Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A1. Examples: Belt Drives Examples and Worksheet
Uploaded by
Ab_AlizadehOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A1. Examples: Belt Drives Examples and Worksheet
Uploaded by
Ab_AlizadehCopyright:
Available Formats
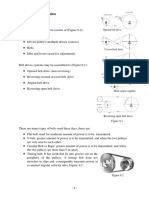
BELT DRIVES EXAMPLES AND WORKSHEET (Mechanical Design, P. Childs, p.
105)
A.
BELT DRIVES (EXAMPLES WORKSHEET)
A1.
EXAMPLES
1. Select a wedge belt and determine the pulley diameters for a reciprocating compressor driven by a 28 kW two-cylinder diesel engine. The engine speed is 1500 rpm and the compressor speed is 950 rpm. The proposed distance between the engine and compressor shaft centres is approximately 1.5 m. The system is expected to be used for less than 10 hours per day. 2. A fan is belt driven by an electric motor running at 1500rpm. The pulley diameters for the fan and motor are 500 mm and 355 mm respectively. A flat belt has been selected with a width of 100 mm, thickness of 3.5 mm, coefficient of friction of 0.8, density of 1100kg/m3 and permissible stress of 11MN/m2 (11MPa). The centre distance is 1500 mm. Determine the power capacity of the belt.
A2.
WORKSHEET
1. A four-cylinder diesel engine running at 2000 rpm, developing 45 kW, is being used to drive a medium duty agricultural machine running at 890 rpm. The distance between the pulley centres is approximately 80 cm. The expected use is less than 10 hours per day. Using a wedge belt drive, select suitable pulley diameters and determine the type and number of belts required. 2. A wedge belt drive is required to transmit 18.5 kW from an electric motor running at 1455 rpm, to a uniformly loaded conveyor running at 400 rpm. The desired centre distance is 1.4 m and expected use is 15 hours a day. Select a suitable belt, or belts, and determine the pulley diameters. 3. A wedge belt drive is required for an electric motor driven crusher. The electric motor speed and power are 720 rpm and 11 kW respectively. The desired crusher speed is 140 rpm. Limitations on space within the crushing machine restrict the use of the maximum pulley diameter to 90 cm and the pulley centre distance to less than 1 m. The device will be operated for approximately 12 hours a day. Select a suitable belt drive and pulley diameters for this application. 4. A flat belt is required to transmit 22 kW from a 250 mm diameter pulley running at 1450 rpm, to a 355 mm diameter pulley. The coefficient of friction can be taken as 0.7, the density of the belt is 1100kg/m3 and the maximum permissible stress is 7 MPa. The distance between the shaft centres is 1.8 m. The proposed belt is 3.5mm thick. Calculate the width required.
5. A flat belt drive is required for a surface grinder to transmit 5kW from a 100 mm diameter pulley running at 1500 rpm, to a 250 mm diameter pulley. The coefficient of friction can be taken as 0.75, the density of the belt as 1100kg/m and the maximum permissible stress as 9 MPa. The distance between the shaft centres is 0.6 m. The proposed belt is 3.5 mm thick. Determine the belt width required. 6. A flat belt drive is required for a piston pump. The pump is driven by a 37 kW electric motor, running at 1470 rpm, with a pulley of 250 mm diameter. The pump pulley is 700 mm in diameter. The coefficient of friction can be taken as 0.8, the density of the belt as 1100kg/m3 and the maximum permissible stress as 6 MPa. The distance between the shaft centres is 1.2m. The proposed belt is 2.9 mm thick. Determine the belt width required. 7. The application of an existing machine has changed such that the desired transmission power has increased to 120kW. The existing design consists of a driving pulley running at 3000 rpm, with a pulley diameter of 200 mm and the driven pulley of 250 m diameter. The belt is 150 mm wide, 4.2 mm thick and has a maximum permissible stress of 6.6 MPa. The belt density and coefficient of friction are 1100kg/m3 and 0.75 respectively. The centre distance is 1.4 m. Is the belt drive suitable? 8. An extractor fan is belt driven by a 75 kW electric motor running at 2946 rpm. The pulley diameters on the fan drive and the motor drive are 300 and 200 mm respectively. The centre distance is approximately 1.4 m. Using a flat belt with a coefficient of friction of 0.8, density 1100kg/m3 and maximum permissible stress of 6 MPa, 4.3 mm thick, determine the belt width required.
CHAIN DRIVES EXAMPLES AND WORKSHEET (Mechanical Design, P. Childs, p.105) B. CHAIN DRIVES (EXAMPLES WORKSHEET)
B1.
EXAMPLES
1. A chain drive is required for a gear pump operating at 400 rpm, driven by a 5.5 kW electric motor running at 1440 rpm. The centre distance between the motor and pump shafts is approximately 470 mm.
