Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solution Chap6
Uploaded by
Cheik Farouck SanaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solution Chap6
Uploaded by
Cheik Farouck SanaCopyright:
Available Formats
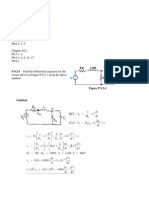
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.1 An u1charged 1 0 0 - ~ - t F cap cit 1' i chrug Cl by a constant
c1.1.rrent of I mA. Hnd tb v.o]tag aero s tb capacitm
after 4 s.
SOLUTION:
V(t)
-
-
'
V(-1)
-
-
V(:t)
-
-
V(r)
v
T
I
f
J_ (f)
dt
(
()
lf
I
J
I m cit
(00)-J..
0
I ['m(4)-0]
(00 _).)
Lfov
()9-{_
Lfov
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.1
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.10 Th voltage acmss a 25-!J..F capacitor j hown in
Fig. P6JO. Det rmin the cur1'ent w v f nn.
v(t) (v)
Figure P6.1o
SOLUTION:
t
1
- 0 2.
_2 = 0 -y 1)105
.1
3
= 08-rn.S
-*u =- I 'YYl s.
Js =- 1-2rns
0
)
/) __ ,._, , = 0
) V= LA \A..
) v= ro5 * v
) V=20V J l=-0
)
v= 6u- to
5
.::tv
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.1 0
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Problem 6.1 0
:k3 ~ - <1-t., , V=O J i:=- 0
. ~ v= -12ox ros x
J.C :t) =
0
25
0
-2'5
0
25
0
25A
;t<O
() ~ J < o2ml
0.2m.s s :t < oy ms
Ol.frm( ~ :t < a c9m s
0 gms. ~ J:: < 1-rr.s
)"rfi.s ~ 1: < 12mS
J: 7/ /2 rns
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.11 Th voUage aero sa 2-F capacitor is given by tb wav -
onn jn Flg. P6. ll . Fi.nd tb wav tlorm for th cun nt in
tlle capacit r.
vc{t) v)
- t2
Fi gure P6.11
SOLUTION:
-t<o
; v=O
J .i= 0
0 ( :t < 205
)
J- cdv 2(06)
ct:1:
J = /2A
2o s < f < 3 o ~
J
v=6o-2YfV
J= 2G2LtJ
J..- -::: - Lf ~ A
3 OS < i < 50-S
)
V= - 3o -t 06;t V
J=2[o6]- 12A
J 7 sos
) v:::::o
)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.11
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
J (.t)
-
0
ct <o
-
12A
0 <: J <
'los
2o.s <..:t
<
12A
< ;t < :ru.s
0
7 SDs
Problem 6.11
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6 . 12 The voltage .across a 2-jiiF c:apadt r j given by the wave-
form in Ag. P6.12. C mput th c11..1uent wavefonn.
v(t v)
2 3 6
- 11.2
Fi gure P6 . 12
SOLUTION:
t<o ) v-o
o < J: <.. 2 ms
2m.s <' x< 3ms
3 ms ( :t < 6 m.s
}
t ~ m s )
) v : -6 000 ;t v
l = C dV
ell
}
J = 2 u ( -6ooo)
J-= -12rnA
v= -I2V
._1 = 0
v = - 2Y-t LrooqJ V
.
J V=::O
1 vl=o
J( j:) -
()
-12rnA
0
gmP\
0
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
:t<O
0<1<1Y'Y'S
' 2 m ~ ( .1.. < 3rns
~ M s < .t < Gms
t 7 6ms
Problem 6.12
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.13 Dmw the warv form fort 1e cun nt in a capacitor
wh nth capacitor voltage is as described in Fig. P6.13.
v t (v
Fi gure P6.13
SOLUTION:
-t<o
)
J_==O
v= ;t v
L=c%'f
:t < IOOJ..,tJ
u.=
(2'-1}...{) (-2SXro
5
)
vl:::. -6A
I oo U S $ .:t < J 6 o u ) V = -5 2 + I 0
6
t V
3 I)
J - 24u [
=- / G A
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.13
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
s // 160JJS ) v=o
)
i==O
J.{ i)
-:::- 0
;t<O
J < 6 o)-JS
-2L.fA
60J.JS t
<
J6 A
/OO).J. S <. J6o)..1S
0
J- //(bOLLS
Problem 6.13
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
o o ~
....-....
<C
'-'
........
0
~
..........
- ~
-oo<-f
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.14 Th.e vo tag acms a 10-p.F capacit r i give.n by the
wav form in Fg. P6.14l. Plot th wav l!onn f 1' the
capac tor Clm' nt.
SOLUTION:
v(t v
Fi gure P6.14
V(.t) := 12 _2inw.f
w==2TI
I
2TL
I om
W::: 2 OO)[ 1"'-c:J./s
itt) = (\oM) (__\4.) (_w) Los. t.Ot
j__ U.) '; 7 S: '-1 (_o.t w-t "''V' A
t L-t) vs. t
- = : - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ~
;
\
\
I
\
~ . . - -
oOIS
\
0 005
001 .,
\
0'01
\
\
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.14
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.15 The warvefonn for the current ]o a capacitor is
howu in Fig. P6. 15. D tennine the wavefonn for the
capadtOl' voUag .
i(t) (rnA)
110
0 10 20 30 40 t ( ms)
Fi gure P6.15
SOLUTION:
t. < o } i{ x) = o
J V(:t)-= 0
) 1 ( :t ) :::: 0 2 5 .t
V(.:t) - d f J.(.t)dJ: -tVa
V{;:)
f 025 .d..t
\lc:t) -
>/ 40mJ ) lC:1) = o
'v(t) - Joct..t 1soo{ Yoh"'J'-
50 ,u.
V( 1.) == YV
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.15
2
V(t )=
Problem 6.15
0
'25DO.t
2
V
l-JV
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
::t<o
o ~ .:t < ltam s
.f 4 4 0 t n ~
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.16 The waveti rm f r th cmrent in a 50-p.F injfally
unch rged capac"tor shown in Hg. P6.16. D termine
th wav form or th capacit r 's voltag .
i(t) mA) .
10
0
0
-10
Fi gure P6.16
SOLUTION:
10 20 30 40 50 t (ms)
VcCtl - -t S Jc C:t J cU i V0
l(f) - /Omf\
Vcct)-=_1_ (lomrutv
0
50 ).A J
Vc(t) - 2oo_t + Vo
J.( 1)
-lornA
Vc(t) -
SD
vc{U = - 2oo t -+ Vo
~ o ~ t <o
Vc t.t-) = 0
Vc(t)
2 0 o ~ V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.16
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
'-{-o .?\. I am s :1: 'l o Y'Y'-S
Problem 6.16
Vc Lt) = -200.t t Y V
1 oms ..:t S. 3 o fY!.S
Vc (t) - 2 OO;t-- L( V
f lforru
- 200 .f: -t g v
4-0h- 4 J: S,. 5-0(Y).S
vcll) = - v
t 7 5ams
\; c c ;t) = ov
0
2 OO.t V
"-!- L- OO;i V
-Lf+ 100 v
? - L_oot..V
- L_OotV
0
-t<a
'
/DmJ $ :J $.. '2 OfYJS
20m5 $ 1
3orn5' j { lfc:::.ms
yo ms )::
roms Gums
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.17 The waveform for the cmrent flowi ng through th ! 0-J.l.F capaci t r in Fig. P6. l7a is bown in Fig. P6. 17b. If
Vc (t = 0) = 1 V, d tem1ine vc(t) at t = 1 ms, rns, 4 rns, and 5 rns.
SOLUTION:
i t) ( mA)
15 +------.....,
3 5
+
I I I
I I I
1 0 ~ F
1 2 4
- 10
(a)
Cb)
Figure P6. 17
VcCo)
lv
-);
Vc r :t)
- Vc (to J
-t
~
f
.i(r)d:t
c
tb
hn
Vc C o) -t 7 ) (lr;m) ctJ:
0
I vn
I"-+ J ( t5m)clt
I OJ-A
0
Vc ( lrns) -
Vc ( I rn s ) = ~ +- I '5o o ( 1 m )
Vc .( lms) - 25 V
I
t (m )
I
6
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.17
2
Problem 6.17
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
t
Vc(Jrns) = Vc. ( lms) -t- _.l_ f 15 md.:t
lo.u
lrn
t-
VcC3"'rllS) =-25 -ttooXIo
3
(1S'XIa
3
) CtJ]
lro
Vc C 1 ms) -= 2 5 + t 5bo [ t - I m J
Vc. ( 3 Y'r1 - 5 5 V
J:.
Vc ( C{ms) = \Jc C sm) +_I_ f -1 o 1"nd..:t
I 0 )..J.
