Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Uploaded by
Bern Jujoy BetayoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Uploaded by
Bern Jujoy BetayoCopyright:
Available Formats
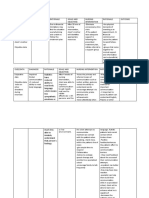
NAME Pritor
DOSAG E 40mg PO
CLASSIFICATION Angiotensin II antagonist used as an antihypertensive.
INDICATION This drug is used to treat hypertension, either alone or in combination with other drugs.
CONTRAINDICATION Biliary obstructive disorders, severe hepatic impairment. Fructose intolerance. Pregnancy (2nd & 3rd trimesters) & lactation.
SIDE EFFECTS CNS: dizziness, headache, fatigue CV: chest pain, peripheral edema, hypertension EENT: sinusitis, pharyngitis GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain GU: urinary tract infection Musculoskeleta l: myalgia, back and leg pain Respiratory: cough, upper respiratory infection Other: pain, flu or flulike symptoms
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Drugs that react on the renin angiotensin system can cause fetal and n e o n a t a l morbidity and death when given to pregnant women. These problems havent been detected when exposure has been limited to the first trimester. Use cautiously in patients with biliary obstruction disorders or Renal and hepatic insufficiency and in those with and activated Renin angiotensin system such as volume or salt depleted patients Monitor patient for hypotension after starting drug. Place patient supine
i f hypotension occurs, and give I.V. normal saline is needed. Most of the antihypertensive effect occurs within 2 weeks. Maximal blood pressure reduction is usually reached after 4 weeks. Diuretics may be added if blood pressure isnt controlled by drug alone. For patients whose renal function may depend on the activity of the r e n i n - angiotensinaldosterone system (such those with severe heart failure), treatment with A C E inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists has cause oliguria o r progressive
azotemia and (rarely) acute renal failure. Drug isnt removed by hemodialysis. Patients undergoing dialysis may develop orthostatic hypotension. Closely monitor blood pressure. Assess condition before therapy and reassess regularly thereafter to monitor drugs effectiveness Monitor for any adverse GI reactions, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Assess for adverse reactions For patient with hepatic encelopathy, regularly assess mental condition Monitor I & O
Lactulose
30cc at bed time
Gastrointestinal agent, hyperosmotic laxative
Patient who require a low lactose diet. Constipation, Galactosemia salmonellosis. Tre deficiency .Intestinal atment of hepatic obstruction encephalopathy
Abdominal discomfort associated with flatulence and intestinal cramps. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea on prolonged use.
monitor for Increase glucose level in diabetic patients Relief of pain including muscular, rheumatic, traumatic, dental, post-op and postpartum pain, headache, migraine, fever, dysmenorrheal Pregnancy &lactation, hypersensitivity, active ulceration or chronic inflammation of either upper or lower GIT, blood disorders, poor platelet function, kidney or liver impairment, children < 14 yrs GI discomfort, diarrhea or constipation, gas pain, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness
Analgesic Mefenamic acid 500mg PRN q6
Assess patients pain before therapy Monitor for possible drug induced adverse reactions Advice patient not to take drug for more than 7 days
Cardiovascular Beta-blockers Metoclopromide (plasil) 10mg IV
Gastrointestinal motility, nausea, vomiting of central and peripheral origin associated with surgery
GI hemorrhage, epileptics, hypersensitivity, lactation, patients with breast cancer
Restlessness,d rowsiness,fatig ue,insomnia,he adache,dizzines s,nausea
Advice patient to report immediately persistence or failure to relieve pain Give 30 minutes before meals and at bed time Assess mental status during treatment Tell patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities
Enteral Nutrition Isocal 5scoops q5
Nutritionally complete and well-balanced to provide the total dietary needs of most tube-fed patients. High calorie nutrition with less sodium content, suitable for people with sodium restrictions.
Contraindicated with: Pregnancy, lactation, children 1 year below and geriatrics
for at least 2 hrs Aspiration pneumonitis may occur with enteral tube feedings, and is more common in the elderly. Advice patient to avoid alcohol and other CNS depressant that enhance sedating properties of this drug
Celecoxib
Central nervous system agent, analgesic, NSAID,
Celecoxib is used for the relief of signs and symptoms of Arthritis Celecoxib should not (Osteoarthritis be given to patients and Rheumatoid Arthritis) in adults. who have
Celecoxib is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to celecoxib.
