Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1zzVS2zz 6
Uploaded by
Ofi de MoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1zzVS2zz 6
Uploaded by
Ofi de MoCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
JENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General
The engine control system for the 1ZZ-FE and 2ZZ-GE engines have following system. System SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection ESA Electronic Spark Advance IAC (Idle Air Control) Intake Air Flow Control VVT-i Variable Valve Timing-intelligent VVTL-i Variable Valve Timing and Lift-intelligent Outline D An L-type SFI system directly detects the intake air volume with a hot-wire type mass air flow meter. D The fuel injection system is a sequential multiport fuel injection system. D Ignition timing is determined by the ECM based on signals from various sensors. The ECM corrects ignition timing in response to engine knocking. D The torque control correction during gear shifting has been used to minimize the shift shock.* A rotary solenoid type IAC valve controls the fast idle and idle speeds. The intake air duct is divided into two areas, and the ECM controls the variable intake valve and the actuator that are provided in one of the areas to reduce the amount of engine noise. Controls the intake camshaft to an optimal valve timing in accordance with the engine condition. Controls the intake and exhaust camshafts and the cam changeover mechanism to realize an optimal valve timing and valve lift in accordance with the engine conditions. D Fuel pump operation is controlled by signal from the ECM. D To stop the fuel pump during operation of the SRS airbag. For details, see page 58. Maintains the temperature of the oxygen sensors at an appropriate level to increase accuracy of detection of the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. D The ECM controls the purge flow of evaporative emissions (HC) in the charcoal canister in accordance with engine conditions. D Using 3 VSVs and a vapor pressure sensor, the ECM detects any evaporative emission leakage occurring between the fuel tank and the charcoal canister through the changes in the tank pressure. By turning the air conditioning compressor ON or OFF in accordance with the engine condition, drivability is maintained. When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM diagnoses and memorizes the failed section. When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM stops or controls the engine according to the data already stored in memory. 1ZZ-FE 2ZZ-GE Engine Engine f f
f f
f f
Fuel Pump Control
Oxygen Sensor Heater Control
Evaporative Emission Control
Air Conditioning Cut-off Control Diagnosis Fail-Safe
f f f
f f f
* Only for the Automatic Transaxle Model
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
2. Construction
The configuration of the engine control system in the 1ZZ-FE and 2ZZ-GE engines in the new CELICA is as shown in the following chart.
SENSORS ACTUATORS SFI #10 #20 #30 #40 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
: Only for FLOW METER Model *1MASS AIR the Automatic Transaxle VG *2: Only for the 2ZZ-GE Engine Model
INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
THA THW VTA NE G2
No.1 INJECTOR No.2 INJECTOR No.3 INJECTOR No.4 INJECTOR ESA IGNITION COIL with IGNITER SPARK PLUGS VVT-i, VVTL-i*2
IGT1 X IGT4
IGF CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR VVTL OIL D Comfirmation signal of cam switching HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 1, Sensor 1) HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 1, Sensor 2) KNOCK SENSOR VAPOR PRESSURE SENSOR COMBINATION METER D Vehicle Speed Signal IGNITION SWITCH D Starting Signal D Ignition Signal PARK/ NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH*1 POWER STEERING OIL PRESSURE SWITCH AIR CONDITIONING ECU AC METER ECU ILL TAILLIGHT RELAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR 3 SWITCH*2
OSW
OCV
OIL CONTROL VALVE (Variable Valve Timing)
VVTL-i*2 OVL OX1A VSV OX1B KNK1 PTNK ECM RSO
OIL CONTROL VALVE (Variable Valve Timing and Lift)
INTAKE AIR FLOW CONTROL VSV IAC CONTROL VALVE FUEL PUMP CONTROL FC CIRCUIT OPENING RELAY
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CONTROL
SPD HT1A STA IGSW P, R, N 2, L, D PS MPX1 MPX2 HT1B
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER
Bank 1, Sensor 1 Bank 1, Sensor 2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
CCV TBP EVP1
VSV (for Canister Closed Valve)
VSV (for Pressure Switching Valve)
VSV (for EVAP) METER ECU MPX+ MPX
AIR CONDITIONING CUT-OFF CONTROL
MPX1 MPX2
AIR CONDITIONING ECU FAN MREL COOLING FAN RELAY EFI MAIN RELAY
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
SIL TC +B
W BATT BATT ERY
EFI MAIN RELAY
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
3. Engine Control System Diagram
*1: Only for the Automatic Transaxle Model Park / Neutral *2: Only for the 2ZZ-GE EnginePosition Switch*1 Model
Ignition Switch
Vehicle Speed Signal Meter ECU
Air Conditioning ECU Taillight Relay
Battery
Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch
MIL
ECM
Circuit Opening Relay
DLC3
VSV (for EVAP)
Vapor Pressure Sensor
VSV for Pressure Switching Valve VSV for Canister Closed Valve Charcoal Canister
Throttle Position Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor
Oil Control Valve Valiable Valve Timing
Fuel Pump
Oil Control Valve Valiable Valve Timing and *2 Lift
VSV Intake Air Flow Control
Air Cleaner
IAC Valve Mass Air Flow Meter Built-in Intake Air Temp. Sensor
DIS
VVT-i
Injector
VVTL-i*2 VVTL-i*2
VVTL Oil Switch*2
AIR
Knock Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Heated Oxygen Sensor Bank 1, Sensor 1
Heated Oxygen Sensor Bank 1, Sensor 2
169EG31
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
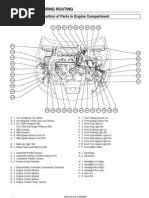
4. Layout of Main Components
*1: Only for the Automatic Transaxle Model *2: Only for the 2ZZ-GE Engine Model Power Steering Oil Heated Oxygen Sensor Pressure Switch (Bank 1, Sensor 2) Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) Camshaft Position Sensor
Data Link Connector 3 Charcoal Canister VSV for Pressure Switching Valve
Ignition Coil with Igniter Injector
Oil Control Valve Variable Valve Timing
Crankshaft Position Sensor
ECM
Vapor Pressure Sensor
Knock Sensor VSV (for EVAP)
VSV (for Canister Closed Valve)
VVTL Oil Switch*2 Park/Neutral Position Switch*1 Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor Throttle Position Sensor Oil Control Valve Variable Valve *2 Timing and Lift
VSV Intake Air Flow Control
Mass Air Flow Meter Built-in Intake Air Temp. Sensor
IAC Valve
169EG32
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
5. Main Components of Engine Control System
General The main components of the 1ZZ-FE and 2ZZ-GE engines control system are as follows: Components Mass Air Flow Meter Crankshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Camshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Throttle Position Sensor Knock Sensor Oxygen Sensor Injector IAC Valve *1: Only for the 1ZZ-FE Engine Model *2: Only for the 2ZZ-GE Engine Model ECM The ECM is installed in the ECM box in the engine compartment. As result, the wiring harness has been shorted, thus realizing weight reduction. Outline Hot-Wire Type Pick-Up Coil Type (36-2) Pick-Up Coil Type (3) Linear Type Built-In Piezoelectric Element Type Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 12-Hole Type*1, 4-Hole Type*2 Rotary Solenoid Type (1-Coil Type) Quantity 1 1 1 1 1 2 4 1
ECM
169EG32
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
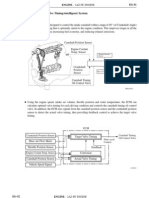
6. Intake Air Flow Control
The intake air duct is divided into two areas, and a variable intake valve and an actuator have been provided in one of the areas. When the engine is operating in the low-to mid-speed range, this control operates the variable intake valve to close one side of the intake air duct. When the engine is operating in the high-speed range, it turns OFF the variable intake valve, allowing both sides of the intake air duct to effect the intake of air. Accordingly, the level of engine noise has been reduced without using an intake resonator. Throttle Body ECM
Air Intake Chamber Check Valve Vacuum Tank Actuator Variable Intake Valve
VSV
Mass Air Flow Meter
Intake Air
169EG34
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
7. VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) System
General This system controls the intake camshaft valve timing so as to obtain balance between the engine output, fuel consumption and emission control performance. The actual intake side valve timing is feed back by means of the camshaft position sensor for constant control to the target valve timing.
