Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Predisposing Factor Precipitating Factor
Uploaded by
Aiko MizushimaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Predisposing Factor Precipitating Factor
Uploaded by
Aiko MizushimaCopyright:
Available Formats
Aids/hiv CA: HIV (Human Immunodefienciency Virus) Incubation Period: 4-6 weeks after exposure
Reverse transcription (HIV's RNA is converted to DNA) Integration (Inserting of dna) Transcription (DNA to RNA)
RESERVOIR: Humans infected with the disease POE: blood, secretion MOT: Sex, needles, blood tranfusion, perinatal transmission SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: Imunocompromised patients, Polygamous relationship, pregnancy (HIV +), blood transfusion, sharing of needles POE: Mucous membrane, skin, blood PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Predisposing Factor -age -all races -History -Gender Precipitating Factor -Immunosuppression -Work -Pregnancy -Sexually Active exposure Human Immunodeficiency Virus invasion of HIV HIV antibodies are produced but do not appear immediately (INCUBATION PERIOD 4-6 Weeks) HIV attaches to a protein molecule called CD4 Cells w/c is on the surface of T4 Cells
Translation (RNA goes out of Nucleus) Assembly (Assembly of the parts of VIRUS) Budding (Protection of cells [RNA]) T4 cells dies releasing HIV on the body
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS CA: Mycobacteriun tuberculosis Incubation Period: 4-6 weeks after exposure
RESERVOIR: Humans infected with the disease POE: Respiratory System MOT: Droplet, Airborne SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: Immunocompromised POE: Skin, Nose, Mouth PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Chronic exposure to infected persons Microorganisms settle throughout the airways
Viral replication inside T4 Cells (endocytosis entry of the virus inside the cells) Uncoating- The nucleocapsid needs to be partially dissolved so that the virus's RNA can be converted into DNA, a necessary step if HIV's genetic material is to be incorporated into the T-cell's genetic core. Bacteria in droplets bypass the mucocilliary system and reach the alveoli Complement protein C3 binds to the cell wall
Opsonization by C3 is rapid Engulfed by alveolar macrophages
Proliferation and widespread dissemination
HEPATITIS B CA: Hepatitis B virus Incubation Period: 30180 days (mean, 812 weeks)
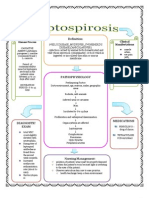
RESERVOIR: Humans infected with the disease Attracts T-Lymphocytes to the site Formation of Granuloma 2-3 weeks necrosis occurs Caseous necrosis LEPTOSPIROSIS CA: Leptospira interrogans Incubation Period: 6-15 days POE: Blood MOT: direct exchange of blood, contact with contaminated secretions and Sexual contact and perinatal transmission SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: Polygamous relationship, pregnancy (HIV +), blood transfusion, sharing of needles POE: Mucous membrane, skin, blood PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Entry to blood stream entry to the liver binds to the surface receptors of the kupffer cells entry of core particle to cytoplasm Transcription Translation Budding into endoplasmic reticulum Leptospires penetrate through broken skin, mucous membranes, inhalation of respiratory droplets, and waterlogged contact with intact skin and conjunctivae Bacterial clearance is by phagocytosis and humoral mechanism vesicular transport to cell membrane APC CD4 ( T-helper cell)
RESERVOIR: Rodents POE: Urine MOT: Mucous Membrane of the eyes, nose, mouth, and through a break through the skin. SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: People in flooded areas POE: blood PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Rodents and small mammals are the most common hosts they will excrete or shed leptospires in their urine
B cells Antibody (IgM) chronic infection IgG
FEMALE ANOPHELES MOSQUITO Incubation Period: 2-5 days RESERVOIR: Humans POE: Skin, blood mucous membrane MOT: mosquito bite SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: children POE: skin, blood, mucuous membrane
