Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Master Data
Uploaded by
Rj RonquilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Master Data
Uploaded by
Rj RonquilloCopyright:
Available Formats
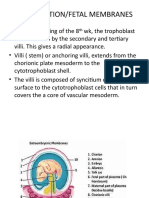
TERM 1st stage 2nd stage 3rd stage 4th stage abortion abruptio placentae afterbirth amni/o, amnion/o
amniocentesis amniocentesis amniochorial amniochorial/amniochorionic amnion amnion/o amnionitis amniorrhea amniorrhea amniorrhexis amnioscope amnioscopy amniotic sac amniotomy ante-, preantepartum apgar score breech cephal/o cephalic cesarean section chori/o chorioamnionitis choriocarcinoma chorion chorionic villus sampling cleft lip & cleft palate colostrum conception congenital anomalies copulation cyestiology Down syndrome dystocia eclampsia embry/o embryo embryogenic embryoid eneterocele episiotomy erythroblastosis fetalis esophag/o esophageal atresia fertilization fet/i fet/o, fet/i fetal alcohol syndrom (FAS) fetal monitoring fetography fetus gamete gastrochisis gestation period gestation/pregnancy gonads gravid gravid/o
DEFINITION cervical dilation. Onset of regular when the cervis is dilated and effaced. Infant is completely expelled occurs after the child is born and does not end until the placenta and membranes are expelled part of labor. Postpartum stage. Hour or 2 after delivery when muscle tone is restored to the uterus termination of pregnancy by the expulsion from the uterus of an embro before fetal viability, usually before 20 weeks of gestation premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall. placenta is expelled after childbirth amnion, amniotic fluid surgical puncture to aspirate amniotic fluid to assess fetal health surgical puncture to aspirate amniotic fluid to assess fetal health pertaining to the amnion and chorion anything pertaining to both the amnion and chorion thin, but tough membrane lining the chorion. Contains the embryo and later the fetus amnion, amniotic fluid inflammation of the amnion leaking or discharge of the amniotic fluid discharge (escape) of amniotic fluid rupture of the amnion instrument used for visual exam of both the amniotic fluid and the fetus visual exam "bag of waters": an outer layer of cells and an inner cell mass yolk and the amniotic cavity incision into the amnion using a special hook. It is performed in order to induce labor before event occuring BEFORE childbirth checking to make sure the infant is breathing, heart rate, muscle tone, oclor, and response to skin stimulation butt,knees and feet first head baby's head, brow, face and chin first C/S, C-section. Removal of the fetus through an incision in the badomen and uterus chorion inflammation of both the chorion and amnion malignany neoplasm of the uterus that arises from the chorionic membrane chori/o: outermost layer of the membrane surrounding the embryo aspitation of placental tissue congenital split of the lip and root of the mouth during pregnancy and 1st days after birth, breasts secretes thin, milky fluid this union forms a viable zygote abnormalities that are present at birth. Often discovered prior to birth by ultrasound sexual intercourse study of pregnancy inherited chromosomal abnormality: mental retardation difficult labor toxemia: gravest form of pregnancy induced embryo, to be full embry/o: from the 4th day after fertilization to the end of the 8th week something that produces an embryo resembling to embryo hernia that contains intestine perinieotomy. surgical incision of the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening for delivery condition in which the incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood types leads to the destruction of red blood cells in the newborn esophagus congenital abbsence of part of the esophagus union of a sperm and ovum fetus, unborn child fetus, unborn child a condition caused by excessive alcohol consumption by the mother during pregnancy use of procedures such as pelvic ultrasound and ECG, can provide infor about heart rate, development, positioning within the uterus radiographic visualization of the fetus embryo becomes fetus beginning with the 9th week mature ovum or sperm fissure in the abdominal wall that does not occue near the umbilicus duration of pregnancy; normally 38 to 42 weeks, which can be divided into three equal periods, called trimesters development of a new individual from conception to birth essential organs of reproduction means pregnant pregnancy
gravida gravidopuerperal hydrocephalus hysterorrhexis implantation in vitro fertilization (IVF) infertility intrapartum labor lact/o lactation lactorrhea laparotomy lochia meconium micromicrocephalus midwife midwifery multimultigravida multipara nat/o natal neonate (NB) neonatologist neonatology nulli0 nulligravida nullipara obstetrician (OB) obstetrics obstetrics (OB) oligohydramnios omphal/o omphalitis omphalocele ovary ovulation par/o, part/o para part/o parturition pelv/i pelv/o, pelv/i pelvic sonography pelvic ultrasonography placenta placenta placenta previa polyhydramnios postpostnatal postpartum prepreeclampsia pre-eclampsia pregnancy premature infant prenatal prim/i primigravida primipara pseud/o pseudocyesis puerper/o puerpera puerperal
pregnant woman pertaining to pregnancy and the puerperium enlargement of the head. Fluid in the breain rupture of the uterus embedding of the zygote into the uterin lining method of fertilizing human ova outside the woman's body and then placing the zygote into the uterus inability to achieve pregnancy after attempting for one year event occuring DURING labor and childbirth process that results in the birth of a newborn milk production and secretion of milk in the mother's breasts spontaneous discharge of milk. incision into the abdominal wall to remove the fetus safely vaginal discharge that can continue for 3 to 6 weeks after childbirth first postnatal stoll of the newborn :) small very small head practice of assisting at childbirth the practice of assisting in childbirth many 2 or more pregnancies a woman who has given birth to viable offspring 2 or more times birth or born pertaining to birth newborn. Infant from birth to 4 weeks old physician who specialized diagnosis and treatment of disorders in newborns none never been pregnant a woman who has not given birth to a viable offspring physician who specializes in obstetrics branch of surgery dealing with pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium medical specialty dealing with pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium scanty amount of amniotic fluid umbilicus, navel inflammation of the umbilicus herniation of part of the intestine through the abdominal wall near the umbilicus female gonad expulsion of the ovum bear, give birth to, labor, childbirth a woman who has given birth, live or stillborn bear, give birth to, labor, childbirth birth of the child pelvic bone, pelvis pelvic bone, pelvis recording of sound in the area of the pelvis to produce ultrasound images of the fetus procedure that directs ultrasound waves through the mother's pelvis to visualize the fetus and evaluate the pregnancy highly vascular organ that serves as a bridge to the maternal circulation for the exchange of nutrients and wastes aka afterbirth. A structure that grows on the wall of the uterus during pregnancy and allos for nourishment of the unborn child condition in which the placenta has developed in the lower portion of the uterus in such a way as to partially/completely over the cervical opening excessive amount of amniotic fluid after after birth cevent occuring AFTER childbirth before abnormal condition encountered during pregnancy or shortly after delivery characterized by high blood pressure, edema, and proteinuria, but with no convulsions. occurs during pregnancy shortly after delivery. Large quantities of protein in the urin and swelling of the legs and feet gravi/o, cyes/o, cyes/i infant born before completing 37 weeks before birth first first pregnancy a woman who has given birth to an offspring after the point of viability false pregnancy false pregnancy childbirth puerper/o: woman who's just given birth pertaining to the puerperium
puerperium pylor/o pyloric stenosis quickening respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) salpingocyesis shunt spina pifida suf: -amnios suf: -cyesis suf: -e suf: -is suf: -partum suf: -rrhexis suf: -tocia: suf: -um suf: -us surfactant terat/o terat/o teratogenic testis tracheesophageal fistula transverse VBAC yolk sac zygote acquired immunity acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) acute coronary syndrome (ACS) acute leukemia adenoids allergen allergist
period from delivery until reproductive organs return to normal, usually about 6 weeks pylorus narrowing of the muscular tinr, the pyloric sphincter that separates the stomach from the first portion of the small intestine the first feeling of movement of the fetus in utero by the pregnant woman. It usually occurs between 16 to 20 weeks of gestation formerly called hyaline membrane disease. Acute lung disorder often associated with prematurity and low birth weight ectopic pregnancy: pregnancy in the uterine/fallopiann tubes tube to drain the excess fluid and relieve pressure on the brain divided spine. Congenital defect in the vertebral column caused by the failure of the vertebral arch to fuse. amnion, amniotic fluid pregnancy noun suffix, no meaning noun suffix, no meaning childbirth, labor rupture of the amnion birth, labor noun suffix, no meaning noun suffix, no meaning substance formed from protein and produced by special cells in the lungs. Allows the easy movement of air in and our of the lungs monster. Malformation of any kind malformations producing malformations male gonad abnormal passageway between the esophagus and trachea shoulder first vaginal birth after cesarean section production of blood cells the cell formed when a sperm and ovum unite acquired when the presence of a disease generates the production of antibodies disorder in which the imune system loses its ability to resist infection sudden symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the heart indicatin ubstable angina or acute myocardial infarction sudden onset, a rapid progression, and large numbers of undifferentiated, immature leukocytes in the blood pharyngeal tonsils sensitizing agent physician who studies and treats allergic conditions life-threatening hypersensitivity reaction that occurs throughout the body and is characterized by hypotension, shock, respiratory distress, and edema of the larynx leading to airway obstruction reduction in the number of red blood cells. Loss of blood dilation, or balooning, of a weakened portion of an arterial wall ballooning of a weakened portion of an arterial wall surgical excision of the aneurysm large blood vessels vessel chest pain, which may radiate to the left arm and jaw, that occurs when there is an insufficient supply of blood to the heart muscle inflammation of the heart and the lasre blood vessels process of recording radiographic images of the blood vessels benign tumor made up of blood or lymph vessels surgical repair of a blood vessel type of microscope in a fiberoptic catheter visual examination of the lumen (interior cavity) of blood vessels using an instrument called an angioscope narrowing of a blood vessel specifically designed to interact only with the antigen that brought about its synthesis in the lymphoid cells agent used to slow the blood clotting process a substance capable of inducing an immune response aorta largest artery in the body connects the left ventricle and the aorta narrowing, pertaining to aorta fatty substance, plaque disturbance or abnormality in the rhythm of the heart artery carry blood containing oxygen and other nutrients away from the heart to the body cells small artery. Carry blood to the tiniest of the blood vessels thickening, loss of elasticity and calcification of the walls of smaller arteries
anaphylaxis anemia aneurysm aneurysm aneurysmectomy angi/o angi/o angina pectoris angiocarditis angiography angioma angioplasty angioscope angioscopy angiostenosis antibody anticoagulant antigen aort/o aorta aortic valve aorticc stenosis arher/o arrhythmia arteri/o arteries arteriole arteriosclerosis
ather/o atherectomy atherosclerosis atri/o atria atrial fibrillation ablation atrioventricular (AV) valves autoimmune disease autoimmunity B cell bacterial endocarditis bicuspid valve blast crisis blood dyscrasia blood pressure (BP) bone marrow aspiration bone marrow biopsy bone marrow transplant bradybradycardia capillaries cardi/o cardiac arrest cardiac catheterization (cath) cardiac cycle cardiac pacemaker
fatty substance, plaque surgical removal of atheromas, or deposits of fat, from an arterial wall common arterial disorder in which deposits of yellowish plaques of cholesterol, lipids, and cellular debris are formed in the walls of arteries atrium the two upper chambers. Receive blood returning to the heart from the veins throughout the body a procedure in which abnormal cells that trigger atrial fibrillation are destroyed by using radiofrequency energy tricuspid and bicuspid valves a disease caused by the body;s inability to distinguish its own cells from foreign bodies, thus producing antibodies that attack its own tissue condition in which a person's T cells attack healthy cells, causing extensive tissue damage and organ dysfunction lymphocytes that transform into plasma cells to secrete antibodies occurs when microorganisms infect the endocardial surface mitral. Connects the left atrium and left ventricle a rise in bone marrow or peripheral blood blast counts or by spread of leukemic infiltrates into soft tissue or skin abnormal or phatologic condition of the blood force that the circulating blood exerts against the walls of the blood vessels a syringe is used to aspirate a sample of the liquid portion of the bone marrow for study. small amount of bone marrow is aspirated for microscopic examination infusion of healthy bone marrow cells from a donor with matching cells and tissue to a recipient slow slow heart rate or < 60 bpm tiny, microscopic blood vessels. Exchange of oxygen and nutrients from the blood into the tissue fluid surrounding the body's cells heart sudden cessation of the heart's activity establish a diagnosis of congenital heart disease. two-phase process of the heart's pumping activity battery-powered device implanted under the skin that leads placed on the heart or in the chamber of the heart. Can be used to restore normal rhythm compression of the heart caused by the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pericardium. Excessive amount of fluid in the pericardial sac may slow the return of blood from the lungs to the heart originating in the heart physician who studies and treats iseases of the heart enlargement of the heart disease of the heart muscle consists of the heart and a closed network of blood vessels that carry blood throughout the body cell-mediated immunity. T cells lymphocytes do act directly on foreign substances. develop more slowly the time required for blood to clot, and a relative inability to form blood clots type of congenital abnormality characterized by a localized narrowing of the aorta measures the number of red and white cells per cubic millimeter of blood. noninvasive procdure that uses a high-resolution CT system to study vascular structures of the body after the injection of intravenous contrast media structural or functional abnormalities of the heart that are present from birth condition in whch the heart is unable to pump the amount of blood required surgical procedure when a blood vessel is grafted onto one of the coronary arteries to bypass the area of occlusion aka heart scan. Noninvasive procedure used to assist in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease obstruction of an artery of the heart, usually from atherosclerosis. Coronary occlusion can lead to acute myocardial infarction blood or bone marrow a blood test to measure the amount of C-reactive protein in the blood, which, when elevated, indicates inflammation in the body. blood test used to measure the level of creatine phophokinase, an enzyme of heart and skeletal muscle relesased into the blood after muscle injury or necrosis. cell proteins that aid cells in destroying antigens painful swelling of the fingers or toes condition of thrombus in a deep vein of the body. Most often occurs in the lwower exteremities. A clot can break off and travel to the lungs, cauding a pulmonary embolism application of an leectrical shock to the chest wall for delivery to the myocardium stimulate B- and T- cell responses by binding and presenting antigens to these lymphocytes. Can be exposed in culture to an antigen and then infused into a patient. period during which the heart relaxes between contractions technique that improves upon traditional angiography
cardiac tamponade cardiogenic cardiologist cardiomegaly cardiomyopathy cardiovascualr system cellular immunity chronic leukemias coagulation time coarctation of the aorta complete blood count (CBC) computer tomography angiography (CTA) congenital heart disease congestive heart failure (CHF) coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) coronary occlusion cras/o C-reactive protein (CRP) creatine phosphokinase (CPK) cyt/o cytokines dactylitis deep vein thrombosis (DVT) defibrillation dendritic cells diastole digital substraction angiography (DSA)
