Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2G Call Flow BSC to GGSN
Uploaded by
vinpagOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2G Call Flow BSC to GGSN
Uploaded by
vinpagCopyright:
Available Formats
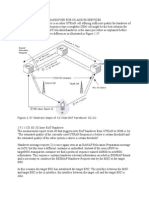
Call Flow for 2G
BSC IPs are defined in gbctx in CGSN. Also defined in gbctx are the MCC/MNC of the circles and their location area codes which are homed to the particular CGSN. When a 2G call lands on gbctx it is diverted to context ss7ctx via an associate-service map (associateservice map map context ss7ctx) The ss7ctx is connected to the HLR. The map-service map has IMSI ranges defined which act as filters to allow a range of IMSI The map-service map also indicates use of SCCP protocol Then the SGSN refers to global-title-translation association instance 1. This defines the action id for incoming IMSI and also the STP to which it has to be forwarded. Action id 1 indicates match only the 1st digit of the IMSI. Also the global-title-translation address-map instance 11 defined the self GT of the SGSN for reverse routing for STP. Thus it is forwarded to the HLR for authentication. Now after authentication the user is trying to access data services. It will hit the sgsn-global table in Global configuration mode. In this table operator-policies are defined for imsi-ranges of MCC/MNC The operator-policies in turn direct the APNs to their apn profiles. Also each operator policy directs the call to its call-control-profile (* Dont know what call-control-profiles decide) The apn-profiles provide the GGSN gateway address and pdp properties. For Eg. An APN of Rcomnet for a Mumbai Subscriber (MCC/MNC 405/15) on Mumbai CGSN has and operator policy of 3. The operator-policy-3 has a call-control-profile of 0 & apn profile for rcomnet is 0 The apn-profile-0 has a GGSN gateway address of 115.255.8.82 which is the local GGSN IP address. Now a create PDP request is sent to the gateway GGSN with the virtual apn for rcomnet.2g.postpaid or rcomnet.2g.prepaid The virtual apn is formed by concatenating a) The APN user is trying (rcomnet, rcomwap, rcommms or blackberry), b) The network user is latching to (2G or 3G) c) Customer type (postpaid or prepaid) as obtained from HLR The GGSN searches for the APN in the 4 contexts
a) giintctx ( for rcomnet) b) gibbctx ( for blackberry) c) giwdvpnctx ( for vpn apns) d) girapctx ( for mms) These 4 contexts have a parent APN configured in which we define the virtual APNs The virtual apn profile defines what is to be done with the subscriber in terms of accounting, authentication and charging. For eg Rcomnet postpaid requests are forwarded to Tekelec PCRF for policy control. Whereas Rcomnet prepaid requests are forwarded to Comverse IN for prepaid charging. In addition to this the virtual apn profile also defines the IP address to be given to the subscriber, DNS servers, the accounting mode and QoS action in case QoS is not provided by the PCRF. For VPN the parent apn defines the virtual apn domain name. The domain name defines the L2TP TEP for the customer. Now the IP address is assigned to the subscriber and the PDP is created. Now the user can access his 2G services.
You might also like
- Five Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomDocument1 pageFive Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomAmto Hosima0% (1)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Unbalance On Bearing LifeDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Unbalance On Bearing LifejaypallaNo ratings yet
- RCDD Flash Cards - Chapter 1 Principle of TransmissionDocument286 pagesRCDD Flash Cards - Chapter 1 Principle of TransmissionTony Leonard80% (5)
- HAZOPDocument47 pagesHAZOPMiftakhul Nurdianto100% (4)
- D000-EL-701 Rev 4Document19 pagesD000-EL-701 Rev 4Sardar PerdawoodNo ratings yet
- OpenSees Geotechnical Analysis Workshop 2017Document70 pagesOpenSees Geotechnical Analysis Workshop 2017Tariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Maryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsDocument2 pagesMaryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsNicusor BuleteanuNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cbs of Huawei July2012Document31 pagesLecture Cbs of Huawei July2012Mahidul Islam Sumon95% (19)
