Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science F4 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Keen WayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science F4 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Keen WayCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Scientific Investigation
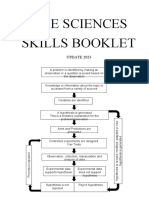
1.1 Analysing method in scientific investigation the process of gathering facts based on an observable event or phenomenon. Need to be adopted in learning Biology Steps involve in the Scientific Investigation:
1. Identifying a problem 2. Forming a hypothesis 3. Planning the experiment 4. Identifying and controlling variables 5. Conducting the experiment 6. Collecting data 7. Recording data 8. Analysing and interpreting data 9. Making Decision 10. Writing a report
1. Identifying a problem
observe a specific phenomenon pose question related to the phenomenon in the form of statement/question Example: Situation: A plant grows under sunlight. Problem Statement: Do plants need sunlight to grow?
2. Forming a hypothesis
Hypothesis general statement or a possible explanation to the problem under investigation. Based on observation could be tested through experiment Example: Problem Statement: What is the effect of light intensity to the photosynthesis process in plant? Hypothesis: The higher the light intensity, the higher the rate of photosynthesis. Relate the manipulated variable with responding variable. gathering relevant information about the experiment determining the materials and apparatus needed.
3. Planning the experiment
Identifying variables that will influence the result of the experiment determining the technique to be used determining the procedure to do the experiment determining how to make observation and measurements to be taken 4. Identifying and controlling variables Variables factors/condition which influence the result of the experiment Three types: a. Manipulated variables factors/condition that we change in the experiment b. Responding variable factor/condition that change according to the one that we change c. Fix/Constant variable factor/condition that are kept the same throughout the experiment follow the procedure and technique that have been decided include control experiment, which is similar in every aspect to the test experiment except that the manipulated variable is kept constant for comparison At the end of the experiment, clean the apparatus, put them back at the right place and dispose the unwanted materials in a proper disposal box. Data result of the experiment Obtained by means of observation and measurement Should be accurate and objective presenting the data can be presented in the form of tables, graphs, charts or diagram in a table, the quantity must have unit, the first column shows the manipulated variables and the second row shows the responding variable. In a graph, x-axis shows the manipulated variable and the y-axis shows the responding variable. include calculation determine the relationship between manipulated variable with responding variable. Relate the information gathered with the problem that is being investigated. find out whether the result support or refute the hypothesis if the hypothesis is rejected, form a new hypothesis and repeat the investigation until the hypothesis is accepted. present the result of the experiment in writing must be accurate, complete and clear Format of a report objective/aim
5. Conducting the experiment
6. Collecting data 7. Recording data
8. Analysing and interpreting data
9. Making conclusion 10. Writing a report
problem statement hypothesis variables materials and apparatus technique procedure results discussion conclusion
1.2 Scientific Attitudes and Noble Values Have inquiring mind and a keen interest in nature and the environment cooperative and considerate towards others and the environment show honesty and accuracy in conducting experiment and in recording data be objective and rational have a sense of responsibility and accountability to the community as a whole. Revision: 1. 2. 3. 4. What is scientific method? What are the steps involve in scientific investigation? Why do experiment usually require a control? Give two (2) examples of scientific attitudes and noble values?
