAT IS INFORMATION SECURITY?
0.2 WHY INFORMATION SECURITY IS NEEDED?
0.3 HOW TO ESTABLISH SECURITY REQUIREMENTS
0.4 ASSESSING SECURITY RISKS
0.5 SELECTING CONTROLS
0.6 INFORMATION SECURITY STARTING POINT 6.1 INTERNAL ORGANIZATION
0.7 CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS 6.1.1 Management commitment to information security
0.8 DEVELOPING YOUR OWN GUIDELINES 6.1.2 Information security co-ordination
6.1.3 Allocation of information security responsibilities
1 SCOPE
6.1.4 Authorization process for information processing facilities
2 TERMS AND DEFINITIONS 6.1.5 Confidentiality agreements
6.1.6 Contact with authorities
ity controls3 directly address
STRUCTURE risks
OF THIS to the organization, therefore risk analysis is a starting point for designing controls.
STANDARD 6.1.7 Contact with special interest groups
3.1 CLAUSES 6.1.8 Independent review of information security
3.2 MAIN SECURITY CATEGORIES 6.2 EXTERNAL PARTIES
6.2.1 Identification of risks related to external parties
4 RISK ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT
ers, desktops and laptops.
6.2.2 Addressing security when dealing with customers
4.1 ASSESSING SECURITY RISKS
6.2.3 Addressing security in third party agreements
policies, standards, procedures
4.2 TREATING and guidelines drive risk management, security and control requirements throughout the organization
SECURITY RISKS
5 SECURITY POLICY
5.1 INFORMATION SECURITY POLICY
5.1.1 Information security policy document
protection
5.1.2 Review of the information security policy
Physical protection of computer and telecoms equipment including s
require adeq
employment
7 ASSET MANAGEMENT 9.2.4 Equipment maintenance
7.1 RESPONSIBILITY FOR ASSETS 9.2.5 Security of equipment off-premises
assets
7.1.1 Inventory of assets 9.2.6 Secure disposal or re-use of equipment
and after
7.1.2 Ownership of assets 9.2.7 Removal of property
7.1.3 Acceptable use of assets
Information
10 COMMUNICATIONS AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
7.2 INFORMATION CLASSIFICATION
Information security controls primarily within the IT service delivery function
10.1 OPERATIONAL PROCEDURES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
7.2.1 Classification guidelines
10.1.1 Documented operating procedures
Informing employees of their security obligations prior to, during
7.2.2 Information labeling and handling
10.1.2 Change management
8 HUMAN RESOURCES SECURITY 10.1.3 Segregation of duties
8.1 PRIOR TO EMPLOYMENT 10.1.4 Separation of development, test, and operational facilities
8.1.1 Roles and responsibilities 10.2 THIRD PARTY SERVICE DELIVERY MANAGEMENT
8.1.2 Screening 10.2.1 Service delivery
8.1.3 Terms and conditions of employment 10.2.2 Monitoring and review of third party services
8.2 DURING EMPLOYMENT 10.2.3 Managing changes to third party services
8.2.1 Management responsibilities 10.3 SYSTEM PLANNING AND ACCEPTANCE
8.2.2 Information security awareness, education, and training 10.3.1 Capacity management
8.2.3 Disciplinary process 10.3.2 System acceptance
8.3 TERMINATION OR CHANGE OF EMPLOYMENT 10.4 PROTECTION AGAINST MALICIOUS AND MOBILE CODE
8.3.1 Termination responsibilities 10.4.1 Controls against malicious code
8.3.2 Return of assets 10.4.2 Controls against mobile code
8.3.3 Removal of access rights 10.5 BACK-UP
10.5.1 Information back-up
9 PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY
10.6 NETWORK SECURITY MANAGEMENT
9.1 SECURE AREAS
10.6.1 Network controls
9.1.1 Physical security perimeter
10.6.2 Security of network services
9.1.2 Physical entry controls
10.7 MEDIA HANDLING
9.1.3 Securing offices, rooms, and facilities
10.7.1 Management of removable media
9.1.4 Protecting against external and environmental threats
10.7.2 Disposal of media
9.1.5 Working in secure areas
10.7.3 Information handling procedures
9.1.6 Public access, delivery, and loading areas
10.7.4 Security of system documentation
9.2 EQUIPMENT SECURITY
10.8 EXCHANGE OF INFORMATION
9.2.1 Equipment siting and protection
tems and data