- CH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsDocument13 pagesCH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mobile Number Portability in India ExplainedDocument28 pagesMobile Number Portability in India ExplainedphanivyasNo ratings yet
- QKNA For Mining GeologistDocument10 pagesQKNA For Mining GeologistAchanNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Networks (In) and CAMELDocument11 pagesIntelligent Networks (In) and CAMELnaggu1983No ratings yet
- Summary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkFrom EverandSummary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkNo ratings yet
- Location Update DescriptionDocument12 pagesLocation Update Descriptionpradeepkumarverma07No ratings yet
- Copper Wire and Cable: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesCopper Wire and Cable: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediatanwar_anuj1990No ratings yet
- MSOFTX3000 Ring Back Tone Service - 20060411-B-1.1 PDFDocument13 pagesMSOFTX3000 Ring Back Tone Service - 20060411-B-1.1 PDFCoachArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Virtual Roaming Systems for GSM, GPRS and UMTS: Open Connectivity in PracticeFrom EverandVirtual Roaming Systems for GSM, GPRS and UMTS: Open Connectivity in PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3g 4g Call FlowDocument16 pages3g 4g Call Flowpoiuytreza26No ratings yet
- GPRS Core Network ArchitectureDocument6 pagesGPRS Core Network ArchitectureJince KappanNo ratings yet
- Irat Eutran To UtranDocument4 pagesIrat Eutran To UtranshikhaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Number Portability in IndiaDocument27 pagesMobile Number Portability in Indiasamir_ttNo ratings yet
- Siemens Compressor PackageDocument8 pagesSiemens Compressor PackageMilos ObrenovicNo ratings yet
- IN and CAMEL OverviewDocument11 pagesIN and CAMEL OverviewAmiteshNo ratings yet
- GPRS Network ArchitectureDocument133 pagesGPRS Network ArchitectureNagashruthi BalasubramanyaNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- GPRS or EDGE AccessDocument2 pagesGPRS or EDGE AccessLebohangNo ratings yet
- PCRFDocument10 pagesPCRFvivekgeethaNo ratings yet
- GPRS Architecture BSSRDocument29 pagesGPRS Architecture BSSRMahesh Kumar NigamNo ratings yet
- E2E Bandwidth ControlDocument14 pagesE2E Bandwidth ControlMonique RichardsonNo ratings yet
- 2G To 3G HandoverDocument6 pages2G To 3G HandoverJagdish MathpalNo ratings yet
- VASDocument50 pagesVASPrashant BediNo ratings yet
- MNP PP PresentationDocument37 pagesMNP PP PresentationJaySharanNo ratings yet
- OCI Connect Between TenanciesDocument8 pagesOCI Connect Between Tenanciessss pppNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of GPRS and UMTS Features Introduced in Prior ReleasesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Overview of GPRS and UMTS Features Introduced in Prior ReleasessongoNo ratings yet
- MNP PP PresentationDocument37 pagesMNP PP PresentationNealNo ratings yet
- 50A95 Statya 1 Umts GSMDocument144 pages50A95 Statya 1 Umts GSMaleksey2012No ratings yet
- MNP Call FlowDocument27 pagesMNP Call FlowKumar SajjanNo ratings yet
- The GPRS Network: ContentsDocument13 pagesThe GPRS Network: ContentsChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. GPRS Attach SIM AuthenticationDocument4 pagesFigure 1. GPRS Attach SIM AuthenticationS. Siva ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- TSGS2#4 (99) 175Document9 pagesTSGS2#4 (99) 175Ashok GuptaNo ratings yet
- GPRS Protocols FamilyDocument18 pagesGPRS Protocols FamilybetomboNo ratings yet
- Presentation of 3GPP Charging Management-Sep 2004Document46 pagesPresentation of 3GPP Charging Management-Sep 2004khubaib_maharNo ratings yet
- 3G-2G Handover for CS and PS ServicesDocument4 pages3G-2G Handover for CS and PS ServicesdearvittNo ratings yet
- KA CGN ScaleoutDocument13 pagesKA CGN ScaleoutpabloNo ratings yet
- Radio Access Network Signalling: PS Call SetupDocument20 pagesRadio Access Network Signalling: PS Call SetupAbd El-Rahman Essam Anis100% (1)
- Inter Rat Handover GSM UmtsDocument4 pagesInter Rat Handover GSM UmtsadanakebapNo ratings yet
- Roaming and intra-circle roaming explainedDocument7 pagesRoaming and intra-circle roaming explainedKaran ParmarNo ratings yet
- Connect Leica1200 To RTN Using NtripDocument21 pagesConnect Leica1200 To RTN Using Ntripdika wahyuNo ratings yet