Doppler ultrasound dysdyscrasia dysrhythmia ech/o echocardiam (ECHO) echocardiography electr/o electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) electrocardiograph electrocardiograph electrocardiography electrocardiography electronic beam CT scanner (EBCT)
probe transmitter measures the velocity of blood through a vessel abnormal abnormal condition or temperament of the blood or bone marrow disturbance or abnormality in the rhythm of the heart sound record of the heart using sound diagnostic tool which uses high-frequency sound waves to visualize the structures and record the function of the heart electricity, electrical activity record procedure for electrocardiography device instrument used to record the electrical activity of the heart records the electrical activity of the myocardium process of recording the helectrical activity of the heart an electron beam to create 3d images of the heart. surgical removal of an embolus or clot, usually with a balloon catheter, inflating the balloon beyond the clot, then pulling the balloon back to the incision and bringing the clot with it blood clot that travels removal of the thickened intimal lining of the artery inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, particularly the heart valves inner layer. Made of smooth membranous tissue. Lines the interior of the heart and the heart valves closure of the vein by application of intravenous heat aka WESTERN BLOT. Reveal the presence of anti-HIV antibodies. thin, outer layer red blood cells (RBC). Carries oxygen. Maintaining pH balance and carrying respiraty gases to and from the cells. erythrocytes are produced in response to the kidney's secretion of this hormone occurs most frequently and has no identifiable cause but is associated with obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, increased sodium intake, smoking, high cholesterol levels, and a family history of high blood pressure a strudy that evaluates cardiac function during physical stress by riding a bike or walking on a treadmill. occurring outside the body escape of blood from the blood vessel into the tissue surgery to establish an alternate route from femoral artery to popliteal artery to bypass an obstruction type of dysrhythmia in which there is a marked disturbance of the heart's rhythm. Rapid, disorganized, and ineffectual contractions of the atria or ventricles outer fibrous portion muscular, cone-shaped. Serves as the pump for the cardiovasculat system a short-duration humming sound of cardiac or vascular origin surgical removal of a donor heart and transfer of the organ to a recipient consists primarily of blood vessels blood blodo test to measure the volume of red blood cells. Used in the diagnosis and evaluation of anemic patients abnormal reduction in the number of blood cells physician who studies and treats diseases of the blood study of the blood tumor of blood normal development of blodo cells within the bone marrow peripheral stem cells from a compatible donor are administered into a recipient's oxygen-carrying component of the cell breakdown of red blood cells that normaly occurs at the end of a cell's life hereditary bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency in one of the factors necessary for the blood to clot rapid loss of blood process by which bleeding is stopped unknown origin and is characterized by progressive enlargement of lymphoid tissue blood test used to measure the amount of homocysteine in the blood. An amino acist that, if elevated, may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular disease
embolectomy embolus endarterectomy endocarditis endocardium endovenous laser ablation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) epicardium erythrocyte erythropoietin (EPO)
essential hypertension exercise stress test extracorporeal extravasation femoropopliteal bypass fibrillation fibrous pericardium heart heart murmur heart transplantation hemangioma hemat/o hematocrit (HCT) hematocytopenia hematologist hematology hematoma hematopoiesis hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HST) hemoglobin hemolysis hemophilia hemorrhage hemostasis Hodgkin disease homocysteine
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) RNA-containing virus. humoral immunity type of immune system excessive amount of cholesterol in the blood; associated with heightened risk of cardiovascular hypercholesterolemia disease excessive amount of triglycerides in the blood; associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular hyperlipidemia disease hypersensitivity reactions occure when the immune system's response to a sensitizing agent is excessive hypertension sustained elevation of blood pressure. >140/90 mm Hg hypertensive heart disease (HHD) disorder of the heart caused by persistent high blood presusure
hypochromic hypothermia immun/o immune immune system immunity immunodeficiency immunoglobulin immunologist immunology immunology
lacking in color condition of (body) temperature that is below normal protection, immune being resistant to specific invading pathogens to protect itself against foreign organism. Generate secretions that help block the entry of diseasecausing agents. body is resistant to a specific invading pathogen deficient immune response caused by the immune system dysfunction brought on by disease or immunosuppressive drugs antibodies that react with the antigens, transforming them into harmless substances or rendering them more easily disposed of by phagocytes a physician who studies and treats immune system disorders brance of medicine dealing with immune system brach of medicine dealing with immune system disorders measures venous flow of the extremities with a plethysmograph to detect clots by meadusing changes in blood volume and resistance in the vein; to etect deep vein thrombosis
impedance plethysomography (IPG)
implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) a device implanted in the body that continuously monitors the heart rhythm. localized area of tissue death due to local ischemia resulting from an interruption in the blood supply to the area infarction an acute infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus characterized by swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, fatigue, and fever. The disease affects mostly young people and is usually transmitted by infectious mononucleosis saliva intermittent claudication cramp-like pain in the calf muscles that is caused by exercise and relieved by rest interstitial fluid fluid surrounding the body's cells intracoronary thrombolytic therapy isch/o ischemia leukapheresis leukemia leukocyte lipid profile lipids lymph lymph capillaries lymph node lymph vessels lymph/o lymphaden/o lymphadenitis lymphadenopathy lymphadentitis lymphanden/o lymphangioma lymphangitis injection of a medication either intravenously or intraarterially used to dissolve the clots deficiency decreased supply of oxygenated blood to the heart process in which blood is withdrawn from a vein, WBCs are selectively removed, and the remaining blood is reinfused in the donor malignant white blood cell diseases white blood cells (WBC). Fights infection blood test used to meausre the amount of lipids in a sample of blood. fats and fatlike substances that serve as a source of fuel in the body and are an important constituent of celll strucure clear, watery fluid liquid that flows through the lymphatic vasculature intercellular spaces of the soft tissues of the body when fluid that has filtered out of the blood capillaries flows into single-layered vessels small oval structure. Occursi n clusters. A filter by removing invading microorganisms and other noxious agents. larger tubules of lymph capillaries. Valves to ensure a one-way flow of lymph toward two large ducts in the upper chest. lymph. Lymph tissue lymph node inflammation affecys the glands of the lymphatic system any disease of the lymph nodes or vessels inflammation of the lymph nodes lymphatic system mass composed principally of lymph vessels inflammation of one or more lymphatic vessels caused by a streptococcal infection complex network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs that performs many important functions in the body. Transports proteins and excess tissue fluid that leak from the capillaries and returns them to the venous blood. Absorb and transport fat from the small intestine into general circulation. plays an important role in immunity by helping protect the body from pathogen, bacteria, etc. malignant neoplasm of the lymph nodes and lymph tissues large pathogen-consuming cell found in various locations throughout the body. Ingest bacteria, old or defective cells, tissue debris and virus-infected cells. noninvasive procedure that does not require catherterization or the injection of dye and uses specialized MR imaging to study vascular structures of the body heart lies in the thoracic cavity between the lungs between the lungs closed-heart surgical treatment of mitral stenosis that involves dividing the mitral valve at the junction of its cusps when the mitral valve undergoes kinds of inflammatory changes. mononuclear leukocytes. Largest of the leukocytes tumors of the bone marrow capable of scanning multiple images during each gantry rotation abnormal, prolonged sound heard between normal heartbeats. Result of alterations in blood flow and/or structure of the heart or blood vessels bone marrow formation of bone marrow
lymphatic system lymphoma macrophage magnetic resonanct angiography (MRA) meadiastinum meadiastinum mitral commissurotomy mitral valve stenosis monocytes multiple myeloma multislice spiral CT scanner (MSCT) murmur myel/o myelopoiesis
myocarditis myocardium natural immunity natural killer (NK) cells Non-Hodgkin lymphoma occlude panpancytopenia parietal layer passive immunity percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) pericardi/o pericardiocentesis pericarditis
inflammation of the thick, muscular middle layer of the heart thick,middle layer. Made of cardiac muscle produces a nonspecific defensive reaction against any foreign organism. leukocyte that recognized and destroys foreign cells a group of malignant tumors of lymphoid tissue to close tightly, to block all abnormal reduction of all blood cells outer layer of the pericardium. Lines the heart's outer fibrous coat acquired when preformed antibodies are received, not produced internally. Transfer of antibodies across the placental membrane is an example. nonsurical intervention for treatment of coronary artery disease pericardium surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from the outer layer of the heart inflammation of the pericardium two-layer sac surround the heart, consisting of an external fibrous and internal serous layer. The serious layer secretes a fluid that facilitates movement of the heart. It consists of two layers, one lining the fibrous pericardium and one covering the heart, called epicardium disease of the arteries in the arms and legs, resulting in narrowing or complete obstruction of the artery. Aka peripheral vascular disease (PVD) involves the progressive narrowing and eventual obstruction of the blood vessels in the lower extremities another kind of lymphocyte that nonspecifically attacks tumor cells and virally infected cells by releasing cytokine process which WBC, neutrophils, and macrophages surround and destroy the bacteria vein excision of a vein inflammation of a vein physician who studies and trests diseases of the veins study of veins plasma straw-colored fluid portion in which the particulate elements are suspended removal of plasma tiny punctures in the skin through which the damaged veins can be pulled out for surgical removal inflammation of many arteries deeply lobed nucleus or one that is so divided that it seems to be more than one aka peripheral vascular disease (PVD). Disease of the larger arteries in the arms and legs that results in the narrowing or complete obstruction of an artery. enzyme protease spreads the AIDS virus throughout the body blood test used to determine certain coagulation activity defects an to monitor anticoagulation therapy for patients taking Coumadin. located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery force of the blood being ejected from the heart causes a regular expansion and contraction of the arterial walls disapeparance of the signs of disease reverses the normal process for synthesization of a DNA molecule inflammatory disease that potentially involves all the layers of the heart and often follows streptococcal infection of the respiratory tract damage to the heart muscle and heart valves a solution injected into the varicose vein causes it to thrombose and then close over a month or two causes include renal disease, endocrine disorders, and neurologic disorders pulmonary and aortic valves. Valve with cusps that are shaped like half moons. blood infection condition in which pathogenic microorganisms invade the blood or other tissues causing an overwhelming blood infection separation of the left and right sides of the heart thin sheet of tissue clear, watery fluid portion of the blood that remains after a clot has formed. farming tool with a semicircular blade that is used cutting corn :) genetic disorder characterized by production of abnormal hemoglobin. The red blood cells develop a distorted crescent, or sicke, shape acute episodes. Symptoms of which include joint pain, abdominal pain, and painful swelling of the finers or toes a nuclear medicine scan that visualized the heart from several different angles. referes to targeted immune responses against particular microorganisms instrument used to measure BP located in the left upper portion of the abdominal cavity. Ovoid-shaped organ. Largest lymphatic organ in the body, acts as a reservoir for blood storage spleen
pericardium peripheral arterial disease (PAD) peripheral vascular disease (PVD) phagocytes phagocytosis phleb/o phlebectomy phlebitis/thrombophlebitis phlebologist phlebology plasm/o plasma plasmapheresis plebectomy polyarteritis polymorphonuclear (PMN) preipheral arterial disease (PAD) protease inhibitors prothrombin time (PT) pulmonary valve pulse remission retrovirus rheumatic fever rheumatic heart disease sclerotherapy secondary hypertension semilunar valves seps/o sepsis septum serous membrane/ serous pericardium serum sickle sickle cell anemia sickle-cell crises single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) specific immunity sphygmomanometer spleen splen/o
splenectomy splenomegaly splenopexy staging stent suf: -ac suf: -apheresis suf: -centesis suf: -emia suf: -graph suf: -lysis suf: -oma suf: -oma suf: -penia suf: -poiesis suf: -sclerosis suf: -stasis systole T cell tachycardia thallium test therm/o thromb/o thrombocyte thrombolysis thrombophlebitis thrombosis thrombus thym/o thymectomy thymoma thymus tonsils transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) tricuspid valve troponin vaccination vaccine valv/o, valvul/o valves valvulitis valvuloplasty varicose veins (varicosities) vasconstrictor vein vena cava venipuncture venography ventricles ventricul/o venules visceral layer visceral pericardium Western blot abdomen abdomin/o, celi/o, lapar/o abdominal ultrasonography abdominal ultrasonography abdominocentesis abdominoperineal resection (A&P resection) abdominoplasty absorption absorption adhesiolysis or adhesiotomy adhesion
excision of the spleen enlargement of the spleen surgical fixation of the spleen treatment for lymphoma. Guides the choice of treatment. prevent closure of the vessel during and after angioplasty pertaining to separation, removal surgical puncture to aspirate fluid blood condition instrument used to record; record breakdown tumor, mass mass deficiency formation hardening stop cardiac cycle when the heart contracts lymphocytes formed in the thymus gland that act directly on antigens to destroy them or produce chemicals, such as interferons and interleukins, that are toxic to antigens. fast heart beat. >100 bpm a nucear medicine test used to diagnose coronary artery disease and assess revascularization after coronary artery bypass surgery heat clot platelet. Helps the blood to clot dissolution of a clot inflammation of a vein associated with a clot development of a blood clot that blocks a coronary artery blood clot thymus gland excision of the thymus gland benign tumor of the thymus gland single organ, consisting of two lobes which contain lymphoid cells. Is essential to the devleopment of the body's immune system paired masses of lymphatic tissue located in the throat an ultrasound test that examines cardiac function and structure by using an ultraouns probe placed in the esophagus, which provides views of the heart structures connects the right atrium and the right ventricle blood test that measures troponin, a heart muscle enzyme a modified toxin, or poison, capable of inducing antibody production a suspension of inactivated microorganisms adminitered by injection, mouth, or nasal spray to prevent infectious diseases by inducing immunity valve val/o, valvul/o. Keep the blood flowing in one direction only inflammation of a valve surgical repair of a vallve swollen and twisted veins that are usually found in the lower extremities agent or nerve that enlarges the blood vessels blood travels from various parts of organs back to the heart venae cavae. Largest veins in the body. puncture of a vein to remove blood, instill a medication, or start an IV infusion process of recording an x-ray image of the vein after injection of a contrast medium the lower two chambers. Pump blood from the heart, through the arteries and back to the body's tissues ventricle small veins when oxygen-poor and waste-filled blood travels inner layer of pericardium. Adheres to the heart's surface loose-fitting, double-layered sac reveal the presence of anti-HIV antibodies portion of the body between the thorax and the pelvis abdomen (abdominal cavity) process of recording images of internal organs using high-frequency sound waves produced by a transducer placed directly on the skin covering the abdominal cavity. pertaining to the abdomen aka paracentesis surgical puncture to remove fluid form the abdominal cavity