10.8.1 Information exchange policies and procedures
9.2.2 Supporting utilities
10.8.2 Exchange agreements
9.2.3 Cabling security
Definition, management and control of access rights to networks,
security into the process for specifying, developing, testing, implementing and supporting IT systems
10.8.3 Physical media in transit 11.5 OPERATING SYSTEM ACCESS CONTROL
10.8.4 Electronic messaging 11.5.1 Secure log-on procedures
10.8.5 Business information systems 11.5.2 User identification and authentication
10.9 ELECTRONIC COMMERCE SERVICES 11.5.3 Password management system
10.9.1 Electronic commerce 11.5.4 Use of system utilities
10.9.2 On-Line Transactions 11.5.5 Session time-out
10.9.3 Publicly available information 11.5.6 Limitation of connection time
10.10 MONITORING 11.6 APPLICATION AND INFORMATION ACCESS CONTROL
10.10.1 Audit logging 11.6.1 Information access restriction
10.10.2 Monitoring system use 11.6.2 Sensitive system isolation
10.10.3 Protection of log information 11.7 MOBILE COMPUTING AND TELEWORKING
10.10.4 Administrator and operator logs 11.7.1 Mobile computing and communications
10.10.5 Fault logging 11.7.2 Teleworking
10.10.6 Clock synchronization
12 INFORMATION SYSTEMS ACQUISITION, DEVELOPMENT AND
11 ACCESS CONTROL MAINTENANCE
11.1 BUSINESS REQUIREMENT FOR ACCESS CONTROL 12.1 SECURITY REQUIREMENTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS
11.1.1 Access control policy 12.1.1 Security requirements analysis and specification
11.2 USER ACCESS MANAGEMENT 12.2 CORRECT PROCESSING IN APPLICATIONS
11.2.1 User registration 12.2.1 Input data validation
11.2.2 Privilege management 12.2.2 Control of internal processing
11.2.3 User password management 12.2.3 Message integrity
11.2.4 Review of user access rights 12.2.4 Output data validation
11.3 USER RESPONSIBILITIES 12.3 CRYPTOGRAPHIC CONTROLS
11.3.1 Password use 12.3.1 Policy on the use of cryptographic controls
11.3.2 Unattended user equipment 12.3.2 Key management
11.3.3 Clear desk and clear screen policy 12.4 SECURITY OF SYSTEM FILES
11.4 NETWORK ACCESS CONTROL 12.4.1 Control of operational software
11.4.1 Policy on use of network services 12.4.2 Protection of system test data
11.4.2 User authentication for external connections 12.4.3 Access control to program source code
11.4.3 Equipment identification in networks 12.5 SECURITY IN DEVELOPMENT AND SUPPORT PROCESSES
11.4.4 Remote diagnostic and configuration port protection 12.5.1 Change control procedures
11.4.5 Segregation in networks 12.5.2 Technical review of applications after operating system changes
11.4.6 Network connection control 12.5.3 Restrictions on changes to software packages
11.4.7 Network routing control 12.5.4 Information leakage
Integrating informa
porting,
diting
porting managing
compliance and legal
with learning
business-critical andfrom security
regulatory
processes for breaches
obligations,
reliability plus corporate
and contingency security policies
planning
12.5.5 Outsourced software development
12.6 TECHNICAL VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT 15 COMPLIANCE
12.6.1 Control of technical vulnerabilities
13 INFORMATION SECURITY INCIDENT MANAGEMENT
15.1 COMPLIANCE WITH LEGAL REQUIREMENTS
15.1.1 Identification of applicable legislation
13.1 REPORTING INFORMATION SECURITY EVENTS AND WEAKNESSES 15.1.2 Intellectual property rights (IPR)
13.1.1 Reporting information security events 15.1.3 Protection of organizational records
13.1.2 Reporting security weaknesses 15.1.4 Data protection and privacy of personal information
13.2 MANAGEMENT OF INFORMATION SECURITY INCIDENTS AND IMPROVEMENTS 15.1.5 Prevention of misuse of information processing facilities
13.2.1 Responsibilities and procedures 15.1.6 Regulation of cryptographic controls
13.2.2 Learning from information security incidents 15.2 COMPLIANCE WITH SECURITY POLICIES AND STANDARDS, AND TECHNICAL
13.2.3 Collection of evidence COMPLIANCE
15.2.1 Compliance with security policies and standards
14 BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT 15.2.2 Technical compliance checking
