Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plans
Uploaded by
Tels Dela PeñaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plans
Uploaded by
Tels Dela PeñaCopyright:
Available Formats
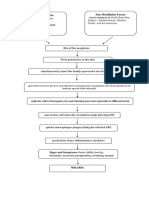
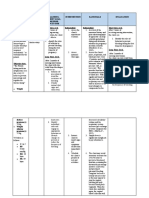
NURSING CARE PLANS Hyperthermia Assessment Nursing Diagnosis s> Hyperthermia Scientific Explanation Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a chronic
c o> manifested: metabolic disease impairing insulin >increased body temp. of 38.3 production in the pancreas and/or insulin resistance, therefore leading to >weakness its hallmark sign, hyperglycemia. The >pale nail beds excess glucose in the blood exerts >skin warm to touch hyperosmolar effect, After 3 days of NI, the pt. will maintain thus increasing blood volume and viscosity leading to >flushed skin decreased perfusion as manifested in >diabetic right pale nailbeds. In the core temp within normal range. >encourage an increase in oral fluid intake. >for hygiene maintenance Long term: >monitor all sources of fluid loss such as urine. >to prevent dehydration. The pt. shall have maintained a core temp within normal range. >to determine further loss of fluids. Long term: After 3 hrs of NI, the pt.s temp will decrease from 37.8C to 36.8C >monitor and record VS. >to monitor pts condition and to establish baseline data. Short term: >establish rapport >to gain trust and cooperation. The pt.s temp shall have decreased from 37.8C to 36.8C Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short term:
foot
long run, a decreased peripheral perfusion leads to a decreased sensation because of delayed transport >auscultate breath sounds. of nutrients and O2 to peripheral >emphasize importance of proper hand washing.
and prevent infection.
may manifest:
>to determine presence of abnormal breath sounds like rales.
>tachycardia
>seizure
>convulsions
nerves, which causes peripheral nerve degeneration. The pt then becomes susceptible to wound, and upon the development of wound, there will be poor wound healing resulting from a delayed biochemical mediation caused by the hyperviscosity of >administer replacement fluids and electrolytes. >render TSB.
>to promote heat loss by evaporation and conduction.
>loss of consciousness
>to support circulating volume and tissue perfusion.
>headache
>to reduce metabolic demands and oxygen consumption.
blood. Bacteria take this opportunity and proliferate easily in a hyperglycemic environment. Their presence initiates an inflammatory response, thus pyrogens are released which act upon the thermoregulatory center of the brain, leading to an increase in core temperature AEB body temp of 37.8 and skin warm to touch >administer medications as indicated. >encourage high calorie diet. >to mange the underlying cause. >regulate IVF as ordered. >to meet increasing metabolic needs. >maintain bed rest. >to maintain proper hydration.
Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased hemoglobin concentration in the blood.
Assessment
Nursing Diagnosis S> Ineffective O> The patient tissue may manifest: perfusion >Headache related to >Body decreased weakness hemoglobin >Chest Pain concentration in the blood.
Scientific Explanation Reduced arterial blood flow causes decreased nutrition and oxygenation at the cellular level. Management is directed at removing vasoconstricting factors improving peripheral blood flow, and reducing metabolic demands on the body. Decreased tissue perfusion can be transient with few or minimal consequences to the health of the patient. If the decreased perfusion is acute and protracted, it can have devastating effects on the
Objectives Short Term: After 3 hrs of nursing interventions patient will verbalize understanding of condition and therapeutic regimen.
Interventions >Establish rapport
Rationale
Evaluation Short Term: The patient shall have verbalized understanding of condition and therapeutic regimen. Long Term: The patient shall have demonstrated increased perfusion as effectively available.
>to gain the trust and cooperation of the patient. >Assess >to have a patients general health condition status of the patient. > Monitor vital >to obtain signs baseline data > to prevent further complications of the disease condition > to boost immune system
> Emphasize Long Term: the recommended After 2 days o diet Nursing Intervention the patient will >Instruct demonstrate patient to increased increase intake perfusion as of vitamin C effectively like orange available. juice, calamansi juice
>Instruct > to promote patient to tissue repair increase intake of protein like meat and tofu
patient. Diminished tissue perfusion, which is chronic in nature, invariably results in tissue or organ damage or death.
>Circulation is potentially compromised with a cannula. It should be removed as soon as therapeutically safe. >Administer >This saturates oxygen as circulating needed. hemoglobin and increases the effectiveness of blood that is reaching the ischemic tissues. >This promotes >Position optimal lung properly. ventilation and perfusion. The patient will experience optimal lung expansion in upright position.
>Do passive range-ofmotion (ROM) exercises to unaffected extremity every 2 to 4 hours. >Prepare for removal of arterial catheter as needed.
>Exercise prevents venous stasis.
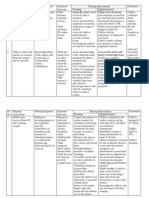
Impaired skin integrity related to presence of scars and dry wound on left legs secondary to BKA Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome
Impaired skin integrity to O> the patient related presence of may manifest: scars and dry >irritability wound on left legs >itchiness secondary to BKA >pain
S>
Skin or integumentary system is the largest multifunctional organ of the body. It becomes altered when there are internal and external forces occur such as invasion of microorganisms that could trigger infection.
>To gain trust Short Term: from the patient. The patient shall have baseline verbalized >Monitor vital >For feelings of data. signs. increased self assess esteem and >Identify underlying >To ability to contributing condition. manage factors. situation. >Instruct patient to increase fluid intake up to 8- 10 > to prevent Long Term: The patient dehydration glasses of water shall have Long Term: displayed > Remind the client After 2 days of to avoid eating timely healing > to not alleviate nursing of skin lesions foods that are fatty the patients interventions, without and sweet. condition the patient will complications be able display >Instruct patient to timely healing increase intake of of skin lesions vitamin C like >to boost without orange juice, immune system complications. calamansi juice >Instruct patient to increase intake of protein like meat >Topromote and tofu tissue repair
Short Term: After 4-6 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to verbalize feelings of increased self esteem and ability to manage situation.
>Establish rapport.
>Stretch linens
>to comfort
provide
>Helpful in alleviating >Encourage patient and to verbalize anxiety feelings about the refocusing attention, which condition. can relieve pain, and to know pain development >Keep the area clean/dry, carefully dress wounds, support incision, prevent infection. >To prevent cross contamination and to assists bodys natural process of repair.
Activity Intolerance related to Fatigue and discomfort
Nursing Diagnosis S> Activity O> the patient Intolerance may manifest: related to >abnormal Fatigue and heart rate or discomfort blood pressure response to activity >cyanosis Assessment
Scientific Explanation Activity Intolerance a psychological or physiological energy to endure or complete required or desired daily activities. And due to previous pain and blood loss that cause oxygen that decreases muscle tone and result to body weakness.
Objectives
Short Term: After 4-6 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will >Assess patients be able to condition verbalize and use energyconservation techniques. > Monitor vital signs Long Term: After 2 days of >Instruct patient to nursing increase fluid interventions, intake up to 8- 10 the patient will glasses of water be able to maintain Remind the activity level > client to avoid within capabilities, as eating foods that fatty and evidenced by are sweet. normal heart rate and blood pressure during >Instruct patient to activity, as well increase intake of C like as absence of vitamin orange juice, shortness of calamansi juice breath, weakness, and >Instruct patient to fatigue. increase intake of protein like meat and tofu
Nursing Interventions >Establish rapport
Rationale >to gain the trust and cooperation of the patient. >to have a general health status of the patient.
Expected Outcome Short Term: The patient shall be able to verbalize and use energyconservation techniques.
Long Term: >to obtain The patient shall be able to baseline data maintain activity within > to prevent level capabilities, as dehydration evidenced by normal heart rate and blood pressure during > to not alleviate activity, as well the patients as absence of condition shortness of breath, weakness, and fatigue. > to boost immune system
>To promote tissue repair
>Stretch linens
>to comfort
provide
aids in >Assess patient's >This defining what level of mobility. patient is capable of, which is necessary before setting realistic goals. >Observe document response activity. and >Close monitoring serves as a guide for optimal to progression of activity.
>Depression over >Assess inability to emotional perform required response to activities can change in physical further aggravate status. the activity intolerance. >Rest between activities provides time for energy conservation and recovery.
>Encourage adequate rest periods, especially before meals, other ADLs, exercise sessions, and ambulation. >Refrain
>Patients with limited activity from tolerance need to
performing nonessential procedures. > Teach energy conservation techniques like: Sitting to do tasks, Changing positions often, Storing frequently used items within easy reach
prioritize tasks. > To conserve energy also because Standing requires more work, Changing positions often This distributes work to different muscles to avoid fatigue. Changing positions often This distributes work to different muscles to avoid fatigue, Storing frequently used items within easy reach This avoids bending and reaching.
Disturbed Body Image related to below the knee amputation Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
S> O> The patient may manifests: >body malaise >pallor on the extremities >decrease movement >discomfort > BKA left >Low self esteem >Irritability >depressive mood state.
Disturbed Body Image related to below the knee amputation
After 2 days o Nursing Intervention the patient will demonstrate techniques that to increase enables of resumption of intake vitamin C like activities. Throughout the life orange juice, span, body image calamansi juice changes as a matter of development, >Instruct patient growth, maturation, to increase changes related to intake of protein childbearing and like meat and pregnancy, changes tofu that occur as a result of aging, and changes >Acknowledge that occur or are normalcy of imposed as a result of emotional injury or illness. response to actual or
Body image is the attitude a person has about the actual or perceived structure or function of all or part of his or her body. This attitude is dynamic and is altered through interaction with other persons and situations and influenced by age and developmental level. As an important part of ones self-concept, body image disturbance can have profound impact on how individuals view their overall selves.
Short Term: After 3 hrs of nursing interventions patient will verbalize willingness to participate in therapeutic activities. Long Term:
>Establish rapport
>to gain the trust Short Term: and cooperation The patient shall of the patient. have verbalized willingness to in >to have a participate >Assess general health therapeutic patients status of the activities. condition patient. Long Term: >to obtain The patient shall > Monitor vital baseline data signs have demonstrated techniques that to prevent enables resumption > Emphasize > further the of activities. complications of recommended the disease diet condition > to boost immune system >Instruct patient
> to promote tissue repair
>Stages of grief over loss of a body part or function are normal, and
In cultures where ones appearance is important, variations from the norm can result in body image disturbance. The importance that an individual places on a body part or function may be more important in determining the degree of disturbance than the actual alteration in the structure or function. Therefore the loss of a limb may result in a greater body image disturbance for an athlete than for a computer programmer. The loss of a breast to a fashion model or a hysterectomy in a nulliparous woman may cause serious body image disturbances even though the overall health of the individual has been improved. Removal of skin lesions, altered elimination resulting
perceived typically involve a change in body period of denial, structure or the length of function. which varies from individual to individual. may >Help patient >Patients identify actual perceive changes that are not changes. present or real, or they may be placing unrealistic value on a body structure or function. >It is worthwhile to encourage the >Encourage patient to verbalization of separate feelings positive or about changes in negative body structure feelings about and/or function actual or from feelings perceived about self-worth. change. >Opportunities for positive feedback >Assist patient and success in in incorporating social situations actual changes may hasten into ADLs, adaptation. social life, interpersonal relationships, and
from bowel or bladder surgery, and head and neck resections are other examples that can lead to body image disturbance.
occupational activities.
>Professional caregivers >Demonstrate represent a positive caring microcosm of in routine society, and their activities. actions and behaviors are scrutinized as the patient plans to return to home, to work, and to other activities. >This compensates for actual changed >Teach patient body structure adaptive and function. behavior >Asking patients to remember other body image issues and how they were managed may help patient adjust to the current issue.
>Help patient identify ways of coping that have been useful in the past.
You might also like
- FNCP PoorsanitationmarwahDocument3 pagesFNCP PoorsanitationmarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- A Mini Case Presentation On Influenza VirusDocument22 pagesA Mini Case Presentation On Influenza Virusangelo100% (1)
- NCP BPHDocument1 pageNCP BPHyasiraNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument12 pagesNeonatal JaundiceJustine NyangaresiNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On: Ca OvaryDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan On: Ca Ovaryvaishali TayadeNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Document5 pagesActivity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Cameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DDocument7 pagesCataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DKismet SummonsNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument10 pagesNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Document36 pagesCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document10 pagesEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective AirwayMark Ronhel Gallardo PerenalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health and Environmental Sanitation PDFDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Community Health and Environmental Sanitation PDFKaty SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document4 pagesNCP 3bananakyuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMiru มิริวNo ratings yet
- Problem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseDocument3 pagesProblem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseRolandNo ratings yet
- 4 Flow Chart PretermDocument4 pages4 Flow Chart PretermYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Document32 pagesN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreNo ratings yet
- Lapkas HegDocument1 pageLapkas HegkurniaNo ratings yet
- Corrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPDocument2 pagesCorrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case Study FinalllDocument56 pagesPneumonia Case Study Finalllbethrice melegritoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDDocument8 pagesPRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDAloha ItsmeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Educational ApplicationsDocument10 pagesUnit 6 Educational ApplicationsBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (StudentDocument6 pagesNrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (Studentmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- Name: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumDocument7 pagesName: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumshinloNo ratings yet
- DDSTDocument61 pagesDDSTji payNo ratings yet
- Case Simulation 112 NNNNNNDocument5 pagesCase Simulation 112 NNNNNNLuiezt BernardoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Post PartumDocument3 pagesDrugs Post PartumanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument4 pagesCare PlangopscharanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ospital NG Sampaloc)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Ospital NG Sampaloc)Flauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesIntussusception: PathophysiologyNaufal AndaluNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan D-CDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan D-CGian MonillaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunitySaira SucgangNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationDocument22 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationCess Dunwan100% (1)
- CHN - IdbDocument11 pagesCHN - IdbCharm RoweNo ratings yet
- NCP IcuDocument2 pagesNCP IcuDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objective Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objective Intervention Evaluationjezreel ibarraNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument2 pagesNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarNo ratings yet
- Request Letter For CHNDocument1 pageRequest Letter For CHNdusty kawiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLSG ApprenticeNo ratings yet
- NSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestDocument2 pagesNSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestMaha AmilNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 pagesICS Pedia Wardsweet061991No ratings yet
- IDPS Chapter 15Document10 pagesIDPS Chapter 15002No ratings yet
- Mga NCP For Preterm Birth Case 2Document9 pagesMga NCP For Preterm Birth Case 2John Rendel LopezNo ratings yet
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDocument3 pagesPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument17 pagesFNCPRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Crisostomo Soapie ChartingDocument2 pagesCrisostomo Soapie ChartingMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument17 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalNo ratings yet
- Planning (Nursing Care Plans)Document10 pagesPlanning (Nursing Care Plans)Kier Jucar de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDocument19 pages5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- Mwalya Wambua Final ProjectDocument49 pagesMwalya Wambua Final ProjectWILSON MACHARIANo ratings yet
- Spondyloarthritis ResidentDocument70 pagesSpondyloarthritis Residentviraaj pawar100% (1)
- Report of Mangalore VisitDocument6 pagesReport of Mangalore VisitAmal DominicNo ratings yet
- How To Rid The Body of CandidaDocument2 pagesHow To Rid The Body of Candidaradio53fingerNo ratings yet
- Music and Health June 2020utasv PDFDocument4 pagesMusic and Health June 2020utasv PDFPayneOgden54No ratings yet
- Acceptance SamplingDocument52 pagesAcceptance SamplingA MNo ratings yet
- Guidance To Understanding Implications of IRMERDocument52 pagesGuidance To Understanding Implications of IRMERrochimNo ratings yet
- A Day in The Life of A Clinical Research AssociateDocument4 pagesA Day in The Life of A Clinical Research AssociatenishitpataniNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Arjuna Terminalia Cardio Protective Potential in Ayush & Modern MedicineDocument12 pagesA Review Paper On Arjuna Terminalia Cardio Protective Potential in Ayush & Modern MedicineDR MEENAKSHI SONINo ratings yet
- 2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationDocument15 pages2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationMehroze MunawarNo ratings yet
- MindfulnessDocument192 pagesMindfulnessNatalia Rojas Sattui96% (26)
- 1.01 Sleep Management - Catalog - PSG - pdf.01 Sleep Management - Catalog - PSG PDFDocument57 pages1.01 Sleep Management - Catalog - PSG - pdf.01 Sleep Management - Catalog - PSG PDFjohn100% (1)
- WP Content Uploads 2014 03 Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Probationary Officer Exam 2012 Freshers AddaDocument22 pagesWP Content Uploads 2014 03 Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Probationary Officer Exam 2012 Freshers AddaPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocument152 pagesGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Check List of Claim DocumentsDocument2 pagesCheck List of Claim Documentsmohammed hussainNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics and Diagnosis Venous Disease-Jvs 1207Document21 pagesHemodynamics and Diagnosis Venous Disease-Jvs 1207Fahrudin ŠabanovićNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Free Weight Squat To Smith Machine Squat Using ElectromyographyDocument6 pagesA Comparison of Free Weight Squat To Smith Machine Squat Using ElectromyographyJoão CasqueiroNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 pagesBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Safe Use of UltrasoundDocument5 pagesGuidelines For The Safe Use of UltrasoundLiCruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of AnemiaDocument6 pagesDrug Treatment of Anemiavingul2006No ratings yet
- Breeder Hatchery Bio SecurityDocument43 pagesBreeder Hatchery Bio SecurityAzam RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Eye OintmentsDocument4 pagesEye OintmentsAnke NemirovskyNo ratings yet
- PREP & COGENT - 13th and 14th December 2014Document6 pagesPREP & COGENT - 13th and 14th December 2014FdghNo ratings yet
- Renal Cell Carcinoma - Nursing Considerations With The Use of Targeted TherapyDocument50 pagesRenal Cell Carcinoma - Nursing Considerations With The Use of Targeted TherapyMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesDigestive Systemtessacruz1186No ratings yet
- Immuno Cheat Sheet 1Document2 pagesImmuno Cheat Sheet 1yolo51No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Text Book Based Revision NoteDocument6 pagesGas Exchange Text Book Based Revision NoteJamesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study Guide - Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 3ed PDFDocument245 pagesClinical Case Study Guide - Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 3ed PDFraquelbibi0% (1)
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocument70 pagesBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYODocument10 pagesDrug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYOMARIA JULIANA RENGIFO LARANo ratings yet