Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport Process General Descrip-Tion IS Energy Needed? Concen - Tration Gradient Example IN Humans Signif - Icance
Uploaded by
Tiera NicoleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transport Process General Descrip-Tion IS Energy Needed? Concen - Tration Gradient Example IN Humans Signif - Icance
Uploaded by
Tiera NicoleCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANSPORT PROCESS SIMPLE DIFFUSION OSMOSIS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION spreading out of molecules to equilibrium water moving through the cell membrane (c.m.) to dilute a solute using a special c.m. carrier protein to move something thru the c.m. using pressure to push something through a cell membrane opposite of diffusion at the expense of energy bringing a substance into the cell that is too large to enter by any of the above; Phagocytosis= cell eating; Pinocytosis = cell drinking. expelling a substance from the cell into ECF
IS ENERGY NEEDED? NO
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT [HIGH] TO [LOW] [HIGH] TO [LOW]
EXAMPLE IN HUMANS O2 into cells; CO2 out of cells. maintenance of osmotic balance of 0.9% saline manner in which glucose enters and leaves cell manner in which the kidney filters things from blood K+-Na+ATPase pump Phagocytosed (foreign) particles fuse with lysosomes to be destroyed
SIGNIFICANCE Cellular respiration maintenance of osmotic balance of 0.9% saline Cellular respiration
NO
FACILITATED DIFFUSION
NO
[HIGH] TO [LOW]
FILTRATION
NO
[HIGH] TO [LOW]
removal of metabolic wastes
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
YES
[LOW] TO [HIGH] [LOW] TO [HIGH]
maintenance of the resting membrane potential help fight infection
ENDOCYTOSIS
YES
EXOCYTOSIS
YES
[LOW] TO [HIGH]
Exporting proteins; dumping waste
Exporting proteins; dumping waste
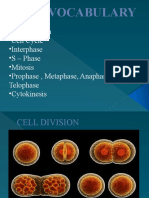
NAME OF PHASE
DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS Cell is growing and duplicates (replicates) DNA during S phase;
EVEN MORE DESCRIPTION
INTERPHASE DNA appears as chromatin in nucleus.
PROPHASE
Distinct chromosomes become apparent (i.e. sister chromatids held together by a centromere); Centrioles migrate to opposite poles of cell and spindle fibers form between them; nucleolus disintegrates; Nuclear envelope disintegrates. Chromosomes line up in an orderly fashion in the middle of the cell (on metaphase plate); Each centromere holding chromatids of the chromosome together attaches to a spindle fiber. The centromere holding the chromosome together splits; Resulting chromosomes migrate toward opposite poles of the cell being pulled by spindle fibers; Cytokinesis begins. Cleavage furrow between daughter cells is apparent (i.e. dumbbell shaped); Chromosomes complete migration to poles; Nuclear envelope & nucleolus reappear; Cytokinesis is complete.
METAPHASE
ANAPHASE
TELOPHASE
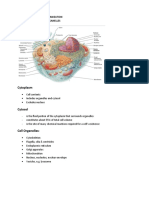
CELL COMPONENT CELL MEMBRANE
DESCRIPTION/ STRUCTURE Bilayer of phospholipids with proteins dispersed throughout jelly-like fluid (70% water) Central control center of cell; bound by lipid bilayer membrane; contains DNA dense spherical body within nucleus; RNA & protein RNA & protein; dispersed throughout cytoplasm or studded on ER Membranous network studded with ribosomes Membranous network lacking ribosomes Stack of Pancakes; cisternae Membranous sac of digestive enzymes Membranous sacs filled with catalase enzymes (catalase) Kidney shaped organelles whose inner membrane is folded into cristae.