15.3 INFORMATION SYSTEMS AUDIT CONSIDERATIONS
15.3.1 Information systems audit controls
15.3.2 Protection of information systems audit tools
14.1 INFORMATION SECURITY ASPECTS OF BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT
14.1.1 Including information security in the business continuity
management process
14.1.2 Business continuity and risk assessment
14.1.3 Developing and implementing continuity plans including
information security
14.1.4 Business continuity planning framework
14.1.5 Testing, maintaining and re-assessing business continuity plans
You might also like
- 03 Information Security and Acceptable Use of ICT Policy v3 0Document16 pages03 Information Security and Acceptable Use of ICT Policy v3 0proftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- CISM BrochureDocument2 pagesCISM BrochureholaNo ratings yet
- Incident Management in Multi-Vendor Environment: Interview-Based Case StudyDocument50 pagesIncident Management in Multi-Vendor Environment: Interview-Based Case StudyarmandoparhusipNo ratings yet
- Module 7 AssignmentDocument13 pagesModule 7 Assignmentapi-360051483No ratings yet
- Shameless Insurance LTD' Case Study ISMSDocument6 pagesShameless Insurance LTD' Case Study ISMSSTANLEY HARRISON50% (2)
- Example/sample ISMS Scoping StatementsDocument1 pageExample/sample ISMS Scoping StatementsA ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ISO 18028-2 and ISO 27001/2 Contribution Document Structure: August 10, 2006Document22 pagesISO 18028-2 and ISO 27001/2 Contribution Document Structure: August 10, 2006Manohar KothandaramanNo ratings yet
- Information System Audit Guide: Australian Government Department of DefenceDocument39 pagesInformation System Audit Guide: Australian Government Department of DefenceParam StudyNo ratings yet
- ABC Technologies - Coursework Case StudyDocument13 pagesABC Technologies - Coursework Case StudyZaheer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Isms Doc 5Document3 pagesIsms Doc 5Natália Gomes100% (1)
- Getting Started with Building an ISO 27001 Compliant Cybersecurity ProgramDocument2 pagesGetting Started with Building an ISO 27001 Compliant Cybersecurity ProgramMarcio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Isms NotesDocument6 pagesIsms Notesvishnu.avasaralaNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 27001 2013 PDFDocument9 pagesChecklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 27001 2013 PDFKaran MehtaNo ratings yet
- ISMS RequirementsDocument6 pagesISMS RequirementsWellington Watanabe Filho100% (1)
- Using Business Impact Analysis To Inform Risk Prioritization and ResponseDocument24 pagesUsing Business Impact Analysis To Inform Risk Prioritization and ResponseCristian Gamonal CastroNo ratings yet
- Procedure On Risk ManagementDocument14 pagesProcedure On Risk ManagementRajagopal RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- ISMS Documented Information by Andrey Prozorov v.5.1 230305Document3 pagesISMS Documented Information by Andrey Prozorov v.5.1 230305kenyrNo ratings yet
- System Configuration and ManagementDocument138 pagesSystem Configuration and ManagementirsmarNo ratings yet
- ISO Network Management ModelDocument22 pagesISO Network Management ModelOkemwa Jared100% (1)
- Business Impact AnalaysisDocument11 pagesBusiness Impact AnalaysisCarlos RamosNo ratings yet
- Operational procedures and responsibilities documentationDocument19 pagesOperational procedures and responsibilities documentationIRIENo ratings yet
- Minimizing Disruption Maximizing Recovery: BS 25999 Business Continuity ManagementDocument5 pagesMinimizing Disruption Maximizing Recovery: BS 25999 Business Continuity ManagementEduardo Ramirez LasoNo ratings yet
- ISO27k ISMS Implementation and Certification Process 4v1 PDFDocument1 pageISO27k ISMS Implementation and Certification Process 4v1 PDFJMNAYAGAMNo ratings yet
- Internal - Audit Checklist ISMSDocument6 pagesInternal - Audit Checklist ISMSAnand BhattNo ratings yet
