Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 1
Uploaded by
Nguyễn Quốc ThúcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 1
Uploaded by
Nguyễn Quốc ThúcCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS 1, CHAPTER 1 ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 1. A jet lands on an aircraft carrier at 63 m/s. (a) What is its acceleration if it stops in 2.
0 s? (b) What is the displacement of the plane while it is stopping? ANSWER: (a) -31 m/s2 (b) 63 m 2. A person walks first at a constant speed of 5.00 m/s along a straight line from point A to point B and then back along the line from B to A at a constant speed of 3.00 m/s. What are (a) her average speed over the entire trip and (b) her average velocity over the entire trip? ANSWER: (a) 3.75 m/s (b) 0 3. A 50.0-g superball traveling at 25.0 m/s bounces off a brick wall and rebounds at 22.0 m/s. A high-speed camera records this event. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 3.50 ms, what is the magnitude of the average acceleration of the ball during this time interval? ANSWER: 1.34 104 m/s2 4. A particle moves along the x axis according to the equation x = 2.00 + 3.00t t 2 where x is in meters and t is in seconds. At t = 3.00 s, find (a) the position of the particle, (b) its velocity, and (c) its acceleration. ANSWER: (a) 2.00 m (b) - 3.00 m/s (c) - 2.00 m/s2 5. A particle moves along the x axis. Its position is given by the equation x = 2.00 + 3.00t t 2 with x in meters and t in seconds. Determine (a) its position at the instant it changes direction and (b) its velocity when it returns to the position it had at t = 0. ANSWER: (a) 2.56 m (b) -3.00 m/s 6. A jet plane lands with a speed of 100 m/s and can accelerate at a maximum rate of -5.00 m/s2 as it comes to rest. (a) From the instant the plane touches the runway, what is the minimum time it needs before it can come to rest? (b) Can this plane land at a small tropical island airport where the runway is 0.800 km long? ANSWER: (a) 20.0 s (b) no 7. A student throws a set of keys vertically upward to her sister, who is in a window 4.00 m above. The keys are caught 1.50 s later by the sister. (a) With what initial velocity were the keys thrown? (b) What was the velocity of the keys just before they were caught? ANSWER: (a) 10.0 m/s up (b) 4.68 m/s down 8. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground with an initial speed of 15.0 m/s. (a) How long does it take the ball to reach its maximum altitude? (b) What is its maximum altitude? (c) Determine the velocity and acceleration of the ball at t = 2.00 s. ANSWER: (a) 1.53 s (b) 11.5 m (c) -4.60 m/s, -9.80 m/s2 9. At t = 0, a particle moving in the xy plane with constant acceleration has a velocity of r r r vi = 3.00i 2.00 j m / s when it is at the origin. At t = 3.00 s, the particles velocity is r r r v = 9.00i + 7.00 j m / s . Find (a) the acceleration of the particle and (b) its coordinates at any time t . r r r r ANSWER: (a) 2.00i + 3.00 j m / s 2 (b) (3.00t + t 2 )i + (1.50t 2 2.00t ) j m
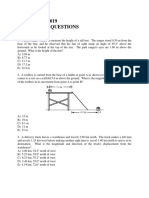
10. An artillery shell is fired with an initial velocity of 300 m/s at 55.0 above the horizontal. It explodes on a mountainside 42.0 s after firing. What are the x and y coordinates of the shell where it explodes, relative to its firing point? ANSWER: x = 7.23 km; y = 1.68 km 11. A projectile is fired in such a way that its horizontal range is equal to three times its maximum height. What is the angle of projection? Give your answer to three significant figures. ANSWER: 53.1 12. A cannon with a muzzle speed of 1 000 m/s is used to start an avalanche on a mountain slope. The target is 2 000 m from the cannon horizontally and 800 m above the cannon. At what angle, above the horizontal, should the cannon be fired? ANSWER: 22.4 or 89.4 13. A placekicker must kick a football from a point 36.0 m from the goal, and hopes the ball will clear the crossbar, which is 3.05 m high. When kicked, the ball leaves the ground with a speed of 20.0 m/s at an angle of 53.0 to the horizontal. (a) By how much does the ball clear or fall short of clearing the crossbar? (b) Does the ball approach the crossbar while still rising or while falling? ANSWER: (a) The ball clears by 0.889 m (b) while descending 14. A tire 0.500 m in radius rotates at a constant rate of 200 rev/min. Find the speed and acceleration of a small stone lodged in the tread of the tire (on its outer edge). (Hint: In one revolution, the stone travels a distance equal to the circumference of its path, 2r.) ANSWER: 10.5 m/s; 219 m/s2 15. A train slows down as it rounds a sharp horizontal curve, slowing from 90.0 km/h to 50.0 km/h in the 15.0 s that it takes to round the curve. The radius of the curve