Dengue Fever CA: Aedes Egypti Incubation Period: 2-5 days MENINGITIS RESERVOIR: Humans CA: POE: Skin, blood mucous membrane Incubation Period: 1-10 days MOT: mosquito bite RESERVOIR: Humans SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: children POE: Skin, blood mucous membrane POE: skin, blood, mucuous membrane MOT: mosquito bite PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: SUSCEPTIBLE HOST: children Aedes Egypti bites infected person POE: skin, blood, mucuous membrane Incubation period of the Aedes Egypti Bites the susceptible host Susceptible host incubation period Bites the PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Neisseria meningitides PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
MALARIA CA: Plasmodium Falciparum (malignant tertian) Plasmodium Vivax (Benign Tertian) Plasmodium Malariae (Quartan) Plasmodium ovale
You might also like
- Meningitis Definition and CausesDocument16 pagesMeningitis Definition and CausesPatziedawn GonzalvoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease FinalDocument16 pagesCommunicable Disease FinalPatziedawn Gonzalvo50% (2)
- Rotavirus To Scrapies March 28,2007Document4 pagesRotavirus To Scrapies March 28,2007api-26938624No ratings yet
- Virology ReviewDocument5 pagesVirology ReviewTerence Eday100% (1)
- Virus Envelope DNA Structure Capsid Clinical Importance Vaccines & MiscDocument4 pagesVirus Envelope DNA Structure Capsid Clinical Importance Vaccines & Miscnydia_burgos100% (1)
- 8.sti 2Document44 pages8.sti 2Mahrukh SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Infection and ImmunityDocument68 pagesInfection and ImmunityWilliam EwingNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument24 pagesVirologyRohama Qubra 279No ratings yet
- DR - Dr.efrida Warganegara, M.Kes., SP - MKDocument30 pagesDR - Dr.efrida Warganegara, M.Kes., SP - MKDedy SantosoNo ratings yet
- Purnomo Hadi: FK UNDIP - SemarangDocument36 pagesPurnomo Hadi: FK UNDIP - SemarangandreasNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Ventilation Part V - Respiratory PandemicsDocument84 pagesAlterations in Ventilation Part V - Respiratory Pandemicsirish felixNo ratings yet
- Patologi Penyakit Infeksi: Willy Sandhika, Dr. M.Si. SP - PA Bagian Patologi Anatomi FK - Unair - SurabayaDocument38 pagesPatologi Penyakit Infeksi: Willy Sandhika, Dr. M.Si. SP - PA Bagian Patologi Anatomi FK - Unair - SurabayaArum Rasyiidta Windi SumbogoNo ratings yet
- DNA Viruses IIDocument4 pagesDNA Viruses IIkep1313No ratings yet
- Sporozoa PDFDocument61 pagesSporozoa PDFsummer djNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Trachomatis: Lack Peptidoglycan: Genital Pregnant Women WomenDocument2 pagesChlamydia Trachomatis: Lack Peptidoglycan: Genital Pregnant Women Womennur fitrahana sururiNo ratings yet
- Addendum To "Bare Minimum, 2004: Staph AureusDocument3 pagesAddendum To "Bare Minimum, 2004: Staph AureusKiana TehraniNo ratings yet
- Basic virus structure and classificationDocument47 pagesBasic virus structure and classificationIsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument6 pagesCommunicable DiseasesLory LynNo ratings yet
- Clinical Virology (Dental)Document134 pagesClinical Virology (Dental)samar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Viral Skin Infections Caused by Herpesviridae and PoxviridaeDocument55 pagesViral Skin Infections Caused by Herpesviridae and PoxviridaeGita RizkiNo ratings yet
- I&V II Virology Lecture 2 of 9Document33 pagesI&V II Virology Lecture 2 of 9Alros ManteltNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Document32 pagesPenyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Bendy Dwi IrawanNo ratings yet
- Version 3.0 Summer 1998Document0 pagesVersion 3.0 Summer 1998frabziNo ratings yet
- RETROVIRIDAEDocument1 pageRETROVIRIDAEjcpacate1178qcNo ratings yet