- Principles of User Data Retrieve at SRNS Relocation and GSM-UMTS Hand-Over for IP domainDocument10 pagesPrinciples of User Data Retrieve at SRNS Relocation and GSM-UMTS Hand-Over for IP domainpradeepkumarverma07No ratings yet
- 3GPP Charging Standards OverviewDocument46 pages3GPP Charging Standards Overviewram4uintptNo ratings yet
- Gprs Based Vehicle Tracker in Network System: Dr. Yogesh Kumar Sharma & Poonam R. ShityalkarDocument6 pagesGprs Based Vehicle Tracker in Network System: Dr. Yogesh Kumar Sharma & Poonam R. ShityalkarTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Carrier Grade NAT Configuration Guide: Global CacheDocument9 pagesCarrier Grade NAT Configuration Guide: Global CacheDũng Hoàng ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Nsa Application Paper Irat Handover AnalysisDocument58 pagesNsa Application Paper Irat Handover AnalysisadanakebapNo ratings yet
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureDocument7 pagesGPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureSrinivas KaratlapelliNo ratings yet
- Radio Network GPRS/EDGE Concept and ParametersDocument73 pagesRadio Network GPRS/EDGE Concept and ParametersClive MangwiroNo ratings yet
- GPRS: How It Works: An O2 White PaperDocument23 pagesGPRS: How It Works: An O2 White PaperKonstantinos ChrisNo ratings yet
- Gprs PosterDocument1 pageGprs PostermathcueiNo ratings yet
- DCG Subgroup 1 DCC Scope - Option 1 Draft - 0Document3 pagesDCG Subgroup 1 DCC Scope - Option 1 Draft - 0Taşem PlanlamaNo ratings yet
- CDMA Basic Call Flows 09 Nov 2004Document21 pagesCDMA Basic Call Flows 09 Nov 2004ezaxisNo ratings yet
- IGWBDocument8 pagesIGWBCloud BeezerNo ratings yet
- c2 PDFDocument38 pagesc2 PDFroginimNo ratings yet
- 9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingDocument35 pages9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingHồ ThôngNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic properties of R740 (ammonia) in SI unitsDocument1 pageThermodynamic properties of R740 (ammonia) in SI unitsJose LuisNo ratings yet
- VW T4 Automatic Gearbox Adapter Kit InstallationDocument2 pagesVW T4 Automatic Gearbox Adapter Kit InstallationLuke HazelgroveNo ratings yet
- Product Overview - COMFORT OVERVIEWDocument16 pagesProduct Overview - COMFORT OVERVIEWDam Ngoc KienNo ratings yet
- Enum Types JavaDocument3 pagesEnum Types JavaAmandeep PuniaNo ratings yet
- CV Edin Fatic2Document2 pagesCV Edin Fatic2yousab creator2No ratings yet
- Spreading Sequences: Tan F. Wong: Spread Spectrum & CDMADocument23 pagesSpreading Sequences: Tan F. Wong: Spread Spectrum & CDMAadeeb_2006No ratings yet
- BassoonBocals PDFDocument3 pagesBassoonBocals PDFnheyminkNo ratings yet
- Assignment Fall2018Document2 pagesAssignment Fall2018Frans LoekitoNo ratings yet
- CamlabDocument22 pagesCamlabviswamanojNo ratings yet
- Ryu RingkasanDocument20 pagesRyu RingkasanBest10No ratings yet
- Airworthiness Directive: Design Approval Holder's Name: Type/Model Designation(s)Document4 pagesAirworthiness Directive: Design Approval Holder's Name: Type/Model Designation(s)Kaung MyatToeNo ratings yet
- Synergy in The Urban Solid Waste Management With APPENDIXDocument25 pagesSynergy in The Urban Solid Waste Management With APPENDIXvincent jay ruizNo ratings yet
- Radiscreen-C Coarse Screen BR-ENDocument4 pagesRadiscreen-C Coarse Screen BR-ENmriosqNo ratings yet
- User Guide For Gateway NV57H / NV55SDocument1,087 pagesUser Guide For Gateway NV57H / NV55SAudrey D. ChatmanNo ratings yet
- JMeter OAuth SamplerDocument3 pagesJMeter OAuth SamplerFredy NataNo ratings yet
- Versidrain 150: Green RoofDocument2 pagesVersidrain 150: Green RoofMichael Tiu TorresNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between Multinational and Private IT Industries To Understand The Effect of Talent Management and Managerial Competencies On Employee Engagement Seema PanickerDocument369 pagesA Comparative Study Between Multinational and Private IT Industries To Understand The Effect of Talent Management and Managerial Competencies On Employee Engagement Seema PanickerMd Delowar Hossain MithuNo ratings yet
- TLE 9 1st Quarter Exam With Answer Key PDFDocument3 pagesTLE 9 1st Quarter Exam With Answer Key PDFJymaer GeromoNo ratings yet
- District Sales Manager or Territory Manager or Regional ManagerDocument3 pagesDistrict Sales Manager or Territory Manager or Regional Managerapi-121327024No ratings yet