)n"
J
Vc ( lf me; ) =- 5 5" X ( o o )( I 0 (-16 X I o)) [ ..t ]
3
vn
55- looo[.:t-3m]
Vc ( '-1ms) ::: 55- Joo o [ Ym-
;t
Vc. (5ms) = "t_/ J -lomcU
lop_
C,m .x
Vc C 5
== Lt 5 + 1 oo x , o3 ( -1 ox 1 c?) [ _t J
1-ft"n
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 3
Vc C 5ms) L-r5 -tooo [.x-LrmJ
Y5- tooo [5m- Ltm]
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.17
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.18 The waveform for the voltage aero 1 0 0 - ~ capacitor shown Fig. 6. l8a is given in Fig. 6.18b. Detemli ne the following
quantities: (a) the energy stored in the capacitor at t = 2.5 ms, (b) the energy stored in the capacitor at t = 5.5 ms, (c)
ic(t) at t = 1.5 m , (d) ic(t ) at t = 4.75 ms, and (e) ic(t ) at t = 7.5 ms.
v(t) 100 11F
0
~ ( 1 )
(a)
Figure P6.t8
SOLUTION:
v(t) (V)
(b)
c foour=-
(O-J UJ( t) =- _, c v1-c t)
2.
-
-
I
_L ( Joo.u) C 15 fl-
2
(b)
W(t)
-
( V
2
[t)
2..
LJJ ( 5"5niS)
we ss )'y)s)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
_)_ ( 100.4) (- 5 }L
2..
12.o mJ
Problem 6.18
2
Problem 6.18
(C)
/YI::: 15-5
"LX I 0- 3 - I X I 0-]
)'Y) = 10 J()-00
V(-J:)= /OOOO.t f g
lo = lm)+ g
13=
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
\J(;t) -= IDOoot - 5 V '1o9-t
et
V( t} =- I 0/)00 X t. - 5 VoJ.::t!
i, (i) -=. c
Jc (t )= fOOD., [loooo]
{lj = I A
( cLJ VC :t) =- -5 V '{ott -Hvz. 1 hfe1 voJ. ef-
= C (i.v Ctl
eXt-
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 3
icC:t} = oA
s-- 0
-=moo
Vc.t J =
5ooo :t + B
5 ==- 50oo( rn) t B
B= -35
vc f) 5 ooo.f - 35 V , nf-fovuJ
Ef
ic C;t)
c .t)
( C!VC.t)
clt
I oo 1J [ Sooo]
lc ( -=/5 ms) = os A
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6. 18
I
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.19 If vc(t = 2 s) = 10 V in the ci.rcu.it in Fig. P6. I9, find
the n:ergy tore in the cap.adtor and th pow r uppli. d
by til s me at t = 6 s.
3fl: 60.
Figure P6.19
SOLUTION:
6
V(J h) - L s 2. oLt i I 0
)._..
2-6V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
1
Problem 6.19
2
Problem 6.19
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
We u,J ::: fC [ "c f;hJ J 2
WcC .t1J =- f ( -t) [ 2(;]
2
Wc(1
1
) = /bq]
VR ( ct1) = J(-tt) -L [ J
VR (1L) =
Vs C tl) = Vc c tl) t vR.. C ;tL)
\Js ( .t 2- ) = 2_ Y
v c 1-'l) ::: 3 0 v
P
5
C:t2-) = \JsC:tl-) is
p ( ;t") = 0 c 2)
?s(-1,_)=-
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.2 A I2-jiiP capacitor has an accl n1Uiat d charg of 480 ~ J ~ . C .
Determin tb voltage acmss the capac"tor.
SOLUTION:
c
Q
v
v=
en_
c
v=
L( ~ 0 ~ _
I 2 JJ
V= lfov
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.20 Th cun nt in au inductor chnngeCI fmm 0 to 200 mAin
4tns and induce a voltage of 100 mV. What is the value
of the inductor?
SOLUTION:
Vc:tJ
L cU.' c .t)
Ckt
V==L
AT
n..t
[J.t -
L=
L=
L==
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
I oom ( Lfm -)
2oom
2.rnH
Problem 6.20
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.21 Th curr nt in a 100'-mH inductor is i( t) = 2 sin 377t A.
Rnd (a) tb voUage acm s tb indllctor and (b) th
ex:p.ress 'on fm th . enetgy sl:o1' dl io the ]em nt
SOLUTION:
(Q) V{t) = L di c J)
d..t .
V( t ) -:: 0 'I ( l ) ( ] 7 7 ) COS 3 ll
Vet> -
(b) w( :t) L
. 2(.1-)
k'
X_ (O I) [ 2 ~ i n 3 ll.* j 2-
wt
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.21
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.22 If the Clll'r ilt i(t) = 1l.5! A flows th.rough a 2-H
inductor, fi.nd th energy stored at t = 2s.
SOLUTION:
wt
2
LuC 2) = iC l) (_ t ~ ( 1.))
2-
'2
C ~ a p t e r 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.22
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.23 Tihe current in a is gi.ven by the
expres i.on
i(t)=O t < O
i(t) = 10{1 - e-
1
t) rnA t > 0
Hnd (a) the vo]tag acm the inductor and b) the
XJUe sion f 1' the tor d in "t
L(t)
-
IO(l-e-t)
SOLUTION:
(Q) V(J..)
L
di CtJ
eli
t<O
)
)
k /0
V(:t J
0 )
j: < 0
-..t
JJV
I f_ /0
25D
\b) wCtJ
_L Li
1
(:t)
2
w(:t)
- L o5 , t <o
1.
t
125 0-e ) IJ'J"
)
70
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.23
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.24 Giv 11 d1e data in the previ.on pr blem, wd the
voltage acros til indJJct rand the n rgy tored nit
after 1 s.
SOLUTION:
V ( t)
) :t 70
V( I)
w( f)
W(l)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
-1:) )_
125 ( 1--'
o 5 IJ-I
UJ , 70
Problem 6.24
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.2.5 Th curr 11t in -o-mH i11duct r is specified a
foUows .
i(t) = 0 t < 0
i(t) = 2te -
41
A t > 0
F".nd (a) the V ao acm induct r, ( ) the thne t
which th current i.s a maximum, and (c) d1 tim at
which th volt ge i a minimum.
SOLUTION:
i.(t) -=-oA ,
-4tA
i(l)-= 2.te
t <o
J t 70
\j L (t ) := CJ V
);t<O
(b)
r Ju t1 ~ wh.o.n i( 1:)
~ U J " ( J . . ~
d; c 1) 0
oil
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
) -;t 70
~
Problem 6.25
-
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.26 The vohag ac a 2-H inductor i g:iv 11 by th wave-
f rm hown in Fig. P6.26. Find tb wav form for the
ct tTent in the ]mluct r.
v t v
Fi gure P6.26
SOLUTION:
i (t) := _I_J V(:f) ill
L
V(.t) V-1 a. eac.J.1 {pan,
otncl :tlv- con btL. cu _.-
i{_t) =- jL * -t Io
L
t <o
0 ::{_ t s:: 2.5
J(t-)=2-t
2._ 5t- A
2
i C ;t) = Of 2 5 ( 1)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.26
S
S
S
S
s
s
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.27 Th voltage across a 4-H induct r i giv n by the
waveform h wn in Fig. P6.27. Find the wavef rm
forth cun ut in the induct r. v(t) = 0, t < 0.
v t
0 10 20 30 40 50 t(ms)
Fi gure P6.2]
SOLUTION:
i.{_i) = + J \1 ( J::) cU:
V(t) WN;l:Qr\t Qc.J>-OSS f:IY)"..Q,
0 ret i._ ( -) brt 0:
l( i) == :y_t + 'Io
L
-J: < 0 ) l ( t) = o
i (t) = 2Lfm t-
Y
L{ t) - Goot JJ-A
ton roms s f 1oms
J(t) :::: fOm)
i(:t) =
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.27
t
2
Problem 6.27
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
- b -= 6 oo :l - 6 M f\
J(t) = 12-)J.A
vi( t) = - 12-f6oot )).A
t ?/
vt(.t) = fg ).JA
-
0
600t J)A
b)-(1\
- 6 f6oot .UA
12M A
_,'L-+ 6 ool )JA
ltMA
t <a
0$ -J L... /0YY>'5.
1 o mJ .t 20'fY1J
20'MS t
] o m s .$ :): l.f Oyy-.J'
L( on1 r- S f r-orrd'
r 7/ 5bms
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.28 The vo tag aero a 10-mH ]nductor sh w.n in
Fg. P6.28. D renuine th wavelonn ~ r the inducto
Cli.UTent
v(t) (mv
10-
0 11
Fl gu re P6 .28
SOLUTION:
._jl (;t)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
.2
t (ms)
IO,k"Yn V
t s VL!t)c{i;
/00 J {Oj Oi
500 1
1
"m A
1 oo Jt-Jot t 2o) d..:t
-'-5o at L t '200t m A
Problem 6.28
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
t ( l'fr1S)
Problem 6.28
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.29 The current in a 10-mH inductor is shown in Flg. P6.29.
