Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BBIT 241 Introduction To Computer Networks
Uploaded by
liliwanguiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BBIT 241 Introduction To Computer Networks
Uploaded by
liliwanguiCopyright:
Available Formats
BBIT 241 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS / CISY 231 TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS Prerequisite: BBIT 111/ CISY 131 Purpose
of the Course: This course introduces the students to the fundamental concepts in Computers Networks, communication models and network topologies that form a basis for subsequent networks related courses. And enables the student understand and describe telecommunication concepts Expected Learning Outcomes: At the end of the course, the student should be able to: Understand the basic information on computer networks. Explain different network classifications. Explain network architectures and topologies and protocol . Understand telecommunication networks and technologies. Understand various multi-service network topologies. Explain how circuit and packet switched networks are designed and implemented in order to provide Wide Area Communication.
Course Outline 0 Introductions to Computer Networks. Uses of Computer Networks. Network Hardware. Network Software. Reference Models. Example Networks. Network Standardization Computer network elements 1 The Physical Layer. The Theoretical Basis For Data Communication. Guided Transmission Media. Wireless Transmission. Communication Satellites. The Public Switched Telephone Network. The Mobile Telephone System. Cable Television.
2 The Data Link Layer. Data Link Layer Design Issues. Error Detection and Correction. Elementary Data Link Protocols. Sliding Window Protocols. Protocol Verification. Example Data Link Protocols. 2 The Medium Access Control Sublayer. The Channel Allocation Problem. Multiple Access Protocols. Ethernet. Wireless Lans. Broadband Wireless. Bluetooth. Data Link Layer Switching.
3. The Network Layer.
Network Layer Design Issues. Routing Algorithms. Congestion Control Algorithms. Quality of Service. Internetworking. The Network Layer in the Internet.
4. The Transport Layer. The Transport Service. Elements of Transport Protocols. A Simple Transport Protocol. The Internet Transport Protocols: UDP. The Internet Transport Protocols: TCP. Performance Issues. 5. The Session Layer. Types and characteristics of Sessions, 6. Presentation layer Format conversion; ASCII/EBCDIC; Encryption functions. 7. The Application Layer. DNSThe Domain Name System. Electronic Mail. The World Wide Web..
8. Network Security. Mode of Delivery: Lectures. Practical lab sessions. Group discussions. Instructional materials and/or Equipment: A computer loaded with Ms Windows XP or later version. Course Assessment Continuous Assessment End of Trimester Examination.
30 % 70 %
Core Reading Material Comer D. E, Computer Networks and Internet. 5th Edition. Pearson Education Limited London. 2009 Horak, R. ;Telecommunications and Data Communications Handbook: John Wiley and Sons Inc., 2007. Recommended Reference Material: FitzGerald J, Dennis A. Business Data Communications and Networking 10th Edition 2009. Lacerwords Privace limited. Stallings, W. Data and computer communications, Eighth edition. Pearson Prentice Hall. USA 2007. Sarkar N. Tools for teaching computer networking and hardware concepts Information science Publishing USA. 2006. Stallings, W. Business Data Communications. 6th Edition, Pearson Education. 2009 Tanenbaum, S; Computer Networks: 4th Edition, Pearson Education. 2004.
You might also like
- Analaysis On ChristianityDocument26 pagesAnalaysis On ChristianitySherif GaballaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Data Processing - MainDocument15 pages1 - Data Processing - MainMaina RajputNo ratings yet
- Summary of Clayton M. Christensen, Jerome H. Grossman & Jason Hwang's The Innovator's PrescriptionFrom EverandSummary of Clayton M. Christensen, Jerome H. Grossman & Jason Hwang's The Innovator's PrescriptionNo ratings yet
- Laudon MIS13 ch14Document36 pagesLaudon MIS13 ch14Annisa 'anis' Dwi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 3Q14 Roadmap To ValuationDocument30 pages3Q14 Roadmap To ValuationRyan BrookmanNo ratings yet
- Singtel SWOTDocument4 pagesSingtel SWOTSally TeoNo ratings yet
- Precision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandPrecision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Controls A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandInformation Technology Controls A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SID - Telecommunications OSS and BSSDocument3 pagesIntroduction To SID - Telecommunications OSS and BSSKowshik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Applications of Data WarehousingDocument10 pagesApplications of Data WarehousingAnan SirwalNo ratings yet
