Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Washing Machine Motor Controller
Uploaded by
Rev. MatthewOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Washing Machine Motor Controller
Uploaded by
Rev. MatthewCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCUIT IDEAS
WASHING MACHINE S.C.
DWIV
EDI
MOTOR CONTROLLER
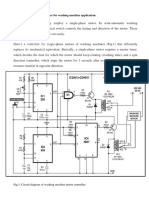
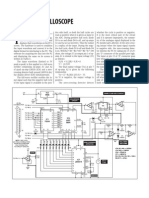
SANTHOSH VASUDEVAN efficiently replaces its mechanical equiva- trolled as shown in Fig. 2. When switch
lent. Basically, a single-phase motor re- S1 is in position A, coil L1 of the motor
W
ashing machines usually employ quires a master timer, which decides the receives the current directly, whereas coil
a single-phase motor. In semi- time for which the motor should keep L2 receives the current with a phase shift
automatic washing machines, a rotating (washing time), and a spin direc- due to capacitor C. So the rotor rotates in
purely mechanical switch controls the tim- tion controller, which stops the motor for clockwise direction (see Fig. 2(a)). When
ing and direction of the motor. These 3 seconds after every 10 seconds and switch S1 is in position B, the reverse hap-
switches are costly and wear out easily. then resumes rotation in opposite direc- pens and the rotor rotates in anti-clock-
Here’s a controller for single-phase tion. wise direction (see Fig. 2(b)). Thus switch
motors of washing machines (Fig. 1) that The direction of rotation can be con- S1 can change the rotation direction.
The motor cannot be re-
versed instantly. It needs a
brief pause between switch-
ing directions, or else it may
get damaged. For this
purpose, another spin di-
rection control timer (IC2)
is employed. It is realised
with an IC 555. This timer
gives an alternate ‘on’ and
‘off’ time duration of 10
seconds and 3 seconds, re-
spectively. So after every l0
seconds of running (either
in clockwise or anticlock-
wise direction), the motor
stops for a brief duration of
3 seconds. The values of
R3 and R4 are calculated
accordingly.
The master timer is
realised with monostable IC
555 (IC1) and its ‘on’ time
is decided by the resistance
of 1-mega-ohm potmeter
VR. A 47-kilo-ohm resistor
Fig. 1: Circuit diagram of washing machine motor controller is added in series so that
even when the VR knob is
in zero
resis-
tance po-
sition,
the net
series re-
sistance
is not
zero.
The
on-off
cycle in
the mas-
ter timer
Fig. 2: Direction of motor Fig. 3: Timing diagram for rotation of motor should
SEPTEMBER 2003 ELECTRONICS FOR YOU
CIRCUIT IDEAS
go on only for the set time (here it is 18 only when the output from NAND gate relay RL2 and washing machine motor
minutes). Once the master timer goes off, N1 is low. As the mains 220V line is rotates in one direction. During the off
the cycle should stop. To achieve this, taken through relay RL1, the motor turns time of IC2, the output of N1 goes high
the outputs of both the timers are con- off during the 3-second off period after again to de-energise relay RL1, which
nected to NAND gate N1 (IC3), which the set time of 10 seconds is over. The cuts off the mains supply to RL2 and the
gives a low output only when both the graph is shown in Fig. 3. motor stops rotating.
timers are giving high outputs.The output During ‘on’ time of spin direction timer Floating point trouble may occur at trig-
pin 2 of N1 is connected to relay RL1 via IC2, the output of negative-edge triggerd ger pin 2 of IC1. Resistor R8 overcomes this
pnp transistor T1, so the relay energises JK flip-flop at pin 2 goes low to energise problem by holding pin 2 high.