removal of the distal colon and rectum through both andominal and perineal approaches surgical repair of the abdomen transfer of digested food from the small intestine to theb lood stream the passage of the nutrients (end products of digestion) from the small intestine to the blood stream, take place through the villi surgical treatment abnormal growing together of two surfaces that normally are separated. May occus after abdominal sugery
alimentary canal an/o anal
aka gastrointestinal tract (GI). Long continuous tube comprising the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Accessory organs of the digestive tract are the salivary glands, liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas anus pertaining to the anus an opening created by surgically joining two structures, such as blood vessels or bowel segments excision of the anus eating disorder characterized by a prolonged refusal to eat, resulting in emaciation. Amenorrhea in females, and abnormal fear of becoming obese. It occurs primarily in adolescents and young adults antrum lower portion of the stomach sphincter muscle (ringlike band of muscle fiber that keeps an opening tight) at the end of the digestive tract without swallowing (the inability to) appendix incision into the abdominal cavity appendix inflammaiton of the appendix aka vermiform appendix. small pouch, which has no known function in digestion, attached to the ceum. abnormal collection of fluid in the peritoneal cavity surgical reduciton of gastric capacity to treat morbid obesity causeing serious illness series of radiogrpahic images taken of the large intestine after the contrast agent barium has been administered rectally. Aka lower GI series passageways that carry bile passageways that carry bile central portion of the stomach an eating disorder involving gorging with food, followed by induced vomiting or laxative abuse )binging and purging) area around the opening of the esophagus cecum blind U-shaped pouch that is the first portion of the large intestine abdomen (abdominal cavity) a malabsorption syndrome caused by an immune reaction to gluten )a protein in wheat, rye, and barley), which may damage the lining of the small intestine that is responsible for absorption of food into the blood stream. pertaining to the abdomen suture of the lip lip suture of the lip gall, bile bile duct radiographic image of bile ducts radiographic imaging of the bile ducts (after administration of contrast media to outline the ducts) tumor of the bile duct excision of the gallbladder inflammation of the gallbladder common bile duct condition of stones in the common bile duct incision into the ocmmon bile duct to remove a stone condition of gallstones cronic disease of the liver with gradual destruction of cells and formation of scar tissue colon (usually denoting the large intestine) excision of the colon next portion of the large intestine. The colon is divided into 4 parts: ascending oclon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon colon (usually denoting the large intestine) instrument used for visual examinaiton of the lon visual examination of the colon pertaining to the colon and rectum creation of an artficial opening into the colon (through the abdominal wall) conveys bile to the duodenum chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract usually affecting the ileum and colon radiographic imaging of the oclon (using a CT scanner and software) carries bile from the gallbladder aka gluten enteropathy pruritic skin rash frequent discharge of liquid stool the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food for use by body cells is completed in the small intestine diverticulum, or blind pouch, extending from a hoolow organ excision of a diverticulum inflammation of a diverticulum
anastomosis anoplasty
anorexia nervosa antro/o antrum
anus aphagia append/o, appendic/o appendectomy appendic/o appendicitis
appendix ascites bariatric surgery
barium enema (BE) bile ducts biliary tract body
bulimia nervosa cardia cec/o cecum celi/o
celiac disase celiac disase celiotomy cheil/o cheilorrhapy chol/e cholangi/o cholangiogram
cholangiography cholangioma cholecystectomy cholecystitis choledoch/o choledocholithiasis choledocholithotomy cholelithiasis cirrhosis col/o, colon/o colectomy
colon colon/o colonoscope colonoscopy colorectal colostomy common bile duct Crohn disease CT colonography cystic duct dermatitis herpetiformis diarrhea digestion digestion divericul/o diverticulectomy diverticulitis
diverticulosis duoden/o duodenal duodenum dysentery dyspepsia dysphagia elimination emesis endoscope endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) endoscopy enter/o enteropathy enterorrhapy esophag/o esophageal esophagitis
abnormal condition of having diverticula duodenum pertaining to the duodenum first 10-12 inches (25 cm) of the small intestine disorder that involves inflammation of the intestine (usually the large intestine) deifficult digestion (often used to describe GI stmptoms, such as abdominal pain and bloating) difficult swallowing the removal of solid waste from the body expelling matter from the stomach through the mouth. Aka vomiting instrument used for visual examination within a hollow organ radiographic examination of the biliary ducts and pancreatic ducts with contrast media, fluuoroscopy, and endoscopy. a procedure using an endoscope fitted with an ultrasound probe that pprovides images of layers of the intestinal wall visual examination within a hollow organ intestine (usually denothing the small intestine) disease of the intestine suture of the intestine esophagus pertaining to the stomach inflammation of the esophagus
esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) visual examination of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum esophagogastroplast surgial repair of the esophagus and the stomach aka esophagram and barium swallow . radiographic image of the esophagus (barium is used as esophagogram contrast media) esophagoscopy visual examination of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum esophagus fecal occult blood test (FOBT) feces flatus fundus gallbladder gastr/o gastrectomy gastric lave gastritis gastrocope gastrocopy gastroenteritis gastroenterocolitis gastroenterologist gastroenterology gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) 10-inch (25cm) tube that is a passageway for food extending from the pharynx to the stomach a test to detect occult blood in feces. Aka guaiac test waste from the digestive tract expelled through the rectum. Aka stool or fecal matter gas in the digestive tract or expelled through the anus uppermost domed portion of the stomach small, saclike structure that stores bile stomach excision of the stomach (or part of the stomach) washing out of the stomach inflammation of the stomach instrument used for visual examination of the stomach visual examination of the stomach inflammation of the stomach and intestines inflammation of the stomach, intestines, and colon a physician who studies and treats diseases of the stomach and intestines (GI tract and eccessory organs) study of the stomach and intestines )a branch of medicine that deals with treating diseases of the GI tract and accessory organs) the abnormal backward flow of the gastrointestinal ocntents into the esophagus, causing heartburn and the gradual breakdown of the mucous barrier of the esophagus aka alimentary canal. Long continuous tube comprising the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Accessory organs of the digestive tract are the salivary glands, liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas creation of an artificial opening between the stomach and jejunum softening of the stomach surgical repair of the stomach creation of an artificial opening into the stomach (through the abdominal wall) process of feeding a person through a nasogastric tube gum surgical removal of gum (tissue) inflammation of the gum tongue disease of the tongue suture of the tongue a protein in wheat, rye, and barley aka FOBT. A test to detect occult blood in feces anterior portion, supported by bone a blood test to determine the presence of H. pylori bacteria vomiting of blood passage of bloody feces excision of half of the colon an iron metabolim disorder that occurs when too much iron is absorbed from food, resulting in excessive deportis of iron in the tissue excision of hemorrhoids, the swollen or distended veins in the rectal region
gastrointestinal tract (GI) gastrojejunostomy gastromalacia gastroplasty gastrostomy gavage gingiv/o gingivectomy gingivitis gloss/o, ling/o glossopathy glossorrhaphy gluten guaiac test hard palate helicobacter pylor (H. pylori) antibodies test hematemesis hematochezia hemicolectomy hemochromatosis hemorrhoidectomy
hemorrhoids hepat/o hepatic duct hepatitis hepatoma herni/o herniorrhapy ile/o ileocecal ileostomy ileum ileus ingestion intussusception irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) jejun/o jejunum lapar/o laparoscope laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) laparoscopy laparotomy laparotomy
swollen or distended veins in the rectal area, which may be internal or external, and can be source of rectal bleeding liver passage way for bile from the liver inflammation of the liver tumor of the liver hernia, protrusion of an organ through a membrane or cavity wall suturing of a hernia (for repair) ileum pertaining to the ileum and cecum creation of an artificial opening into the ileum )through the abdominal wall creating a stoma)
third portion of the small intestine, apprx 11 ft (3.3m) long, which connects with the large intestine obstruction of the intestine, often caused by failure of peristalsis the taking in of nutrients through the mouth telescoping of a segment of the intestine periodic disturbances of bowel fuction, such as diarrhea and/or constipation, usually associated with abdominal pain jejunum second portion of the small intestine, approx 8ft (2.4m) long abdomen (abdominal cavity) instrument used for visual examination of the abdominal cavity creation of a small gastric pouch by the placement of a band around the upper portion of the stomach visual examination of the abdominal cavity incision into the abdominal cavity incisional surgery of the abdominal cavity canal that is apprx 5 ft (1.5m) long and extends from the ileum to the anus. Absoprtion of water and elimination of the solid waste products of digestion take place in the large intestine tongue produces bile, which is necessary for the digestion of fats. The liver performs many other functions concerned with digestion and metabolism impaired digestion or intestinal absorption of nutrients chewing black, tarry stool that contains digested blood pertaining to the nose and stomach urge to vomit excess of body fat (not body weight) mouth pertaining to the mouth palate separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity inflammation of the palate surgical repair of the palate produces pancreatic juice, which helps digest all types of food and secretes insulin for carbohydrate metabolism pancreas pertaining to the pancreas inflammation of the pancreas aka gastric or duodenal ulcer (depending on the location) eroded area of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum associated with increased secreiton of acid from the stomach. involuntary wavelike movements that propel food along the digestive tract, begins in the esophagus peritoneum pertaining to the peritoneum serous saclike lining of the abdominal and pelvic cavities inflammation of the peritoneum performs the swallowing action that passes food from the mouth into the esophagus tumor like growth extending outward form a mucous membrane polyp, small growth excision of a polyp abnormal ocndition of (multuple) polyps (in the mucous membrane of the intestine, esp the colon; high potential for malignancy) half rectum physician who stidues and treats diseases of the rectum study of the rectum (a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the rectum and anus) prolaps of the rectum instrument used for visual examination of the rectum visual examination of the rectum pylorus, pyloric sphincter
large intestine lingu/o liver malabsorption mastication melena nasogastric nausea obesity or/o, stomat/o oral palat/o palate palatitis palatoplasty pancreas pancreat/o pancreatic pancreatitis
peptic ulcer peristalsis peritone/o peritoneal peritoneum peritonitis pharynx polyp polyp/o polypectomy polyposis prefix: -hemi proct/o, rect/o proctologist proctology proctoptosis proctoscope proctoscopy pylor/o
pyloric sphincter pyloromytomy pyloroplasty pylorus rect/o rectal rectocele rectum reflux regional ileitis roux-en-Y Gastric by pass (RYGB) salivary glands sial/o sialolith sigmoid/o sigmoidoscopy small intestine soft palate steat/o
steatorrhea steatosis stoma stomach stomat/o stomatitis stomatogastric sublingual suf: -pepsia throat
tongue tsteatohepatitis ulcerative colitis upper GI series uvul/o uvula uvulectomy uvulitis uvulopalatopharyngoplasty *UPPP) vagotomy vertical banded gastroplasty (VBG) villi volvulus accommodation age-related macula degeneration (ARMD) ambly/o amblyopia ananisocoria aphakia aqueous humor astigmatism (Ast) bi-, binbinocular blephar/o blepharitis blepharoplasty blepharoptosis canthus
ring of muscle that guards the opening between the stomach and the duodenum incision into the pyloric muscle rsurgical repair of the pylorus poertion of the stomach that connects to the small intestine rectum pertaining toe the rectum protrusion of the rectum remaining portion of the large intestine, apprx 8 to 10 in(20cm) long, extending from the sigmoid colon to the anus abnormal backward flow aka regional enteritis intestinal obstruction creation of a small gastric pouch with drainage of food to the rest of the gastrointestinal tract through a restricted stoma produce saliva, which flows into the mouth saliva, salivary gland stone in the salivary gland sigmoid colon visual examination of the sigmoid colon 20 foot (6m) canal extending from the pyloric sphincter to the large intestine posterior portioin, not supported by bone fat discharge of fat (excessive amount of fat int the stool, causing frothy, foul-smelling fecal matter usually associated with the malabsorption of fat in conditons such as chronic pancreatitis and celiac disease_ abnormal conditon of fat (ncreased fat at the cellular level often affecting the liver) mouthlike opening. May be permanent or temporary J-shaped sac that mixes and stores food. It secretes chemicals for digestion and hormones for local ocmmunication control mouth inflammation of the mouth (mucous membrane) pertaining to the mouth and stomach pertaining to under the tongue digestion performs the swallowing action that passes food from the mouth into the esophagus consists mostly of skeletal mucle; attached in the posterior region of the mouth. Provides movement of food for mastication, directs food to the pharynx for swallowing, and is a major organ for taste and speech inflammation of the liver associated with (excess)fat; (often caused by alcohol abuse and obesity; over time may cause cirrhosis) inflammation of the oclon with the ofrmation of ulcers. series of radiographic images taken of the stomach and duodenum after the contrast agent barium has been swallowed uvula soft v-shaped structure that extends form the soft palate; directs food into the throat excision of the uvula inflammation of the uvula
surgical repair of the uvula, palate, and pharynx cutting of certain branches of the vagus nerve, performed with gastric surgery to reduce the amount ofgastric acid produced and thus reduce the recurrence ofu ulcers creation of a small gastric pouch with a vertical line of staples and the connection of a band for the drainage of food into the small intestine. Aka stomach staplin. fingerlike projectiosn that line the walls of the small intestine twisting or kinking of the intestine, causing intestinal obstruction where the ciliary body can contract and relax, and as it does, it changes the size and shape of the lens that allows ust o see both near and far objects
leading cause of legal blindness in persons odler than 65 y.o dim or dull reduced vision in one eye caused by disuse or misuse associated with strabismus, unequal refractive errors, or otherwise impaired vision. Aka lazy eye unequally condition of absence of equal pupil (size) (unequal size of pupils) condition of without a leans (may be congenital, though often is the result of extraction of a cataract without the placement of an intraocular lens) watery liquid found in the anterior cavity of the eye. It provides nourishment to nearby structures and maintains shape in the anterior part of the eye defective curvature of the refractive surfaces (cornea or lens) of the eye two pertaining to two or both eyes eyelid inflammation of the eyelid surgical repair of the eyelid drooping of the eyelid. Aka ptosis each corner of the eye.
