Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DSP Lect Plan
Uploaded by
Shyam Pratap SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DSP Lect Plan
Uploaded by
Shyam Pratap SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
NOIDA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
LECTURE PLAN
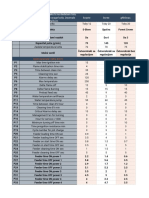
Course Title : TEC 602: Digital Signal Processing L T P Semester : VI - EC 4 2 0 Faculty Name : Mr. Prabhakar Agarwal Course Description: This gives complete knowledge about Digital Signal Processing. Stress is given to cover the basic concepts of Signals and Systems as the same is a prerequisite for Digital Signal Processing. Uni t No. Topic Name Discrete Fourier Transform: 1. Frequency Domain Sampling: The Discrete Fourier Transform Frequency- Domain Sampling and Reconstruction of Discrete-Time Signals. 2. The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). 3. The DFT as a linear Transformation. Relationship of the DFT to Other Transforms. 4. Properties of the DFT. Periodicity, Linearity, and Symmetry Properties. 5. Multiplication of two DFTs and Circular Convolution. 6. Additional DFT Properties. Frequency analysis of signals using the DFT. Efficient Computation of DFT 1. Efficient Computation of the DFT: FFT Algorithms. 2. Direct Computation of the DFT. 3. Radix-2 FFT algorithms. 4. Efficient computation of the DFT of two real sequences 5. Efficient computation of the DFT of a 2NPoint real sequences 6. Gortezel Algorithm 7. Chirp Z-transform algorithm. Basic Filter Structures Book/ Ref. No. 1/3 1/2 1/2 1/2/3 1/2 1 1/2/3 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/3 1/3 1 No. of Lect. 1 2 2 2 2 1 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 Lect. No. 1 2-3 4-5 6-7 8-9 10 11-13 14-15 16 17 18 19 20 Conducted Lecture Dates Tutorial / Assignment Detail Remarks
II
NOIDA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY III 1. Direct forms (I & II) 2. Cascade and parallel realizations. 3. Signal flow graph, Transposed structure 4. Basic FIR filter structures-. Direct form structure 5. Frequency sampling structure 6. Lattice structure, Linear phase FIR structure . FIR structures. Design of FIR Filters: 1. Symmetric and Anti-symmetric FIR Filters 2. Design of Linear-Phase FIR Filters Using Windows 3. Design of Linear-Phase FIR Filters by the Frequency Sampling Method 4. Design of FIR, Equiripple filter design Differentiators 5. Design of Hilbert Transformers. Design of IIR Filters From Analog Filters: 1. IIR Filter Design by Approximation of Derivatives V 2. IIR Filter Design by Impulse Invariance. IIR Filter Design by the Bilinear Transformation 3. The Matched-z Transformation, Characteristics of Commonly Used Analog Filters. 4. Application of above technique to the design of Butterworth Filters. 5. Chebyshev filters. 1/2/3 1/2/3 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1 /2 1 /2 1 /2 1 1 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 21 22-23 24 25 26 27-28 29 30-32 33-34 35 36 37 38-39 40-41 42-43 44
IV
Text Books: 1. Proakis, J.G. & Manolakis, D.G., Digital Signal Processing: Principles Algorithms and Applications, Prentice Hall (India). 2. S. Salivahanam, A Vallavaraj, C Gnanapriya, Digital Signal Processing, TMH. 3. Oppenheim A.V. & Schafer, Ronald W., Digital Signal Processing, Pearson Education.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Adaptive FiltersDocument30 pagesAdaptive FiltersShyam Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- RF Vs Molecular Wireless CommunicationDocument1 pageRF Vs Molecular Wireless CommunicationShyam Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Original IdeaDocument1 pageOriginal IdeaShyam Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Conclusion and Future WorkDocument2 pagesConclusion and Future WorkShyam Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Draw 224-1Document8 pagesDraw 224-1Alther Dabon33% (3)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Operaional Manual: YZBF-120LDDocument16 pagesOperaional Manual: YZBF-120LDMohamed AnwarNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Seminar ReportDocument27 pagesSeminar ReportnitinNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Vacuum Gauges 45Document20 pagesVacuum Gauges 45Sameeksha AnandNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Active Suspension System of Quarter CarDocument70 pagesActive Suspension System of Quarter CarMarcu SorinNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CEN ISO TR 17844 (2004) (E) CodifiedDocument7 pagesCEN ISO TR 17844 (2004) (E) CodifiedOerroc Oohay0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- IntroductionCorporate Social Responsibility To Gati by PrashantDocument9 pagesIntroductionCorporate Social Responsibility To Gati by PrashantvarshaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Spot Cooling ResearchDocument7 pagesSpot Cooling ResearchAkilaJosephNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Lexmark-E 321 Service ManualDocument184 pagesLexmark-E 321 Service ManualRemysNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- CE ThesisDocument210 pagesCE ThesisKristin ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Value Creation Through Project Risk ManagementDocument19 pagesValue Creation Through Project Risk ManagementMatt SlowikowskiNo ratings yet
- Sample Acceptable Use Policy From Southern Regional High SchoolDocument4 pagesSample Acceptable Use Policy From Southern Regional High Schoolapi-356000194No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mdce InstallDocument67 pagesMdce Installrmehta26No ratings yet
- Feasibility Study Notes Revised PDFDocument10 pagesFeasibility Study Notes Revised PDFGilbert BettNo ratings yet
- 4-2.0L Gasoline EngineDocument187 pages4-2.0L Gasoline EngineMarco Antonio Tomaylla Huamani100% (1)
- Advance Java Sem 5Document18 pagesAdvance Java Sem 5Gunjan Pratim JadhavNo ratings yet
- Cembrit Patina Design Line - LowresDocument11 pagesCembrit Patina Design Line - LowresRaul AntonieNo ratings yet
- KEDA Quotation of 2 3 4 Inch Mini Gold DredgerDocument3 pagesKEDA Quotation of 2 3 4 Inch Mini Gold DredgerShane CapstickNo ratings yet
- Period Based Accounting Versus Cost of Sales AccountingDocument13 pagesPeriod Based Accounting Versus Cost of Sales AccountingAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Geothermal Project TimelinesDocument10 pagesGeothermal Project TimelinesAldwin EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Chopra Scm5 Ch13Document58 pagesChopra Scm5 Ch13Faried Putra SandiantoNo ratings yet
- Sony NX Series PDFDocument62 pagesSony NX Series PDFMaya Tes0% (1)
- LogDocument2 pagesLogFerdian SumbaNo ratings yet
- Code PICDocument6 pagesCode PICsongbao527No ratings yet
- Flight Training Instruction: Naval Air Training CommandDocument174 pagesFlight Training Instruction: Naval Air Training CommandITLHAPN100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Arni AdvertisementDocument2 pagesArni AdvertisementHemanthNo ratings yet
- Parametri TobyDocument111 pagesParametri TobyZoran MilovicNo ratings yet
- IRGC (2021) - Spotlight - Risk Governance and The Rise of DeepfakesDocument4 pagesIRGC (2021) - Spotlight - Risk Governance and The Rise of DeepfakessaidNo ratings yet
- Surveyor C.VDocument2 pagesSurveyor C.VMasood Shabbir Khan Niazi100% (1)
- Macmillan English Grammar in Context Advanced PDFDocument3 pagesMacmillan English Grammar in Context Advanced PDFAnonymous l1MDLhBFXNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)