- HIV & AIDS (Final Draft)Document17 pagesHIV & AIDS (Final Draft)SivaNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis and Lung Flukes: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionDocument37 pagesSchistosomiasis and Lung Flukes: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionKenny NgowiNo ratings yet
- Malaria: A Protozoan Disease Transmitted by MosquitoesDocument6 pagesMalaria: A Protozoan Disease Transmitted by MosquitoesJoharaNo ratings yet
- Dams Lastlook Microbiology PDFDocument27 pagesDams Lastlook Microbiology PDFChauhan Monika100% (1)
- Microbiology: Eukaryotes & ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesMicrobiology: Eukaryotes & ProkaryotesJohn Christopher Luces100% (1)
- RetrovirusesDocument79 pagesRetrovirusesrasimmozturkNo ratings yet
- HerpesvirusDocument61 pagesHerpesvirusAnida HasnaNo ratings yet
- Swine 5&6Document57 pagesSwine 5&6Keegan McElroyNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanDocument29 pagesViruses: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Biology of Hiv Particle Description of HIV Particle A) Classification of HIV ParticleDocument10 pagesBiology of Hiv Particle Description of HIV Particle A) Classification of HIV ParticlevictoriousNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDS Worldwide Statistics and StagesDocument59 pagesHIV/AIDS Worldwide Statistics and StagesNindya Fajriyati UtamiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infection On Respiration Tract: Ike Irmawati P.A, Msi Med Mikrobiologi FK YarsiDocument39 pagesBacterial Infection On Respiration Tract: Ike Irmawati P.A, Msi Med Mikrobiologi FK YarsiCamila SuhendarNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of VirusesDocument32 pagesPathogenesis of VirusesSamuel OgaroNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument41 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingPagarigan VianNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke-2 REPRODocument74 pagesPertemuan Ke-2 REPROAdi Joyo NegoroNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems: Measles, Rubella, Roseola, VaricellaDocument60 pagesViral Exanthems: Measles, Rubella, Roseola, VaricellaClaire GuanteroNo ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIROSISDocument3 pagesLEPTOSPIROSISNi Kanaya MuliaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases ExplainedDocument7 pagesPathogenesis of Infectious Diseases ExplainedRana zaatrehNo ratings yet
- The Viruses: Agent of InfectionDocument62 pagesThe Viruses: Agent of InfectionAhimsa MartawigunaNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHDocument55 pagesPresented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Papovaviridae PowerpointDocument53 pagesPapovaviridae PowerpointMia Fernandez100% (3)
- Canine DistemperDocument18 pagesCanine DistemperJ Elver SilvaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: DR - Biswajeeta Saha (1 Yr PG) Moderator: Dr. N. Sahu, Dept of Pathology, Kims, BBSRDocument43 pagesPresented By: DR - Biswajeeta Saha (1 Yr PG) Moderator: Dr. N. Sahu, Dept of Pathology, Kims, BBSRBiswajeeta SahaNo ratings yet
- Micro I ReviewDocument15 pagesMicro I ReviewEmilee Tu100% (1)
- Viral IsolationDocument18 pagesViral Isolationsshiffana7558No ratings yet
- Presented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHDocument55 pagesPresented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHwira guna pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Virus ChartDocument18 pagesVirus Chartezaz000No ratings yet
- Rabies: Fatal Viral Infection Transmitted by Animal BitesDocument13 pagesRabies: Fatal Viral Infection Transmitted by Animal Bitesميمونه عبد الرحيم مصطفىNo ratings yet
- 6 Mikro Viral Gastroenteritis and Hepatitis Lecture 2017Document41 pages6 Mikro Viral Gastroenteritis and Hepatitis Lecture 2017Bunga CitraNo ratings yet
- Foot and Mouth DiseasesDocument9 pagesFoot and Mouth Diseaseseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Dengue AutosavedDocument12 pagesDengue AutosavedMaricris PallarNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument42 pagesVirusesPaul SavvyNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus pptx3Document15 pagesCoronavirus pptx3Ace Ashley Baron75% (4)
- UNIT Five: Arthropod or Intermediate Vector Borne DiseasesDocument53 pagesUNIT Five: Arthropod or Intermediate Vector Borne DiseasesYakob TadeseNo ratings yet
- The Landmarks of MartinismDocument7 pagesThe Landmarks of Martinismcarlos incognitosNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Cooling IBDocument11 pagesPower Plant Cooling IBSujeet GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- ACC8278 Annual Report 2021Document186 pagesACC8278 Annual Report 2021mikeNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Abu Bakar, Jalan Beserah, 25300 Kuantan, PahangDocument18 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Abu Bakar, Jalan Beserah, 25300 Kuantan, PahangChandrika RamodaranNo ratings yet
- Sample-Network-Vulnerability-Report 11Document47 pagesSample-Network-Vulnerability-Report 11Kennedy OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Common Law MarriageDocument3 pagesCommon Law MarriageTerique Alexander100% (1)
- FREE MEMORY MAPS FOR ECONOMICS CHAPTERSDocument37 pagesFREE MEMORY MAPS FOR ECONOMICS CHAPTERSRonit GuravNo ratings yet
- By Omar Mustafa Ansari and Faizan Ahmed Memon - Islamic Finance NewsDocument5 pagesBy Omar Mustafa Ansari and Faizan Ahmed Memon - Islamic Finance Newshumasd453No ratings yet
- GonorrhoeaDocument24 pagesGonorrhoeaAtreyo ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- KPK Progress in PTI's Government (Badar Chaudhry)Document16 pagesKPK Progress in PTI's Government (Badar Chaudhry)badarNo ratings yet
- Roadmap To Prayer Lesson 16Document18 pagesRoadmap To Prayer Lesson 16Krisztian KelemenNo ratings yet
- Trial of Warrant Cases by MagistrateDocument15 pagesTrial of Warrant Cases by MagistrateSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing MetricsDocument29 pagesMarketing Metricscameron.king1202No ratings yet
- Paper 3 IBIMA Brand Loyalty Page 2727-2738Document82 pagesPaper 3 IBIMA Brand Loyalty Page 2727-2738Sri Rahayu Hijrah HatiNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing Pledge Assignment ADocument34 pagesReceivable Financing Pledge Assignment AJoy UyNo ratings yet
- Wagner Group Rebellion - CaseStudyDocument41 pagesWagner Group Rebellion - CaseStudyTp RayNo ratings yet
- Harga MethanolDocument1 pageHarga MethanolYuli NugraheniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Imc 407Document14 pagesChapter 1 Imc 407Mayson Chua ShangNo ratings yet
- Memorandum Personnel Memo 21-11 To:: A B G D. WDocument2 pagesMemorandum Personnel Memo 21-11 To:: A B G D. WLEX18NewsNo ratings yet
- Municipal Best Practices - Preventing Fraud, Bribery and Corruption FINALDocument14 pagesMunicipal Best Practices - Preventing Fraud, Bribery and Corruption FINALHamza MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Return To The Source Selected Speeches of Amilcar CabralDocument112 pagesReturn To The Source Selected Speeches of Amilcar Cabraldjazzy456No ratings yet
- PW Show Daily at Frankfurt Day 1Document68 pagesPW Show Daily at Frankfurt Day 1Publishers WeeklyNo ratings yet
- HCB 0207 Insurance Ad Risk ManagementDocument2 pagesHCB 0207 Insurance Ad Risk Managementcollostero6No ratings yet
- Poetry and PoliticsDocument21 pagesPoetry and Politicshotrdp5483No ratings yet
- Shiva Gayathri Mantra - Dhevee PDFDocument4 pagesShiva Gayathri Mantra - Dhevee PDFraghacivilNo ratings yet
- Prossional Ethics Notes CH-1 To CH-6 by DbrathodDocument64 pagesProssional Ethics Notes CH-1 To CH-6 by Dbrathodtempuser26No ratings yet
- Growth Pole Theory PDFDocument5 pagesGrowth Pole Theory PDFlokesh singh100% (1)
- KEY TO THE SWIMMING POOL TIMETABLE AND PROGRAMMEDocument2 pagesKEY TO THE SWIMMING POOL TIMETABLE AND PROGRAMMEthomas homerNo ratings yet
- Late Birth Registration Form for KenyaDocument2 pagesLate Birth Registration Form for KenyaSarati80% (5)
- Akhtar Non IT RecruiterDocument3 pagesAkhtar Non IT RecruiterMohiddinNo ratings yet