FUNCTION(S) cell boundary; controls what enters and leaves the cell (Transport) suspends organelles in cell controls all cellular activity by instructing the cell what proteins to make (i.e. enzymes) synthesis of ribosomes
CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
NUCLEOLUS
RIBOSOMES
protein synthesis
ROUGH ER SMOOTH ER GOLGI LYSOSOMES
protein synthesis lipid & cholesterol synthesis modification, transport, and packaging of proteins destruction of worn cell parts (autolysis) and foreign particles detoxification of harmful substances (i.e. ethanol, drugs, etc.) Site of Cellular Respiration; Powerhouse
PEROXISOMES
MITOCHONDRIA
CYTOSKELETON
Protein filaments: microtubules, microfilaments, etc
provide scaffolding for cell; allows for intracellular transport
CELL COMPONENT FLAGELLA CILIA
DESCRIPTION/ STRUCTURE long, tail-like extension; human = sperm short, eyelash extensions; human = respiratory tract & fallopian tube microscopic ruffling of cell membrane paired cylinders of microtubules at right angles near nucleus
FUNCTION(S) locomotion to push substances through passageways increase surface area aid in chromosome movement during mitosis
MICROVILLI
CENTRIOLES
You might also like
- Biology Staar Eoc ReviewDocument62 pagesBiology Staar Eoc Reviewapi-26963416No ratings yet
- Mindsight EssayDocument4 pagesMindsight EssayTiera Nicole100% (1)
- Biology-Unit 2 Revision Powerpoint (Autosaved)Document153 pagesBiology-Unit 2 Revision Powerpoint (Autosaved)nhmerali786100% (1)
- MSF Medical Protocol For Sexual Violence Care - 2020 - FINAL - 30 06 20Document47 pagesMSF Medical Protocol For Sexual Violence Care - 2020 - FINAL - 30 06 20Dulce Paola Herrera100% (3)
- Cells AnatomyDocument16 pagesCells AnatomyHoneylaine MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Document55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Yasin Putra EsbeyeNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument5 pagesGen BioDanilo JR. BuaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument54 pagesCell StructuresWilliam DC RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCell PhysiologyReslie Joy Serrano100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- Teas NotesDocument31 pagesTeas NotesjanettNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesCell Structure and FunctionBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument68 pagesCell Biologyleanavill100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-530699294No ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument54 pagesThe Cellular Level of OrganizationGraziela Sagun RepuyoNo ratings yet
- The CELLDocument4 pagesThe CELLJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument45 pagesCellsapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Nor Fadila Kasim Fakulti Sains Sukan Dan Kejurulatihan Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (Upsi)Document135 pagesNor Fadila Kasim Fakulti Sains Sukan Dan Kejurulatihan Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (Upsi)syafiqahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Document12 pagesLecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Pia GalagalaNo ratings yet
- Human Cell BiologyDocument49 pagesHuman Cell Biologykgzyvqqr4jNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReportDocument49 pagesGen Bio ReportlgNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure LaboratoryDocument53 pagesCell Structure LaboratoryKyle RoaNo ratings yet
- Cells AND TISSUESDocument8 pagesCells AND TISSUESJanica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument44 pagesCell Structure and FunctionPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- HistologeDocument62 pagesHistologe89sar2365No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologySylvanus Rein LangreoNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Dr. Samia ShahbazDocument26 pagesCell Membrane: Dr. Samia Shahbazreema aslamNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument89 pagesCells and TissuesJoy CuanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument6 pagesCell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeRiy KimNo ratings yet
- As OCR Biology Revision PackDocument28 pagesAs OCR Biology Revision PackJoel TrelivingNo ratings yet
- CellDocument13 pagesCellNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- I. Cell StructureDocument5 pagesI. Cell StructureAllyson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Bio HomeworkDocument1 pageBio HomeworkshamooNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyDocument12 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyJean Rose SalahayNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class IxDocument57 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class IxAthar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its StructureDocument70 pagesCell and Its StructureEDLYN BRAZILNo ratings yet
- The Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima HashmiDocument53 pagesThe Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima Hashmibeverly brittoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 2Document12 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 2Carina DioblesNo ratings yet
- Membrane and TransportDocument30 pagesMembrane and TransportOmer KareemNo ratings yet
- רזי 7 חלוקת תאDocument24 pagesרזי 7 חלוקת תאBoba BanayNo ratings yet
- Pathobiology: Modul Dr. Lidwina S. Sengkey, SP - KFR-KDocument21 pagesPathobiology: Modul Dr. Lidwina S. Sengkey, SP - KFR-KPatrick MuljonoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: By: Grace Nichols, Coral Friend, and Amanda Trussell Mr. Taylor's 8 Grade Gifted Class January, 2006Document17 pagesCell Division: By: Grace Nichols, Coral Friend, and Amanda Trussell Mr. Taylor's 8 Grade Gifted Class January, 2006Rahul UniyalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Terms and Definitions Review MaterialDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Terms and Definitions Review Materialcvsu.viado.lielchzeinoreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Study GuideKristina Ann VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class IxDocument56 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class IxIftikhar Hussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument5 pagesCell Structures and Functions9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Membran PlasmaDocument58 pagesMembran PlasmaIqbalullohNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument10 pagesCells and TissuesChelanie Vidad AndaweNo ratings yet
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (14)
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Cellsaira sharidaNo ratings yet
- Basics of CytologyDocument54 pagesBasics of Cytologychocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Cellular Transport RevisedDocument38 pagesThe Cell and Cellular Transport RevisedSavanha Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsNo ratings yet
- Cell CompartmentalizationDocument36 pagesCell Compartmentalizationanuj2907No ratings yet