B2.
WORKSHEET
1. Specify a suitable chain drive for a gear pump operating at 400 rpm, driven by a 18.5 kW electric motor running at 725 rpm. The centre distance between the motor and pump shafts is approximately 470 mm. 2. Specify a suitable chain drive for a packaging machine operating at 75 rpm, driven by a 2.2 kW electric motor running at 710 rpm. The maximum permissible centre distance between the motor and pump is 1 m. 3. Specify a suitable chain drive for a gear pump operating at 400 rpm, driven by a 30 kW electric motor running at 728 rpm. The centre distance between the motor and pump shafts is approximately 1 m. 4. Specify a suitable chain drive for a packaging machine operating at 75 rpm, driven by a 2.2 kW electric motor running at 710 rpm. The maximum permissible centre distance motor running at 2820 rpm. The centre distance between the motor and pump shafts is approximately 300 mm. 5. An agricultural application which runs for up to 16 hours per day requires a drive system to step down an 18.5 kW electric motor running at 725 rpm to 30 rpm. Determine a suitable drive system.
You might also like
- Belt Drive Module 1 ProblemsDocument3 pagesBelt Drive Module 1 ProblemsKerr GenebraldoNo ratings yet
- Design V-belt DrivesDocument1 pageDesign V-belt DrivesPraba Karan DNo ratings yet
- ME2352-DTS Question BankDocument8 pagesME2352-DTS Question BankNaresh015No ratings yet
- A. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsDocument3 pagesA. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsVijaya Prabhu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Belt Drives ExamplesDocument3 pagesBelt Drives ExamplesMuhd Afiq AzmirNo ratings yet
- Belt, Rope and Chain Drives Denition: M Arshad Zahangir ChowdhuryDocument12 pagesBelt, Rope and Chain Drives Denition: M Arshad Zahangir ChowdhuryMelindaNo ratings yet
- Unit-3.1.3-Gib and Cotter JointDocument28 pagesUnit-3.1.3-Gib and Cotter JointAsvath GuruNo ratings yet
- ME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsDocument16 pagesME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecturer - Belt DriveDocument38 pagesChapter 2 Lecturer - Belt DriveNadz ReenNo ratings yet
- Gears: Classification, profiles, advantagesDocument18 pagesGears: Classification, profiles, advantagesSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Gears - ClassificationDocument19 pagesModule 3 Gears - ClassificationBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingDocument11 pages5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingShayneBumatay0% (1)
- Introduction to Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Kinematics of MachinesEmmanuelRomaresNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Mechanism Design: Quick Return, Timing ChartsDocument6 pagesMechanism Design: Quick Return, Timing ChartsAsim AshrafNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet No 1 On Spur GearDocument3 pagesTutorial Sheet No 1 On Spur GearChirayuNo ratings yet
- Chain DrivesDocument14 pagesChain Drivesniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- MD ShaftDocument18 pagesMD Shaftiftikhar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneDocument4 pagesMechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneShuja MarwatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Coupling and ClutchesDocument40 pagesChapter 2-Coupling and Clutcheskibromgidey12No ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingsDocument11 pagesRolling Contact BearingsritNo ratings yet
- Ball BRG Chapeter-JBK DasDocument26 pagesBall BRG Chapeter-JBK DasNaresh Kini50% (2)
- Worm GearsDocument33 pagesWorm GearsRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- 4-SPEED GEAR BOXDocument17 pages4-SPEED GEAR BOXKhanna Dhinesh100% (1)
- Kom Unit 1Document5 pagesKom Unit 1M.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Belt Tension Steady State CalculationDocument1 pageBelt Tension Steady State CalculationMary Antoinette C. MadoloraNo ratings yet
- Design and Study of Helical Gears2Document24 pagesDesign and Study of Helical Gears2AmjathNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument5 pagesBrayton CycleDanang Wahdiat Aulia IshaqNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission System Unit IIIDocument57 pagesDesign of Transmission System Unit IIIRaj MohanNo ratings yet
- Helical GearsDocument12 pagesHelical Gearsgamini ranaweera100% (1)
- Stepped PulleyDocument4 pagesStepped PulleyKram YnarNo ratings yet
- Chain Drive Design Problems Mechanical Engineering Department Benha UniversityDocument1 pageChain Drive Design Problems Mechanical Engineering Department Benha UniversityAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Me405Document1 pageTutorial Questions Me405Blessed ZiyambeNo ratings yet
- Md-14 Belt and Chain DrivesDocument8 pagesMd-14 Belt and Chain DrivesRemartin MaglantayNo ratings yet