Camshaft Position Sensor
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Throttle Position Sensor
ECM
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing)
Mass Air Flow Meter
Crankshaft Position Sensor
169EG35
ECM Crankshaft Position Sensor Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Sensor
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing)
Target Valve Timing Feed back
Correction Actual Valve Timing
Duty Control
Camshaft Position Sensor
157EG23
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
Construction 1) VVT-i Controller This controller consists of the housing driven from the timing chain and the vane coupled with the intake camshaft. The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake camshaft causes rotation in the VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing continuously. When the engine is stopped, the intake camshaft will be in the most retarded state to ensure startability. When hydraulic pressure is not applied to the VVT-i controller immediately after the engine has been started, the lock up pin locks the movement of the VVT-i controller to prevent a knocking noise. Lock Pin Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Intake Camshaft
Housing Oil Pressure At a Stop In Operation Lock Pin
169EG36
2) Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing) The oil control valve (variable valve timing) controls the spool valve position in accordance with the duty cantrol from the ECM thus allocating the hydraulic pressure that is applied to the VVT-i controller to the advance and the retard side. When the engine is stopped, the oil control valve (variable valve timing) is in the most retarded state. To VVT-i To VVT-i Controller Controller (Advance Side) (Retard Side) Sleeve Spool Valve
Connector
Drain Drain Spring Oil Pressure
Coil
Plunger
165EG34
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
Operation D The oil control valve (variable valve timing) selects the path to the VVT-i controller according to the advance, retard or hold signal from the ECM. The VVT-i controller rotates the intake camshaft in the timing advance or retard position or holds it according to the position where the oil pressure is applied. Operation Oil Control Valve Drive Signal Advance Signal Vane VVT-i Controller Housing ECM When the oil control valve (variable valve timing) is positioned as illustrated at left by the advance signal from the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing advance side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft in the timing advance direction.
157EG35
Description
Advance
Rotating Direction
Duty Ratio Oil Pressure
169EG37
Retard Signal When the oil control valve (variable valve timing) is positioned as illustrated at left by the retard signal from the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing retard side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft in the timing retard direction.
157EG36
Retard
Rotating Direction
ECM
Duty Ratio Oil Pressure
169EG38
Hold Signal
ECM
Oil Pressure
Duty Ratio
169EG39
157EG37
The ECM calculates the target timing angle according to the traveling state to perform control as described above. After setting at the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the oil control valve (variable valve timing) in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes. This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out when it is unnecessary.
Hold
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
D In proportion to the engine speed, intake air volume, throttle position and water temperature, the ECM calculates an optimal valve timing under each driving condition and control the oil control valve (variable valve timing). In addition, ECM uses signal from the camshaft position sensor and the crankshaft position sensor to detect the actual valve timing, thus performing feed back control to achieve the target valve timing.
"
Operation During Various Driving Conditions (Conceptual Diagram) A Full Load Performance
Range 4 Engine Load
Range 5
Range 3
Range 1, 2
162EG46
Engine Speed Operation state Range During idling 1 EX At light load 2 Valve timing TDC IN
Latest timing
Objective Minimizing overlap to reduce blow back to the intake side IN
Effect Stabilized idling rpm Better fuel economy Ensured engine stability Better fuel economy Improved emission control Improved torque in low to medium speed range Improved output Stabilized fast idle rpm Better fuel economy Improved startability
EX
Decreasing overlap to eliminate To retard side blow back to the intake side IN Increasing overlap to increase internal EGR for pumping loss elimination
At medium load
EX
To advance side
In low to medium speed range with heavy load In high speed range with heavy load
IN 4 EX
To advance side
Advancing the intake valve close timing for volumetric efficiency improvement BDC
EX
At low temperatures
EX
Retarding the intake valve close timing for volumetric efficiency To retard side improvement Minimizing overlap to prevent blow back to the intake side for IN reduction of fuel increase at low temperatures, and stabilizing the idling rpm for Latest timing decreasing fast idle rotation IN IN Minimizing overlap to minimize blow back to the Latest timing intake side
Upon starting/ stopping the engine
EX
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
8. VVTL-i (Variable Valve Timing and Lift-intelligent) system (2ZZ-GE Engine)
General Based on the VVT-i system, the VVTL-i system has adopted a cam changeover mechanism that varies the amount of lift of the intake and exhaust valves while the engine is operating at high speeds. In addition to achieving higher engine speeds and higher outputs, this system enables the valve timing to be optimally set, resulting in improved fuel economy. When the engine is operating in the low-to mid-speed range, the low-and medium-speed cams of the camshafts operate to move the two valves via the rocker arms. Then, when the engine is operating in the highspeed range, the signals from the sensors cause the ECM to change the hydraulic passage of the oil control valve (for variable valve timing and lift), thus changing to the operation of the high-speed cams. Thus, the lift of the intake and exhaust valves increases, allowing the introduction of a greater volume of air-fuel mixture, and the discharge of a greater volume of exhaust gases. As a result, the engine operates at higher speeds and higher outputs. The construction and the operation of the valve timing control are basically the same as in the VVT-i system.