ELECTRONICS FOR YOU SEPTEMBER 2003
You might also like
- A Microcontroller Based Water Level Indicator Using Radio Frequency RF Technology and Ultrasonic Sensor1Document6 pagesA Microcontroller Based Water Level Indicator Using Radio Frequency RF Technology and Ultrasonic Sensor1amey salunke100% (1)
- HC05 BluetoothDocument16 pagesHC05 BluetoothDaniel Eneas Calderon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Micro Controller Based Digital Visitor CounterDocument33 pagesMicro Controller Based Digital Visitor Counterprathameshas90No ratings yet
- Dam GateDocument18 pagesDam GateAbdul Razzak100% (1)
- Monitoring and Control of a Wireless Water Tank Level SystemDocument8 pagesMonitoring and Control of a Wireless Water Tank Level SystemDipak GayakwadNo ratings yet
- GSM 8051 Microcontroller SMS IrrigationDocument6 pagesGSM 8051 Microcontroller SMS Irrigationamism24100% (1)
- Cellphone Based Agricultural Water Pump ControlDocument3 pagesCellphone Based Agricultural Water Pump Controlpraveen_kodgirwarNo ratings yet
- Permanent Switch Board ContentDocument56 pagesPermanent Switch Board ContentCrispNo ratings yet
- 2.development of Blind Assistive Device in Shopping MallsDocument4 pages2.development of Blind Assistive Device in Shopping MallsJashuvaNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument34 pagesFinal ProjectihtishamNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2801Document89 pagesScientech 2801Santiago Alberto Ramirez MarinNo ratings yet
- Green House Intelligent Control System PDFDocument15 pagesGreen House Intelligent Control System PDFMuhammadAbbasJafriNo ratings yet
- Timers and CountersDocument4 pagesTimers and Countersivan10mNo ratings yet
- 25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentDocument84 pages25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentdileeppatraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Water Level ControllerDocument23 pagesWireless Water Level ControllerSankeerthana GadeNo ratings yet
- Short Range Radar SystemDocument14 pagesShort Range Radar SystemKaththi Karthick100% (1)
- AT89C2051 Traffic Light ControllerDocument39 pagesAT89C2051 Traffic Light ControllerNagesh RayNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CSE360 Course Title: Computer Architecture Section: 02 Project Title: Suggest and Design A Minimal CPU Group NumberDocument7 pagesCourse Code: CSE360 Course Title: Computer Architecture Section: 02 Project Title: Suggest and Design A Minimal CPU Group NumberrimonNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Dam Gate Control System ProjectDocument108 pagesMicrocontroller Based Dam Gate Control System ProjectArun Golwara50% (4)
- Lab Manual 20100728Document320 pagesLab Manual 20100728Kuro070% (1)
- 20.motion Based Automatic Door OpenerDocument16 pages20.motion Based Automatic Door OpenerKelvin Ceejay100% (1)
- Transmission in 132KV SubstationDocument39 pagesTransmission in 132KV SubstationZain MunawarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Ration Distribution by Using Raspberry PiDocument5 pagesAutomatic Ration Distribution by Using Raspberry PiIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Design an IGBT Inverter for AC Motor Drive ApplicationsDocument40 pagesDesign an IGBT Inverter for AC Motor Drive Applicationselectron1999100% (1)
- Alcohol Detection System in CarsDocument12 pagesAlcohol Detection System in CarsRat.T67% (3)
- We Use Arduino and A RTC Ds3231 Module To Display The Time and DateDocument4 pagesWe Use Arduino and A RTC Ds3231 Module To Display The Time and DatembogNo ratings yet
- Displaying Text On 16x2 LCD With ArduinoDocument5 pagesDisplaying Text On 16x2 LCD With ArduinofaqihfadillahNo ratings yet
- Rfid Based Security System: A Project ReportDocument22 pagesRfid Based Security System: A Project ReportHeartin HariNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Temperature Measurement and ControllingDocument94 pagesMicrocontroller Based Temperature Measurement and ControllingNitesh Chauhan67% (3)
- VNC Function Operation InstructionDocument11 pagesVNC Function Operation InstructionArnaldo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Automatic Water Irrigation SystemDocument31 pagesAutomatic Water Irrigation SystemGetahun AsnakeNo ratings yet
- Human Following Robot: Major Project Report ONDocument31 pagesHuman Following Robot: Major Project Report ONAshish Ranjan SinghNo ratings yet
- Control AC Lamp Dimming via Mobile BluetoothDocument2 pagesControl AC Lamp Dimming via Mobile BluetoothHari KishorNo ratings yet
- What Is Speaker ?Document3 pagesWhat Is Speaker ?Siva ViratNo ratings yet
- Electronics Washing Machine ControlDocument4 pagesElectronics Washing Machine ControlMohd ShukriNo ratings yet