D tenuin.e th wav form for the voUag aero t 1
inductm.
i(t)
012 3 4 56
Fi gure P6.29
SOLUTION:
'\1'-+-) _ L di.Ctl
cU:-
) V(t)= 0
V(l)
0
-somv
6omV
()
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
-3omV
6omv
:t < 0
0(
Y'(\..5 <. t 6YY" 5
;t 7 6ms
Problem 6.29
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.3 A capaci.tor h.as an accumulated charge of 600 ~ C with 5
V acros H. What is th vah] of capacUanc ?
SOLUTION:
c
(Q_
v
c= 6 QO J-1.
5
c
-
110 uF
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.3
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.30 Th cnl'ent in a 50-mH induct r given in Fig. P6.30.
S!<;, lch the indu.ct r vol.tage.
i(t (mA
1 00 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
0
-1 00
Figure P6.3o
SOLUTION:
J-0"-'
V(.J) = L di (1)
elf-
0 < .:f 1.nts
vc ;t):::: 0
LYY1 s <( t lf))"LS
vc .1-) =
SOm [-5b]
V( :t) =
-25 v
Ltm.s
V(f) JOI"tl [50]
ms < t /OYY' s
'v(l) = :>om[- 50]
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.30
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
V( t)::.- 2 5V
\X:t)(V)
'"
2'5
~
.
y
le
~
6
8
11.
~ c
25
Problem 6.30
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.31 The lUTent in a - o-mH induct r i shown in Fig. P6.3l.
Fi11d the voltage .acros the inductor.
i(t ~ m A )
+10
0
Figure P6.31
SOLUTION:
V(:J)
{-o"-
-
-
L eLl l .:t)
cU
-t<O
V(i: )= 0
v
0 < J: ~ '20yyt<;
V(t) = 50TY1 [-I J
'v( t) = - 50/"() v
2-om S. S :t . YOYYI ~
V ( -J:) = 50)"() [I 5]
'v(:t-) = l 5 m V
Ltoms < .t:_ .::: 6om ~
v(:t) = Ov
6orns z t ~ lorns
Vl:t)= 50m[-1]
V(:J.)=
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.31
2
V(tJ
Problem 6.31
/lams
v( :1:) = ov
0\1
-somv
l5mV
0\J
-50)')'")\J
ov
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
-L ..( 0
0 <. !- ~ 20ri'-1
1 OY"il s ~ j. S: ltorns
YoYY1s .S t ~ 6o)'Y'IJ
6orru ~ ; t ~ (om')
t /lOY'f\.C
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.32 Dr, w the wavef rm. for the voUage acros a 24-mH
inductor when the inductor cun ntis given by lit wav -
rm t wn in Fig. P6.3 .
i(t) (A)
8
4
-2
Figure P6.32
SOLUTION:
V(f) L cit (f)
d.t
)
V(:JJ=-=0
V[-):) 2Ym [
V(t) 3lO')f)V
0 3 s < .J: $ 0 '6 s
V(:J-)
24m [ - 2 o]
\J(:t)
o6s < oqs
V{J) ::: 0
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.32
2
Problem 6.32
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
~ o ~ Oq :S < .k $ I IS
V(:1) =- 2Lrm [sc]
V(:t)= 12oom\J
~ . 9 1 . :t 71 IS
V(;t)-= ()
V( t) =
0
32orn\J
-ygomV
0
12oornV
0
t_.{ 0
0 (_ t ~ 0 3 s
o3s < :ts 06 s
0 6 s < :k ~ o q s
oqs< : t ~ lls
u / I Is
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
3
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
VCt)
vs.
;t
?
.....:14Jo:;
--J2o-
-loao
'
-8oo -
- boO
......- ~ -
-4oo ----
--200 -------------- - - - - ~ - -
..
,...
' l
.,
.._ ...._
-f\i lo
Oi. 04
0
~
.,.
0 ~ 10 I ~ 2
-
vol;' --
- ~ -
--
Problem 6.32..
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.33 The current in a jnductol' is given by tb
wav form in Hg. P6.33. Hnd the wavef nn for the
voltage acmss the in.ductol.'.
it (A
Fi gure P6.33
SOLUTION:
V(t) = L di(:t)
cit
{o9t
i 0
V(t-) =
[- 12 "X lo
3
]
-
V[tJ =
L t 5h"S
\.(t) =- 2Lfl11 [ 11- 1<16
3
]
V( -t) == 3V
5m.s. < f qm.s
V(t) ::::0\1
Cims
v(t) -= 2-Ym [ -IL.XI o
3
]
VLt) = -2 '9'tV
I hnS' L .t 12 )"Y)S
'v( t) = 2 Lfln [ I 2. X I J
V(i) = 2'? S V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.33
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
--f>oJL
t / /2rY"S
V(t)
::: ov
ov
v(t) 'V
0 t: s. 2h'L.S
z J: 5 rf\3
()V
5 rns < :i ..c s
- v
CjyY!_s ( :t II 'YYtS
IIYn5 <. t !'Lrll8
ov
t ?l2r0'S..
Problem 6.33 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.34 Th Cltnnt "11 a 4-mH .indlllctor i given by l:be
in Fig. P6.34. PI t the v Hage acros the indu t r.
i(t (mA) .
0. 12
1
0
t (ms)
Fi gure P6.34
SOLUTION:
ll;t) =
-120
,gin wJ:
J._.,tA.
w=
L.TI
T
T=
lrnS
w===
200011
..l
( -t)
= -120 A i Y'l
2.000 TCt
v c t) L cii C ;t:J
cU
V( J) y )'Y) [- 1'2 0 1--1 ( 2000 Jl) Co.& 2000 JT:): J
v(f:) - 3()2.. co.s 2oooJlt rnv
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.34
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
V(t) vs.t
~
:)
1..
,........,
>
~
0 ~
--..
......
-I
00015
'1
-2
-s
-y
-------------- - ~ - - - - - - - - - - - -
( ~ )
Problem 6.34 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.35 The waveform forth current in th 2-H inductor shown Fig. P6.35a is given in Fig. P6.35b. D termine the
following quantities (a) the energy stored in the inductor at t = 1.5 ms, b the energy tored in the inductor
at t = 7.5 ms, (c vL(t) at t = 1.5 m , (d) vL(t) at t = 6.25 ms, and vL(t) at t = 2.75 ms.
i(t) (rnA)
(a) (b)
Figure P6.35
SOLUTION:
w()
w(tSms)
w(I Sms)=
(b) w( t)
11_ L i
2
( t)
lo( 15 Y'A8)
!{_(2)
(C)
.t(t)=-
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
L &i Ct)
ru
3om A
Problem 6.35
2
Problem 6.35
vL(t)= 2[o]
VL(t) = OV
VL( 15r0s)= OV
(d) VL( ;t) - Lch(1)
clt
(1) :::
(Ct -f 60
VL(;t) = 20V
vL(b25ms) =-2ov
X I a-s - 2 X I a-s
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
A 1n tnKtvol
0 b I ntt sc...st
= -2(J
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
i.Lt):: -2ok te
.((t) -
3 D X I 0-
3
::: - 2 0 ( 2 !'t ICf 3) f g
&= CrOi
- 2at t Q 0 7 A tn ~ irtfi'r-val
e(- I ) ' \ j - ( ~
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
3
Problem 6.35
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.36 Find the pos ible capacitanc range of the foUowing
capacitOl's.
(a) 0.0068
1
jUJ. F with a of 10%.
(b) 120 pF with a tolerance of 20o/ .
(c) 39 wi.th a to] rnnce of 20o/ .
SOLUTION:
(O.) C = Q.(X)6 8' )..J. F
(b)
nanr--:
G I 2 r, F C s 7Y' 8' n F
(;('L c 7
c-=- 12opr:
Rnnr:j- ;
([) C -::: ] q ).J F w i :H-> 2 0 X tolrl -ya Q
Range,.
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.36
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.37 Fnd the po sibl inductanc range of the foUowiog
(a) ll O mH wHh a toleranc of W%.
(b) 2.0 nH wHh a toleranc of -%.
(c) 68 IJ-H with a to I ranee of 1 Oo/ .
SOLUTION:
(Ct)
L- {OmH wit--h fC)-tnuna
qY1H L /1-mH
(b)
L-=- 1 n H (J._)j th 5 % f&-lo1 G Ylt9..
lq Y'IH L '2 IY)H
(C)
L== 6 8' .L1 H w J 0 ;t-o.Q_t r O..Y
1
U.
6 ) '2 u H L a- Y 8.J.J t-f
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.37
2.24
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.38 Tt1e capndtor in Rg. P6.38a is 51 nF with a to]erance of
10%. Given tb voltage wavefmfll in Rg. 6.38b, graph
the cmnnt i ( 1) or the nuniml tn and maxin l tn capad-
t r va u s.
60
40
20
S'
..._.. 0
<:"
..._..
o;:, - 20
-40
SOLUTION:
c
(a)
t-
r-
1\
t-
v \
t-
\ J
'
v
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Time (ms)
{b)
i[t) =- c d v
clt
{a""' 0 (. .t
j_ l:t) = OA
I l'YU < f 2W'S.