You might also like
- 1.2 The Scientific InvestigationDocument16 pages1.2 The Scientific InvestigationIMELDA100% (3)
- 1 The Scientific InvestigationDocument3 pages1 The Scientific InvestigationImelda Nyaun100% (1)
- Form 4 Biology Chapter OverviewDocument21 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter OverviewKar KuanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Study of BiologyDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Study of BiologyachikgaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Science Introductory ClassDocument4 pagesSPM Science Introductory ClassPriya BalkerishnaNo ratings yet
- The Lab ReportDocument2 pagesThe Lab ReportjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Bstat DesignDocument47 pagesBstat DesignAby MathewNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- Chapter_1 (1)Document17 pagesChapter_1 (1)Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Biophysics Lab (Prelims Reviewer)Document6 pagesBiophysics Lab (Prelims Reviewer)Shaniah Azel GaodgaodNo ratings yet
- Science: The Scientific Method of InvestigationDocument8 pagesScience: The Scientific Method of InvestigationFe GullodNo ratings yet
- Modelo Reporte de LaboratorioDocument3 pagesModelo Reporte de LaboratorioNataRondonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ResearchDocument8 pagesReviewer in ResearchLeana Mae LaguneroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scientific InvestigationDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Scientific InvestigationFazza Rudy100% (8)
- Science Grade 7 Handout 1 Scientific MethodDocument5 pagesScience Grade 7 Handout 1 Scientific MethodClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- 2023 Scientific Method - Skills BookletDocument18 pages2023 Scientific Method - Skills BookletenochscribdNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledShikayna RunaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument31 pagesScienceEthan Ckrizjadon N. ObispoNo ratings yet
- Etit LectDocument16 pagesEtit LectPatel JigneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scientific InvestigationDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Scientific InvestigationanamarietuvNo ratings yet
- LS GR 10 Introduction and Scientific Method 2021Document7 pagesLS GR 10 Introduction and Scientific Method 2021SLUNGILE MKHONTONo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument5 pagesResearch ReviewermaeesotoNo ratings yet
- Module AGRI 214Document55 pagesModule AGRI 214Queenie Gwyneth MananganNo ratings yet
- Scienific MethodDocument29 pagesScienific MethodPaul Victor TamuriaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab - PHY102 Manual - Monsoon 2016 (With Correction) PDFDocument82 pagesPhysics Lab - PHY102 Manual - Monsoon 2016 (With Correction) PDFlanjaNo ratings yet
- Section 1.3 NotesDocument12 pagesSection 1.3 NotescoachmcmahonNo ratings yet
- Biophysics Lab (Prelims Reviewer)Document5 pagesBiophysics Lab (Prelims Reviewer)Shaniah Azel GaodgaodNo ratings yet
- DBIS Science Fair 2009Document2 pagesDBIS Science Fair 2009stanhopekrisNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination Introduction & PlanningDocument2 pagesSeed Germination Introduction & PlanningjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Steps of The Scientific MethodDocument2 pagesSteps of The Scientific MethodOlivia SardinaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Steps in Scientific InvestigationDocument10 pages1.3 Steps in Scientific Investigationliefeng81100% (2)
- AQA Practical Handbook FinalDocument35 pagesAQA Practical Handbook FinaljannyankiriNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Scientific MethodDocument20 pagesWeek 1 Scientific MethodsycpasocialmediaNo ratings yet
- Online ENVR 1401-Scientific Method Lab-JcDocument6 pagesOnline ENVR 1401-Scientific Method Lab-JcsameerNo ratings yet
- Scientific Skill LinkDocument10 pagesScientific Skill LinkKiTTyNo ratings yet
- Cri BDocument6 pagesCri BZarna KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method ExperimentDocument4 pagesScientific Method ExperimentCarissa Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - The Scientific Method - Experimental DesignDocument5 pagesSection 7 - The Scientific Method - Experimental DesignJehanieNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 1 NotesDocument2 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 1 NotesCheah Foo Kit58% (12)
- 1 Scientific MethodDocument17 pages1 Scientific MethodViviane O. BaylonNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 MDocument24 pagesBIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 Mwienna1987No ratings yet
- Scientific InvestigationDocument7 pagesScientific InvestigationNOUIEA BERNARDELLE ACABALNo ratings yet
- GEC 6 - Scientific Method and Process SkillsDocument4 pagesGEC 6 - Scientific Method and Process SkillsMaria Desiree AgustinNo ratings yet
- Lab Write UpDocument14 pagesLab Write UpRachel StandringNo ratings yet
- Botany LAB MANGO AND LEAVESDocument15 pagesBotany LAB MANGO AND LEAVESEPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGNo ratings yet
- 6au1 4scientificmethodDocument12 pages6au1 4scientificmethodapi-333988042No ratings yet