Camshaft Position Sensor
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing and Lift)
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Throttle Position Sensor
ECM
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing)
Mass Air Flow Meter
Camshaft Position Sensor
169EG40
ECM
Low and Medium Lift or High Lift
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing and Lift)
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Sensor
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Target Valve Timing Feed back
Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing)
Duty Control Correction Actual Valve Timing
169EG41
Camshaft Position Sensor
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
Construction and Operation 1) Cam Changeover Mechanism (Rocker Arm Type) a. Construction D A rocker arm type cam changeover mechanism has been adopted. The main components of the rocker arm type are the rocker arm, rocker arm pad, rocker arm pin, and the rocker shaft. This mechanism is provided for both the intake and exhaust camshafts, with each connected to its respective rocker arm shaft. D Both the intake and exhaust camshafts contain low-and medium-speed cams and high-speed cams. Low and Medium Speed Cam Exhaust Camshaft Intake Camshaft
169EG14
High Speed Cam
Needle Roller (Integrated with Rocker Arm) Rocker Arm Pad Rocker Arm Rocker Shaft
High Speed Cam
Low and Medium Speed Cam
Rocker Arm Pad Adjusting Shim
A Rocker Arm Pin
Adjusting Shims Rocker Arm Pin A of View
169EG15
Valve
169EG16
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
b. Operation D When the engine coolant temperature is higher than 60_C and the engine speed is higher than 6000 rpm, this system changes the operation of the low-and medium-speed cams on the camshafts to the high-speed cams. When the engine is operating in the low-to mid-speed range (below 6000 rpm), the low-and mediumspeed cam pushes the needle roller of the rocker arm down to operate the two valves. At this time, the high-speed cam is also pushing down on the rocker arm pad, but because the rocker arm pad moves freely, this movement does not cause the rocker arm and the valves to move. Thereafter, when the engine reaches a high speed (over 6000 rpm), the hydraulic pressure pushes the rocker arm pin out to lock the bottom of the rocker arm pad. Because the high-speed cam has a greater cam lift than the lowand medium-speed cam, this time, the high-speed cam operates the two valves via the rocker arm pad and the rocker arm.
"
Low and Medium Speed A High Speed Cam Low and Medium Cam High Speed Cam
Needle Roller
Low and Medium Speed Cam
Rocker Arm Pad
Rocker Arm Pin Moves Freely A of View
169EG42 169EG43
"
High Speed A
Rocker Arm Pad Hydraulic Pressure A of View
169EG44 169EG45
Locked State
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
2) Oil Control Valve (Variable Valve Timing and Lift) The oil control valve (for the variable valve timing and lift) controls the spool valve position in accordance with the duty control from the ECM, thus allocating the hydraulic pressure that is applied to the high-speed cam side of the cam changeover mechanism. Cam Changeover Mechanism (Rocker Arm Type) Sleeve Spool Valve Connector
Spring 3) Oil Pressure Control
Drain Oil Pressure
Coil
Plunger
169EG46
When the engine is operating in the low-to mid-speed range, the oil control valve opens on the drain side so that the oil pressure will not be applied to the cam changeover mechanism. Then, when the engine reaches a high speed, the oil control valve closes on the drain side in order to apply the oil pressure to the high-speed cam of the cam changeover mechanism.