- Erp Domain PDFDocument2 pagesErp Domain PDFJuan0% (1)
- Improve Business Practice LO 1 2016Document35 pagesImprove Business Practice LO 1 2016John YohansNo ratings yet
- DWM Unit 1Document27 pagesDWM Unit 1Edu FreeNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Management SystemDocument30 pagesReal Estate Management Systemrajesh mechNo ratings yet
- Project Title: Hospital Management System Description: Hospital Management System Is A Web Based Project. It Consists of Client RegistrationDocument68 pagesProject Title: Hospital Management System Description: Hospital Management System Is A Web Based Project. It Consists of Client Registrationshahid198950% (2)
- User Interface Evaluation Methods For Internet Banking Web Sites: A Review, Evaluation and Case StudyDocument6 pagesUser Interface Evaluation Methods For Internet Banking Web Sites: A Review, Evaluation and Case StudyPanayiotis ZaphirisNo ratings yet
- Mboo31 - Management Information Systems Set - 1 Solved AssignmentDocument10 pagesMboo31 - Management Information Systems Set - 1 Solved Assignmentved_laljiNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Layered Approach To CRM Implementation: An Integration PerspectiveDocument15 pagesA Multi-Layered Approach To CRM Implementation: An Integration PerspectivepankajNo ratings yet
- CSC101 - L1 - Intro To Computer SystemsDocument25 pagesCSC101 - L1 - Intro To Computer SystemsBryan GallegoNo ratings yet
- IT3355 - Project Assignment 1Document3 pagesIT3355 - Project Assignment 1rhynos42No ratings yet
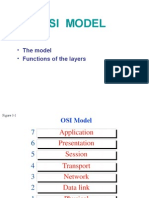
- Osi ModelDocument51 pagesOsi Modelapi-3703205No ratings yet
- NOC DescDocument1 pageNOC DescSokhan SereyVisithNo ratings yet
- Report WritingDocument10 pagesReport WritingKavya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- ICON College of Technology and ManagementDocument20 pagesICON College of Technology and ManagementClaudiu IordanNo ratings yet
- Sample CV of TEDocument3 pagesSample CV of TEAlzum ShahadatNo ratings yet
- 32524L&R - Case Study - 2011ADocument9 pages32524L&R - Case Study - 2011AamazingmengNo ratings yet
- Real Time SystemDocument76 pagesReal Time Systemjkj90No ratings yet
- Design Principles For Connected DevicesDocument37 pagesDesign Principles For Connected Devicesநட்ராஜ் நாதன்No ratings yet
- D7.2 Data Managment Plan v1.04Document14 pagesD7.2 Data Managment Plan v1.04gkoutNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 (Service Oriented Architecture)Document9 pagesUnit-4 (Service Oriented Architecture)Binay YadavNo ratings yet
- E-Marketplaces: Structures, Mechanisms, Economics, and ImpactsDocument57 pagesE-Marketplaces: Structures, Mechanisms, Economics, and ImpactsKrisel Ibanez100% (1)
- Yahoo! Information SystemsDocument16 pagesYahoo! Information SystemsArnab Aditya SethiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On E-CommerceDocument12 pagesAssignment On E-CommerceMd Kowsar HamidNo ratings yet
- 7ITHelpDesk PDFDocument30 pages7ITHelpDesk PDFiqbal raisnawanNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Enterprise Resource Planning ImplementationDocument14 pagesRisk Management in Enterprise Resource Planning Implementationclemen_angNo ratings yet
- PrimitivesDocument3 pagesPrimitivesaravisiv100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3RedhwanAL-AkbariNo ratings yet
- OOMD Final Oral QuesDocument7 pagesOOMD Final Oral QuesAjinkya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Customer Analysis: Strategic Market SegmentationDocument25 pagesCustomer Analysis: Strategic Market SegmentationWan Muhammad Abdul HakimNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - Inventory ControlDocument8 pagesCase Studies - Inventory ControlShweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- PHP ONLINE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMDocument16 pagesPHP ONLINE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMbharti_prajyahoocomNo ratings yet
- What Is R3 CordaDocument5 pagesWhat Is R3 CordaCorda Blockchain Development CompanyNo ratings yet
- LAN RedundancyDocument33 pagesLAN RedundancyJoseph Al BayonasNo ratings yet
- M HealthDocument81 pagesM HealthAbebe ChekolNo ratings yet
- An Automated Medical Duties Scheduling System Using Queing Techniques (Chapter 1-5)Document19 pagesAn Automated Medical Duties Scheduling System Using Queing Techniques (Chapter 1-5)ABUBSAKAR SIDIQ AMINUNo ratings yet
- Delivering Itil Best PracticesDocument11 pagesDelivering Itil Best PracticesDavid Carter100% (1)