-== t II{'Jln) {Lf')(I0'-1)-=-
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.38
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
2tYlS $ "3 ms
1 ( t) =- I J (51n) /OY) =yU i rnA
i"rninlt) = 09 ( SJn) (-'&'X 3(lmA
3rns-<. t .( Lfms
i-Ct) =at\
bO"t. LtY'ns < t 5 ms
imo.x Lt) -= \ \ ( 5 h,) IO '1) = 2-l Y "rYYI\
im;YlL;t):: OCf( 51YI) {Lt1-.fo'1)::: 18LfmA
..JOh 6 mJ
l(.t) =- 0 A
i(x) Cm")
1!\
3
'
2,ly ..
'
18'1
------ -----
.....
/
I
2
3 4 5 6 1
t
161.-
I I c.
----
441
t
-----
octc.
Problem 6.38 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
,
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.39 Giv 11 Ul capacitors in Fig. 6.39 ;u C
1
= 2.0 t.tF wi.th a
o]erance of 2o/ and C
2
= 2.0 p.F with a to]erance of
20%, find the foHowing.
(a) T 1e nonnnal value of Ceq
(b) T 1 minimum and maximum po sib]e vatu of
Ceq.
(c) T 1e p rcent enor of th minimum and maximum
vah es.
SOLUTION:
(9.)
(b)
o------i 1----1
cl
Figure P6.39
Cett =
c "YYC.J{
C 1.-'ldo-
6
) C 2- K Ia-' J
2 X ta-6 -t 2 X 10_,
(LD L1 X to-<:. ) ( lL(X /o-6 J
204,>\ I o-6 + 1Y ~ ~ o - 6
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.39
I
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
(C}
Problem 6.39
cnYM - ,,, .Ll r
CMin =- C
1
rnin C1..N1iYl
c, min cl-YY">;n
CM;n :- U96X la-
6
) ( l-b Xto-
6
)
( IY 6 X I o-<;) +
1
6 i-lo-
6
-r o /o ea---b - Ch1a.x-
cecv
T fo
-
, .. , 'XlQ_, - ;f 10-&
--+ % erro1
-% (!YYDV
IX lo-6
lo /o
-
Cm;Yl-
C e_q,
CectJ
08 Kl)( Jo-
6
- I '/do-
6
))(/0-6
-I f -q :;;
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.4 A ..:5-ptF capacitor laitiaUy charged to - 10 V i charged
by a constaRt curr nt o 2.5 IJI.A. Find til voltage across
the capacit .i after 2t min.
SOLUTION:
V(t-)
V(t)
V(J)
V( -t)
t-
+f
J- C :J-) ct:.t -t VC o)
0
150
_j_
f
25 jJ d1
-10
25 }..J
0
2 5 JJ- [I 50] - 10
25 }v{
5V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.4
,
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.40 T"he inductor in Fi.g. P6AOa i.s 4. 7 w h a tolel'anc
of 0%. G"ven lli CliH' nt waveform n Fig. 6.40b, gntrpll
the v tage v(t) for the III.inimum and n aximwn induc-
torv,h s.
(a)
f-
.--. 5
1 0
[7
\ J
\
I
\
I
I
- 115
0 10 .20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Tlrne
(b)
Fi gure P6.-4o
SOLUTION:
Vrrp_t L ;t) :::: ( 1 2-) ( '-{' {- 15) =- -';l.f6 1..1 V
Vm.-Y1Lt) Lfl,u.)(-15)= -546uV,
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.40
2
,
Problem 6.40
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
S:. t: Ltul'Y'&
V'(Y)Qt. { t):::: OlJ ( (o5) =: -2 8 2 J.-t V
V m i Yl ( .f) -::: (6 ( Lr 1LI) (- G 5 )= - I . 8 1-A V
Dh- YuYYlJ -;t 5 () YY"S
(t) = 02.) ( Lfl.u) (f)= 5 6'-f,
V m in ( f. ) ={ o. K ) l Y 1t.-t) ( I) = l .U v
5. t <
V(t) = av
v Ct) :::
ov
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
/
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 3
v<
'"
/
-
-
----....
2-f2
-
--- ._,.... --
so
l(o
lo
20 So
6o 10
-188
t(ms}
----
-2.
-
'""
- S6Y
-
...
'
' 2(
-----
-
1-
C=
F
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.40
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.41 If the t tal energy in t re circuit in Fg. P6.41 is
80 mJ what i.s l:h valll L?
200{} 80 p.F
Fi gure P641
SOLUTION:
.l c :::
c. dv,
L oUL.
1<2.. d '"J CoJJ
:tPu_
IPI
2oo..Q
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
l
;-
80.JJ - v
-::: o
) v (_
50{}
L ..t._
-----
A..h CA..
=o,
iL
..lj) a
'
[_ 't r-(.U...L:t"
-t
Vc.
Q...b:
conAJof\i
CD('-) -lo r.J
Problem 6.41
c
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Reey= ? oo 11 SD - 2 oQ{ 5-o)
Rea;::.
yo.J2
c I)( ~ 0 )
_L c v 1.
l.
20a+50
lAJc = k_ ( J'O J-.l) ( LID),_
We: GYmJ
,( L - ( LOO ) ( I)
2oo+5o
L L = D z A
WL=- ' ~ t _ LiL'l.
L=-
liiVL
.i_L
)...
WtotcU =
WL i We
WL =.
gem- 6 '-f YY1
WL =-
/6mH
L=
2..[ Ibm)
(p g )'1-
L::::. 5ornH
Problem 6.41 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.42 Find 1e val.ue of C i.f tb . energy in th ca adtor
.in Hg. P6A2 eqt a. s lhe energy stored in the indl1ctor.
c
0.1 H
Fi gure P6 .42
SOLUTION:
-t Vc-
c
l 00-fl..
12-V
1 oo.tl-
j_,_
0
.1 H
Ac. (_ d. Vc = 0 J Vc i.A 0 Co'N}:t1(\i
cJ.;I.
cliL =-o ,
leU
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Ci
-t Vc-
---.
I 00..>\-
JL
Problem 6.42
2
Problem 6.42
12
20oftoo
i L = Lt C.Ym A
2.-
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
c=
L(t5)
(::
o I ( C to->,f)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.43 Given th network in Fig. P6.43, find fu power diss]-
pat di in the 3-0. re i.stot' and th energy stored j u th
capacitor.
3fi
i 2 v
sn
2 F
Figure P6-43
SOLUTION:
.
VL
L
d.JL=O
)
L L .JJ'J
-
,
.A. c.
12. v
otA
c_ d V c. = o J v c ..J...A coru:taAt
Olt
GJL
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.43
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
'
.AR. /2-3'-
3f6
_g A
J.R -
]
We=
!{ C Vc 'l =
k_(2.)(12-)"'L
PR - iR
2
c ~ ) -= (- g / ~ ) l..( 3)
pR.-=- 2133 w
Problem 6.43 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.44 What va]{l s of capaci.tanc can b obtain d by intercon-
necting a 4-p.F capacitor, a 6-IJLF capac"tor, and a 12-IJI.F
capacitor?
SOLUTION:
Cet
l
1
l
--!i>
I
c.,
J c ~ Jc1
Ce1..1 -= C, + cL +c
3
-=
Lf).{ t 6 M t 12 L-1 =
2l...U F
1
Ce1}-
Ic,
Cetl-
---7 1 CL
C e . z ~ .
Tc!
Ce
2
2
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
-
-
_L -L_L -f J_
cl cl-- cs
_L +j_+_L
Lf..u
I:,V.
ll..U
2..uF
CC2. -tc
3
) C c, )
c,-t C1- t-C1
Problem 6.44
2
l
T
---}.
T c.
l
h
Cets
c1-
1
Jc'
Problem 6.44
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Cezt.t
-
c
3
t
c, c}_
c,-1- cl.
Ce
2
r., I \..t . '--1 J.J F
Ce1s-
- (C,tcJ ( C
-
C
1
4cl tc!
- 5 '15 ...u F
-
(CI+c
3
)Cc,_)
f LJ
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Ce21
)
c1-
I
I
1
Cect")
-
Ct(CLfCl)
-
C,-f c.J_ 1CJ
c,
=
p )..A F
Ceq, 8 :: c 1 c c I + c J )
C
1
-t c1_ + c
3
po-1sib&.<
2 2 ..u r
Ce12 :: '2uf
3 = 3 , 2- 7 )--(. f
c e.z"' ::. ,u F
C e1s :::. '5 4 5 LJ F
. L1<1t:,.UF
C et7 -= g }....t F
qu F
3
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.44
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.45 Given our cap< itors, lind th maximl m va1lle
aud minim111.m value tb,at can be obtain.ed by iutercon-
necth g th c. pac"to.r i.t ries/paraUe] combinations.
SOLUTION:
Clv\;Y\
?
l l
'
c1
cl.