- Stem 12 Cell DivisionDocument38 pagesStem 12 Cell DivisionJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureMayleen LeeNo ratings yet
- Cell Physio MedDocument90 pagesCell Physio MedjandaniellerasNo ratings yet
- CellDocument10 pagesCelljuju on the beatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Week 2) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonDocument5 pagesLecture 3 (Week 2) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonMohammad FotovatNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)Document7 pagesAnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)HyvieNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Management 4Document2 pagesManagement 4Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Location DecisionsDocument10 pagesLocation DecisionsTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Marketing PlanDocument17 pagesMarketing PlanTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Haitian RuleDocument2 pagesHaitian RuleTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Business FunctionsDocument2 pagesBusiness FunctionsTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ali Bakri 8227 Appleton St. Dearborn Heights, MI 48127 313-409-9093Document3 pagesAli Bakri 8227 Appleton St. Dearborn Heights, MI 48127 313-409-9093Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Marketing EnvironmentDocument4 pagesMarketing EnvironmentTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Discussion Part 1 and 2Document7 pagesWeek 2 Discussion Part 1 and 2Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Discussion Board 2Document5 pagesDiscussion Board 2Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Case 2 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCase 2 AssignmentTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Measuring Performance of Employees Working RemotelyDocument4 pagesMeasuring Performance of Employees Working RemotelyTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Discussion Week 1Document4 pagesDiscussion Week 1Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- 436 6Document3 pages436 6Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Assessing Strategy: Center For Organ Recovery & EducationDocument6 pagesAssessing Strategy: Center For Organ Recovery & EducationTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- 436 8.2Document4 pages436 8.2Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- 317 7.4 2Document4 pages317 7.4 2Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- 436 6Document3 pages436 6Tiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Article ReviewDocument5 pagesArticle ReviewTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Apple Price and PromotionDocument6 pagesApple Price and PromotionTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Terminating The Employee-Employer RelationshipDocument5 pagesTerminating The Employee-Employer RelationshipTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Artifact RationaleDocument5 pagesArtifact RationaleTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- The Two EscobarsDocument5 pagesThe Two EscobarsTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Debate Team ArticleDocument2 pagesDebate Team ArticleTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Harlem RenaissanceDocument7 pagesHarlem RenaissanceTiera NicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosing in CRRT FinalDocument42 pagesDrug Dosing in CRRT FinalVrushali MahajanNo ratings yet
- Cat Immunization RecordsDocument1 pageCat Immunization RecordsAnne-MarieNo ratings yet
- Ms ExamDocument35 pagesMs ExamJackie AbarraNo ratings yet
- Gibco Neurobiology Protocol Handbook Withcover 2021Document136 pagesGibco Neurobiology Protocol Handbook Withcover 2021zikrilchaniagoNo ratings yet
- Is AIDS God's PunishmentDocument4 pagesIs AIDS God's Punishmentsunilthomas177No ratings yet
- Praktikum Patologi Ikan 2020Document33 pagesPraktikum Patologi Ikan 2020Syifa ekhiasanNo ratings yet
- Susceptibility of Drug-Resistant Clinical Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Strains To Essential Oils of Ginger, Thyme, Hyssop, and Sandalwood 0426-06Document4 pagesSusceptibility of Drug-Resistant Clinical Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Strains To Essential Oils of Ginger, Thyme, Hyssop, and Sandalwood 0426-06Anonymous i71HvPXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument44 pagesChapter 1 Microbiology and ParasitologyGrachel Ann Pariente DayuhaNo ratings yet
- Aw y Gin 2011 - Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Waterborne Pathogenic Viruses in Surface Waters of Tropical Urban CatchmentsDocument13 pagesAw y Gin 2011 - Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Waterborne Pathogenic Viruses in Surface Waters of Tropical Urban CatchmentsYoNo ratings yet
- Ihc PDFDocument28 pagesIhc PDFJean Bosco ByendaNo ratings yet
- Neet PreprationDocument295 pagesNeet PreprationTrishul IsNo ratings yet
- Family Planing and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument34 pagesFamily Planing and Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRina KawamuraNo ratings yet
- Review of Companion Animal Vaccine and ImmunoprophylaxisDocument14 pagesReview of Companion Animal Vaccine and ImmunoprophylaxisVictor FelterNo ratings yet
- Mcqs On Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesMcqs On Excretory SystemIshfaq LoneNo ratings yet
- My MCAT Bio NotesDocument14 pagesMy MCAT Bio NotesCarishma BudhuNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document42 pagesCovid 19ok100% (3)
- ADN Descubrimiento 2018Document37 pagesADN Descubrimiento 2018Paul Suarez MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- (Biol 12) 200 MCQ On Microorganisms + AnswersDocument23 pages(Biol 12) 200 MCQ On Microorganisms + Answersjemal12174No ratings yet
- Basic MicrobiologyDocument45 pagesBasic MicrobiologycaraNo ratings yet
- Batterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013Document14 pagesBatterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013edain84No ratings yet
- Bone Marrow, Blood, Formation, Med TechDocument47 pagesBone Marrow, Blood, Formation, Med TechAngela Louise SmithsNo ratings yet
- International Clinical LaboratoriesDocument23 pagesInternational Clinical Laboratoriesmihret geneneNo ratings yet
- Nelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial PDFDocument331 pagesNelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial PDFMADHANKUMAR MANICKAVELNo ratings yet
- PATH505PDocument11 pagesPATH505PMohsin SialNo ratings yet
- OTITIS Concept MapDocument7 pagesOTITIS Concept MapElleNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument53 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyJanlyn Ricci S. TañoNo ratings yet
- Rice GenomeDocument26 pagesRice GenomePavani Gaja100% (1)
- 012 Mod 3 - BiotransformaciónDocument11 pages012 Mod 3 - BiotransformaciónJohanna Bustos NutricionistaNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument5 pagesQuiz LetTrisha SamparaniNo ratings yet