"
Low and Medium Speed A
LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH
ECM
Rocker Shafts Oil Control Valve OFF Drain
169EG47
OCV
HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW
Oil Pressure Cam Changeover Mechanism
"
High Speed A
LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH
ECM
OCV
HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW HIGH LOW
Oil Control Valve ON
Oil Pressure
169EG48
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
9. Fuel Pump Control
A fuel cut control has been adopted to stop the fuel pump when the SRS airbag is deployed, thus helping reduce fuel leakage. In this system, the ECM detects the airbag deployment signal from the airbag sensor assembly and turns OFF the circuit opening relay. After the fuel cut control has been activated, turning the ignition switch from OFF to ON cancels the fuel cut control, thus engine can be restarted. Front Airbag Sensor (RH and LH) Side Airbag Sensor (RH and LH)
Airbag Sensor Assembly
ECM
Circuit Opening Relay
Fuel Pump Motor
169EG28
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE AND 2ZZ-GE ENGINES
10. Evaporative Emission Control System
The method for detecting evaporative emission leaks has been changed from the previous internal pressure monitor type to the vacuum type. The vacuum type forcefully introduces the purge vacuum into the entire system and a leak is detected by monitoring the transitions in pressure. The changes associated with this system are as follows: D A VSV for canister closed valve has been added to the fresh air introduction line. D The 3-way VSV for vapor pressure sensor has been discontinued, and a VSV for pressure switching valve has been added. D The installed position of the vapor pressure sensor has been changed from the charcoal canister to the fuel tank in order to enhance the precision of the vapor pressure sensor. D The fresh air valve characteristics of the charcoal canister have been changed. D DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) have been added. For details on the DTCs, refer to the 00 CELICA Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM744U). VSV (for Pressure Switching Valve)
Vapor Pressure Sensor
Chacoal Canister
VSV (for Canister Closed Valve)
VSV (for EVAP) Fuel Tank Purge Line Fresh Air Line Drain Fresh Air Valve
170EG08
You might also like
- Control Engine 1kd FTV and 2kd FTDDocument41 pagesControl Engine 1kd FTV and 2kd FTDMuxumad Cabdulahi0% (1)
- Engine Control Celica 2000Document12 pagesEngine Control Celica 2000Giovanni Morales100% (2)
- Ta1248 PDFDocument38 pagesTa1248 PDFbad_boyz1989No ratings yet
- 1kr Fe Starting Starting MotorDocument320 pages1kr Fe Starting Starting MotorTalleban Tal0% (1)
- Toyota 1NZ-FE Wiring DiagramDocument6 pagesToyota 1NZ-FE Wiring DiagramTomy100% (1)
- 2004-2005 Honda Accord Wire Color Code GuideDocument9 pages2004-2005 Honda Accord Wire Color Code GuideYen N Chia100% (2)
- 2zz Engine ControlDocument3 pages2zz Engine ControlIshtiaq Arain100% (1)
- Toyota 1AZ-FSE Engine Repair Manual (RM1019E) - PDFs Free OnlineDocument5 pagesToyota 1AZ-FSE Engine Repair Manual (RM1019E) - PDFs Free OnlineMark Anthony Fletcher100% (1)
- 2zz Ge Electrical Wiring Routing PDFDocument8 pages2zz Ge Electrical Wiring Routing PDFnazar750100% (1)
- d2fee44ce3373b7c092a008235dbd2f5Document153 pagesd2fee44ce3373b7c092a008235dbd2f5Ovvc100% (2)
- Engine Control (1KR-FE) ECS-1KR PDFDocument1 pageEngine Control (1KR-FE) ECS-1KR PDFMuhammad Abbas Khan Niazi100% (1)
- Daihatsu EJ-DE Ignition SystemDocument2 pagesDaihatsu EJ-DE Ignition SystemJohnny VantherNo ratings yet
- 3grfse 1pdf PDFDocument42 pages3grfse 1pdf PDFzerospace100% (4)
- Toytoa Wire DiagramDocument8 pagesToytoa Wire Diagramspybot1331100% (1)
- 1NZ Fe PDFDocument4 pages1NZ Fe PDFVinh PhạmNo ratings yet
- 1kr Fe ChargingDocument92 pages1kr Fe Chargingfguij33% (3)
- 2uz-Fe SfiDocument84 pages2uz-Fe SfiAe Manual100% (1)