C'1 c3
I I I
-' -t..Ltj_fJ_
c, c1.- c
1
cy
05)-.tF
u.ih-tn CU1 111
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.45
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
C ma_x. 8 .u. F
Problem 6.45 Chapter 6: Capacitance and lnd'uctance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.46 Giv n a l -, 3-, and capaci or, can. bey be inl:erooo-
nected to obtain an equival nt 2-11F
SOLUTION:
I ,.u_ F
Ceq_,-
( I X I o-
6
+ X I a
6
) ( Y X I o -t;")
)( lo-
6
-t Y Xlo-'
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.46
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.47 D tenu"ne the v iue of inductance that can be obl'lined
by intet'COIUl ct".ng a 4-mH a 6-mH inductor,
and a 1--mH induct r.
SOLUTION:
I
Le.t2.
---::::>
let,3
' -
----:)
L.t
\
j_+ ... L.:+ j_
L, Lt
2mH
Ll.
Leq,2 =
L1
L-,
Le.z_3
Let_3
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
L, + L1.... tL
3
2 )....-n H
L l. L!
-t Ll
L}__ + Lj
-
-
Problem 6.47
2
1
L e t ~
l
~ L
\ I
"">
~
)
L ~
L2.
I
I
L ~
LL
L ~ t '
---7
L,
Ls
Problem 6.47
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Lecv'-f = l L,+ L,J I J
Lez_Lt
-
( L, f L2-) ( L3) -
L, -f LL -t LJ
~ : :
5 L-f5 mH
Le.!s ::. L, Ll_ -t Ll
L
1
-t L
2
Le.!5 = IY'YY'nH
Ll
L e . . t ~ ::.
( L, ll L ~ ) + LL
le26 ==
L, LJ
+ L2.
l,+ L ~
le.t'
=qrn H
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
---;;>
= (LL f L,
L1t L,+ L
3
L,
Ll.
L3
=- ( L
1
+ L
3
) C L2J
. L
1
-t L l--t L
3
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
3
leq_? -= I '-1 y "r() H
qmH
le't7 == s L l m H
Leq,t -= Lt 3 m H
Problem 6.47
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.4.8 Giv; o f m 4--mH jnductors, det rmin the max.inmm
and tninimum vallues of inductan:c that c<1n b obtained
by illteroonnectil]g th.e inductor ill erieslparaU l
combinations.
SOLUTION:
L,
L ~
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6 ~ 4 8
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.49 Given <1 6- , 9- and 18-mH lndlnctor, can th y
"ntetomulecred to obtaill an equi.val nt n -mH indll.ctor?
SOLUTION:
:: \ 1 mH
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.49
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6 .. 5 Til energy that i.s stored in a 2 5 - ~ F capacitor i.s w t) =
12 si11
2
377t. Find the current in til: capacUor.
SOLUTION:
w(t) _L c V
2
(f)
2
Lu( j_-)
-
12 Sl.n
2
3ll ;;t
V
1
C)
-
c /2_ s;i;?31l t) (2)
25 X \o-
6
V( :t)
-+
ql Cf S' Sin 377 :t
C c1 V( :t-)
d.:t
v
J-(1:) ::: ( 25X to-t:) [ T q 1q. ~ (311) cos31l.:t J
j(f)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.5
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.50 Find th . tot, I. c pacitance Cr of tb iletw rk itl
Fig P6.50.
1
Cr ---
2 fl.F 3 IIJ>F
Figure P6.so
SOLUTION:
1
/..u_F
\----It-
')uf'
. ....__ _ ___..
,-
j,uF"
}'-----'
C, = ( Lu-+ 2).(t 3u )( 4v)
c, =-
l.t.t -t l..Ll-1'1 ,Lt t 4/J
6 ).J ( '-f-U)
6u-t ltM.
C, + /1M
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.50
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6 . 51 Find the t tal. capac"tanc Cy of th network in
Fig. P6.- 1.
t
G T
Figure P6.51
SOLUTION:
c1
-c .___a...-c-'1-1 ...... _____.
C
1
= 1ul=' .)cL:::GuF 3MF;
Ct..t ::: Gt...U F ) C
5
= 6 U. F
C'=-
6.u. +c
1
c' y.u. i 6M. r1.uJ
Gu. +34
C'
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.51
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
c..'
T
JbuF
CT =
C/(6.u) -t-c,
c'-t 64
CT -
ML 6Lt)
T3J..-t
-
Gu+ 64
Cr
GuF
Problem 6.51
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.52 Hml the t tal capacitanc Cr shown in tb netwo1k in
Hg. P6.52 .
~ F T ~ . . . ____ c_ T_ ....... r _____ ____J T 2 ~ F
Fi gure P6.52
SOLUTION:
..
c, :: G M F ) c
1
= ~ JJ.. F
1
c3 ;; ~ .u. F)
1
Cy =- J 1-M F ) Cs-:::- 4 ,u r:- ) C
6
= 2 JJ FJ
QY'\Cl ( 1 ~ 2J..LF
C' =-
Ccs + c,) C C. to, 2. -t- c 3
CL-i+Cs+(&
C
1
(Lf_u+l2.J-t)(12_L..f) i-i,U.,
ll.u_ t y..U. + 2).{
C' -
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.52
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
I lc,
c.,
I
cl.
1
c1
T
t_Lt-_L
(/'
c..,
cl.
c._ I
-'
I
t
+_L_
c''
6J.A
C,f,..u
ll.u
c"
Cll l..U. F
Problem 6.52
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6. 53 Cmnpnt the qu]va] nt caprrdtance of Ute n tw rk ]u
Fig. P6. if a 1 the cap it are 4 ~ J . F .
'-'
;;: ::;::' ::::::::::
If
:::::: ::
1\
::: :::
,..,
Fi gure P6.53
SOLUTION:
c ' = c 2- +c J = '? J.J ,::-
I
I
lc
5
Cecv
I c,
~ c ~
J
~
c_l
I
C"=-
c c
1
I
261J.J F
cr+C
1
Chapter 6: Capacitance-and Inductance
Problem 6.53
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Problem 6.'53 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.54 Find CT n fu network in Fig. P6.54 if (a) th. switch is
op n nd (b) h swi.tch is do d.
SOLUTION:
(a)
1
3,f!!-F
Fi gure P6.54
Swi.J-01 op.en :
Cr
:)
C'=
~ p .
I
Tct
6J.J.-
~ c 2
b (3)
6-tJ
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
6 ,f!!- F
sMl
c ~
I
6u
J c ~
..
l c"
J
Problem 6.54
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
( b) S'wi-JC.h dO:\E'cL
Problem 6.54
C
1 c.l
3
..
J1
-
---.a....- ___ bM
C 6..U. I
lc,
I c''
T
Cr :::::- c'cu
c.'+ C''
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.55 In th 11 l:w rk in Fig. P6.5- md the capacHance CT if
(a) th switch i.s p nand (b ) th switch is do ed.
112 6 f1F
Cr -
3 f.i> F 112 !JI.F
Fi gure P6 55
SOLUTION:
c,
C6
c.= 61-fF Jcl=
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.55
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
(G.J Cr =
c,( C6 2
-t
C1-(Cy)
-I-
C3CCs-)
c,+c6 (2---tC..y
(T::
Gu(I?M) + ,, J.J._ ( 6.U )
+
b't-tf?u}
Gu-t-12..u 12),{ -t6u
6/...t-f 1U
(6) SwitCh cto.recL .
Cs
c'=
C c 2. tc
3
) C c'-1 +C
5
) = C 12)..{ + 6 r3J...tJ
cl t (
3
t cl.f+Cs IIJ..t +6u + 6U +J.M
Problem 6.55
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 3
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.55
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.56 Select tile value of C to p.roduce the d sired t tal
capac-Hanc of Cr = 10 in the c'_rcu' t i n
Hg. P6.56.
o------
l e
Cr = 10 f.LF
Figure P6.s6
SOLUTION:
Cr-= ( C
1
+ Cz._) (c)
c,+c)..+c.
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.56
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Problem 6.56
C = _CrC C
1
+ ck)
C
1
+C2- -cr
C== IOJ...t ( 8..u t I bu)
F u -t I l;.Lt - I
0
-4
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.57 S .ec t the vah of C to pmduc b , e ired tota]
capacitance of CT = 1 p.:F in the c"rcu"t in
Fi.g. P6.57.
0
Fi gure P6.57
SOLUTION:
"t
I
Cr
---4-
he
c,
T 1 Ct_
Cx -= ( C+ C J) ( C 4)
C+ cJ+ c'1
C'-1 ~ (Cr+Ct) ( ()
c tc, -1-c l.
Cr :::- ~ + C y
J c ~
Cy::: (C+C
3
)CC42 t CCrtCl-)(C)
ct c,-t c ~
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.57
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
lu= (CttJ..t)(Ju) -+ (tu-+2,u)Cc)
C t I Lt -t (l.J C -t I Ll + 2 LA.
Ct2u
I= Cfl + 3c
C+2 Ct-l
C t I + 3C ( C t l)
Ct-1
(Ct2.) ( C-+2..)