- Common Iso 27001 Gaps Issa0111Document4 pagesCommon Iso 27001 Gaps Issa0111nishu128No ratings yet
- ISO 27001:2013 Gap AnalysisDocument8 pagesISO 27001:2013 Gap AnalysisTSANIA MAULIDIANo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Create A Business Continuity PlanDocument11 pages7 Steps To Create A Business Continuity Planpragya pathakNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Business Continuity Plan - Industrial Field Lecico EgyptDocument41 pagesCyber Security Business Continuity Plan - Industrial Field Lecico EgyptshehabaldinNo ratings yet
- Project Plan For ISO 20000 Implementation: Subtitle or PresenterDocument11 pagesProject Plan For ISO 20000 Implementation: Subtitle or PresenterSwadhin PalaiNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001:2005 ISMS Implementation ChecklistDocument31 pagesISO 27001:2005 ISMS Implementation Checklistth3.pil0tNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 Contents List GuideDocument6 pagesISO 27001 Contents List GuideAngelo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Implementing An ISMS: The Nine-Step ApproachDocument13 pagesImplementing An ISMS: The Nine-Step ApproachevilsashoNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001-2005 AwarenessDocument14 pagesISO 27001-2005 Awarenessqadir147No ratings yet
- Business Continuity PlanDocument4 pagesBusiness Continuity PlanR HNo ratings yet
- Vijay - Challenges of An ISMS ImplementationDocument29 pagesVijay - Challenges of An ISMS Implementationshaheem_m100% (1)
- Doc02 - ISO 27001-2013 ISMS Manual TOPDocument22 pagesDoc02 - ISO 27001-2013 ISMS Manual TOPIRIE100% (1)
- Business Group Continuity Plan: Company AddressDocument31 pagesBusiness Group Continuity Plan: Company AddressSarfraz EPIC ConsultingNo ratings yet
- ISO27k ISMS 2 ISO27k Standards Listing 2022Document10 pagesISO27k ISMS 2 ISO27k Standards Listing 2022sungrayNo ratings yet
- ArmyTech ISMS PresentationDocument25 pagesArmyTech ISMS Presentationlaliaga30100% (1)
- Business Recovery EOC GuideDocument23 pagesBusiness Recovery EOC GuideAntonio JorgeNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About The ISO 27001 2022 Standard Update 1Document4 pagesEverything You Need To Know About The ISO 27001 2022 Standard Update 1Sudhanshu Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Tech Mag Business Continuity Sept06Document32 pagesTech Mag Business Continuity Sept06fuyeusNo ratings yet
- DWP Information Security PolicyDocument6 pagesDWP Information Security PolicyIkhlasAmbiarGuntaraNo ratings yet
- 405-2 - Kobal AVDF 12.1Document31 pages405-2 - Kobal AVDF 12.1NguyenNo ratings yet
- BCMDocument20 pagesBCMNOGENENo ratings yet
- Information Technology Audit Process - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesInformation Technology Audit Process - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasamyseriousNo ratings yet
- Er Sit Risk Assessment ReportDocument5 pagesEr Sit Risk Assessment ReportJefri ParaNo ratings yet
- Information Risk PDFDocument11 pagesInformation Risk PDFJose Carlos Laura RamirezNo ratings yet
- A1 ISMS Manual - v1Document13 pagesA1 ISMS Manual - v1Rharif AnassNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Roles and Responsibilities For Contingency PlanningDocument15 pagesISO27k Roles and Responsibilities For Contingency PlanningvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- IT Strategy OverviewDocument15 pagesIT Strategy OverviewEdwin G Garcia ChNo ratings yet
- Business Impact AnalysisDocument21 pagesBusiness Impact AnalysisJoel AFFIAN100% (1)
- Iso/Iec: Group 3Document37 pagesIso/Iec: Group 3Abdunnajar MahamudNo ratings yet
- ISO Audit IsacaDocument45 pagesISO Audit IsacaCosti Aldalou100% (1)
- OT Cyber Security Non-Conformance ManagementDocument14 pagesOT Cyber Security Non-Conformance ManagementKPNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 Annex A.9 - Access Control PDFDocument12 pagesISO 27001 Annex A.9 - Access Control PDFJeya Shree Arunjunai Raj0% (1)
- ISO27k Controls Cross CheckDocument6 pagesISO27k Controls Cross CheckChristen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Information Security Policy May 2020Document3 pagesInformation Security Policy May 2020Pullappa naiduNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Information Security Through ISO27001 (ISMS)Document31 pagesEnsuring Information Security Through ISO27001 (ISMS)jehanzebqamarNo ratings yet
- BSADocument1 pageBSAvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Toolkit Overview and Contents 3v2Document8 pagesISO27k Toolkit Overview and Contents 3v2vishnukesarwani100% (1)
- ISO27k Roles and Responsibilities For Contingency PlanningDocument15 pagesISO27k Roles and Responsibilities For Contingency PlanningvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Model ScopesDocument1 pageISO27k Model ScopesvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k SOA SampleDocument10 pagesISO27k SOA Samplevishnukesarwani100% (4)
- ISO27k Model Policy On OutsourcingDocument10 pagesISO27k Model Policy On Outsourcingvishnukesarwani100% (1)
- ISO27k The Business Value of ISO27k Case StudyDocument45 pagesISO27k The Business Value of ISO27k Case StudyvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Security Metrics ExamplesDocument10 pagesISO27k Security Metrics Examplesvishnukesarwani100% (3)
- ISO27k Organization of Information SecurityDocument5 pagesISO27k Organization of Information Securityvishnukesarwani100% (1)
- ISO27k Model Policy On Laptop SecurityDocument43 pagesISO27k Model Policy On Laptop Securityvishnukesarwani0% (1)
- ISO27k Model Policy On Change Management and ControDocument11 pagesISO27k Model Policy On Change Management and Controvishnukesarwani100% (1)
- ISO27k Model Policy On Email SecurityDocument6 pagesISO27k Model Policy On Email SecurityvishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k ISMS Implementation and Certification ProcessDocument1 pageISO27k ISMS Implementation and Certification Processvishnukesarwani100% (2)
- ISO27k ISMS Auditing Guideline Release 1Document35 pagesISO27k ISMS Auditing Guideline Release 1vishnukesarwani100% (2)
- ISO27k Implementation Guidance 1v1Document16 pagesISO27k Implementation Guidance 1v1vishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Information Classification GuidelineDocument1 pageISO27k Information Classification GuidelinevishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k FMEA SpreadsheetDocument28 pagesISO27k FMEA Spreadsheetvishnukesarwani100% (2)
- ISO27k Generic Business CaseDocument57 pagesISO27k Generic Business CasevishnukesarwaniNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Corrective Action ProcedureDocument2 pagesISO27k Corrective Action Procedurevishnukesarwani67% (3)
- Minggu 4 - JavascriptDocument58 pagesMinggu 4 - Javascriptcikiaaulia anisNo ratings yet
- Remedy API call log analysisDocument2 pagesRemedy API call log analysisLuis A. VarelaNo ratings yet
- Nissan 9 FullDocument2 pagesNissan 9 FullShahzee SoomroNo ratings yet
- Power System Vulnerabilities from DER Cyber AttacksDocument13 pagesPower System Vulnerabilities from DER Cyber Attacksyma ymaNo ratings yet
- Il 04300001 eDocument8 pagesIl 04300001 eA Angiie SilvaNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument43 pagesData Link LayerVenkatakrishnan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Acc We Gb000a Fire Safety BTHDocument12 pagesAcc We Gb000a Fire Safety BTHtienlamNo ratings yet
- Manual FL16Document37 pagesManual FL16leonardoNo ratings yet
- 312 Curtain WallDocument78 pages312 Curtain WallkalidindivenkatarajuNo ratings yet
- PTC Creo View Design Check DatasheetDocument2 pagesPTC Creo View Design Check Datasheetrlnjay2003No ratings yet
- Cable Fault DetectorDocument25 pagesCable Fault DetectorHarshalNo ratings yet
- 385045Document982 pages385045dilligas1234No ratings yet
- British Standards BS EN 50290-2-23-2013Document14 pagesBritish Standards BS EN 50290-2-23-2013rofe100% (3)
- Atp ProcedureDocument26 pagesAtp ProcedurePrima EvenNo ratings yet