is 150 m. Compute the acceleration at the moment the train speed reaches 50.0 km/h. Assume that the train slows down at a uniform rate during the 15.0-s interval. ANSWER: 1.48 m/s2 inward at 29.9 behind the radius 16. A bomber is flying horizontally over level terrain, with a speed of 275 m/s relative to the ground, at an altitude of 3 000 m. Neglect the effects of air resistance. (a) How far will a bomb travel horizontally between its release from the plane and its impact on the ground? (b) If the plane maintains its original course and speed, where will it be when the bomb hits the ground? ANSWER: (a) 6.80 km (b) 3.00 km vertically above the impact point 17. A river has a steady speed of 0.500 m/s. A student swims upstream a distance of 1.00 km and swims back to the starting point. If the student can swim at a speed of 1.20 m/s in still water, how long does the trip take? Compare this with the time the trip would take if the water were still. ANSWER: 2.02 103 s; 21.0% longer 18. The pilot of an airplane notes that the compass indicates a heading due west. The airplanes speed relative to the air is 150 km/h. If there is a wind of 30.0 km/h toward the north, find the velocity of the airplane relative to the ground. ANSWER: 153 km/h at 11.3 north of west
You might also like
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Nguyễn KhôiNo ratings yet
- Physic 1-Homework Chapter 1Document2 pagesPhysic 1-Homework Chapter 1Dương Ngọc ThếNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsDocument6 pagesTutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsSamson ManyanyeNo ratings yet
- 1D Worksheet PDFDocument2 pages1D Worksheet PDFGenesis ValerioNo ratings yet
- College PhysicsDocument23 pagesCollege PhysicsDiana Lync SapurasNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsBOSS BOSS100% (1)
- CH 04Document3 pagesCH 04Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Chaptr 3Document11 pagesChaptr 3Shashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Physics Problems Nov. 5Document5 pagesPhysics Problems Nov. 5Kenneth BailadorNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document3 pagesCH 02Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 5 AnswersJose Popoff100% (1)
- Ch03 PDFDocument8 pagesCh03 PDFElizabeth WrightNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review ProblemsDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Review ProblemsIrina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Physics QuizDocument8 pagesPhysics QuizUzma RaufNo ratings yet
- Choose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each QuestionsDocument12 pagesChoose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each QuestionsJerick MadrileñoNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreDocument5 pagesExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - KinematicsDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 - KinematicsDanny MutamboNo ratings yet
- 2 - Quiz - Free Fall ProjectileDocument2 pages2 - Quiz - Free Fall ProjectileMiya GomezNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document9 pagesSheet 1Tony AtefNo ratings yet
- Ch02test 1DMotionDocument3 pagesCh02test 1DMotionLulun LunkimNo ratings yet
- 10-1-12 Projectile Motion Practice Problems APBDocument14 pages10-1-12 Projectile Motion Practice Problems APBAngel MereteNo ratings yet
- AP Phys C Fall Final Web RevDocument12 pagesAP Phys C Fall Final Web RevNadhya FadlillahNo ratings yet
- Practice Projectiles 2Document4 pagesPractice Projectiles 2fatpelicanNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)Document6 pagesAIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)MOHAMMED ASIF100% (1)
- Homework Problems Chapter 3: Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionDocument4 pagesHomework Problems Chapter 3: Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionHamidNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument2 pagesDynamicsJosef EdrickNo ratings yet
- Physics 3 Probset 1 2nd 13-14Document2 pagesPhysics 3 Probset 1 2nd 13-14Aaron Paul AguasNo ratings yet
- 1d WorksheetDocument2 pages1d WorksheetJohnCarloTigue100% (1)
- Assignment Motion and ProjectileDocument2 pagesAssignment Motion and ProjectileVyom KapurNo ratings yet
- Revision MCQ - KinematicsDocument2 pagesRevision MCQ - Kinematicsgaya8404No ratings yet
- Physics Test STUDY QuestionDocument11 pagesPhysics Test STUDY QuestionFiedDinieNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Test OneDocument7 pagesPractice Problems Test OneOtieno MachariaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument19 pagesProjectile MotionJorge Rodríguez SedanoNo ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 2Document5 pagesCP S HW CH 2Steve Julius100% (1)