3C1--t- 5C. -3 ==-o
c = -5 :t ,)25-lt( st
L.( J)
c = -5 ::t 1-gl
'
c-= L(65 nF
Problem 6.57 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.58 Th tw capacHms ]n Fi.g. P6.58 were charg d and l:h 11
connected as hown. D tennine the eqniva1 nt ca aci-
tance, the "nitia1 voltage at the t rminals, and the t tal
n gy t .red in the 11etwork.
SOLUTION:
+
~ 4 ~ F
Fi gure P6. s8
C,: /2JAF
Ct ~ C1-- l1..Lt F
V-t 6::: 2
v = - yv
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
j
Problem 6.58
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Problem 6.58 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6 . 59 Th two capacitor shown in Fig. P6.59 hav been
connect d for som tim aud hav .reached their p.resent
values. Fnd VQ.
SOLUTION:
+
~ 4 ~ F
Figure P6.59
SQT'I\.a
CQ = cv
Co \Jo =- C,\1,
V
0
= y)..L( t bj
ll.u
V
0
= 533 V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.59
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.6 A capacitor i charg d by a constant curren.t of 2 mA and
r suUs in a voltage increas of n V in a 1 0- interval
\\rhat i.s th vatu of th c paci.tanc ?
SOLUTION:
12 = l_( ID)
c
C 2 X 1 0 ~ ( 1o)
12.
c 167 mF
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.6
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.60 The th.ree capadtor lmwo in Fig. P6.60 have e.n
co.IUJ!ected for orne Ume and have l' ached their present
vah s. Find Vi and v2.
+
vl
+
y.
Fi gure P6.6o
SOLUTION:
V,Ct)
'1 (t)
B,IJ!IF
+
4l ,pJF
12V
11.2V
v. -
-v.
2..
-t
12V
...L
c,
I
-
cl.
v
I -
cl
--
\J,_
c.,
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.60
2
Problem 6.60
v,:: CL VL
c,
c2- vL-tVl== 12
c,
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
v
2
-= ~ v
v,+g= 12.
V
1
::: 4V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.61 D term.in the inductanc at terminals A-B in th netw rk
in Fi.g. 6.61.
1 mHI 1 mH
B o - - - - - - ~
Figure P6.61
2mH
2 mH
SOLUTION:
A
lr
l ~
L I = L] = L6 = I YY\ H
L2..= I'L m ~
Ly = G mH J Lr- = L(mt-1
L l:: Lg =- lq ::: 2mH
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.61
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
LtmH
Le - L
L1 i-Lb-+ Ltt
Le = 3mH
Problem 6.61 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
B
A
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.62 Detenui.ne tb indue nc at te.rmi.1uds A-Bin the
network in Hg. P6.62.
1 mi-t
A
.2 mH
4ml-l
B
Fi gure P6 .62
SOLUTION:
L
1
=1mti
LAg ::: ~ yY) f ~ yY")
~ F I ~ =- b mH
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.62
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.63 Find the total i nductance at th terminals of tt1 n rwol'k
in Hg. P6.63.
SOLUTION:
Fi gure P6.63
CicrcuA! :
0 l'1
Ll.
'('
Sho9t..h.cl.
Lr == [c L'-11 -n., J /I L . .,
L r = [ ( I 2 ) I G m) + l-m J I/ Lt m
lr ::: [ 11 m(f>m) + J II Lf M
l2m-f6m
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.63
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Lr
Problem 6.63 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.64 Comput th equiv lent indm:: ta11c of th network i.n
Fig. P6.64 if an inductm's ar 4 mH.
SOLUTION:
~
Fi gure P6.64
lt
CL
b
c
La :::_L_, L_t._
L,-f LL
L1 LL.f
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Lf
b
c
2mH
Red oC.U..U i -rut
d-
c
Problem 6.64
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
-
L
-
b { y)
-r
2
-
e.ay
2-
-
"'(Y\.'t-1
-
Problem 6.64 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.65 Find Lr n tll n rwork in Fig. P6.65 {a) wi.th the w"tch
op u and (b) with the switch c o eel AU induct rs ar
12mH.
LT -.
Figure P6.65
SOLUTION:
Lr
---'}
L8
LLt
L1
leA.
(L 1-t Lg ) I J L6
24yy, J I 12m
Lo.
~ m H
Lb
(LL II L ~ )
12m I) I2W)
Lb
6mH
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.65
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
L
a.
Lr - [ ( LytLQ.) II C Lb + Ls) J + L1
Lr= [ct2m-tJ'rn) II a>'YltiLm)]+l2YYl
Ly=- (2o-m /IIZm) +12Yl-l
(b)
L,
Lr
Lb
Lt.,
-
Ls
Problem 6.65 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Lr = ( La II Ls ) + ( L6 I I Ly ) i L
1
Lr ::. ( 8m ll I 2.. m ) -t ( 6 m J J 12 rn)-+- 12 YYI
Lr-
3
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.65
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.66 Given. th 11 twork shown i.n fig. P6.6 , find , a ll
equ.ivai 11 indnctanc at terminals A-B w"tb
t rminai C-D bon circait d, and (b) the equival nt
inductance at termina]s C-D wi th tenninals A-B p n
cll'CilitOO.
20 mHI
6 mH
Figure P6.66
SOLUTION:
(a)
C-D s : h o ~
A
lLf
L
1
- 20 rnH ) L2. = 5mH
LJ =- )2mH
a rd.- LL.f = 6mrl
L,
L ~
L'-1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
D
Problem 6.66
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
l.J1R =
(_ ll II LL)
t ( L
3
II Ly)
lAg= ( 1o r-n 115m)
-t ( 11 m II 6 Y"() J
LAJ] =
g'mH
(b)
wd--l-1
A--e of-0n:
c
L ~
ly
b
Lc 0 = c L I + l L ) 11 ( LJ + ~ ' - f )
Leo= (2omt5m) I/ (1'lrnT6mJ
Leo = 25'rn ) I IFrn
LeD - lal.ilmH
Problem 6.66 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6. 67 Find the value of Lin l:be network in F'g. P6.6i so that
the total indudance L, wi.U b mH.
Ly -
Figure P6. 67
SOLUTION:
'lm:::
1m=
2 mHI
6 mHI
A
...
L
[c L II L 3 ) -t l2. J /I L 1
+ '-rn J /I 4rf1
[
( 6m)L
Ltm L t ~ m
Y'Y"n -r 6m ( L)
Li6m
+ 2W'\
L.m l6m+ 6m(L) J==-ym[6m(L) +lm]
L L+ 6m L+ 6m
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.67
2
(12 rn) ( L) + y m
Lf6m
~ 1 Y)'l)( L) -(6m) ( L)
Lt6m
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6m -t-(GYYI)L
L t Grn
2m
(bm) ( L)
-
2m ( L-+ 6Y') -
(Ym) ( L)
- }2 )A
-
L= 12J.A
Lrm
L= ~ 1 ' n H
Problem 6.67 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.68 .Ftnd the valu of Lin th 11 tw rk in Fig. P6.68 that
th valu of Lr will b mH.
2 mHI
Fi gure P6.68
SOLUTION:
2
L,
s
(
~ L
.
L-r
\LT 4L )
II L
y-tL
L-r
( L-+ YL) L
i...1tL
Lt 2-*
l.fL
y+L
LT-=
2L -+
L( L 1...
y-fL
l( \....f+L) -f- 2( 4+L) -t L.(L
LriL
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.68
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Problem 6.68
LT = 2l(LftL) + Y L ~
YtL
~ L t LL +S?t'LL t yL
YtL
l T = ~ L + '2LL -t Y L ')..
?L + L L t ~ -t'l..L
LT::: GL,_ + 2L
L
2
tiDL1.?
L T = 6 L 'L t ~ L
L
1
i IOL -tf
2L'l. -t 20l +I b
L( L 't - I'LL -I b = 0
L'l- sL-Y-=0
( L-LI) ( L -t I ) = 0
)
L===-1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.69 A 20-mH indtuctot and 1 -mH imJuctor are com1 . cted
in sedes with l -A curent urc . Find (a) th equiva-
l.e.nt 'ndl ctan.c and b) th motaJ 11 rgy stored.
SOLUTION:
JA
(b)
\N t4>-\:a..l
w
1
+ w,_
Yt_L1I'l. +){L2-IJ..
I; ('LOm)(1)2--t ,k'(ilm)(1)1.
/'L 1-
I G mJ
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.69
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6. 7 Th CUIIl'ent j n 1 00-!i-F capaci t r is sh wn n Fi.g. P6. 7.
D t rm.i ne th \V v f rm for th v ltage acr s th apa i -
or jf it j inillaUy 1.1.ncharged.
i(t) (mA)
10 P-----.
0 2
t (ms)
Figure P6.7
SOLUTION:
1
1
= 2mS
* <O
1
i=O J Qhd V=O
) l = Ia 'YYlA ) o.rd
L_W\
s
torn c:J..L
Joo.u.