- Course: Research Methods in Education (8604) Semester: Autumn, 2022Document17 pagesCourse: Research Methods in Education (8604) Semester: Autumn, 2022عابد حسینNo ratings yet
- Step by Step How To Write The IaDocument11 pagesStep by Step How To Write The IaMayur VanjaniNo ratings yet
- Jameel Ur Rehman 8604 1Document18 pagesJameel Ur Rehman 8604 1Khaksar KakarNo ratings yet
- Affects The Availability of Plant Nutrients When A Plant Is Growing in Soil. When Ph. Is Too Low (Acidic)Document3 pagesAffects The Availability of Plant Nutrients When A Plant Is Growing in Soil. When Ph. Is Too Low (Acidic)Lexii UncomparableNo ratings yet
- 8604.1 Assignment No 1 AIOU Autumn 2022Document16 pages8604.1 Assignment No 1 AIOU Autumn 2022سعید اللہNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice GuideDocument3 pagesLab Practice GuideVictoria PenillaNo ratings yet
- Research 2: Quarter 1 MODULE 5 (Week 5 &6) : GUIDED EXPERIMENTSDocument5 pagesResearch 2: Quarter 1 MODULE 5 (Week 5 &6) : GUIDED EXPERIMENTSChelsea BialaNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument11 pagesScientific MethodPatricia100% (2)
- Scientific MethodDocument1 pageScientific MethodSto. Domingo, Jenica Joyce R.No ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument22 pagesScientific MethodJeraldine BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Is A Form of Research That Relies On The MethodsDocument19 pagesQuantitative Research Is A Form of Research That Relies On The MethodsRoela Marie AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Exploring Mathematical Modeling in Biology Through Case Studies and Experimental ActivitiesFrom EverandExploring Mathematical Modeling in Biology Through Case Studies and Experimental ActivitiesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 18 and 19 - Jonathan CaliriDocument4 pagesLesson 18 and 19 - Jonathan Caliriapi-610129783No ratings yet
- UET Research Proposal TemplateDocument9 pagesUET Research Proposal TemplateEngr AhmadNo ratings yet
- EspDocument3 pagesEspNuriNo ratings yet
- HY3012 POT Revision Part 1Document2 pagesHY3012 POT Revision Part 1judgelightNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Home ArticleDocument19 pagesMeaning of Home Articlebrainhub50No ratings yet
- NSTP ActivitiesDocument7 pagesNSTP ActivitiesHanna Mae D. Valmonte100% (1)
- Engagement Question AssignmentDocument5 pagesEngagement Question AssignmentestherNo ratings yet
- SVN 2017 000101.fullDocument13 pagesSVN 2017 000101.fullStephenNo ratings yet
- Action Research ProposalDocument3 pagesAction Research ProposalZaira Lipana100% (1)
- Literary Criticism Russia Roman Jakobson Poetic Mikhail Bakhtin StructuralismDocument5 pagesLiterary Criticism Russia Roman Jakobson Poetic Mikhail Bakhtin StructuralismJockimNo ratings yet
- AERO2379 & AERO2350 Lecture 5 Prezzi Style - 24 Mar 2020-1Document71 pagesAERO2379 & AERO2350 Lecture 5 Prezzi Style - 24 Mar 2020-1samala sonuNo ratings yet
- Summary, Conclusion and RecommendationsDocument5 pagesSummary, Conclusion and RecommendationsRosielyn Fano CatubigNo ratings yet
- RM Anand SirDocument14 pagesRM Anand Sirp2270304No ratings yet
- Sped 603 - Module2 - Lesson 2Document14 pagesSped 603 - Module2 - Lesson 2Maricris LlanoNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph College Learning Resources: Field Studies on Technology and CurriculumDocument46 pagesSt. Joseph College Learning Resources: Field Studies on Technology and CurriculumEvalyn M. SalvaNo ratings yet
- Managing and OrganizationsDocument845 pagesManaging and OrganizationsSwarali Kamath100% (2)
- General Concepts and Principles of Planning: Module No.1Document10 pagesGeneral Concepts and Principles of Planning: Module No.1Brian TiangcoNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Precis HandoutDocument3 pagesRhetorical Precis Handoutapi-264183025No ratings yet
- Drum ImprovDocument3 pagesDrum Improvdl1485No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Conformity and ObedienceDocument21 pagesChapter 6 - Conformity and ObediencemNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement Quiz: 10 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesSubject Verb Agreement Quiz: 10 Multiple Choice QuestionsBio BioytNo ratings yet
- Mark Sanders (STEM)Document8 pagesMark Sanders (STEM)elefantemartinezNo ratings yet
- Course of ML at IITDDocument2 pagesCourse of ML at IITDPrateekNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Implementation PhilosophyDocument5 pagesCurriculum Implementation Philosophyapi-476189522100% (1)
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridaySheilaMarB.Esteban100% (1)
- Subject Outline - GLSCM - SCND - MBA (Global) May 16Document14 pagesSubject Outline - GLSCM - SCND - MBA (Global) May 16Siddharth GargNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plans for Grade 3Document17 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plans for Grade 3Cy DacerNo ratings yet
- Exploring Computer Science v5.0Document306 pagesExploring Computer Science v5.0Jeremy See100% (1)
- StewartDocument13 pagesStewartdewi arumNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Infancy and Toddler HoodDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Infancy and Toddler HoodNicz Lanz DejzNo ratings yet