- Automatic Irrigation System Using AURDINO Uno (Mine)Document41 pagesAutomatic Irrigation System Using AURDINO Uno (Mine)Shobha HebballiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Chapter 13: ADC, DAC and Sensor InterfacingDocument33 pagesEmbedded Systems Chapter 13: ADC, DAC and Sensor Interfacingsumbal_iqbal100% (1)
- Automatic water level indicator using ultrasonic sensor and GSM moduleDocument9 pagesAutomatic water level indicator using ultrasonic sensor and GSM moduleUrooj ButtNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report 1Document56 pagesMini Project Report 1Pavan KPNo ratings yet
- Automatic Railway Gate CrossingDocument12 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate CrossingKapil NakumNo ratings yet
- Arduino, Components, Sensors Product List with PricesDocument3 pagesArduino, Components, Sensors Product List with PricesuyaiekanemNo ratings yet
- Automatic Speed Control with RF WirelessDocument19 pagesAutomatic Speed Control with RF WirelessmukulNo ratings yet
- Real Time ClockDocument7 pagesReal Time ClockMohsinRazaNo ratings yet
- On DTHDocument23 pagesOn DTHAkash Tyagi100% (2)
- DC Motor CTRL Using Single SwitchDocument44 pagesDC Motor CTRL Using Single SwitchAbhijeet NayakNo ratings yet
- Smart Irrigation Using Low Cost Moisture Sensor and Cortex Arm m3Document7 pagesSmart Irrigation Using Low Cost Moisture Sensor and Cortex Arm m3meenachiNo ratings yet
- Renesas Flash Programmer Sample Circuit For Programming PC Serial PDFDocument5 pagesRenesas Flash Programmer Sample Circuit For Programming PC Serial PDFAjay J VermaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of FC68Document6 pagesIntroduction of FC68Nguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Original Project WorkDocument65 pagesOriginal Project WorkKonda PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Automatic Plant Irrigation System Using RTCDocument51 pagesAutomatic Plant Irrigation System Using RTCRajeshMudulakarNo ratings yet
- Fatek PLC Modbus AdresleriDocument1 pageFatek PLC Modbus Adreslerisamet gozubolNo ratings yet
- Temporizador Naranja AlemanDocument3 pagesTemporizador Naranja AlemanHugo HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Motor Controller For Washing Machine ApplicationDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Motor Controller For Washing Machine ApplicationVenkata Rajkumar ChNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine Motor Controller Replaces Mechanical SwitchDocument2 pagesWashing Machine Motor Controller Replaces Mechanical SwitchSuneel Venkat100% (1)
- Dynamic BrakingDocument3 pagesDynamic BrakingMikhael Glen LatazaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Speed Controls: Theory of OperationDocument17 pagesElectronic Speed Controls: Theory of OperationChristian BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Relé de Tempo RXKL-1 e RXKM-2H 508002 (En)Document6 pagesRelé de Tempo RXKL-1 e RXKM-2H 508002 (En)leonardoNo ratings yet
- SMC of BLDC Motor Speed With Chattering Reduction PDFDocument6 pagesSMC of BLDC Motor Speed With Chattering Reduction PDFNadeshiko KinomotoNo ratings yet
- Programmable Appliance TimerDocument2 pagesProgrammable Appliance TimerRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- CI Aug04 Flashing HOTDocument1 pageCI Aug04 Flashing HOTRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Variable Power SupplyDocument1 pageVariable Power Supplyapi-3736447100% (1)
- TDA1554QDocument12 pagesTDA1554QerrozoNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Bright LED LampDocument1 pageUltra-Bright LED LampRev. Matthew100% (2)
- Solar Bug NoiseDocument1 pageSolar Bug NoiseRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Solar Light SystemDocument2 pagesSolar Light Systemneeru28No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic DetectorDocument2 pagesUltrasonic DetectorRev. Matthew100% (3)
- FM TransmitterDocument1 pageFM TransmittersunilhknNo ratings yet
- PWM Motor Speed ControlDocument1 pagePWM Motor Speed ControlRev. Matthew100% (3)
- Mains ManagerDocument1 pageMains ManagerRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Programmable Appliance TimerDocument2 pagesProgrammable Appliance TimerRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Seven Segment DiceDocument2 pagesSeven Segment DiceRev. Matthew100% (2)
- Invisible Broken Wire DetectorDocument1 pageInvisible Broken Wire DetectorRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Non Contact AC Power MonitorDocument1 pageNon Contact AC Power MonitorRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- PC Based OscilloscopeDocument3 pagesPC Based OscilloscopeRev. Matthew100% (1)
- Patent 7379286Document3 pagesPatent 7379286Antipliroforisi AktibistesNo ratings yet
- Seven Segment DiceDocument2 pagesSeven Segment DiceRev. Matthew100% (2)