0
2 N ~
V=
lcrm
[ t] lOOt V
IOO)J.
D
v = 02V
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.7
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
V(t) ov
J
:t<.o
lOOt V ,
02 v
Problem 6.7 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.]0 For tb network i.ll Hg. P6.70, Vs( t) = no c 377t v.
Find Vo(t) .
1 kO
+
Figure P6.7o
SOLUTION:
'
c
_l.,
C= l,t.Jf=""
a.rcl R = I k_Q_
Vs ( -t) ::: 12 0 C06 3 ll-t V
C ctVs
eLf
( irucu op- etm_p)
- Vo
-
~
V
0
=- - Q c clVs_
cit
Vo= -(I K) C /.Lt) Gl2o( j 77) cos ~ l l i ]
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6. 70
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Vo (t)
Problem 6.70
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.71 For tbe n twodc in Fig. P6. 71 cbo C l ch that
v
0
= -1l0 J v
5
dt .
Source mode'! C
Fl gu re P6.71
SOLUTION:
+
V
0
= - I o S VscU:
Vs-O
Recv
R s t 7 0 K. = f OK + l 0 1<.
Recy =- ~ 0 K.Jl.
-CdVo
cU
V
0
I fVsct.t
f<ettc
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.71
2
c-=
Problem 6. 71
I
10
12Sur
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
3
t
t
t
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Vo(t)
-2111 Stn37lt V
Problem 6. 72 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.73 Th circuit shown in Fig. P6.73 i known as a "D bo '
int grat r.
(a) Express the utput vol. age in t rms o. tb ' npu voU-
ag and circuit p ram ters.
(b) How j d1 D bo int performance differe11
t' m hat of a standard integrator?
(c) \Vhat kind of application w uld j u ti y d1 use of
tbi device?
-y
...
Fi gure P6.73
SOLUTION:
+
R
..
l's
+
Vo
-i
cr
R,.,
'
CO.)
V
5
-v,... C. JVA t
VA-Vo
R
CiT
R3
Vs. cdVA
+
VA-Vo.
-tVA
-
-
R
dl
. R
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6. 73
2 Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
Vs =
;z, R c_
d.Vo
-t 0 R1 R. -
R ) Vo
(( ,-t 12.,_
C}.J;:
(R,+RJ
-t ( R1 ) v
R ,+ r<,_ o
'vs =-
R,f?-.C
dVo t ( Rif<d - (!_
]Vo
R,-t-R.l..
cl.:t
R
3
( R.,-t.z..)
(b) the. c. w h.e. Y\ ;
Problem 6. 73
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
3
t
M n!l.tu prui Ji ve .
(c)
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6. 73
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.7 4 An integrator is required that ha the oiiowing
perf rman e
v
0
( t) = lcfl J dt
wher b capaci.tor val ue must b great r than
10 nF and the r si t r values mu t b gr at r than
10k.fl.
(a) Design tb int gratol.'.
(b) If ::!: 1 0-V uppUe are used, what are the maxi .mum
and minimum vah1.e of v
0
?
(c) S 1ppose = 1 V. \\'hat .i the rate of d1, l'lge of v
0
?
SOLUTION:
c
v.
=
rJ..
.,....,
J cU:
20flF
)
(<.1. -;:: 2...
rz Mft-
-
-
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.74
2
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
(b)
-tt0\1
(C)
\Is= IV
Problem 6. 7 4 Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.75 A driverless bile .i under deve]opm nt On criti-
cal i sue i braking, patticubdy at red lights. It d cid-
ed that th braking ffort shoul d d p nd on distance to
the tight (i f you're c] , you bett r top now) and peed
if you're going fast, you'll. need more brake ). Th
resulting design ation i
braking eff rt = Kt [ + K
2
x(t)
where x, the distance from th vebi.cle o th .i11te1s cdon,
i m asured by a ns ..r who output is prop rtionai to
X, Vsen.se = CiX. U SUp .!pOSition to l1 W that th circuit
in Fig. P6.75 can produc the brak"ng effort signal.
Ra
V euse
Figure P6.75
SOLUTION:
c
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.75
3
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.8 Th voltage across a 50-!J..F capacitor i hown io
Fig. P6.8. D tennine the current wav fomi .
v t v
Figure P6.8
SOLUTION:
i(t)
iC t)
50 ).A [ )000]
25omA
2 ms <: t- S:.. Llms
OA
LpYIS
<
?ms
i(t)
5o [- s-ooo]
i(t-)
-L5b
gms
IOm.s
j(t-) = OA
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.8
2 Irwin, Basic ,Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
loms /2mS
i(r) = 50..u. [ 5Qoo]
l(;t} = 25DmA
l(f)
-
-
(tn mA)
Problem 6.8
:t 7 /2m.s
iCt)-= oA
250
0
-250
0
250
0
0 :t :S 2ms
2ms :t Wrns
Lrms'
I a'rf"'6
/O'YnS :J:
12 YYIS
t- 7 I 2... m s
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
6.9 Draw the wavef rm fi .1!' the m'fellt in a 1 -j.LF capacitor
wh nth c paci.tor voltag i as described in Fig. P6.9.
v(t) (v)
12
t (fl-S)
- 8
Figure P6.9
SOLUTION:
l(t)
i(:t) = 2LJA.
6 u.S <.. t: IOJ.A.S
12.U [ - 5 'X/0
6
J
i (:t)
-6oA
lop-s :t .$. 16J.JS
i(:t)
j(:J.:) -= 16A
r / 16
i(J:.)=O
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Problem 6.9
2
'30
2..0
r------- -- ----
IO
0
-lo
,........
4:
-20
..._,
r--
+I.
-3,() ...........
-.(_
-40
-s-o
t----------- --
-60
-:to
Problem 6.9
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E
2YA.
-6oA
16 A
OA
i(:t) vst=
. ----------------------
D t 6 I-tS
6w s :t
!6J.AS
t>16us
------
20
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.FE-1
SOLUTION:
The correct answer is a.
Yes. The capacitors should be connected as shown.
F 2
F 4
F 6
eq
C
F C
eq
3
6 6
) 6 ( 6
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.FE-2
SOLUTION:
The correct answer is c.
}
= dt t i t q ) ( ) (
>
s <
s
=
s t C
s t C t
t C
t q
1 , 6
1 0 , 6
0 , 0
) (
C
t q
t v
) (
) ( =
>
s <
s
=
s t V
s t V t x
t V
t v
1 , 6
1 0 , 10 6
0 , 0
) (
6
) (
2
1
) (
2
t v C t w =
>
s <
s
=
s t J
s t J t x
t J
t w
1 , 18
1 0 , 10 18
0 , 0
) (
2 6
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 1
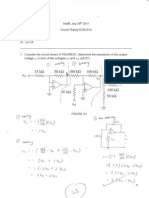
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.FE-3
SOLUTION:
The correct answer is b.
The voltage across the unknown capacitor C
x
is (using KVL):
x
V 8 24
V V
x
16
v C q
The capacitors are connected in series and the charge is the same.
C q 480 ) 8 ( 60
F
v
q
C
x
30
16
480
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.FE-4
SOLUTION:
mH 6
eq
L
mH 12
mH 3
mH 3
mH 9
mH 2
The correct answer is d.
m m m m m m L
eq
2 ] 3 6 ] 12 ) 9 3 [( [
m m m m m L
eq
2 ] 3 6 ] 12 ) 12 [( [
m m m m L
eq
2 ] 3 6 6 [
m m m L
eq
2 ] 3 3 [
m m L
eq
2 5 . 1
mH L
eq
5 . 3
Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9/E 1
Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance Problem 6.FE-5
SOLUTION:
The correct answer is a.