cataract chalazion choroid choroid layer ciliary body conjunctiv/o conjunctiva conjunctivitis cor/o, core/o, pupill/o core/o corne/o, kerat/o cornea corneal corneoiritis cry/o cryoextraction of the lens cryoprobe cryoretinopexy cyst/o dacry/o, lacrim/o dacrycystotomy dacryocystitis dacryocystorhinostomy detached retina dipl/o diplopia emmetropia (Em) endophthalmitis enucleation fluorescein angiography glaucoma hyperopia intraocular intraocular lens (IOL) ir/o, irid/o irid/o iridectomy iridoplegia iridosclerotomy iridotomy iris iritis is/o isocoria kerat/o keratitis keratomalacia keratometer keratoplasty lacrim/o lacrimal lacrimal glands and ducts
clouding of the lens of the eye obstruction of an oil gland of the eyelid aka meibomian cyst middle layer of the eye, which is interlaced with many blood vessels that supply nutrients to the eye choroid/o. thin vascular layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera joins the iris with the anterior part of the choroid. connjunctiva mucous membrane lining the eyelids and covering the anterior portion of the sclera inflammation of the conjunctiva aka pinkeye pupil pupil cornea transparent anterior part of the sclera, which is anterior to the aqueous humor and lies over the iris. Allows the light rays to enter the eye pertaining to the cornea inflammation of both the cornea and iris cold surgical procedure in which the cataract is lifted from the eye with an extremely cold probe instrument used for cryoextraction surgical fixation of the retina by using extreme cold (carbon dioxide) sac tear, tear duct incision of the tear (lacrimal) sac inflammation of the tear (lacrimal) sac creation of an artificial opening between the tear (lacrimal) sac and the nose (to restore drainage into the nose when the nasolacrima duct is obstructed or obliterated) separation of the retina from the choroid in back of the eye two, double double vision normal refractive condition of the eye inflammation within the eye surgical removal of the eyeball (also, the removal of any organ that comes out clean and whole) (digital) process of recording blood vessels (of the eye with fluorescing dye) eye disorder characterized by optic nerve damage usually caused by the abnormal increase of intraocular pressure (IOP) farsightedness pertaining to within the eye an artificial lens implanted within the eye during cataract surgery iris iris excision (of part) of the iris paralysis of the iris incision into both the edge of the iris and into the sclera incision of the iris the pigmented muscular structure that regulatese the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the size of the pupil inflammation of the iris equal condition of equal pupil (size) cornea inflammation of the cornea softening of the cornea (usually a bilateral condition associated with vitamin A deficiency) instrument used to measure (the curvature of ) the cornea (used for fitting contact lenses) surgical repair of the cornea (corneal transplant) tear, tear duct pertaining to tears produce and drain tears a laser procedure that reshapes the corneal tissue beneath the surface of the cornea to correct astigmatism, hyperopia, and myopia. Is a combination of Excimer laser and lamellar keraoplasty. It differs from PRK in that it reshapes corneal tissue beneath the surface rather than on the surface lies directly behind the pupil; its function is to focus and bend light condition of white pupil oval yellow spot at the "center" of the retina, 2 mm from the optic nerve. Contains a small depression, no blood vessels, and the fovea centralis, which contains only retinal cones a progressive deterioration of the portion of the retina called the macula lutea, resulting in loss of central vision along the edges of the upper and lower eyelids are oil glands that help lubricate the eye oil glands found in the upper and lower edges of the eyelids that help lubricate the eye agent that constricts the pupil
LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) lens leukocoria
macula lutea macular degeneration meibomian glands meibomian glands miotic
mydriatic myopia nasolacrimal nyct/o nyctalopia nystagmus ocul/o, opthalm/o oculomycosis ophthalmalgia ophthalmic ophthalmologist ophthalmology (Ophth) ophthalmopathy ophthalmoplegia ophthalmorrhagia ophthalmoscope ophthalmoscopy opt/o opt/o opthalm/o optic optic disc optic nerve optic/o optician optician optometer optometrist optometry orbit phac/o, phak/o
phacoemulsification (PHACO) phacomalacia phak/o phot/o photophobia
photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) photoretinitis
agent that dilates the pupil nearsightedness pertaining to the nose and tear ducts night poor vision at night or in faint light aka night blindness involuntary, jerking movement of the eyes eye abnormal condition of the eye caused by a fungus pain in the eye pertaining to the eye physician who studies and treats diseases of the eye study of the eye (a branch of medicine that deals with treating diseases of the eye) (any) disease of the eye paralysis of the eye (muscle) rapid bleeding from the eye instrument used for visual examination (the interior) of the eye visual examination of the eye eye vision eye pertaining to vision optic nerve arises. Aka blind spot carries vidual impulses from the retina to the brain vision a specialist who fills prescriptions for lenses (cannot prescribe lenses) qualified to fill prescriptions for lenses to measure the power and range of vision a health professional who prescribes corrective lenses and/or eye exercises measurement of vision *visual acuity and the prescribing of corrective lenses) eyes are located in a bony prottective cavity of the skull called the orbit lens method to remove cataracts in which an ultrasonic needle probe breaks up the lens, which is then aspirated softening of the lends lens light abnormal fear of (sensitivity to) light a procedure for the treatment of nearsightedness in which an Excimer laser is used to reshape (flatten) the corneal surface by removing a portion of the cornea inflammation of the retinua caused by extreme light yellowish mass on the conjunctiva that may be related to exposure to ultraviolet light, dry climates, and dust. A ppinguecula that spreads onto the cornea becomes a pyterygium aging impaired vision as a result of aging condition of false lens (placement of an intraocular lens during surgery to treat cataracts)
pinguecula presby/o presbyopia pseudophakia
pterygium pupil pupill/o pupillary pupillometer pupilloscope
refraction retin/o retina retinal
retinal photocagulation
retinitis pigmentosa retinoblastoma retinopathy retinoscopy rhin/o scler/o sclera
scleral buckling sclerokeratitis scleromalacia sclerotomy
thin tissue growing into the cornea from the conjunctiva, usually caused from sun exposure colored iris. opening in the center of the iris pupil pertaining to the pupil instrument used to measure (the diameter of) the pupil instrument used for visual examination of the pupil bending of light rays as they pass through the cornea, lens, and other structures of the eye on their way to the retina retina inntermost layer of the eye, which contains the vision receptors pertaining to the retina an intense beam of light from a laser condenses retinal tissue to seal leaking blood vessels, to destroy abnormal tissue or lesions, or to bond the retina to the back of the eye. Used to treat retinal tears and detachment, diabetic retinopathy, wet macular degeneration, glaucoma, and intraocular tumors hereditary, progressive diseasde marked by night blindness with atrophy and retinal pigment changes tumor arising from a developing retinal cell (a congenital, malignantt tumor) (any noninflammatory) disease of the retina (such as diabetic retinopathy) visuatl examination of the retina (to determine refractive error) nose sclera white of the eye. Outer protective layer of the eye a procedure to repair a detach retina. A strip of sclera is resected, or a fold is made in the sclera. An exoplant is used to hold an buckle the sclera inflammation of the sclera and the cornea softening of the sclera incision of the sclera
sclerotomy slcer/o strabismus sty suf: - stoma suf: -ia suf: -opia suf: -phlegia suf: -phobia tonton/o tonometer tonometry trabeculectomy vascular visual acuity (VA) vitrectomy vitreous humor xerophthalmia acoustic neuroma acute otitis media (AOM) assistive listening devices (ALD) audi/o audimetry audio meter audiogram audiologist audiology audiometer audit/o aur/i, aur/o, ot/o aur/o aural benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) cerumin/o ceruminoma cholesteatoma cochle/o cochlea cochlear implant cochlear implant conductive hearing loss electr/o electrocochleography endolymph eustachian tube external auditory canal (meatus) external ear auricla (pinna) hearing aid incus labyrinth (inner ear) labyrinthectomy labyrinthitis lanyrinth/o macula malleus mastoid bone and cells mastoid/o
incision into the sclera sclera abnormal condition of squint of crossed eyes caused by the visual eaxes not meeting at the same point infection of an oil gland of the eyelid. Stye, hordeolum artificial opening condition vision (condition) paralysis abnormal fear of or aversion to specific things tension or pressure tension, pressure instrument used to measure pressure (within the eye, used to diagnose glaucoma) measurement of pressure (within the eye) surgical creation of a drain to reduce intraocular pressure (used to treat glaucoma) the choroid layer is rich in blood vessels sharpness of vision for either distance or near surgical removal of all or part of the vitreous humor (used to treat diabetic retinopathy) jellylike substance found behind the lens in the posterior cavity of the eye that maintains its shape condition of dry eye (conjunctiva and cornea) benign tumor within the internal auditory canal growing from the acoustic nerve; may cause hearing loss and may damage structures of the cerebellum as it grows caused by a variety of bacteria. Characterized by a sense of fullness in the ear, dimished hearing, pain, and fever. devices other than a hearing aid that help the deaf to hear. hearing evaluates hearing acuity and helps to establish the degree and severity of hearing loss electronic device used to measure hearing sensitivity by delivering a series of acoustic tones that cover a range of frequencies (graphic) record of hearing one who studies and specializzes in hearing study of hearing instrument used to measure hearing hearing ear ear pertaining to the ear when normal calcium cystals break off within the labyrinth, that may trigger an episode of vertigo when the position of the head is changed (usually when turning over or sitting up) cerumean (earwax) tumor of a gland that secretes earwax (cerumen) cystlike mass ocmposed of epithelial cells and cholesterol occurring in the middle ear; may be associated with chronic otitis media cochlea
snail-shaped and contains the organ of hearing. Connects to the oval window in the middle ear pertaining to the cochlea implan (surgically inserted prosthetic device that uses electrical currents to stimulate the auditory nerve and provide hearing) pertaining to the cochlea implan (surgically inserted prosthetic device that uses electrical currents to stimulate the auditory nerve and provide hearing) cuased by conditions that interfere with the collection and transmission of sound waves through the outer and middle ear electrical process of recording the electrical activity in the cochlea (in response to sound) protein-rich fluid inside the membranous labyrinth connects the middle ear and the pharynx. It equalizes air pressure on both sides of the eardrum short tube that ends at the tympanic membrane. The inner part lies within the temporal bone of the skull and contains the glands that secrete earwax (cerumen) external structure located on both sides of the head. The aurical directs sound waves into the external auditory canal electronic device that amplifies sound used by people with impaird hearing anvil bony spaces within the temporal bone of the skull. It contains the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibule excision of the labyrinth inflammation of the labyrinth (inner ear) aka vestibular neuritis labyrinth (inner ear) generates nerve impulses, which communicate through the brain to the body's muscles and provide for the recovery of balance hammer located in the skull bone behind the external auditory canal mastoid bone
mastoidectomy mastoiditis mastoidotomy meat/o
excision of the mastoid bone inflammation of the mastoid bone incision of the mastoid bone meatus. Any passageway or opening into the body chronic disease of the inner ear characterizzed by a sensation of spinning motion (vertigo), ringing in the ear (tinnitus), aural fullness, and fluctuating hearing loss; symptoms are related to a change in volume of composition of fluid within the labyrinth. affects the vestibular labyrinth semitransparent membrane that separates the external auditory canal and the middle ear cavity. The tympanic membrane transmits sound vibrations to the ossicles fungus tympanic membrane (eardrum) inflammation of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) surgical repair of the tympanic membrane incision into the tympanic membrane (performed to release pus or fluid and relieve pressure in the middle ear) aka tympanocentesis sensitive receptor with hair cells that relay sound waves to auditory nerve fibers. These fibers then convey impulses to the auditory region of the cerebral cortex bones of the middle ear that carry sound vibrations ossicle occurs in the ossicles of the middle ear where the hardening of the stapes results in its inability to transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear, causing conductive hearing loss inflammation of the ear and the mastoid bone ear pain in the ear inflammation of the outer ear inflammation of the middle ear. Aka tympanitis physician who studies and treats diseases of the ear study of the ear (a branch of medicine that deals with diseases of the ear) abnormal condition of fungus in the ear (usually affects the external auditory canal) discharge of pus from the ear physician who studies and treats diseases of the ear, nost, and larynx (throat). Aka otolaaryngologist discharge from the ear (may be serous, bloody, consisting of pus, or containing cerebrospinal fluid) hardening of the ear (stapes) (caused by irregular bone development and resulting in hearing loss) instrument used for visual examination of the ear visual examination of the ear transmits the sound vibration to the cochlea of the inner ear clear fluid separating the bony labyrinth from the membranous labyrinth aka auricle. Skin0covered cartilaginous flap that projects form the side of the head hearing impairment in old age tuning fork is placed laternately near the auditory canal and behind the ear on the mastoid bone. Helps to assess both air and bone conduction of sound contains receptors and endolymph that help the body maintain its sense of balance (equilibrium) is caused by disease of, or trauma to, the structures of thei nner ear or the nerve pathways leading to the brain stapes (middle ear bone) excision of the stapes (erformed to restore hearing in cases of otosclerosis; the stapes is replaced by a prosthesis) stirrup hearing recording ear condition discharge ringing in th ear tympanic membrane (eardrum), middle ear instrument used to measure middle ear (function) measurement (of movement) of the tympanic membrane surgical repair (of the hearing mechanism) of the middle ear (including the tympanic membrane and the ossicles) a sense that either one's own body or the environment is revolving; may indicate inner ear disease vestibule pertaining to the vestibule pertaining to the vestibule and the cochlea tuning for is placed on the midline of the skull, assessess bone conduction of sound moving away from the midline large socket in the pelvic bone for the head of the femur. Longest bone in the body. Akathigh bone. formation of the acromoin and clavicle articulate extension of the scapula, which forms the high point of the shoulder moving toward the midline
meniere disease middle ear tympanic membrane (eardrum) myc/o myring/o myringitis myringoplasty myringotomy organ of Corti ossicles ossicul/o ossification ostomastoiditis ot/o otalgia otitis externa otitis media (OM) otologist otology otomycosis otopyorrhea otorhinolaryngologist otorrhea otosclerosis otoscope otoscopy oval window perilymph pinna presbycusis Rinne tuning fork test semicircular canals and vestibule sensorineural hearing loss staped/o stapedectomy stapes suf: -cusis suf: -graphy suf: -otia suf: -rrhea tinnitus tympan/o tympanometer tympanometry tympanoplasty vertigo vestibul/o vestibular vestibulocochlear Weber tuning fork test abduction acetabulum acromioclavicular (AC) joint acromion process adduction
ankyl/o