- MIL std275 PDFDocument50 pagesMIL std275 PDFAnonymous b6JaSWYNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies of Reliance TelecomDocument37 pagesPricing Strategies of Reliance Telecomvenkataswamynath channa100% (9)
- Struts (Printable)Document63 pagesStruts (Printable)sakthimurugan_pNo ratings yet
- BS EN 12568 Foot and Leg Protector RequirementsDocument19 pagesBS EN 12568 Foot and Leg Protector RequirementsArif Hasnat JonyNo ratings yet
- 25d Double Searmer ManualDocument21 pages25d Double Searmer Manuallisya liputoNo ratings yet
- Create Your KML File by KML Editor 18517Document40 pagesCreate Your KML File by KML Editor 18517VIKAS DOGRANo ratings yet
- Iso 179 1 2023Document12 pagesIso 179 1 2023Quin TasyaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Multiplex ResistanceDocument21 pagesToyota Multiplex ResistanceYdelkadiasmela Dominguezmorel100% (4)
- Competency Presentation 1-9Document6 pagesCompetency Presentation 1-9api-483891682No ratings yet
- Experienced DGM seeks senior roleDocument5 pagesExperienced DGM seeks senior rolekavas26No ratings yet
- 7000 118-363, C1, R5 SUPREME AIS Installation Short InstructionDocument4 pages7000 118-363, C1, R5 SUPREME AIS Installation Short Instructionchefradio CFCARTHAGENo ratings yet
- As 62271.201-2008 High-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear AC Insulation-Enclosed Switchgear and Controlgear FDocument10 pagesAs 62271.201-2008 High-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear AC Insulation-Enclosed Switchgear and Controlgear FSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Product Standard: Specification For Re-Filling of Sf6 Gas CylindersDocument3 pagesProduct Standard: Specification For Re-Filling of Sf6 Gas CylindersGabriel Zenarosa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- DOORS DXL - Adventures in Microsoft OLE AutomationDocument32 pagesDOORS DXL - Adventures in Microsoft OLE AutomationLuci OpreaNo ratings yet
- Optical Transport Network Linear ProtectionDocument40 pagesOptical Transport Network Linear Protectionsanjay angadiNo ratings yet
- Ieee C57.12.90Document82 pagesIeee C57.12.90Cae Fue100% (8)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyFrom EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (421)
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetFrom EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)
- Excel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesFrom EverandExcel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesNo ratings yet
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellFrom EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerFrom EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- Learn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIFrom EverandLearn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Content Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessFrom EverandContent Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- How to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksFrom EverandHow to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldFrom EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesFrom EverandUltimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsFrom EverandDesigning Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize Your Website. Learn Effective Techniques to Reach the First Page and Finally Improve Your Organic Traffic.From EverandSEO: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize Your Website. Learn Effective Techniques to Reach the First Page and Finally Improve Your Organic Traffic.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Change Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemFrom EverandChange Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Balanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelFrom EverandBalanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessFrom EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataFrom EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)