Particular attention should be given to water supply for comatose and Gastrointestinal unconscious patients disturbances m and others who ay also be a cannot express the complication of usual sensations of feeding tube thirst. use, with or without Additional water is pneumonitis. important also when renal concentrating ability is impaired, when there is extensive breakdown of tissue protein, or when water requirements are high, Diarrhea, as in fever. Dyspepsia, Headache, Upper respiratory tract infections, Assess patients
200mg 1 cap BID RTC
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, antipyretic
It is also used for the treatment of acute pain and menstrual pain. Celecoxib is also used to reduce the number of adenomatous colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis.
demonstrated allergictype reactions to sulfonamides. Celecoxib should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients Celecoxib is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surger
Abdominal pain, Flatulence, Nausea, Back pain, Peripheral edema, Dizziness, Rash
range of motion, degree of swelling, and pain in affected joints before and periodically throughout therapy. Assess patient for allergy to sulfonamides, aspirin, or NSAIDS. Patients with these allergies should not receive celecoxib. May be administered without regard to meals. Instruct patient to take celecoxib exactly as directed. Do not take more than prescribed dose. Increasing doses does not appear to increase effectiveness.
Advise patient to notify health care professional promptly if signs or symptoms of GI toxicity (abdominal pain, black stools), skin rash, unexplained weight gain, edema occurs. Patient should discontinue celecoxib and notify health care professional if signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, upper right quadrant tenderness, flu-like symptoms) occur. Shock. Gynecomastia, galactorrhea, hysterorrhea; anorexia, catharsis,
AntiInflammatories
Dompenyl
Symptomatic relief of acute nausea & v omiting. Treatment of nausea & vomiting caused by levodopa or
Intolerance. GI bleeding, perforation, prolactinoma.
Watch out for the signs and symptoms of the side effects
10mg 1 tab NGT
bromocriptine administration in Parkinson's disease.
constipation, celialgia, dipsia, vomiting. Extrapyramidal, circulatory & dermatologic effects.
Assess your patient (inspect, palpate, percuss and auscultate)
Inhibitor of Prevention of adenosine vascular ischemic diphosphate (ADP) events in patients with symptomatic athe rosclerosis Clopidrogel Acute coronary
In patients with hypersensitivity to drug or its components and in those with pathologic bleeding (peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage)
The tolerability of clopidogrel is similar to that of aspirin. Platelet aggregation Diarrhea, rash, wont return to normal or itching occur for at least 5 days
75mg 1tab Od
syndrome without ST-segment elevation (NSTEMI), ST elevation MI (STEMI)
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, commonly called "statins." Simvastatin 40mg 1tab PO
To reduce risk of death from disease and CV events in patients at high-risk for coronary events
Contraindicated with allergy to simvastatin, fungal by products, pregnancy, lactation
s in approximately 1 in 20 persons taking clopidogrel. Abdominal pain also occurs in about 1 in 20 persons, but it is less frequent than with aspirin. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, indigestion, and a general feeling of weakness. Rare side effects include joint pain, memory loss, and muscle cramps. Cholestatic hepatitis, hepatic cirrhosis, rhabdomyolysis and myositis have been
after the drug has been stopped Watch out for: drug can cause fatal thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura May be taken without regard to meals. Instruct the patient to notify prescriber if unusual bleeding will occur Assess nutrition. Fat, protein, carbohydrates Monitor bowel pattern daily Monitor triglycerides, cholesterol baseline throughout treatment Past liver disease, alcoholism, severe acute infections, trauma, severe metabolic disorders, electrolyte imbalances,
reported in patients receiving the drug chronically Antivertigo Drugs Betahistine (HCl) is primarily indicated in conditions like Hearing loss, Menieres disease, Tinnitus, Vertigo. 16mg PO TID Betahistine is contraindicated for people with peptic ulcers or tumours of the adrenal gland, such as pheochromocytoma People with bronchial asthma should be closely monitored. Headache. Low level of gastric side effects. Nausea can be a side effect, but the patient is generally already experiencing nausea due to the vertigo so it goes largely unnoticed. Decreased appetite, leading to weight loss Dizziness, headache, swelling of the ankles, feet or
elderly, renal disease
Betahistine
Avoid contact of oral solution or injection with skin Raise bed rails, institute safety measures, supervise ambulation
Calcium Channel Blocker
Management of chronic stable angina, angina du e to coronary artery spasm;
Patients w/ sick sinus syndrome or 2nd/3rd degree AV block except in the presence of a functioning ventricular pacemaker.