- Introduction To eTOM: White PaperDocument13 pagesIntroduction To eTOM: White PaperRobNo ratings yet
- Unit 17 Data Warehousing and Data Mining: StructureDocument33 pagesUnit 17 Data Warehousing and Data Mining: StructureShraddha OnkarNo ratings yet
- Restructuring Information Systems HealthcareDocument11 pagesRestructuring Information Systems HealthcareSteve PanNo ratings yet
- New Century Wellness Group Case Study 2Document4 pagesNew Century Wellness Group Case Study 2akbarNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning For Revenue Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandMachine Learning For Revenue Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- EVO34 - Evolution Implementation Proposal TemplateDocument7 pagesEVO34 - Evolution Implementation Proposal TemplateDickson AllelaNo ratings yet
- Software Project 1Document2 pagesSoftware Project 1Md AzmalNo ratings yet
- A Feedback Based Scheme For Improving TCP Performance in Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksDocument7 pagesA Feedback Based Scheme For Improving TCP Performance in Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksHarish GokulNo ratings yet
- Tutooor18 RWHDocument6 pagesTutooor18 RWHR.S.G.FNo ratings yet
- Chapt144 Os Crcenghb Prof - YwDocument17 pagesChapt144 Os Crcenghb Prof - YwAnuska ThapaNo ratings yet
- CS610 Finalterm MCQsDocument6 pagesCS610 Finalterm MCQsAijaz khan0% (1)
- Computer Networks Lab Manual-17ECL68Document87 pagesComputer Networks Lab Manual-17ECL68LikithaReddy Yenumula80% (5)
- AA.81-V1.2 - Packet Voice Interconnection Service Schedule To AA.80Document35 pagesAA.81-V1.2 - Packet Voice Interconnection Service Schedule To AA.80a_big_friendNo ratings yet
- Google Certified Professional Cloud ArchitectDocument446 pagesGoogle Certified Professional Cloud Architectranga raoNo ratings yet
- Ch6. Transport LayerDocument113 pagesCh6. Transport LayerAbdulaziz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.1 Transport Layer - Process-to-Process DeliveryDocument32 pagesLecture 4.1 Transport Layer - Process-to-Process DeliverySATHEESH ANo ratings yet
- 2 NetworkModelDocument35 pages2 NetworkModelNixon PeraltaNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model - A Seven Layered Architecture of OSI ModelDocument12 pagesOSI Reference Model - A Seven Layered Architecture of OSI ModelKamiyabali MominNo ratings yet
- AMIE-Computer Network Old Question SortedDocument10 pagesAMIE-Computer Network Old Question Sortedsandeepharidas100% (3)
- The OSI Model and The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDocument40 pagesThe OSI Model and The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteAlfred Richie BennettNo ratings yet
- Plc&Scada MergedDocument823 pagesPlc&Scada Mergedmarathi sidNo ratings yet
- Almas BajiDocument21 pagesAlmas BajiiamnomandungeNo ratings yet
- Indian RailDocument19 pagesIndian RailvjkkjfkjljfNo ratings yet
- Cse 306Document2 pagesCse 306Shakib Al HasanNo ratings yet
- RFC 1086Document11 pagesRFC 1086NickyNETNo ratings yet
- 3KC69646KAAATPZZA - V1 - 1830 Photonic Service Switch (PSS) Release 10.0 DCN Planning and Engineering Guide (Photonic Applications)Document142 pages3KC69646KAAATPZZA - V1 - 1830 Photonic Service Switch (PSS) Release 10.0 DCN Planning and Engineering Guide (Photonic Applications)Abdou AbdouNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Security V3.0 Training MaterialDocument788 pagesHCIA-Security V3.0 Training MaterialGaby Torres0% (1)
- AttachmentDocument94 pagesAttachmentAnonymous mPIcV5No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Transport Layer: Our GoalsDocument67 pagesChapter 3: Transport Layer: Our Goalsamanchandra4617No ratings yet
- National Transmission and Despatch Company: SPECIFICATION DDS-110:2012Document26 pagesNational Transmission and Despatch Company: SPECIFICATION DDS-110:2012Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- BSC Computer PDFDocument22 pagesBSC Computer PDFshamalu2011100% (1)
- Unit 3Document98 pagesUnit 3Mayank GhimireNo ratings yet
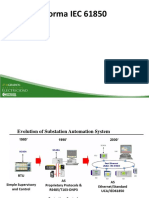
- 4 Iec61850 PDFDocument42 pages4 Iec61850 PDFErick CapusNo ratings yet
- Network Layer AssignmentDocument3 pagesNetwork Layer AssignmentAnuraagKashyapNo ratings yet
- Here's List of Questions & Answers On Computer Networks Subject Covering 100+ Topics: 1. Questions & Answers On IntroductionDocument71 pagesHere's List of Questions & Answers On Computer Networks Subject Covering 100+ Topics: 1. Questions & Answers On IntroductionAhmad Tariq KhiamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On 5G TechnologyDocument27 pagesPresentation On 5G TechnologyMohammad Saleem100% (1)