- Mitsubishi Galant Owners Manual 2001: Read/DownloadDocument2 pagesMitsubishi Galant Owners Manual 2001: Read/DownloadShannanAdams33% (3)
- 2uz Ecm 2006 PDFDocument10 pages2uz Ecm 2006 PDFbob loblaw100% (2)
- Ignition PDFDocument17 pagesIgnition PDFtavi2meNo ratings yet
- 2ZZ-GE Engine DescriptionDocument9 pages2ZZ-GE Engine DescriptionJordan DerrickNo ratings yet
- 2jzgte Uk Spec Ecu PinoutDocument2 pages2jzgte Uk Spec Ecu PinoutWilliamNo ratings yet
- AE101 4AGE 20 Valve Pins 2019Document5 pagesAE101 4AGE 20 Valve Pins 2019jorgeNo ratings yet
- M2000 J1-26 Pin Connector Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesM2000 J1-26 Pin Connector Wiring DiagramRoland AchaiNo ratings yet
- Multiplex-Diagnosis MPX Signal Bean and Avc LanDocument19 pagesMultiplex-Diagnosis MPX Signal Bean and Avc LanMario Alberto Abarca RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2ZZGE Engine - Part of ManualDocument46 pages2ZZGE Engine - Part of ManualDavide Faelli100% (2)
- 2JZ VvtiDocument36 pages2JZ VvtiTeerajet Chumrunworakiat100% (2)
- 4afe O2sensor TestDocument3 pages4afe O2sensor Testkkg4782No ratings yet
- Daihatsu Sirion Model m300 Series Service Manual No9890 EngineDocument32 pagesDaihatsu Sirion Model m300 Series Service Manual No9890 EngineJakub TarasinNo ratings yet
- Engine 2JZ-GEDocument108 pagesEngine 2JZ-GEroy.cheong900% (1)
- Power Source Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Cruise Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE)Document1 pagePower Source Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Engine Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE) Cruise Control (2AZ-FSE, 1AZ-FSE)Alexander Neyra100% (1)
- System Wiring Diagrams 3sDocument45 pagesSystem Wiring Diagrams 3sAlfredo Medina50% (2)
- 1mz Ecu Wiring DiagramDocument7 pages1mz Ecu Wiring Diagram12volt bayNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Chassis EPS - MDPS-Power SteeringDocument99 pagesHyundai Chassis EPS - MDPS-Power SteeringDedi Suwasono100% (2)
- 031 - Engine - Igniter Circuit Malfunction (No. 1)Document6 pages031 - Engine - Igniter Circuit Malfunction (No. 1)Ayun AhmNo ratings yet
- General: Jengine Control SystemDocument29 pagesGeneral: Jengine Control SystemJuan EspinoNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diag 2nzDocument5 pagesWiring Diag 2nzEric Tsayim100% (1)
- Engine Immobiliser System OverviewDocument100 pagesEngine Immobiliser System OverviewMugiraneza100% (1)
- T1 Cam Trigger Instructions 1Document10 pagesT1 Cam Trigger Instructions 1Initial_BG100% (1)
- Brake - Control of Toyota Yaris 2007 US PDFDocument105 pagesBrake - Control of Toyota Yaris 2007 US PDFDavidTrevorPaul100% (2)
- 1jz-Gte Ecu Pinout & Wiring DiagramDocument43 pages1jz-Gte Ecu Pinout & Wiring DiagramJohn Bacsik80% (5)
- Toyota 4a Fe Engine Reference PDFDocument57 pagesToyota 4a Fe Engine Reference PDFeviton luisNo ratings yet
- Nissan Cefiro Wiring Ecu AirflowDocument60 pagesNissan Cefiro Wiring Ecu AirflowKen Eng100% (5)
- 2ZZ Engine DevelopmentDocument9 pages2ZZ Engine Developmentdavid_garlock100% (1)
- Apexi RSMDocument52 pagesApexi RSMAde Rachmat Pandapotan50% (2)
- Camshaft Position Sensor (1Az-Fe/1Az-Fse) : ReplacementDocument17 pagesCamshaft Position Sensor (1Az-Fe/1Az-Fse) : ReplacementMusat Catalin-Marian100% (5)
- Quick Start Guide for ECU TuningDocument27 pagesQuick Start Guide for ECU TuningAce SpadeNo ratings yet
- Optimize Fuel System PerformanceDocument14 pagesOptimize Fuel System Performanceservice_007100% (1)
- ENGINE — 1MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEMDocument11 pagesENGINE — 1MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEMJose Calle100% (1)
- Control Engine - 1kd-Ftv and 2kd-FtdDocument25 pagesControl Engine - 1kd-Ftv and 2kd-FtdEulicer Armengol93% (73)
- Engine Control System DiagramDocument8 pagesEngine Control System DiagramGowher QadriNo ratings yet
- Sfi SystemDocument96 pagesSfi SystemWawan SatiawanNo ratings yet
- VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) SystemDocument4 pagesVVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) SystemJorge Armando VelázquezNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFADocument24 pages4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFARusonegroNo ratings yet
- VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) System: GeneralDocument5 pagesVVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) System: GeneralsadiksnmNo ratings yet
- Engine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmDocument40 pagesEngine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmAlex RonNo ratings yet
- Hybrid 12Document22 pagesHybrid 12squishbug100% (1)
- 1nz Fe PinoutsDocument1 page1nz Fe PinoutsOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- 1nz Fe PinoutsDocument1 page1nz Fe PinoutsOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- 1nz Fe PinoutsDocument1 page1nz Fe PinoutsOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- 1nz Fe PinoutsDocument1 page1nz Fe PinoutsOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: ForewordDocument2 pagesWorkshop Manual: ForewordOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- A26: Air InletDocument4 pagesA26: Air InletOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Combustion by Means of Squish Pistons: Key Words: Gasoline Engine, Combustion, Knocking, PistonDocument10 pagesEnhancement of Combustion by Means of Squish Pistons: Key Words: Gasoline Engine, Combustion, Knocking, PistonOfi de MoNo ratings yet
- Electrical ConnectorsDocument5 pagesElectrical ConnectorsRodrigo SantibañezNo ratings yet
- SKODA SSP 057 EngDocument44 pagesSKODA SSP 057 Engsorinenng100% (3)
- Engine and Vehicle Management Systems Question PaperDocument2 pagesEngine and Vehicle Management Systems Question PaperSUBRAMANIAN PMNo ratings yet
- Early Lucas Electronic Diesel Unit InjectorDocument5 pagesEarly Lucas Electronic Diesel Unit InjectorPablo ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Contents.: The MINI CoupéDocument47 pagesContents.: The MINI CoupéPaul Tan0% (1)
- D4GA - EURO4 For MightyDocument41 pagesD4GA - EURO4 For Mightykingtiger.bkNo ratings yet
- Cat 3612 Propulsion SpecDocument2 pagesCat 3612 Propulsion SpecFajrul Falah RosidNo ratings yet
- San Tirso 2019Document51 pagesSan Tirso 2019Harihara sakthi sudhan mechNo ratings yet
- KDE5000E Parts Listing BreakdownDocument35 pagesKDE5000E Parts Listing BreakdownMiguel ChaconNo ratings yet
- C6.6 Industrial Engine 66600001-Sistema de CombustibleDocument11 pagesC6.6 Industrial Engine 66600001-Sistema de CombustibleJonhNo ratings yet
- Vetus M4.55 OperationDocument100 pagesVetus M4.55 Operationchristian vergaray gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Flushing & Lub For Ball Valves 2987rev0Document76 pagesFlushing & Lub For Ball Valves 2987rev0Jorge GarciaNo ratings yet
- Wolf 250 PDFDocument76 pagesWolf 250 PDFryan hernandesNo ratings yet
- Bosch Automotive Filters Protect Your EngineDocument29 pagesBosch Automotive Filters Protect Your EngineJayesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Honda PgmfiDocument14 pagesHonda Pgmfivivek0630100% (1)
- Catalogo C12, C13, C15,3406e Año 2021Document36 pagesCatalogo C12, C13, C15,3406e Año 2021Alexis SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1GD - 2GD Engine Mechanical PDFDocument326 pages1GD - 2GD Engine Mechanical PDFCarlos Omar Zarate Yataco95% (57)
- Catalog Part Man D2842 Le410Document192 pagesCatalog Part Man D2842 Le410Puang Dudi86% (7)
- Diagnostic Manual DI3200 BSIIIDocument41 pagesDiagnostic Manual DI3200 BSIIIVicky100% (2)
- Diesel Locomotive SystemsDocument19 pagesDiesel Locomotive SystemsManohara BabuNo ratings yet
- Dual Fuel Bike Project ReportDocument23 pagesDual Fuel Bike Project ReportTanviNo ratings yet
- Pinout Corsa Tornado MerivaDocument9 pagesPinout Corsa Tornado MerivaGerardo Cessa67% (3)