- Tut Test 2 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 2 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (2) DqwdqwdasdadxasxzaxaxaDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 (2) DqwdqwdasdadxasxzaxaxaAmeer AmefNo ratings yet
- Additional 3 Chapter 3 PDFDocument16 pagesAdditional 3 Chapter 3 PDFnazreensofeaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document15 pagesChapter 03nourNo ratings yet
- 3 Rectilinear MotionDocument13 pages3 Rectilinear MotionMohamed Jameel100% (2)
- College Physics Quiz 2Document2 pagesCollege Physics Quiz 2jisoo rabbitNo ratings yet
- DS841UwP3CYH PDFDocument3 pagesDS841UwP3CYH PDFEugeo ozoidNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in DynamicsDocument6 pagesProblem Set in DynamicsEugene Embalzado Jr.No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics MCQDocument6 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQeafz111No ratings yet
- PHY1124 Midterm 2020 WinterDocument5 pagesPHY1124 Midterm 2020 WinterMostafa Khattab100% (2)
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocument4 pagesR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion WKSHT KeyDocument3 pagesProjectile Motion WKSHT KeyPATRICE LOIS RACHONo ratings yet
- FREE FALL AND PROJECTILEdsadDocument7 pagesFREE FALL AND PROJECTILEdsadDave BillonaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular MotionDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular Motionapi-3827354100% (4)
- PPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 2: 2 o R o SDocument5 pagesPPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 2: 2 o R o STAN XIN YINo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Es TG Module 2 Climate RevisedDocument23 pagesEs TG Module 2 Climate RevisedNikkieIrisAlbañoNovesNo ratings yet
- Full Scale AnalysisDocument43 pagesFull Scale Analysispaulogud6170No ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerLily CollinsNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation Lecture-PipingDocument34 pagesHydraulic Calculation Lecture-PipingFarzad Rezaei100% (2)
- Study Guide 10thDocument3 pagesStudy Guide 10thIvan Cal VilNo ratings yet
- AmpereDocument28 pagesAmpereJaneth de JuanNo ratings yet
- GD&T Q BankDocument9 pagesGD&T Q Bankmaddy_scribd50% (2)
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2IntanLeeyanaNo ratings yet
- VSP Final ReportDocument53 pagesVSP Final ReportAnand GautamNo ratings yet
- Jan 07Document16 pagesJan 07Evelyn L-XingNo ratings yet
- Cat App 003 (E)Document4 pagesCat App 003 (E)Alexander NhuanNo ratings yet
- GATE Chemical Engineering 2003 PDFDocument12 pagesGATE Chemical Engineering 2003 PDFVenkatesh ChNo ratings yet
- HSAB TheoryDocument3 pagesHSAB Theorykaran113No ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionsDocument15 pagesHW3 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- Exp10 ESC Electron Specific ChargeDocument4 pagesExp10 ESC Electron Specific ChargeUtkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tds Disperbyk-163 enDocument2 pagesTds Disperbyk-163 enpekena_fer2059No ratings yet
- 2nd Half Book Ist Year PHYSICSDocument4 pages2nd Half Book Ist Year PHYSICSranaateeq100% (1)
- Surfaces: Open and Closed SurfacesDocument3 pagesSurfaces: Open and Closed SurfacesrodwellheadNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Basara Gnanasaraswathi Campus Kakatiya HillsDocument4 pagesBasara Gnanasaraswathi Campus Kakatiya HillsNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS Medical-2019 (XII Passed) Test-6 (Code-E & F) (24!02!2019)Document32 pagesSolutions AIATS Medical-2019 (XII Passed) Test-6 (Code-E & F) (24!02!2019)Uday Smith100% (1)
- Chem ch3Document20 pagesChem ch3ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 16 FY13CE Mathematics QPDocument14 pages16 FY13CE Mathematics QPyog deviNo ratings yet
- Mri Physics en Rev1.3Document76 pagesMri Physics en Rev1.3Arbjan Rusi100% (3)
- X-Ray Methods For Analysis of MaterialsDocument97 pagesX-Ray Methods For Analysis of MaterialsOli.TaltyNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pegylated Polypropyleneimine (Ppi) Dendrimer Loaded Prednisolone For Antileukemic ActivityDocument11 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Pegylated Polypropyleneimine (Ppi) Dendrimer Loaded Prednisolone For Antileukemic ActivityRAPPORTS DE PHARMACIENo ratings yet
- ECE795 Math Practice PDFDocument12 pagesECE795 Math Practice PDFadiazNo ratings yet
- Elemental BalanceDocument15 pagesElemental BalanceAlanChevalNo ratings yet
- Proctor Standard Soil CompactionDocument11 pagesProctor Standard Soil CompactionAmin Saufi100% (3)
- 09 Science Notes Ch10 GravitationDocument4 pages09 Science Notes Ch10 Gravitationdvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet