Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Myocardial Infarction
Uploaded by
Vinu PoojapranavamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Myocardial Infarction
Uploaded by
Vinu PoojapranavamCopyright:
Available Formats
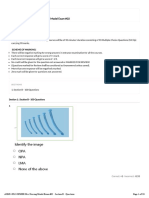
View Questions 1. B. Left sided heart failure causes fluid accumulation in the capillary network of the lung.
Fluid eventually enters alveolar spaces and causes crackling sounds at the end of inspiration. 2. B. Morphine is a central nervous system depressant used to relieve the pain associated with myocardial infarction, it also decreases apprehension and prevents cardiogenic shock. 3. D. Seeing yellow spots and colored vision are common symptoms of digitalis toxicity 4. C. When diuretics are taken in the morning, client will void frequently during daytime and will not need to void frequently at night. 5. B. The primary goal of therapy for the client with pulmonary edema or heart failure is increasing cardiac output. Pulmonary edema is an acute medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. 6. C. Decerebrate posturing is the extension of the extremities after a stimulus which may occur with upper brain stem injury. 7. C. The most frequent side effects of Cascara Sagrada (Laxative) is abdominal cramps and nausea. 8. D. Administration of Intravenous Nitroglycerin infusion requires pump for accurate control of medication. 9. A. By the 2nd day of hospitalization after suffering a Myocardial Infarction, Clients are able to perform care without chest pain 10. B. The left side of the body will be affected in a right-sided brain attack. 11. A. After nephrectomy, it is necessary to measure urine output hourly. This is done to assess the effectiveness of the remaining kidney also to detect renal failure early. 12. B. The lumen of the arteries can be assessed by cardiac catheterization. Angina is usually caused by narrowing of the coronary arteries. 13. C. Blood pressure is monitored to detect hypotension which may indicate shock or hemorrhage. Apical pulse is taken to detect dysrhythmias related to cardiac irritability. 14. A. Protamine Sulfate is used to prevent continuous bleeding in client who has undergone open heart surgery. 15. C. The use of electronic toothbrush, irrigation device or dental floss may cause bleeding of gums, allowing bacteria to enter and increasing the risk of endocarditis. 16. B. Weight gain due to retention of fluids and worsening heart failure causes exertional dyspnea in clients with mitral regurgitation. 17. D. Discomfort or pain is a problem that originates in the kidney. It is felt at the costovertebral angle on the affected side. 18. A. Perfusion can be best estimated by blood pressure, which is an indirect reflection of the adequacy of cardiac output. 19. C. Myoclonic seizure is characterized by sudden uncontrollable jerking movements of a single or multiple muscle group. 20. D. Nicotine (Nicotrol) is given in controlled and decreasing doses for the management of nicotine withdrawal syndrome. 21. D. Raynauds disease is characterized by vasospasms of the small cutaneous arteries that involves fingers and toes.
22. A. Urine testing provides an indirect measure that maybe influenced by kidney function while blood glucose testing is a more direct and accurate measure. 23. C. One liter of fluid approximately weighs 2.2 pounds. A 4.5 pound weight loss equals to approximately 2L. 24. A. Osmosis is the movement of fluid from an area of lesser solute concentration to an area of greater solute concentration. 25. D. Forearm muscle weakness is a probable sign of radial nerve injury caused by crutch pressure on the axillae. 26. B. Neutropenic client is at risk for infection especially bacterial infection of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract. 27. C. Semi-fowlers position will localize the spilled stomach contents in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. 28. C. Positioning the client laterally with the neck extended does not obstruct the airway so that drainage of secretions and oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange can occur. 29. B. Excessive bubbling indicates an air leak which must be eliminated to permit lung expansion. 30. C. Wheat cereal has a low sodium content. 31. A. Enlarged cirrhotic liver impinges the portal system causing increased hydrostatic pressure resulting to ascites. 32. C. Assessing for an open airway is the priority. The procedure involves the neck, the anesthesia may have affected the swallowing reflex or the inflammation may have closed in on the airway leading to ineffective air exchange. 33. A. Typical signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock includes systolic blood pressure of less than 90 mm Hg. 34. D. Aspirin containing medications should not be taken 14 days before surgery to decrease the risk of bleeding. 35. A. Metabolic acidosis is anaerobic metabolism caused by lack of ability of the body to use circulating glucose. Administration of insulin corrects this problem. 36. D. Beta-carotene and Vitamin E are antioxidants which help to inhibit oxidation. Vitamin E is found in the following foods: wheat germ, corn, nuts, seeds, olives, spinach, asparagus and other green leafy vegetables. Food sources of beta-carotene include dark green vegetables, carrots, mangoes and tomatoes. 37. A. Gravity speeds up digestion and prevents reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. 38. B. Abdominal distension may be associated with pain, may indicate perforation, a complication that could lead to peritonitis. 39. D. It may take 4 to 6 months to eat anything, but most people can eat anything they want. 40. D. Clay colored stools are indicative of hepatic obstruction 41. D. Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside and damage on the 8th cranial nerve (ototoxicity) is a common side effect of aminoglycosides. 42. D. Most peptic ulcer is caused by Helicopter pylori which is a gram negative bacterium. 43. D. 12 to 24 hours after subtotal gastrectomy gastric drainage is normally brown, which indicates digested food. 44. C. Watching TV is permissible because the eye does not need to move rapidly with this activity, and it does not increase intraocular pressure.
45. A. Common signs and symptoms of fracture include pain, deformity, shortening of the extremity, crepitus and swelling. 46. C. The dropper should not touch any object or any part of the clients ear. 47. A. Sudden decrease in drainage or onset of severe abdominal pain should be reported immediately to the physician because it could mean that obstruction has been developed. 48. B. Complications of acute appendicitis are peritonitis, perforation and abscess development. 49. D. A client with acute pancreatitis is prone to complications associated with respiratory system. 50. B. Liver inflammation and obstruction block the normal flow of bile. Excess bilirubin turns the skin and sclera yellow and the urine dark and frothy.
You might also like
- Answers and Rationale Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 3Document4 pagesAnswers and Rationale Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 3Anna Marie AmpoNo ratings yet
- Answers and RationaleDocument6 pagesAnswers and RationaleSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG TEST 5 RationalizationDocument4 pagesMEDSURG TEST 5 RationalizationJohn Derama SagapsapanNo ratings yet
- Pnle Answer and Explantion 4Document12 pagesPnle Answer and Explantion 4Lloyd rafaelNo ratings yet
- B. Left Sided Heart FailureDocument20 pagesB. Left Sided Heart FailureKia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument11 pagesCardiovascular DisorderKarlo BallonNo ratings yet
- Renal ExamDocument12 pagesRenal ExamCamille Espinosa100% (6)
- GENITOURINARYDocument24 pagesGENITOURINARYrlinaoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX RN Practice Questions 17Document6 pagesNCLEX RN Practice Questions 17RI NANo ratings yet
- NCLEX RN Practice Questions 17Document29 pagesNCLEX RN Practice Questions 17clarheena89% (9)
- Module 19 23Document5 pagesModule 19 23Mitch TorniadoNo ratings yet
- Packrat Test 2 AnswersDocument5 pagesPackrat Test 2 AnswersMisri MehtaNo ratings yet
- Renal Exam PDF Dialysis HemodialysisDocument2 pagesRenal Exam PDF Dialysis HemodialysispaulzkieyyNo ratings yet
- Check The Pulse Distal To The Insertion SiteDocument12 pagesCheck The Pulse Distal To The Insertion SiteAccey RamirezNo ratings yet
- Kidney Dialysis ExamDocument30 pagesKidney Dialysis Examlouie roderos100% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Bullets Nle NclexDocument95 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Bullets Nle NclexRichard Ines Valino100% (2)
- Renal System Practice Quiz: D. Reversal of The Oliguria Occurs With Fluid ReplacementDocument5 pagesRenal System Practice Quiz: D. Reversal of The Oliguria Occurs With Fluid Replacementمحمد حسينNo ratings yet
- WatermelonDocument27 pagesWatermelonSunny Mae T PuigNo ratings yet
- Icu Skills Assessment ExamDocument5 pagesIcu Skills Assessment ExamJona AureNo ratings yet
- C 30Document7 pagesC 30Dharati PatelNo ratings yet
- Muscle and BoneDocument5 pagesMuscle and Boneali.tariq26No ratings yet
- Surgery 2015 MCQDocument15 pagesSurgery 2015 MCQMohammad Husni Banisalman83% (6)
- Adult I Final ExamanswersDocument10 pagesAdult I Final Examanswersmahmoud fuqahaNo ratings yet
- C. He Will Be Pain Free: B. A Rapid Pulse and Increased RRDocument10 pagesC. He Will Be Pain Free: B. A Rapid Pulse and Increased RRAccey RamirezNo ratings yet
- Physio AdapDocument3 pagesPhysio AdapAijem Ryan100% (1)
- Preboard Ans IIIDocument10 pagesPreboard Ans IIIDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- 75 Items Practice ExamDocument42 pages75 Items Practice ExamTed ChrisNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions GUDocument10 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions GUdee_day_8100% (1)
- Aki and CKDDocument14 pagesAki and CKDMaiden Shebba Pelpinosas TorrejosNo ratings yet
- MS Finals QUIZDocument2 pagesMS Finals QUIZIvan A. EleginoNo ratings yet
- JAMAL MACABANGUN FINAL - Medical-Surgical-Nursing-Exam-group-2Document13 pagesJAMAL MACABANGUN FINAL - Medical-Surgical-Nursing-Exam-group-2KeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- NURSING Review Session (Nur 220) Part 1Document8 pagesNURSING Review Session (Nur 220) Part 1Mariel EstoniloNo ratings yet
- PNLE IV For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part 2)Document23 pagesPNLE IV For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part 2)ASDF ASDFNo ratings yet
- Haad AnswersDocument114 pagesHaad AnswersMohammadKhanNo ratings yet
- QuesDocument26 pagesQuesJoyce LauNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Case StudyDocument20 pagesCirrhosis Case StudyJodi Schaefer100% (1)
- SURGERY Student Note Book CollectionDocument24 pagesSURGERY Student Note Book Collectionhenama100% (1)
- Q - A Random 13 RationaleDocument3 pagesQ - A Random 13 RationaleKristen NateNo ratings yet
- D - 6answer KeyDocument14 pagesD - 6answer KeyJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Cardio NewDocument10 pagesCardio NewnotadagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralDocument23 pagesChapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralAbel C. Idusma Jr.No ratings yet
- June Nle 2009 SRG Final CoachingDocument31 pagesJune Nle 2009 SRG Final CoachingChoki Momoki100% (1)
- QuizDocument28 pagesQuizStephen AdedokunNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions7Document7 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions7dee_day_8No ratings yet
- 50 Item Medical-Surgical Nursing Practice TestDocument13 pages50 Item Medical-Surgical Nursing Practice TestReymund Timog TalarocNo ratings yet
- Cardio NCLEX CHPT 56 7th EditionDocument5 pagesCardio NCLEX CHPT 56 7th EditionParallelNo ratings yet
- MS Powerpoint ExamDocument31 pagesMS Powerpoint ExamBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument8 pagesQuizJohara Mae De RamaNo ratings yet
- INTERNAL MEDICINE - Nephrology SystemDocument8 pagesINTERNAL MEDICINE - Nephrology SystemAiswaryaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials On GenitourinaryDocument15 pagesTutorials On Genitourinaryabangjojo123No ratings yet
- Nursing Q and A (Volume 2) - ANSWERSDocument7 pagesNursing Q and A (Volume 2) - ANSWERSRem Yriz100% (3)
- Gus TDocument21 pagesGus THashemite MedicineNo ratings yet
- NURSING PRACTICE IV Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsDocument31 pagesNURSING PRACTICE IV Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsMatt Lao Dionela100% (1)
- MCQs and Cases 5th YearDocument118 pagesMCQs and Cases 5th Yearyoune6No ratings yet
- BraKay 5th January, Medical Nursing ClassDocument11 pagesBraKay 5th January, Medical Nursing ClassKwasikyie QuarshieNo ratings yet
- Soal Modul 1Document12 pagesSoal Modul 1duo_ngoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ExamDocument8 pagesNursing ExamDa DungNo ratings yet
- Complications of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: The Survival HandbookFrom EverandComplications of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: The Survival HandbookAlistair LindsayNo ratings yet
- Test Series#2Document33 pagesTest Series#2Vinu PoojapranavamNo ratings yet
- CHN Bullets PDFDocument55 pagesCHN Bullets PDFVinu PoojapranavamNo ratings yet
- DME Kerala Staff Nurse New Batch#08 Starting On 15-02-2020 (Online Live Interactive Board)Document1 pageDME Kerala Staff Nurse New Batch#08 Starting On 15-02-2020 (Online Live Interactive Board)Vinu PoojapranavamNo ratings yet
- OBG DR Pranav PDFDocument183 pagesOBG DR Pranav PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (6)
- Pediatric DR PDFDocument135 pagesPediatric DR PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (1)
- MP CHO MODEL TEST PAPER - 04 Dr. Pranav Nursing Academy PDFDocument9 pagesMP CHO MODEL TEST PAPER - 04 Dr. Pranav Nursing Academy PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (2)
- All Aiims Paper PDFDocument409 pagesAll Aiims Paper PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (2)
- 300+ TOP FOOD and NUTRITION Objective Questions & Answers FOOD NUTRITION MCQs PDFDocument1 page300+ TOP FOOD and NUTRITION Objective Questions & Answers FOOD NUTRITION MCQs PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (1)
- 300+ TOP FOOD and NUTRITION Objective Questions & Answers FOOD NUTRITION MCQs PDFDocument1 page300+ TOP FOOD and NUTRITION Objective Questions & Answers FOOD NUTRITION MCQs PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (1)
- Vitaminanaval 170323174936 PDFDocument38 pagesVitaminanaval 170323174936 PDFVinu PoojapranavamNo ratings yet
- Vinu CV 2018Document10 pagesVinu CV 2018Vinu PoojapranavamNo ratings yet
- Treatment Strategies of Acute Myocardial Infarction Updates OnDocument11 pagesTreatment Strategies of Acute Myocardial Infarction Updates OnLilasNo ratings yet
- Nur 4216 Pat 1 Med Surg 2 Noor TamariDocument18 pagesNur 4216 Pat 1 Med Surg 2 Noor Tamariapi-215323958No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Case Write Up: The Medicines CompanyDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Case Write Up: The Medicines CompanyFelipe AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Maestro 4000 Cardiac Ablation System Operator's ManualDocument36 pagesMaestro 4000 Cardiac Ablation System Operator's ManualServiceC ImemedNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Assessment Pocket Reference Card PDFerikaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology: 27 Maret 2021Document52 pagesCardiology: 27 Maret 2021Dian ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Ef9oano Inglesbasico 140621150244 Phpapp02Document104 pagesEf9oano Inglesbasico 140621150244 Phpapp02Diana SimõesNo ratings yet
- Grudgitis BMHegde PDFDocument2 pagesGrudgitis BMHegde PDFsunilreddymNo ratings yet
- Integrative Cardiology - A New Therapeutic Vision (PDFDrive)Document287 pagesIntegrative Cardiology - A New Therapeutic Vision (PDFDrive)angelobuffalo100% (2)
- Recent Trends in The Pharmacotherapy of Angina Pectoris: ArticleDocument14 pagesRecent Trends in The Pharmacotherapy of Angina Pectoris: ArticleLarysuka DenysukaNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument12 pagesCommonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFYannis Zoldenberg100% (1)
- Renr Practice Test 9 FinalDocument12 pagesRenr Practice Test 9 FinalTk100% (2)
- Usmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology PhysiologyDocument117 pagesUsmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology PhysiologySreeNo ratings yet
- Bedside Clinical Teaching Role Play Simulation 121508-Edited EsmDocument16 pagesBedside Clinical Teaching Role Play Simulation 121508-Edited EsmQaseh MaizaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution and Future of ACC/AHA Clinical Practice Guidelines: A 30-Year JourneyDocument12 pagesThe Evolution and Future of ACC/AHA Clinical Practice Guidelines: A 30-Year JourneyYouyouNo ratings yet
- Drug of ChoiceDocument2 pagesDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- Final Case Presentation Unstable AnginaDocument28 pagesFinal Case Presentation Unstable AnginaZendy Nicole Cano SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (CVS) - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)Document10 pagesCardiovascular System (CVS) - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)FarsibalooNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioDocument17 pagesCase Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioMeg YunsonNo ratings yet
- ROLE OF STREPTOKINASE - OdpDocument7 pagesROLE OF STREPTOKINASE - OdpShumyle Mukhtar HussainNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument23 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionLouise NicoleNo ratings yet
- Advanced Proteomics and Cluster Analysis For Identifying Novel Obstructive Sleep Apnea Subtypes Before and After CPAP TherapyDocument34 pagesAdvanced Proteomics and Cluster Analysis For Identifying Novel Obstructive Sleep Apnea Subtypes Before and After CPAP Therapy马三强No ratings yet
- Disease/guide/diseases Cardiovascular#2Document10 pagesDisease/guide/diseases Cardiovascular#2Kristinelou Marie N. ReynaNo ratings yet
- (The European Society of Cardiology Series) Marco Tubaro (Editor), Pascal Vranckx (Editor), Susanna Price (Editor), Christiaan Vrints (Editor), Eric Bonnefoy (Editor) - The ESC Textbook of Intensive ADocument1,088 pages(The European Society of Cardiology Series) Marco Tubaro (Editor), Pascal Vranckx (Editor), Susanna Price (Editor), Christiaan Vrints (Editor), Eric Bonnefoy (Editor) - The ESC Textbook of Intensive AEdu MartinsNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies at The Dental OfficeDocument38 pagesMedical Emergencies at The Dental Officececilled_08No ratings yet
- Contoh Soal KMB Ujikom 1Document34 pagesContoh Soal KMB Ujikom 1RobbyNo ratings yet
- Wellen's Syndrome: Mohan GameshDocument28 pagesWellen's Syndrome: Mohan Gameshmyolie wuNo ratings yet
- Case No. 2:: Chief ComplaintDocument10 pagesCase No. 2:: Chief ComplaintJayson TrajanoNo ratings yet
- CPG CoronaryHeartDisease 2014 PDFDocument52 pagesCPG CoronaryHeartDisease 2014 PDFKarlKoNo ratings yet
- GRE Practice TestDocument47 pagesGRE Practice TestVincent YuNo ratings yet