crooked, stiff, bent form of arthritis that first affects the spine and adjacent structures and that, as it progresses, cuases a forward bend of the spine. Aka Strumpell-Marie arthritis or disease, or rheumatoid spondylitis abnormal condition of stiffness (often referring to fixation of a joint, such as the result of chronic rheumatoid arthritis) muscles that work in opposition to each other aponeurosis suture of an aponeurosis strong sheet of tissue that acts as a tendon to attach muscles to bone made up of the upper and lower extermities plus the should and pelvic girldes. joint pain in the joint inflammation of a joint surgical puncture of a joint to aspirate fluid (surgical) breaking of a (stiff) joint radiographic imaging of a joint (with contrast media) surgical repair of a joint visual examination of a joint (used for a diarthrodial [movable] joint) surgical fixation of a joint aka joint fusion smooth layer of firm, fibrous tissue covering the contacting surface of joints point at which muscle attaches to bone without development (wasting) consists of the skull, spinal column, ribs and sternum
ankylosing spondylitis
ankylosis antagonistic muscles aponeur/o aponeurorrhaphy aponeurosis appendicular skeleton arthr/o arthralgia arthritis arthrocentesis arthroclasia arthrography arthroplasty arthroscopy arthtodesis articular cartilage articulation atrophy axial skeleton
Birmingham hip resurfacing
bone densitometry bone depressions bone marrow bone processes
bone scan
procedure that provides an option for younger, active patients needing a total hip arthroplast. The procedure requires the removal of a few millimeters of bone form the femoral head instead of the removal of the entire femoral head required in total hip arthroplaasty. a metal cap is then placed on top of the femur, and smooth metal is placed in the acetabulum determing the density of bone by radiographic techniques used to diagnose osteoporosis. DEXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) bones that have hollow areas material found in the cavities of bones bones that are raised or projected areas obtained by injecting a radioactive phosphate substance into the area under examination and hten measuring the substance's uptake with a special scanning device to detect the presence of metastatic disease of the bone and tomonitor degenerative bone disease slow movement abnormal prominence of the joint at the base of the great toe. It is a common problem, often hereditary or caused by poorly fiited shoes. Aka hallux valgus bursa (cavity) fluid-filled sac that allows for easy movement of one part of a joint over another excision of a bursa inflammation of a bursa heel bone contains little spaces like a spone and is encased in the layers of compact bone aka myocardium. Forms most of the wall of the heart. Its involuntary contraction produces the heartbear carpals (wrist bones) pertaining to the wrist wrist bones a common nerve entrapment of disorder of the wrist caused by comjpression of the median nerve. Symptoms include pain and paresthesia in portion of the hand and fingers. excision of a carpal bone chondr/o. essentially osseous tissue without the inercellular calcium salts first set of 7 bones, forming the neck specialist in treating and diagnosing diseases and disorders of the foot, including medical and surgical treatment system of treatment that consists of manupulation of the vertebral column specilist in chiropractic cartilage cartilage excision of a cartilage softeinng of cartilage surgical repair of a cartilage clavicle (collarbone) colalrbone clavicle (collarbone) pertaining to the clavicle no incision is necessary to align the bone pertaining to the coccyx four vertebrae fused together to form the tailbone coccq/o. aka tailbone
bone scan (nuclear medicine test) bradykinesia
bunion burs/o bursa (pl. bursae) bursectomy bursitis calcaneus cancellous (spongy) bone
cardiac muscle carp/o carpal carpal bones
carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) carpectomy cartilage cervical vertebrae (C1 to C7)
chiropodist ,podiatrist chiropractic chiropractor chondr/o chondr/o chondrectomy chondromalacia chondroplasty clavic/o, clavicul/o clavicle clavicul/o clavicular closed reduction coccygeal coccyx coccyx
collagen Colles fracture comminuted fracutre compact bone compount fracture computed tomography (CT) cost/o costectomy crani/o cranial cranioplasty cranioschisis craniotomy CREF crepitus debridement depression diaphysis disk/o diskectomy diskitis dorsal vertebrae dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) dyskinesia dystrophy electromyogram (EMG) endosteum epiphyseal plate epiphysis (pl. epiphyses) eversion Ewing sarcoma exostosis extension external fixation femor/o femoral femur fibromyalgia fibul/o fibula flat bones flexion fracture (fx) gout greenstick hairline fracture Haversian canals
dense connective tissue a type of wrist fracture. The fracture is at the distal end of the radius, the distal fragment being displaced backward. a fracture characterized by several breaks in the bone, producing numerous fragments dense, hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the periosteum splits open the skin, which allows more opportunity for infection to take hold of the bones and joints gives accurate definition of bone structure and demonstrates subtle changes such as linear fractures rib excision of a rib cranim (skull) pertaining the cranium surgical repair of the skull fissure of the skull (congenital) incisiion of the skull (as for surgery of the brain) closed reduction and external fixation the crackling sound heard when two bones rub against each other or gratin caused by the rubbing together of dry surfaces of a joint. Aka crepitation removal of debris any groove, opening, or hollow space. Help join bones together and offer protection for blood vessels and nerves in the area shaft of the long bone intervertebral disk excision of an intervertebral disk (a portion of the disk is removed to relieve pressure on nerve roots) aka discectomy inflammation of an intervertebral disk. Aka discitis aka thoracic vertebrae. See thoracic vertebrae a specific bone-density test. Involves taking x-rays of bones in the spinal column, pelvis, and wrist. An x-ray detector then measures how well the x-rays penetrate the bone difficult movement abnormal development record of the (intrinsic) electrical activity in a (skeletal) muscle membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone growth place. Bony end of a long bone. Aka epiphysis end of each long bone turning outward a form of osteosarcoma in children abnormal benign growth on the surface of a bone. Aka spur movement in which a limb is placed in a straight position the use of devices external to the body that produce traction femur (upperleg bone) pertaining to the femur upper leg bone pain in the fibrous tissues and muscles (a common condition characterized by widespread pain and stiffness of muscles, fatigue, and disturbed sleep) fibula (lower leg bone) runs parallel to the tibia cover soft body parts. Include the shoulder blades, ribs, pelvic bones, and skull movement tin which a limb is bend broken bone disease in which an excessive maount of uric aid in the blood causes sodium urate crystals (tophi) to be deposited in the joints, esp that of the great tow, productin arthritis an incomplete fracture in which one side of the bone is broken and the other side is simply bent
herniated disk humer/o humeral humerus hyerkinesia hypertrophy ili/o iliofemoral ilium interintercostal internal fixation intervertebral intervertebral disk intracranial
appears as a thin line on a radiographic image and may not extend completely through the bone channels where blood vessels move through within the compact bone tupture of the intervertebral disk cartilage, which allows the contents to protrude through it, putting pressure on the spinal nerve roots. Aka slipped disk, ruptured disk, herniated intervertebral disk or herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP) humerus (upper arm bone) pertaining to the humerus upper arm bone excessive mvement (overactive) excessive development ilium pertaining to the ilium and femur upper, wing-shaped part on each side between pertaining to between the ribs pins, screws, plates, and so forth are fastened to the bones to maintain correct alignment. Requires an incision in order to palce the necessary devices pertaining ot between the vertebrae cartilaginos pad found between the vertebrae in the spine pertaining to within the cranium
inverison irregular bones ischi/o ischiofibular ischium ischopubic kinesi/o kyph/o
kyphoplasty
kyphosis lamin/o lamina (pl. laminae)
laminectomy
turning inward bones that don t fit into the four basic types of bone. Include vertebrae and the ossicles ischium pertaining to the ischium and fibula lower, rear poriton on which one sits pertaining to the ischium and pubis movement, motion hump (increased convexity of the spine) similar to vertebroplast except a bloonlike device is used to expan the compressed vertebra before the cement is injected abnormal condition of a hump (increased convexity of the thoracic spine as viewed from the side) aka hunchback or humpback lamina (thin, flat plate or layer) part of the vertebral arch excision of a lamina (often performed to relieve pressure on the nerve roots in the lower spine caused by a herniated disk and other conditions) flexible, tough band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches one bone to another at a joint found in the legs and arms bent forward (increased concavity of the spine) abnormal condition of bending forward(increased concavity of the lumbar spine as viewed from the side ) aka swayback loin, lumbar region of the spine third set of five larger vertebrae, which forms the inward curve of the spine pertaining to the loins (part of the back between the thorax and pelvis) pertaining to the loins and the ribs pertaining to the lumbar regions (loin) and the sacrum an infection caused by a bacteria (Borrelia burgdorferi) carried by deer ticks and transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected tick. to evaluate the soft tissue of the knee, spina lstenosis, spinal cord defects, and degenerative disk changes a bone that doesn't mend and realign correctly lower jawbone mandible (lower jawbone) upper part of the sternum maxilla (upper jawbone) maxilla (upper jawbone) upper jawbone excision of the maxilla inflammation of the maxilla bony prominence towards the midline of the body contains yellow bone marrow meniscus (crescent) excision of the meniscus (performed for a torn cartilage) inflammation of a menisus crescent-shaped cartilage found in the knee hand bones as the epiphysis and epiphyseal plates chagne and grow together, they form the metaphysis to rtreat deformities associated with rheumatoid arthritis or hallux valgus and to treat painful or unstable joints foot bones kind of tissue composed of fibers or cells that are able to contract, resulting in movement consists of bones, muscles, bone arrow, joints, cartilage, and bursae. The body contains 206 bones and more than 600 muscles. Joints are located any place that two or more bones meet, and contain cartilage and bursae group of hereditary diseases characterized by degeneration of muscle and weakness muscle muscle weakness chrnoic disease characterized by muscle weakness and thought to be caused by a defect in the transmission of umpulses from nerve to muscle cell. The face, larynx, and throat are frequently affected; no true paralysis of the muscles exists bone marrow tumor of the bnone marrow see cardiac muscle disease of the muscle suture of a muscle muscle see vertebral foramen no healing takes places a slanted fracture of the shaft of the long axis of a bone projection at the upper end of the ulna tht forms the bony point of the elbow proper alignment can only occur by making an incision open reduction and internal fixation
ligament long bones lord/o
lordosis lumb/o lumbar vertebrae (L1 to L5) lumbar vertebrae (L1 to L5) lumbocostal lumbosacral
Lyme disease
magnetic resonance imaging malunion mandible mandibul/o manubrium maxill/o maxill/o maxilla maxillectomy maxillitis medial malleolus medullary cavity menisc/o meniscectomy meniscitis meniscus metacarpal bones
metaphysis
metatarsal arthroplasty metatarsal bones muscle
muscoskeletal system muscular dystrophy (MD) my/o, myos/o myasthenia
myasthenia gravis *MG) myel/o myeloma myocardium myopathy myorrhaphy myos/o neural canal nonuion oblique fracture olecranon process open reduction ORIF
orthopedics (ortho) orthopedist
orthotics orthotist osseous ossification oste/o ostectomy osteoarthritis (OA) osteoblast osteocarcinoma & osteosarcoma osteochondritis osteoclasis
osteoclast
osteoclasts osteocyte osteofibroma osteoitis osteomalacia osteomyelitis osteonecrosis osteopath
osteopathy
osteopenia
branch of medicine dealing with the study and treatment of diseases and abnormalities of the muscoloskeletal system physician who speciaizes in orthopedics mking and fitting of orthopedic appliances, such as arch supports, used to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities a person who specialized in orthotics bony process of bone formation bone marrow excision of bone inflammation of the bone and joint developing bone cell are both malignant tumors of the bone inflammation of the bone and cartilage (surgical) breaking of a bone (to ocorrect a deformity) type of bone cell involved in absorption and removal of bone minerals. It works in balance with osteoblasts to maintain healthy bone tissue aka bone phagocytes. Resorb, or digest, bony tissue and bone minerals inside each bone, thus enlarging the inner cavity bone cell tumor of the bone and fibrous tissue (benign) inflammation of the bone softening of bones inflammation of the bone and bone marrow (caused by bacterial infection) abnormal deat of bone (tissues) physician who specailizes in osteopathy system of medicine that used the usual forms of diagnosis and treatment but places greater emphasis on the role of the relation between body organs and the muscoloskeletal system; manipulation may be used in addition to other treatments abnormal reduction of bone mass (caused by inadequate replacement of bone lost to normal bone lysis and can led to oetoporosis) abnormal condition of stonelike bones (marblelike bones caused by increased formation of bone) malignant tumor of the bone instrument used to cut into the bone abnormal loss of bone density that may lead to an increase in fractures of the ribs, thoracis and lumbar vertebrae, hips, and wrists after slight trauma (occurs predominantly in postmenopausal women) phalanges (finger or tow bones) excision of a finer or toe bone patella (kneecap). Largest sesamoid bone in the body. Flat bone at the front of the knee excision of the patella pelvis, pelvic bone pelvis, pelvic bone pertaining to the pelvis made up of three bones fused together aka hip or pelvic bone. Protects internal organs and supports the lower extremities pertaining to the pelvis and the sacrum minimally invasive operation in which an interventional radiologist places a needle through the skin into the damade vertebra. outermost layer of the bone, made up of fibrous tissue fibula (lower leg bone) stone finger and toe bones specialist in treating and diagnosing diseases and disorders of the foot, including medical and surgical treatment movable end of the muscle, farthest from the trunk unmovable bone at the more stable end (nearest the trunk) pain in multiple joints inflammtion of many muscles areas of attachment for ligaments of muscles movement that turns the palm down an artificial substitute for a missing body part such as leg, eye, or total hip replacement pubis pertaining to the pubis cartilaginous joint at which two pubic bones come together anterior portion of the pelvic bone pertaining to the pubis and femur fever incision into the vertebral column fissure of the vertebral column (congenital) aka spina bifida radius (lower arm bone) pertaining to the radius radiographic imaged to identify fracures of tumors, monitor healing, or identify abnormal structures
osteopetrosis osteosarcoma osteotome
oteoporosis pahalang/o pahalangectomy patell/o patellectomy pelv/I, pelv/o pelv/o pelvic pelvic bone, hip bone pelvic gridle pelvisacral
percutaneous vertebroplasty (PV) periosteum perone/o petr/o phalanges (sing. Phalanx)
podiatrist point of insertion point of origin polyarthralgia polymyositis processes pronation prosthesis (pl.prostheses) pub/o pubic pubic symphysis pubis pubofemoral pyrexia rachiotomy rachischisis radi/o radial
radiography of the bones and joints
ranchi/o range of movement (ROM) red marrow reduction rhabdomy/o
rhabdomyolysis rheumatoid arthritis *RA) rheumatoid factor (RF) rheumatologist rheumatology rotation sacr/o sacral sacroiliac sacrum sarc/o sarcopenia scapul/o scapula sciatica scoli/o scoliosis sesamoid bones short bones simple fracture single-photon emission computer tomography (SPECT) sinus