Monitor blood
Angiozen 60mg TID
alone or in combination, for the treatment of HTN.
Hypotension (<90 mmHg systolic), acute MI, pulmonary congestion. Lactation.
hand
pressure and heart rate when starting therapy and during dosage adjustments If systolic blood pressure is below 90mmHg or heart rate is below 60 bpm, withhold the medication and notify the physician. Advise patient to do hazardous activity
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Wound Healing SchwartzDocument37 pagesWound Healing SchwartzCarla Putri Chandra100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- BaytexDocument7 pagesBaytexArvind AkkNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Euro J of Neurology - 2021 - Van Den Bergh - European Academy of Neurology Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline On DiagnosisDocument28 pagesEuro J of Neurology - 2021 - Van Den Bergh - European Academy of Neurology Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline On DiagnosisSusana RocheNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Tanzania STG 052013 PDFDocument415 pagesTanzania STG 052013 PDFबनकर परिवाराचा लाडका गोट्या100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Glossary of Dental Clinical and Administrative TermsDocument38 pagesGlossary of Dental Clinical and Administrative TermsSarah TanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Kher 2017Document39 pagesKher 2017Evelyn LimNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Renr Study GuideDocument57 pagesRenr Study GuideJerilee SoCute Watts92% (12)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Mycoplasma Genitalium A4Document1 pageMycoplasma Genitalium A4Nauli NasirNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 13 Implant Supported Fixed ProsthesesDocument52 pages13 Implant Supported Fixed ProsthesesJúliaJulieNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Myopia ManualDocument337 pagesMyopia ManualRealPurgatory100% (1)
- TetricDocument14 pagesTetricNico LucaciNo ratings yet
- How I Do CMR Scanning Safely: Elisabeth Burman Research Sister Royal Brompton Hospital, London UKDocument41 pagesHow I Do CMR Scanning Safely: Elisabeth Burman Research Sister Royal Brompton Hospital, London UKYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Honey Badger WorkoutDocument10 pagesHoney Badger WorkoutJeff Ayres100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Country Presentation: CambodiaDocument11 pagesCountry Presentation: CambodiaADBI Events100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 6 Tecar Vs Tens in Phantom Limb PainDocument8 pages6 Tecar Vs Tens in Phantom Limb PainSilvia PluisNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 04.retrievable Metal Ceramic Implant-Supported Fixed ProsthesesDocument9 pages04.retrievable Metal Ceramic Implant-Supported Fixed Prostheses친절No ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry: Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument31 pagesMedicinal Chemistry: Chapter 1 Introductionderghal67% (3)
- Acute Diseases and Life-Threatening Conditions: Assistant Professor Kenan KaravdićDocument33 pagesAcute Diseases and Life-Threatening Conditions: Assistant Professor Kenan KaravdićGoran MaliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AutismDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Autismangeliejoy_110976% (29)
- NSTP ProjDocument11 pagesNSTP ProjLeeroi Christian Q Rubio100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Immunology & Oncology Review 2Document99 pagesImmunology & Oncology Review 2Melchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Stress Management in StudentsDocument25 pagesStress Management in StudentsJangNo ratings yet
- Nurs 205 Concept MapDocument1 pageNurs 205 Concept MapJami SpearsNo ratings yet
- End of Life ManualDocument238 pagesEnd of Life ManualJeffery TaylorNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- TEDPB and Disability Support ServicesDocument3 pagesTEDPB and Disability Support ServicesIrshaad Ally Ashrafi GolapkhanNo ratings yet
- Endo-Perio 2023 Pias DelDocument17 pagesEndo-Perio 2023 Pias Deldidav49167No ratings yet
- Pil 2425Document6 pagesPil 2425Gabriela ChiritoiuNo ratings yet
- Magic Medicine by Cody JohnsonDocument207 pagesMagic Medicine by Cody Johnsonhamza100% (9)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Rexulti PIDocument39 pagesRexulti PIbenaw187No ratings yet
- Wa0004Document10 pagesWa0004Kunal PalNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)