dt
t di
L t v
) (
) ( =
t t t t
te e e te
dt
t di
2 2 2 2
40 20 20 ) 2 ( 20
) (
= + =
| |
t t
te e m t v
2 2
40 20 10 ) (
=
>
<
=
0 , 4 . 0 2 . 0
0 , 0
) (
2 2
t V te e
t V
t v
t t
You might also like
- Irwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9E SolutionsDocument2,662 pagesIrwin, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 9E SolutionsCarlos Fuentes Miranda93% (75)
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (3)
- Ch06 SolutionDocument102 pagesCh06 SolutionSoji Adimula50% (2)
- Duarte Slidedoc DownloadDocument165 pagesDuarte Slidedoc DownloadCheik Farouck Sana100% (13)
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument309 pagesChapter 7 PDFMuhammad Abuzar Khan100% (1)
- Ch08 SolutionDocument240 pagesCh08 SolutionSoji Adimula100% (1)
- !solution Manual Linear Systems and Signals B P LathiDocument154 pages!solution Manual Linear Systems and Signals B P Lathijustme123273% (11)
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysFrom EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Service Manual Buses: Multiplex Electrical System Version 2 Wiring DiagramDocument112 pagesService Manual Buses: Multiplex Electrical System Version 2 Wiring DiagramEdwin U Jimenez SolanoNo ratings yet
- Neamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 011Document34 pagesNeamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 011greyiris7No ratings yet
- CH 13 Solutions Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesCH 13 Solutions Practice Problemssudarshan poojaryNo ratings yet
- Writing Good Requirements Ivy HooksDocument10 pagesWriting Good Requirements Ivy HooksCheik Farouck Sana100% (1)
- Corrupt IMEI and EFSDocument11 pagesCorrupt IMEI and EFSaldobnaNo ratings yet
- SB-104 SSB Transceiver - Operation Manual - Heathkit.1974.166sDocument166 pagesSB-104 SSB Transceiver - Operation Manual - Heathkit.1974.166sJose Luis Sesma100% (2)
- CH 08Document125 pagesCH 08jasohansen100% (1)
- Tutorial Unit 1Document2 pagesTutorial Unit 1mehul jindalNo ratings yet
- 4 PC 30 UDocument8 pages4 PC 30 Usadhanabhawani1278No ratings yet
- Ee281 HW4 SolutionDocument7 pagesEe281 HW4 SolutionEmel İremNo ratings yet
- Bme 516Document6 pagesBme 516Joseph SebastianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesMinYong SungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesRulierNo ratings yet
- G4PC50Document8 pagesG4PC50LidystonPeronNo ratings yet
- EENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnDocument7 pagesEENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnFredy AlbornozNo ratings yet
- IRG4PC50S: Features Features Features Features FeaturesDocument8 pagesIRG4PC50S: Features Features Features Features FeaturesPerica RakićNo ratings yet
- Jntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Document18 pagesJntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Krishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Pspice Tutorial AcDocument89 pagesPspice Tutorial AcZadziorNo ratings yet
- 67652-NilssonSM Ch07Document94 pages67652-NilssonSM Ch07fermisk1212No ratings yet
- Quiz Model Answer (C)Document5 pagesQuiz Model Answer (C)Profvip AbotalebNo ratings yet
- EIT Electrical Review SolutionsDocument19 pagesEIT Electrical Review SolutionsAleki MwauraNo ratings yet
- Irf 9 Z 24 NDocument9 pagesIrf 9 Z 24 NGiovanni Carrillo VillegasNo ratings yet
- T+ Fficv 1: Ivrwfinj 25 Ka 50 KF) ,,/100 KF, Tos KQDocument4 pagesT+ Fficv 1: Ivrwfinj 25 Ka 50 KF) ,,/100 KF, Tos KQCuong Nguyen ChiNo ratings yet
- Irg 4 PC 50 UDocument9 pagesIrg 4 PC 50 Uteam_madNo ratings yet
- Irg 4 BC 30 UDocument9 pagesIrg 4 BC 30 UJesus GongoraNo ratings yet
- IgbtDocument9 pagesIgbtKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Formula ShhetDocument10 pagesFormula Shhetandres2chNo ratings yet
- SOLA2540 - 9001 - Example Test - 2011Document3 pagesSOLA2540 - 9001 - Example Test - 2011AmitChopraNo ratings yet
- Strs6301 TV SonyDocument10 pagesStrs6301 TV SonyArturo NavaNo ratings yet
- Neamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 001Document13 pagesNeamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 001greyiris7No ratings yet
- EE206-1012, Midterm, EE206 PDFDocument2 pagesEE206-1012, Midterm, EE206 PDF820604jasonNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument40 pagesElectrical Engineeringankur_impsNo ratings yet
- Neamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 008Document17 pagesNeamen - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design 2nd Ed Chap 008greyiris7No ratings yet
- Circ 4Document66 pagesCirc 4musa100% (5)
- 4 PC 40 UDocument8 pages4 PC 40 Usadhanabhawani1278No ratings yet
- Irg 4 PF 50 WDocument8 pagesIrg 4 PF 50 WQuickerManNo ratings yet
- UMP Electrical Machine All QuizDocument11 pagesUMP Electrical Machine All QuizMuhammad Zulqarnain IskandarNo ratings yet
- GATE Electrical Engineering 2012Document25 pagesGATE Electrical Engineering 2012Mohammed Shafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment Answer SchemeDocument15 pagesAssignment Answer SchemeRight Luck100% (2)
- Rland RCDocument33 pagesRland RCSyed Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- MATH 1013 Applied Calculus Section D Fall 2012 Test 2/ November 5, 2012Document8 pagesMATH 1013 Applied Calculus Section D Fall 2012 Test 2/ November 5, 2012examkillerNo ratings yet
- Assignment All+Sem+II+20132014Document115 pagesAssignment All+Sem+II+20132014Azlin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework 4 SolutionJennifer100% (1)
- G 4 BC 20 KDDocument11 pagesG 4 BC 20 KDJuan Carlos Terrones NuñezNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator Transient Analysis: EE 4183 - Laboratory Practice VIDocument27 pagesSynchronous Generator Transient Analysis: EE 4183 - Laboratory Practice VIChathura DalugodaNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- SOCI ArntIaWomanDocument2 pagesSOCI ArntIaWomanCheik Farouck SanaNo ratings yet
- Bill of Sale: Attach The Court Order and Provide The Case Number Under The Seller/Transferor Name BelowDocument1 pageBill of Sale: Attach The Court Order and Provide The Case Number Under The Seller/Transferor Name BelowCheik Farouck SanaNo ratings yet
- Apple Partnership AgreementDocument6 pagesApple Partnership AgreementCheik Farouck SanaNo ratings yet
- We o 2015 Electricity Access DatabaseDocument6 pagesWe o 2015 Electricity Access DatabaseCheik Farouck SanaNo ratings yet
- 1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)Document26 pages1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)Tejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Solution Chap6Document142 pagesSolution Chap6Cheik Farouck Sana100% (2)
- Instructors GuideDocument55 pagesInstructors GuideskypaulNo ratings yet
- Sandeepani PDC VLSIDocument2 pagesSandeepani PDC VLSIAvinash BaldiNo ratings yet
- 1.5.4 Translator SoftwareDocument4 pages1.5.4 Translator SoftwareqamarmemonNo ratings yet
- GNS3 MikrotikDocument50 pagesGNS3 MikrotikGuido SullcaNo ratings yet
- Donaldson UK Manual TDS PDFDocument19 pagesDonaldson UK Manual TDS PDFPatricio TamayoNo ratings yet
- Scada FunctionsDocument46 pagesScada Functionspvenky_kkdNo ratings yet
- Eeeg 202Document2 pagesEeeg 202Sailesh DahalNo ratings yet
- ISAT-200 Installation ManualDocument49 pagesISAT-200 Installation ManualkamalmatsaidNo ratings yet
- MIPS Datapath Data MemoryDocument7 pagesMIPS Datapath Data MemoryMartin Fuentes AcostaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Software OptionDocument6 pagesOperating Manual: Software OptionEdgar PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Hi World!Document2 pagesHi World!Oliva MervzNo ratings yet
- Rotex COMPLETE Limit Switch Catalog 2013Document31 pagesRotex COMPLETE Limit Switch Catalog 2013Fikrinala MargaliuNo ratings yet
- Vickers ServoboardDocument8 pagesVickers ServoboardLuis JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Panasonic SA-MAX150PH, MAX250PH, SC-MAX150PH, MAX250PH PDFDocument118 pagesPanasonic SA-MAX150PH, MAX250PH, SC-MAX150PH, MAX250PH PDFboroda2410100% (1)
- FX05Document51 pagesFX05Sean Paul RoganNo ratings yet
- Owa31A Rugged DatasheetDocument2 pagesOwa31A Rugged DatasheetSteven FryeNo ratings yet
- Software Piracy Prevention: TheftDocument11 pagesSoftware Piracy Prevention: TheftSreedhara Venkata Ramana KumarNo ratings yet
- FUJITSUDocument485 pagesFUJITSUvijay yadavNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: P2PMOBILE: A Framework For Remote Execution in Mobile EnvironmentDocument12 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: P2PMOBILE: A Framework For Remote Execution in Mobile EnvironmentGibbs RodrixNo ratings yet
- Electric Actuator: SeriesDocument115 pagesElectric Actuator: SeriesDavid SaymonNo ratings yet
- En Security Chp3 PTActA AAA StudentDocument4 pagesEn Security Chp3 PTActA AAA StudentFnan KifluNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: GS 33K01A10-50EDocument17 pagesGeneral Specifications: GS 33K01A10-50Eabbutalibb5407No ratings yet
- PV Elite QuickStartDocument51 pagesPV Elite QuickStartYahiaNo ratings yet
- Cadre BarDocument45 pagesCadre BarakankwasaNo ratings yet
- Project in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRDocument9 pagesProject in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRRyan CireraNo ratings yet
- 13 GDocument12 pages13 GAhmad SardoukNo ratings yet
- WMT700 User Guide in English M211095EN HDocument210 pagesWMT700 User Guide in English M211095EN HJay SanchaniyaNo ratings yet
- Altronic Digital Pressure GaugeDocument2 pagesAltronic Digital Pressure GaugekaviarasuNo ratings yet