spine, vertebral column varying range through which a joint can be extended and flexed thick, bloodlike material found in flat bones and the ends of long bones; location of blood cell formation process of alignment denotes a relationship to striated or skeletal muscle dissolutin of striated muscle (the severity of the condition and the degree of weakness and pain vary. Some causes of the illness are trauma, extreme exertion, and drug toxicity; in severe cases renal failure can result) a chronic systemic disease characterized by autimmune inflammatory changes in the connective tissue throughout the body lab test htat looks for a substance present in the blood of those who have rheumatoid arthritis specialist in rheumatology branch of medicine concerned with inflammatory disorders of the ocnnective tissue and related structures turning around its own axis sacrum pertaining to the sacrum sacrum and the ilium next five vertebrae, which fuse together to form a triangular bone positioned between the two hip bones denoting relationship to flesh or tissue abnormal reduciton of connective tissue (such as loss of skeletal muscle mass in the elderl) scapula (shoulder blade) shoulder blade radiated pain down the hip crooked, curved abnormal condition of (lateral) a curved spine small rounded bones found near any joiny; they increase the efficiency of the joint muscle around them. The patella (knee cap) is the largest of these bones found in the wrists and ankles does not rupture the skin even more sensitive nuclear method for detecting bone abnormalities sinus/o. small air cavity aka striated muscles. Attached to bones by tendons and make body movement possible. Produce action by pulling and by working in pairs. Aka voluntary muscles. Because we have ocntrol over these muscles aka unstriated muscles. Located in internal organs such as the walls of blood vessels and the digesetive tract. They are called involuntary muscles b/c they respond to umpulses from the autonomic nerves and are not controlled voluntarily narrowing of the spina lcanal with compression of nerve roots. The condition is either congenital or due ot spinal degeneration. vertebra inflammation of the vertebral joints forward slippin of one vertebra over another abnormal condition of the vertebra (a general term used to describe chagnes to the spine form osteoarthritis or ankylosis) fusing together of the vertebrae aka spinal fusion aka cancellous tissue. Found in the inteiror of many bones, where the spaces are usually filled with marrow sternum (breadtbone) pertaining to the sternum and clavicle resemblind the sternum breastbone see skeletal muscles pertaining to below the rib pertaining to below the mandible pertaining to below the maxilla pertaining to below the scapula pertaining to below the sternuum weakness embryonic or immature break break surgical fixation, fusion deficiency growth split, fissure movement that turns the palm up above pertaining to above the patella pertaining to above the scapula
skeletal muscles
smooth muscles spinal stenosis spondyl/o, vertebr/o spondylarthritis spondylolisthesis spondylosis spondylosyndesis spongy bone stern/o sternoclavicular sternoid sternum striated muscles subcostal submandibular submaxillary subscapular substernal suf: -asthenia suf: -blast suf: -clasia, -clasis, -clast suf: -clast suf: -desis suf: -penia suf: -physis suf: -schisis supination suprasuprapatellar suprascapular
sym-, synsymphysis synergistic muscles synovectomy synovi/o synovia synoviosarcoma systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) talus tars/o tarsectomy temporomandibular joint ten/o, tend/o, tendin/o tend/o tendin/o tendinitis tendon tendon tenomyoplasty tenorrhaphy tenosynovitis thoracic vertebrae (T1 to T12) tibi/o tibia tibia nd fibula tibial total hip replacement arthroplasty *THA) total knee joint replacement arthroplasty (TKA) total knee replacement (TKR) transverse fracture uln/o ulna and radius ulnoradial unstriated muscles
together, joined growing together (as in symphysis pubis) muscles that contract together excision of the synovial membrane (of a joint) synovia, synovial membrane fluid secreted by the synovial membrane and found in joint cavities malignant tumor of the synovial membrane the colalgen in conenctive tissue throughout the body becomes chronically inflamed, affecting tendons, ligaments, bones, and cartilage all over the body. the first of the tarsal bones of the foot tarsals (ankle bone) excision of (one or more) tarsal bones aka TMJ. Mandible + temporal bone tendon tendon tendon inflammation of a tendon aka tendonitis band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
surgical repair of the tendon and muscle suture of a tendon inflammation of the tendon and synovial membrane second set of 12 vertebrae. They articulate with the 12 pairs of ribs to form the outward curve of the spine. tibia (lower leg bone) aka shin bone. Distal end of the femur. lower leg bones pertaining to the tibia indicated for degenerative joint disease or rheumatoid arthritis. The operation commonly involves replacement of the hip joint with a metallic femoral head and a plastic-coated acetabulum designed to replace worn surfaces of the knee joint replacement of the entire knee joint, either unilaterally or bilaterally a fracture occurring at right angles to the long axis of the implicated bone ulna (lower arm bone) lower arm bones pertaining to the ulna and radius see smooth muscles made up of bones called vertebrae or vertebra through which the spinal cord runs. The vertebral column protects the spinal cord, supports the head, and provides points of attachment for irbs and muscles aka neural canal. Where the spinal cord passes through pertaining to the vertebrae and ribs surgical repair of the vertebra aka involuntary muscles. See involuntary muscles see skeletal muscles lower portion of the sternum xiphoid process soft, fatty material found in the medullary cavity of long bones a tumor that develops on a cranial nerve and grows within the auditory canal fear of being in high places aka sensory neurons. conveying toward a center (ie. Afferent nerves carry impulses to the CNS) disease characterized by early dementia, confusion, loss of recognition of persons or familiar surroundings, restlessness, and impaired memory progressive muscle atrophy caused by degeneration and scarring of neurons along the lateral columns of the spinal cord that control muscles aka Lou Gehrig disease without (loss of) feeling or sensation an eating disorder characterized by a distrubed perception of body image resulting in failure to maintain body weight, intensive fear of gaining weight, pronounced desire for thinness, and ,in females, amenorrhea an emotional disorder characterized by feelings of apprehension, tension, or uneasiness arising typically from the anticipation of unreal or imagined danger inability or refusal to swallow condition of without speaking (loss or impairment of the ability to speak) delicate middle layer of the meingnes. Is loosely attached to the pia mater by weblike fibers, which allor for the subarachnoid space loosely attached web-like covering lack of muscle coordination a disorer of learning and behavioral problems characterized by marked inattention, distractability, impulsiveness , and hyperactivity unusual sensation before the onset of a seizure
vertebral column vertebral foramen vertebrocostal vertebroplasty visceral muscles voluntary muscles xiiphoid process xiph/o yellow marrow acoustic neuroma acrophobia afferent Alzheimer disease (AD) amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) anesthesia
anorexia nervosa anxiety disorder aphagia aphasia arachnoid arachnoid ataxia attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) aura
autism axon Bell palsy
a spectrum of mental disorders, the features of which include onset during infancy or childhood, preoccupation with subjective mental activity, inability to interact socially, and impaired communicated. Aka Autism spectrum Disorders (ASD) or pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) one long thread-like extension paralysis of muscles on one side of the face, usually a temporary condition a major psychological disorder typified by a distrubance in mood. Is manifested by manic and depressive epidodes that my alternate or elements of both may occur simultaneously brain may be injured at the site of its impact against the cranial wall as well as from rebounding against the opposite skull surface contained with cranium, the center for coordinating body activities largest organs in the body stemlike portion of the brain that conencts with the spinal cord. Ten of the 12 cranial nerves originate in the brainstem. an eating disorder characterized by uncontrolled bing eating followd by purging (induced vomiting) a number of branching projections. Each projection is called a dendrite consists of the braing and spinal cord pain in the head (headache) aka cephalgia cerebellum inflammation of the cerebellum located under the posterior portion of the cerebrum. Fuction is to assist in the coordination of skeletal muscles and to maintain balance. Aka hindbrain. cerebrum, brain pertaining to the cerebrum aneurysm in the cerebrum radiographic imaging of the blood vessels in the brain (after an injfection of contrast medium)
bipolar disorder
blunt trauma brain brain
brainstem
bulimia nervosa cell body central nerous system (CNS) cephalalgia cerebell/o cerebellitis
cerebellum cerebr/o cerebral cerebral aneurysm
cerebral angiography
cerebral embolism
cerebral palsy (CP)
cerebral thrombosis cerebrospinal fluid
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
cerebrum claustrophobia cognitive coma computed tomography of the brain (CT scan)
concussion conscious
an embolus lodges in a cerebral artery ,causing sudden blockage of blood supply to the brain tissue. condition characterized by lack of muscle control and partial paralysis , cuased by a brain defect or lesion present at birth or shortly after pertaining to the crebrum, abnormal condition of a clot (blood clot in a blood vessel of the brain). Cause of ischemic stroke sflows through the subarachnoid space around the brain and spinal cord clear, colorless fluid contained in the ventricles that flows through the subarachnoid space around the brain and spinal cord. It cushions the brain and spinal cord from shock, transports nutrients, and clears metabolic waste largest portion of the brain, divided into left an right hemispheres. Controls the skeletal muscles, interprets general senses, and contains centers for sight and hearing. Intellect, memory, and emotional reactions also take place in the cerebrum fear of small, enclosed places pertaining to the mental processes of comprehension, judgment, memory, and reason state of profound unconsciousness process the includes the use of a computer to produce a series of brain tissue images at any desired depth. Procdure is painless and particualrly useful in diagnosing brain tumors injury to the brain caused by major or minor head trauma; symptoms include vertigo, headache, and possible loss of consciousness awake, alert, aware of one's surroundings injury associated with a blow to the skull in which force of the impact is transmitted through the skull bones to the opposite side of the head, where a bruise, fracture, or other sign ofjinjury appears emotional conflict is repressed and changed into al oss of alteration of physical functioning, including blindness ,anesthesia, paralysis, and involuntary muscle movements sudden, involuntary contratction of a group of muscles; may be present during a seizure origin for a blow to the body reaches the larynx, trachea, bronchi, aorta, esophagus, and stomach and is the only cranial nerve that leaves the head and neck region pertaining to the cranium and cerebrum large round superior portion of the skull, for protection process of recording (scan) the spinal cord condition of confused, unfocused, irrational agitation. May be caused by nutritional imbalances, systemic infections, head injury, neurologic disease, and by ingestion and withdrawal of psychoactive ubstances cognitive impairment characterized bya loss of intellectual brain function. Patients have difficulty in various ways, including difficulty in performing complex tasks, reasoning, learning and retaining new info, orientation, word finding, and behavior. NOT considered part of normal aging threadlike extensions of the cytoplasm of a neuron contains the thalamus and hypothalamus a state of mental confusion as to time, place, or identity hard, dura mater though outer layer of the meninges
contrecoup
conversion disorder convulsion coup
cranial nerve X craniocerebral cranium CT myelography
delirium
dementia dendrite diencephalon disorientation dur/o dura mater
duritis dysarthria dysphasia efferent electroencephalogram (EEG) electroencephalograph electroencephalography embolism
inflammation of the dura mater inability to use speech that is ditinct and connected because of a loss of muscle control after damage to the peripheral or CNS condition of difficulty speaking aka motor neurons. conveying away from the center (ie., efferent nerves carry info AWAY from the CNS) record of the electrical impulses of the brain instrument used to record the electrical impulses of the brain process of recording the lectrical impulses of the brain
movement of a clot from a site outside the brain, through the bloodstream, to the neurovasculature mass, such as blood clot, foreign object, quantity of air, or piece of thrombus that circulates in the embolus bloodstream until it becomes lodged in a vessel encephal/o brain encephalitis inflammation of the brain encephalomalacia softening of the brain encephalomyeloradiculitis inflammation of the brain, spinal cord, and nerve roots encephalosclerosis hardening of the brain condition characterized by recurrent seizures; a general term given to a group of neurologic epilepsy disorders, all characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the brain esthesi/o sensation, sensitivity, feeling a group of diagnostic tests that measure changes and responses in brain waves elicited by visual, auditory, or somatosensory stimuli. Visual evoked response (VER) is a respose to visual stimuli. evoked potential studies (EP studies) Auditory evoked response (AER) is a response to auditory stimuli frontal lobe largest of the lobes. gait a manner or style of walking gangli/o, ganglion/o ganglion gangliitis inflammation of a ganglion ganglion (pl. ganglia) group of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS ganglion/o ganglion ganglionectomy excision of a ganglion aka gangliectomy gli/o glia, gluey substance specialized cells that support and nouris hnervous tissue .some cells assist in the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid and others assist with phagocytosis. They do not conduct impulses. Aka glia neuroglia glicyte glial cell tumor composed of developing glial tissue (most malignant and most common primary tumor of the glioblastoma brain) glioblastoma multiforme malignant and rapidly growing form of glioma. Composed, in part, of immature neuroglia tumor composed of the glial tissue (glioma is used to describe all primary neoplasms of the brain and spinal cord) glioma inner section. Cell bodies and dendrites of what are, predominantly, interneurons and motor gray matter neurons, are unmyelinated and, thus, gray in color any traumatic damage to the scalp, skull, or brain tissue. Range from a minor wound to penetration head injury of the skull with severe injury to brain structures hemiparesis slight paralysis of half (right or left side of the body) hemiplegia hemispheres Huntington disease hydrocephalus hyperesthesia paralysis of half (right or left side of the body); stroke is the most common cause of hemiplegia right and left halves of the brain genetically transmitted degenerative disorder caused by a deficiency in specific neurotransmitters produced in the midbrain increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain, which can cause enlargement of the cranium in infants excessive sensitivity (to stimuli) preoccupation with the fear of having a serious medical condition. Fueled by the person's misinterpretation of real or imagined symptoms and persists despite medical reassurance that no physical illness exists activates and integrates functions of the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system, regulating functios like body temperature, appertite, emotional expression, and sleep cycles treatment, physician moves like a wave along the length of the cell, form the dendrite to the axon begins when the receptors of our sensory neurons detect a change in the environment unable to express one's thoughts or ideas in an orderly ,intelligible manner (occurring) between seizures or attackes pertaining to within the cerebrum bleeding into the brain as aresult of a ruptured blood vessel within the brain. A cause of hemorrhagic stroke, is frequently associated with high blood pressure insertion of a needle into the subarachnoid space usually between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. Aka spinal tap a noninvasive technique that produces sectional images of soft tissues of the brain or spine through a stron magnetic field. Unlike a CT scan, MRI produces images without use of radiation.