- Citroen Xsara I - Wiring DiagramDocument20 pagesCitroen Xsara I - Wiring DiagramDavid VasNo ratings yet
- Engine: Section 1Document13 pagesEngine: Section 1LUIS ARCENo ratings yet
- Automotive ComponentsDocument12 pagesAutomotive ComponentsfightingfalconNo ratings yet
- 3126B Industrial Engine Electrical System: ECM AMP ConnectorsDocument2 pages3126B Industrial Engine Electrical System: ECM AMP Connectorsedcar100% (1)
- MBN C-15Document2 pagesMBN C-15cristian picado100% (1)
- Yamaha 200 - Catalogo - D - Partes - F200bet 2014 1N6S1-200S1Document96 pagesYamaha 200 - Catalogo - D - Partes - F200bet 2014 1N6S1-200S1Esteban Elias Marquez EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Filters Catalogue 2018 PDFDocument492 pagesFilters Catalogue 2018 PDFHaytham Ammer MushtahaNo ratings yet
- Carrier Ct4 114 Ct4 134 Diesel Engine Service Parts ListDocument7 pagesCarrier Ct4 114 Ct4 134 Diesel Engine Service Parts Listkenneth98% (44)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Across the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsFrom EverandAcross the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsNo ratings yet
- Allison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyFrom EverandAllison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ASE A1 Engine Repair Study Guide: Complete Review & Test Prep For The ASE A1 Engine Repair Exam: With Three Full-Length Practice Tests & AnswersFrom EverandASE A1 Engine Repair Study Guide: Complete Review & Test Prep For The ASE A1 Engine Repair Exam: With Three Full-Length Practice Tests & AnswersNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveFrom EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)
- The RVer's Bible (Revised and Updated): Everything You Need to Know About Choosing, Using, and Enjoying Your RVFrom EverandThe RVer's Bible (Revised and Updated): Everything You Need to Know About Choosing, Using, and Enjoying Your RVRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How to Drive an Exotic Car and get PaidFrom EverandHow to Drive an Exotic Car and get PaidRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Making Toys, Revised Edition: Heirloom Cars & Trucks in WoodFrom EverandMaking Toys, Revised Edition: Heirloom Cars & Trucks in WoodRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Official CDL Study Guide: Commercial Driver’s License Guide: Exam Prep, Practice Test Questions, and Beginner Friendly Training for Classes A, B, & C.From EverandOfficial CDL Study Guide: Commercial Driver’s License Guide: Exam Prep, Practice Test Questions, and Beginner Friendly Training for Classes A, B, & C.No ratings yet
- 700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeFrom Everand700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 1)From EverandAutomotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 1)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- How to Design and Install In-Car Entertainment SystemsFrom EverandHow to Design and Install In-Car Entertainment SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LS Swaps: How to Swap GM LS Engines into Almost AnythingFrom EverandLS Swaps: How to Swap GM LS Engines into Almost AnythingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadFrom EverandWhy We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Construction Vehicles to Crochet: A Dozen Chunky Trucks and Mechanical Marvels Straight from the Building SiteFrom EverandConstruction Vehicles to Crochet: A Dozen Chunky Trucks and Mechanical Marvels Straight from the Building SiteRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How to Design, Build & Equip Your Automotive Workshop on a BudgetFrom EverandHow to Design, Build & Equip Your Automotive Workshop on a BudgetRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Modern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingFrom EverandModern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)