- CI Aug04 Flashing HOTDocument1 pageCI Aug04 Flashing HOTRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- Heat Sensitive SwitchDocument1 pageHeat Sensitive Switchvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- US Navy NEETS - NAVEDTRA 14173 Module 01 Introduction To Matter, Energy, and Direct CurrentDocument278 pagesUS Navy NEETS - NAVEDTRA 14173 Module 01 Introduction To Matter, Energy, and Direct CurrentGeorges100% (2)
- Regulated Power Supply with Short-Circuit DetectionDocument1 pageRegulated Power Supply with Short-Circuit DetectionDiego ManchayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Building Data Model in SalesforceDocument78 pagesLesson 2 Building Data Model in SalesforceChaudhary AlishaNo ratings yet
- Why Why Analysis Presentation-TPm-training-materialDocument43 pagesWhy Why Analysis Presentation-TPm-training-materialsaravanananusha67% (6)
- Enum Types JavaDocument3 pagesEnum Types JavaAmandeep PuniaNo ratings yet
- SNMP Tutorial PDFDocument24 pagesSNMP Tutorial PDFSrivignessh PssNo ratings yet
- Precision Waveform Generator/Voltage Controlled Oscillator FeaturesDocument12 pagesPrecision Waveform Generator/Voltage Controlled Oscillator FeaturesCharles Tineo0% (1)
- Activities Plan - Assets Inventory (Lake House, Club Huis & Green Sport)Document8 pagesActivities Plan - Assets Inventory (Lake House, Club Huis & Green Sport)Customer ServiceNo ratings yet
- ReadMe STEP7 Professional V14 enUS PDFDocument74 pagesReadMe STEP7 Professional V14 enUS PDFAndre Luis SilvaNo ratings yet
- Smart Selangor Briefing and Invitation to Express InterestDocument30 pagesSmart Selangor Briefing and Invitation to Express InterestKUSATEX AZMI0% (1)
- Adaptive Bit LoadingDocument10 pagesAdaptive Bit LoadingKrrish BommanaNo ratings yet
- Sunstack Tech SpecDocument2 pagesSunstack Tech SpecAdriel MirtoNo ratings yet
- UnlversDocument55 pagesUnlversCan AcarNo ratings yet
- TH3122 004 PDFDocument14 pagesTH3122 004 PDFSasa MitrovicNo ratings yet
- The Kitchen Science of Crystals Lesson 4Document3 pagesThe Kitchen Science of Crystals Lesson 4api-239297797No ratings yet
- C - EWM - 90 - SAP Certified Application Associate - Extended Warehouse Management 9Document4 pagesC - EWM - 90 - SAP Certified Application Associate - Extended Warehouse Management 9Padma Raju0% (1)
- Design and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Document7 pagesDesign and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Mandeep KaloniaNo ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial College-Marbel INC Bachelor of Science in Tourism ManagementDocument7 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial College-Marbel INC Bachelor of Science in Tourism ManagementRam G. MorteraNo ratings yet
- HILTI Direct Fastening Technical Guide - Ed 18Document212 pagesHILTI Direct Fastening Technical Guide - Ed 18rodriguez.gaytanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Flight Dynamics: at The End of The Course, You Should Be Able ToDocument23 pagesAircraft Flight Dynamics: at The End of The Course, You Should Be Able ToAntony BalabanNo ratings yet
- Optimum Propeller Design Using Computerized MethodDocument10 pagesOptimum Propeller Design Using Computerized MethodPavan KishoreNo ratings yet
- DS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishDocument16 pagesDS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishJosé AdelinoNo ratings yet
- Support Vector Machines & Kernels: David Sontag New York UniversityDocument19 pagesSupport Vector Machines & Kernels: David Sontag New York UniversityramanadkNo ratings yet
- Devops Training in Bangalore - Devops Training in Bangalore MarathahalliDocument8 pagesDevops Training in Bangalore - Devops Training in Bangalore MarathahalliitrainNo ratings yet
- Wind Load On Cable TraysDocument10 pagesWind Load On Cable TraysAaron EasleyNo ratings yet
- Plant Species and Drug Types Weapon StatsDocument4 pagesPlant Species and Drug Types Weapon Statself godNo ratings yet
- Product Overview - COMFORT OVERVIEWDocument16 pagesProduct Overview - COMFORT OVERVIEWDam Ngoc KienNo ratings yet
- EX 9 CompositesDocument2 pagesEX 9 CompositesRenae SavannahNo ratings yet
- Tar 19 GZBDocument11 pagesTar 19 GZBRitesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Earthing of High Voltage Electrical Apparatus For The Protection of PersonnelDocument56 pagesEarthing of High Voltage Electrical Apparatus For The Protection of PersonnelDavoNo ratings yet
- Service QualityDocument11 pagesService QualityMang Abdul RohmatNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Cyber Threat Intelligence Detecting and Responding To Advanced Cyber Attacks at The National LevelDocument566 pagesCollaborative Cyber Threat Intelligence Detecting and Responding To Advanced Cyber Attacks at The National Levelanon_760702463No ratings yet