hypochonriasis
hypothalamus iatr/o impulse impulse conduction incoherent interictal intracerebral intracerebral hemorrhage lumbar puncture (LP) magnetic resonance imaging o the brain or spine (MRI scan)
major depression
a mood distrubance characterized by feelings of sadness ,despair, discouragement, hopelessness, lack of joy, altered sleep patterns, and difficulty with decision making and daily function. Aka clinical depression, mood disorder
medulla oblongata mening/o, meningi/o meninges meningi/o meningioma meningitis meningocele
meningomyelocele ment/o, psych/o mental midbrain mon/o mononeuropathy monoparesis monoplegia
multiple sclerosis (MS) myel/o myelin sheath myelomalacia nauroplasty
nerve nerve tracts
nervous system neur/o neuralgia neurasthenia neurectomy neuritis neuroarthropathy neuroid neurologist neurology neurolysis neuroma neuroma
neuron neuropathy neurorrhaphy neurotomy nuclei
located between the pons and spinal cord. It contains centers that control respiration, heart rate, and the muscles in the blood vessel walls, which assist in determining blood pressure meninges three layers of membrane that cover the brain and spinal cord meninges tumor of the meninges (benign and slow growing) inflammation of the meninges protrusion of the meninges (through a defect in the skull or vertebral arch) protrusion of the meninges and spinal cord (through a neural arch defect in the vertebral column) aka myelomeningocele mind pertaining to the mind most superior portion of the brainstem one, single disease affecting a single nerve slight paralysis of one (limb) paralysis of one (limb) degenerative disease characterized by sclerotic patches along the brain and spinal cord. Include fatigue , balance, and coordination impairments, numbness and vision problems spinal cord covers the axons of many nerves in the body softening of the spinal cord surgical repair of a nerve cordlike structure made up of fibers that carries impulses from one part of the body to another. Thera re 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 spinal nerves large bundle of nerve fibers divided into smaller bundles a complex communication system allowing for the coordination of body functions and activities. Designed to detect changes inside and outsie the body, toevaluate this sensory information, and to send directions to muscles orglands in response. Provides for mental activities usch as thought,memory, and emotions nerve pain in a nerve nerve weakness exciion of a nerve inflammation of a nerve disease of nerves and joints resembling a nerve physicia who studies and treats diseases of the nerves (nervous system) study of nerves separatinga a nerve (from adhesions) tumor made up of nerve (cells) tumor composed of nerve cells. A benign neoplasm. a nerve cell that conducts nerve impulses to carry out the function of the nervous system. Destroyed neurons acannot be replaced disease of the nerves (peripheral) suture of a nerve incision into a nerve small clusters of cell bodies
a disorder characterized by intrusive, unwtned thoughts that result in the tendency to perform obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) repetitive acts or rituals (compulsions), usually as a means of releasing tension or anxiety occupies a relatively small, pyramid-shaped area at the posterior of the cerebrum. Visual images are registered. Contains the visual associative areas, which enable interpretation of images an episode of sudden onset of acute anxiety, occurring unpredictably, with feelings of acute apprehension, dyspnea, dizziness, sweating, and/or chest pain, deprrsonalization, paresthesia and fear of dying, loss of mind or control total paralysis aka pamplegia paralysis from the waist down caused by damage to the lower level of the spinal cord abnormal sensation (s.a burning, prickling, or tingling sensation, often in the extremities; amy be caused by nerve damage or peripheral neuropathy) lies behind the frontal lobe and above the temporal lobe. Serve as centers for language and general sensory functions chronic degenerative disease of the central nervous system. Tremors of the hands and feet, rigidity, expresionles s face, and shuffling gait. Offurs after the age of 50 years madue of cranial nerves, which carry impulses between the brain and neck and head, and spinal nerves, which carry mesasages between the spinal cord and abdomen, kimbs, and chest a number of disorders of the PNS speech
occipital lobe
panic attack panplegia paraplegia
paresthesia
parietal lobe
Parkinson disease (PD)
peripheral nervous systems (PNS) peripheral neuropathy phas/o
phobia
a marked and persistent fear that is excessive or undreasonable cued by the presence or anticipation of a specific situation or object
pia mater
pica poli/o poliomyelitis polyneuritis
polyneuropathy pons
thin, inner layer of the meninges. Has a rich supply of blood vessels that nourish the nervous tissue compulsive eating of nonnutritive substances such as clay or ice. This condition is often a result of an iron deficiency. gray matter inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord inflammation of many nerves disease of many nerves (most often occurs as a side effect of diabetes mellitus, but may also occur as a result of drug therapy, critical illness such as spesis or carcinoma) literally means bridge. It connects the crebrum with the cerebellum and brainstem
positron emission tomography of the nuclear medicine imaging technique with a radioactive substance that produces sectional imaging of rbain (PET scan) the brain to examine blood flow and metabolic activity. Images are projected on a viewing screen postictal (occurring) after a seizure or attack disorder characterized by an acute emotional response to a traumatic event perceived as life threatening or severe emotional stress such as an airplane crash, repeated physical or emotional posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) trauma, or military combat psych/o mind study of the mind (profession that involves dealing with the mind and mental processes in relation psychology to human behavior) psychopathy (any) disease of the mind psychosomatic pertaining to the mind and body (interrelations of) pyschiatrist a physician who studies and treats disorders of the mind specialty of the mind (branch of medicine that deals with the treatment of mental disorders) originating in the mind specialist of the mind abnormal condition of the mind (major mental disorder characterized by extreme derangement, often with delusions and hallucinations) four paralysis of four (limbs) nerve root (proximal end of a peripheral nerve, closest to the spinal cord) incision into a nerve root nerve root (proximal end of a peripheral nerve, closest to the spinal cord) inflammation of the nerve roots disease of the nerve roots condition that may follow acute viral infection and is characterized by acute encephalopathy combined with fatty infiltration of internal organs nerve root (proximal end of a peripheral nerve, closest to the spinal cord) inflammation of the nerve root, meingnes, and spinal cord incision into a nerve root any one of a large group of psychotic disorders characterized by gross distortions of reality, disturbance of language and communication, withdrawal from social interaction, and the disorganization and fragmentation of thought, perception, and emotional reaction inflammation of the sciatic nerve, causing pain that travels from the thigh through the leg to the foot and toes; can be caused by injury ,infection, athritis, herniated disk or from prolonges pressureo n the nerve from sitting for long periods sudden surge of abnormal electrical activity in the brain, resulting in involuntary body movements or behaviors aka herpes zoster. Viral disease that affects the peripheral nerves and causes blisters on the skin that follow the course of the affacted nerves tube implanted in the body to redirect the flow of a fluid disorders characterized by physical symptoms for which no known physical cause exists passes through the vertebral canal extending from the medulla oblongata to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. Conducts never impulses to and from the brain and initiates reflex action to sensory information without input from the brain involves the use of an intrument that helps to target the precise location of a tumor and then delivers a focused beam of radiation to destroy the abnormal growth occurs when there is an interruption of blood supply to a region of the brain, depriving nerve cells in the affacted area of oxygen and nutruents. Aka cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or brain attack bleeding caused by a ruptured blood vessel just outside the brain that raidly fills the space between the brain and skull (subarachnoid space) with blood. pertaining to below the dura mater pertaining to below the dura mater, tumor of blood specialist, physician treatment, specialty shallow depression on the surface of an organ. usually not as deep as a fissure. point of functional contact between neurons or between a nueron and an effector organ, across which nerve impulses are transmitted, usually by a chemical neurotransmitter released by the axon terminal of the stimulated cell fainting or sudden loss of consciousness caused by lack of blood supply to the cerebrum
pyschiatry pyschogenic pyschologist
pyschosis (pl. psychoses) quadr/i quadriplegia radic/o, radicul/o, rhiz/o radicotomy, rhizotomy radicul/o radiculitis radiculopathy
Reye syndrome rhiz/o rhizomeningomyelitis rhizotomy
schizophrenia
sciatica
seizure
shingles shunt somatoform disorders
spinal cord
stereotaxic radiosrugery
stroke
subarachnoid hemorrhage subdural subdural hematoma suf: -iatrist suf: -iatry sulcus
synapse syncope
temporal lobe thalamus thrombosis thrombus transient ischemic attack (TIA) unconsciousness vagus ventricles
found in the lateral region of the cerebrum. Involved with the functions of hearing, taste, smell, and balance. Associated areas for memory and learning are also located within the temporal lobe serves as a major sensory relay station, directing impulses to the cerebral cortex abnormal condition of a clot, or thrombus blood clot attached to the interior wall of ablood vessel, of ten causing vascular obstruction sudden deficient supply of blood to the brain lasting a short time. Sumptoms are temporary and the usual outcome is complete recovery. state of being unaware of surroundings and incapable of responding to stimuli as a result of injury, shock, illness, or drugs 10th cranial nerve. Pair of cranial nerves primarily responsible for parasympathetic control over the heart and several other internal organs spaces within the brain that contain a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid..
vertebral canal white matter zoophobia acidosis acr/o acromegaly Addison disease aden/o adenectomy adenitis adenomegaly adenopathy adenosis adren/o, adrenal/o adrenal cortex adrenal glands or suprarenals adrenal medulla
runs through the protective spinal column. Contains the three meningeal coverings: CSF, cushion of fatty tissue, and blood vessels. Are 31 spinal nerves that are attached to the spinal cord. large bundle of myelinated axons. Surrounds the core of the spinal cord fear of animal and insects condition brought about by an abnormal accumulation of acid products of metabolism such aas seen in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus extremities, height enlargement of the extreimities (and bones of the face, hands, and feet caused by the excessive production of the growth hormone by the pituitary gland after puberty) chronic syndrome resulting from a deficiency in the hormonal secretion of the adrenal cortex. gland excision of a gland inflammation of a gland enlargement of a gland abnormal condition of any gland abnormal condition of a gland adrenal glands outer portion of the adrenal gland paired glands, one of which is located above each kidney. Outer portion is called the adrenal cortex, and the inner portion is called the adrenal medulla. inner part of the adrenal gland excess secretion of androgens by the inner layer of the adrenal cortex. Involves the expression, in women, of male secondary sexual characteristics, including deepening of the voice and abnormal hair growth on the fact and body excision of (one or both) adrenal glands inflammation of the adrenal glands excessive development of the adrenal cortex
adrenal virilism adrenalectomy adrenalitis adrenocorticohyperplasia
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the adrenal cortex adrenomegaly enlargement (of one or both) of the adrenal glands adrenopathy disease of the adrenal gland secreted by the adrenal cortex. Electrolytes (mineral salts) that are necessary for normal body aldosterone function are regulated by this hormone androgen any steroid hormone or substance that promotes masculine traits anterior lobe or adenohypohysis produces and secretes the following hormones antidiuretic hormone (ADH) stimulates the kidney to reabsorb water calc/i calcium calcipenia calcium in blood aka hypocalcemia may be used to teset bone density deficiencies related to hypoparathyroidism. Also help visualize computed tomography (CT) the size of the adrenal glands in cases of Addison's disease cortex outer region of the adrenal gland cortic/o cortex (outer layer of a body organ) cortical pertaining to the cortex cortical disorder disorder pertains specifically to the cortex of the adrenal gland corticoid resembling the cortex secreted by the adrenal cortex. Aids the body during stress by increasing glucose levels to provide cortisol energy aka hydrocortisone cortisone similar glucocorticoid, can be prepared synthetically and are prescribed for inflammation condition caused by congenital absence or atrophy (wasting away) of the thyroid gland, resulting in cretinism hypothyroidism. Aka congenital hypothyroidism group of signs and symptoms attributed to the excessive production of cortisol by the adrenal cortices. This syndrome may be the result of a pituitary tumor or a primary adrenal gland dysfunction. Signs include abnormally pigmented skin, "moon face", pads of fat on the chest and abdomen, "buffalo hump", wasting away of muscle, and hypertension result of decreased secretion of antidiuretic hormone by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Symptoms include excessive thirst (polydipsia), large amounts of urine (polyuria), and sodium being excreted from the body
Cushing syndrome
diabetes insipidus (DI)
diabetes mellitus (DM) diabetic neuropathy diabetic retinopathy dips/o dwarfism endoendocrin/o endocrine endocrine system endocrinologist endocrinology endocrinopathy epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline) erythropoietin eueuthyroid exoexocrine exophthalmic exophthalmometry exophthalmos eyglycemia
chronic disease involving a disorder of carbohydrate mteabolism caused by underactivity of the islets of Langerhands and characterized by elevated blood sugar (hyperglycemia). DM can cause chronic renal disease, retinopathy, and neuropathy. In extreme cases the patient may develop ketosis, acidosis, and finally coma destruction of nerves in the extremities blood vessels of the retina may be affected resulting in visual loss and blindness thirst hyposecretion of growth hormone. Body is properly proportioned, but growth is stunted. Tests such as radioimmunoassay studies (RIA) in or within endocrine secreting substances internally composed of endocrine glands distributed throughout the body. Regulates body activities through the use of hormones physician who studies and treats diseases of the endocrine (system) the study of the endocrine (system) (a branch of medicine dealing with diseases of the endocrine system) (any) disease of the endocrine (system) secreted by the adrenal medulla. Help the body to deal with stress by increasing the BP, heartbeat, and respirations a substance that stimulates the production of red blood cells normal or good resembling a normal thyroid gland (normal thyroid function) out or away sweat glands deliver their secretions through a duct condition is caused by increased deposits of fat in the tissues at the back of the eye socket. diagnostic technique that measures the forward displacement of the eyes in Graves' disease, most common form of hyperthyroidism abnormal protrusion of the eyeball normal (level of) sugar in the blood (within normal range) a blood test performed ater the patient has fasted for 8 to 10 hours to determine the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood at the time of the test. Elevation may indicated diabete mellitus regulate development, growth, and function of the ovaries and testes sometimes develops during pregnancy because of overall hormonal changes at that time. condition brought about by hypersecretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland before puberty a polypeptide hormone, secreted by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhands, that stimulates the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver. Antagonizes, or opposes, the effect of insulin. Stimulates the conversion of glycogen to glucose. triggers the transformation of gatty acids and amino acids into glucose hormone secreted from ells in the middle layer of the adrenal cortex. Help maintain normal blood glucose levels and normal blood pressure measures the body's response to a concentrated glucose solution. Tourinely use to diagnose gestational diabetes a blood test used to monitor diabetic treatment by measuring the amount of glycosylated hemoglobin in the blood. HbAiC provides an indication of blod sugar level over the past 3 months, covering the 120 dat lifespan of the red blood cell. Aka hemoglobin A1C enlargement of the thyroid gland inner layer of the adrenal cortex that secrete male and female sex hormones. Also secreted by the ovaries in the form of estrogen and by the testes. Respnsible for the manifestation of secondary sex characteristics and are required for reproduction. affect the male and female reproductive systems a disorder of the thyroid gland characterized by the presence of hyperthyroidism, goiter, and abnormal protrusion of the eyeballs (exophthalmos) regulates the growth of the body abnormal hair growth stability of the body's internal environment chemical messengers released into the bloodstream influcence metabolic activities, growth, and development. Secreted by the endocrine glands a chemical substance secreted by an endocrine gland that is carried in the blood to a target tissue excessive calcium in the blood excessive sugar in the blood elevation in the amount of insulin. Caused by an insulin-secreting tumor in the islets of Langerhans or by exceeding a prescribed dose of the hormone. excessive potassium in the blood state of excessive pituitary gland activity (characterized by excessive secretion of pituitary hormones) excessive production of hormones state of excessive thyroid gland activity (characterized by excessive secretion of thyroid hormones) signs and symp: weight loss, irritability, and heat intolerance
fasting blood sugar (FBS) follicle-stimulating hormong (FSH), luteinizing hormone gestational diabetes gigantism
glucagon glucocorticoid glucose tolerance test (GTT)
glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) goiter
gonadocorticoids gonadotropic hormones Graves disease growth hormone (GH) hirsutism homeostasis hormones hormones hypercalcemia hyperglycemia hyperinsulin hyperkalemia hyperpituitarism hypersecretion hyperthyroidism
hypocalcemia hypoglycemia hypokalemia hyponatremia
deficient calcium in the blood deficient sugar in the blood deficient potassium in the blood deficient sodium in the blood condition in which low levels of circulating PTH result in deficient quantities of calcium in blood
hypoparathyroidism
hypopituitarism hyposecretion
hypothalamus
hypothyroidism
state of deficient pituitary gland activity (characterized by decreased secretion of one or more of the pituitary hormomes, which can affect the function of the target endocrine gland) underproduction of hormones located superior to the pirtuitary gland in the brain. Secretes "releasing" hormone that functions to stimulate or inhibit the release of pituitary gland hormones state of deficient thyroid gland activity (characterized by decreased secretion of thyroid hormones). Signs and symp: include fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance. naturally occurring protein hormone secreted by the beta celsl of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans in response to elevated levels of blood glucose. Regulates glucose metabolism; promotes entry of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids into the cells. lowers blood glucose levels by transporting glucose from the blood into the cells and by stimulating the cells to burn glucose for energy. promotes the conversion of glucose to glyycogen for storage in the liver see type 1 diabetes clusters of endocrine tissue found throughout the pancreas, made up of different cell types that secrete various hormones, including insulin and glucagon. Non-endoctine cells found throughout the pancreas produce enzymes that facilitate digestion narrow strip of tissue connecting two larger parts in the body, such as the isthmus that connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland potassium buildup of ketoacids that alter the body's metabolic balance. Include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and a fruity odor of the breath. strongs acids that burn to replace the lost glucose condition resulting from uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, in which the body has an abnormal concentration of ketone bodies resulting from excessive fat metabolism promotes development of glandular tissue during pregnancy and produces milk after birth of an infant regulate development, growth, and function of the ovaries and testes can show changes in the size of soft tissues glands that produce milk after childbirth inner region of the adrenal gland secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. Affects the skin's pigment-producing cells. hormone that is secreted into the bloodstream by the pineal gland. Influence the body's biological clock by regulating such functions as the sleep/wake cycle group of signs and symptoms including insulin restistance, obesity characterized by excessive fat around the waist and abdomen, hypertension, hyperglycemia, elevated triglycerides, and low levels of "good" cholesterol HDL. Risks include development of type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, or stroke. aka syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome sum total of all the chemical processes that take place in a living organisms outer layer, or zone, of the adrenal cortex produces a type of hormone. Regulate the amunt of mineral salts in the blood condition resulting from a deficiency of the thyroid hormone thyroxin; a severe form of hypothyroidism in an adult. Sings include puffiness of the face and hands, coarse and thickened skin, enlarged tongue, slow speech, and anemia sodium chemicals in the nervous system that trigger the electrical impulses that send signals from one part of the body to another. They travel rapidly and tend to have effecys that are short-lived see type 2 diabetes. fragile bones subject to the development of cysts serve as secreting glands stimulates uterine contractions during labor and postpartum. Serves an important function in women during the process of labor and delivery, stimulates the smooth musles of the uterus to contract. Responsible for the release, or letdown, of milk from the mammary glands in response to an infant's suckling a long gland that stretches acroos the posterior wall of the upper abdomen. Composed of both endocrine and exocrine tissue. Aids in the digestion of food pancreas total deficiency of pituitary activity. Characterized by decreased secretion of all the pituitary hormones four small bodies embedded in the posterior aspect of the lobes of the thyroid gland. Parathormone (PTH), the hormone produced by the glands, helps maintain the level of calcium in the blood
insulin insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
islets of Langerhans
isthmus kal/i
ketoacidosis ketoacids
ketosis
lactogenic hormone luteinizing hormone
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) mammary gland medulla melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
melatonin
metabolic syndrome metabolism
mineralocorticoid
myxedema natr/o
neurotransmitters non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) osteitis fibrosa cystica ovary and testis
oxytocin
pancreas pancreat/o
panhypopituitarism
parathyroid glands
parathyroid/o parathyroidectomy parathyroidoma
parathyroid glands excision of (one or more) parathyroid glands tumor of a parathyroid gland tumor of the adrenal medulla, which is usually non-malignant and characterized by hypertension, headaches, palpitations, diaphoresis, chest pain, and abdominal pain. Sugical removal of the tumor is the most common treatment. Though usually curable with early detection, it can be fatal if pheochromocytoma untreated housed in the cranial cavity. Cone-shaped strucutre. Appears to receive info about the amount of pineal gland daylight, transmitted by nervous systsem signals gia a branch of the optic tract pituitar/o pituitary gland pituitarism any abnormality of the pituitary approximately the size ofa pea and located at the base of the brain. The pituitary is divided into two lobes. Often referred to as the master gland because it produces hormones that stimulate the function of other endocrine glands. Secretes growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, ACTH, pituitary gland or hypophysis cerebri gonadotropins, FSH, LH, and prolactin-releasing hormone, as well as antidiuretic hormone and or master gland oxytocin. polydipsia abnormal state of much thirst posterior lobe or neurohypophysis prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH), lactogenic hormone protein radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) radioimmunoassay studies (RIA) receptor sella turcica somatotropin (GH) steroid suf: -megaly suf: -tropic syndrome syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) target organ/tissue tetany tetraiodothyronine, thyroxin (T4) thymosin thymus gland thyr/o, thyroid/o thyroid function test (TFT) stores and releases antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin promotes development of glandular tissue during pregnancy and produces milk afterb irth of an infant hormone formed from amino acids a nuclear medicine scan that measures thyroid function. Radioactive iodine is given to the patient orally, after which its uptake into the thyroid gland is measured a lab test that assesses hormone levels in plasma. enable the tissue to "recognize" and respond to specific hormones. depression of the skull see growth hormone. hormone formed from the lipid cholesterol. Ovaries, testes, and the adrenal glands secrete steroid hormones enlargement turning toward or changing
thyroid gland
thyroid scan thyroid/o, thry/o thyroidectomy thyroiditis thyroidotomy thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) thyroid-stimulating hormone level (TSH) thyroparathyroidectomy thyrotoxicosis
run together (signs and symptoms occurring together that are characteristic of a specific disorder) condition that is caused by excessive secretion of antiduiretic hormone from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Abnormal retention of water. near to, or far from, the endocrine gland. condition affecting nerves causing muscle spasms as a result of low amounts of calcium in the blood caused by a deficiency of the parathyroid hormone synthesized from iodine and some dairy products hormone that stimmulates the development of the immune system and the production of lumphocytes. Relatively much larger in children than in adults lies in the mediastinum, beneath the sternum. Organ of the lymphatic system and endocrine that secrete a hormone thyroid assesses TSH, T3, T4, and calcitonin levels largest endocrine gland. Located anteriorly in the neck below the larynx and comprises bilateral lobes connected by an isthmus. Secretes the hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which require iodine for their production. a nuclear medicine test that shows the size, shape, and function of the thyroid gland. Patient is given a radioactive substance to visualize the thyroid gland. An image is recorded as the scanner is passed over the neck area; used to detect tumors and nodules thyroid gland excision of the thyroid gland inflammation of the thyroid gland incision of the thyroid gland stimulates the thyroid gland a blood test that measures the amount of thyroid-stumulating hormone in the blood; usedto diagnose hypothyroidism and to monitor patients on thytoid replacement therapy excision of the thyroid and parathyroid glands a condition caused by excessive thyroid hormones a blood study that gives the diret measurement of the amount of thyroxine in the patient's blood. A greater-than-normal amount indicated hyperthyroidism; a less-than-normal amount indicated hypothyroidism measures the amount of calcium in the blood, particularly relevant in evaluatin parathyroid function synthesized from iodine and some dairy products little or no insulin is produced because the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans that secrete the hormone have been decreased in number by an abnormal autoimmune process.
thyroxine level (T4) total calcium test triiodothyronine (T3)
type 1 diabetes
type 2 diabetes ultrasonography (US) urine glucose urine ketones vasopressin #NAME?
insulin prodction is variable; its leels may be decreased, normal, or elevated. Infividuals affected by this condition are not insulin dependent. Results from tissue unresponsiveness or resistance to insulin, causes of which include hormone receptor defects or too few receptors on the surface of target cell membranes. visualizes the pancreas and also may be used to guide biopsies of the thyroid gland test that measure the presence of glucose and insulin, respectively to help diagnose diabetes mellitus test that measure the presence of glucose and insulin, respectively to help diagnose diabetes mellitus synthetic ADH used in the treatment of diabetes insipidus
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Delivery Room Write-UpDocument24 pagesA Delivery Room Write-UpDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Product DesignDocument68 pagesProduct DesignRj RonquilloNo ratings yet
- DLSU Classes Third Term AY 2013-14Document135 pagesDLSU Classes Third Term AY 2013-14Karlo Marco CletoNo ratings yet
- Avon Products, Inc.:: Developing A Global PerspectiveDocument24 pagesAvon Products, Inc.:: Developing A Global PerspectiveRj RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Corporate Liquidity V 5.2Document38 pagesCorporate Liquidity V 5.2Rj RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Avon Products, Inc.:: Developing A Global PerspectiveDocument24 pagesAvon Products, Inc.:: Developing A Global PerspectiveRj RonquilloNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Purpose of AccountingDocument38 pagesThe Nature and Purpose of AccountingIzhevskNo ratings yet
- Child Development - Conception To Birth From Anthroposophical ViewDocument19 pagesChild Development - Conception To Birth From Anthroposophical ViewAnNo ratings yet
- Session #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document4 pagesSession #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- A&P CH 28aDocument22 pagesA&P CH 28aSam KimNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Development A Life Span View Third EditionDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Human Development A Life Span View Third Editionsteelerversionxs9No ratings yet
- 4th Year Multiple PregnancyDocument57 pages4th Year Multiple PregnancyKingsley Calex100% (2)
- Zelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenDocument18 pagesZelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenCheyenne ProvoostNo ratings yet
- Jaypee Gold Standard Mini Atlas Series® Embryology (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document217 pagesJaypee Gold Standard Mini Atlas Series® Embryology (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)reyod0% (1)
- Early Embryonic DevelopmentDocument48 pagesEarly Embryonic DevelopmentYeyen MusainiNo ratings yet
- Types of PlacentaDocument4 pagesTypes of PlacentaMark Christian CuiNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid & Its AbnormalitiesDocument29 pagesAmniotic Fluid & Its AbnormalitiesSTAR Plus SerialsNo ratings yet
- Word Parts Dictionary ADocument27 pagesWord Parts Dictionary AJosh Flynn100% (1)
- Child Development and Pedagogical Issues PDFDocument196 pagesChild Development and Pedagogical Issues PDFGanesh BoreyNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition Leifer Test BankDocument35 pagesMaternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition Leifer Test Bankmoonseedegoismwjvm695% (21)
- 2nd Week of DevelopmentDocument37 pages2nd Week of DevelopmentSyed Rohan AliNo ratings yet
- OBDocument17 pagesOBMyrna Cecile NonesNo ratings yet
- Embryo REVIEWnotesDocument90 pagesEmbryo REVIEWnotesKapee Theva75% (4)
- Veterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyDocument77 pagesVeterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyFor AstroNo ratings yet
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDocument34 pages48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- Human Physiology-25 (DR Sachin Kapur)Document42 pagesHuman Physiology-25 (DR Sachin Kapur)AmitNo ratings yet
- A Delivery Room Write-UpDocument42 pagesA Delivery Room Write-UpDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2a Embryonic DevelopmentDocument16 pages2a Embryonic DevelopmentLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Williams 03 - Implantation, Embryogenesis, Placental DevelopmentDocument14 pagesWilliams 03 - Implantation, Embryogenesis, Placental DevelopmentAhmed Abou SeifNo ratings yet
- Hatchery ManagementDocument81 pagesHatchery Managementnishant-50No ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes: Is The Amnion The Major Determinant?Document6 pagesPremature Rupture of The Fetal Membranes: Is The Amnion The Major Determinant?Arifah GulamanisNo ratings yet
- Atlas of The Newborn Rudolf S Vol.1Document167 pagesAtlas of The Newborn Rudolf S Vol.1Gabriel Burachi PeruchiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of Zoology 16Th Edition Hickman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument42 pagesIntegrated Principles of Zoology 16Th Edition Hickman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevahuynh4vn8d100% (11)
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- General EmbryologyDocument93 pagesGeneral EmbryologyCharlie Mejos MercedNo ratings yet
- Anat 213, Placentation-EmbryologyDocument16 pagesAnat 213, Placentation-EmbryologyChidera EmmanuelNo ratings yet