- CC2 Topic 6 Keys and Couplings - Lecture NoteDocument34 pagesCC2 Topic 6 Keys and Couplings - Lecture NoteChristian Breth BurgosNo ratings yet
- Machine Design IIDocument23 pagesMachine Design IIBinar Arum OktaviaNo ratings yet
- DTS Unit 5Document20 pagesDTS Unit 5Muthuvel MNo ratings yet
- Optimize Your Gear Drive Design with Proper Material SelectionDocument8 pagesOptimize Your Gear Drive Design with Proper Material SelectionLovely BalajiNo ratings yet
- Belt Drive Types Material Applications Advantages Disadvantages PPT 1Document19 pagesBelt Drive Types Material Applications Advantages Disadvantages PPT 1Sandesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Quiz 1Document17 pagesMachine Elements Quiz 1Quen CuestaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDocument65 pagesKinematics of Machinery NotesVenkatesh Rajamani100% (1)
- Unit VI DME I SpringsDocument69 pagesUnit VI DME I SpringsSachin DhavaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IDocument67 pagesChapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations For A Gear DriveDocument17 pagesDesign Considerations For A Gear Driveمحمدفیضان چوہدریNo ratings yet
- Belt Drives: Geometry Specification ConstructionDocument17 pagesBelt Drives: Geometry Specification ConstructionBalen Karim0% (1)
- Solved Examples For Spur Gear DesignDocument1 pageSolved Examples For Spur Gear Designpawan12340% (1)
- Belts and PulleysDocument17 pagesBelts and PulleysMelindaNo ratings yet
- Torsion Sample Problem 2Document9 pagesTorsion Sample Problem 2Richiel Pasilan LañohanNo ratings yet
- AUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONDocument16 pagesAUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONVinoliaEdwin100% (1)
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Document21 pagesJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Adib AzharNo ratings yet
- Draw The Stress - Strain Diagram For Mild Steel. Explain.: Unit - IDocument9 pagesDraw The Stress - Strain Diagram For Mild Steel. Explain.: Unit - IKomma Hema100% (1)
- Tensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous AlloyDocument7 pagesTensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Alloyrama100% (1)
- SOM - AssignmentsDocument15 pagesSOM - Assignmentssatish448100% (1)
- April 1997 MECHANICAL ENGINEER Licensure ExaminationDocument4 pagesApril 1997 MECHANICAL ENGINEER Licensure ExaminationMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission Systems Question Bank 1Document27 pagesDesign of Transmission Systems Question Bank 1shivesh rockesNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission Systems-Question BankDocument28 pagesDesign of Transmission Systems-Question BankAlfred Franklin V100% (1)
- MDlab FinalsDocument18 pagesMDlab FinalsNarry StrummerNo ratings yet
- ME6601 Transmission Design QuestionsDocument11 pagesME6601 Transmission Design QuestionsMURUGANNo ratings yet
- DTS Question BankDocument21 pagesDTS Question BankSam TirshathNo ratings yet
- 1-Inititive ReportDocument30 pages1-Inititive ReportAb_AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Using MATLAB to solve ODEsDocument2 pagesUsing MATLAB to solve ODEssmit189No ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations: Analytical and Numerical MethodsDocument136 pagesPartial Differential Equations: Analytical and Numerical MethodsMohamed Mounir FekriNo ratings yet
- Elastic Properties and Anisotropy of Elastic BehaviorDocument44 pagesElastic Properties and Anisotropy of Elastic Behaviorkhers_zalNo ratings yet
- Formation of BenzeneDocument39 pagesFormation of BenzenehfrizviNo ratings yet
- Hall Petch Relationship in Nanometer Size RangeDocument5 pagesHall Petch Relationship in Nanometer Size RangeAb_AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Copper Coated Carbon Nanotubes by DecompositionDocument5 pagesPreparation of Copper Coated Carbon Nanotubes by DecompositionAb_AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Critical Points and Properties in Structural AnalysisDocument10 pagesCritical Points and Properties in Structural AnalysisAb_AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Truss DeflectionDocument2 pagesTruss DeflectionAb_AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering: Unit Ii Part I - Fuel Systems Part Ii - Ci EnginesDocument103 pagesAutomobile Engineering: Unit Ii Part I - Fuel Systems Part Ii - Ci EnginesNikhilraj rudraNo ratings yet
- Steam Cycles PDFDocument18 pagesSteam Cycles PDFAmda AmdaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering Exam Reference Manual A Practical Study Guide Third EditionDocument45 pagesControl Systems Engineering Exam Reference Manual A Practical Study Guide Third EditionNaseer Hyden60% (5)
- Catalog Isuzu Elf Euro 2 NKR 55Document5 pagesCatalog Isuzu Elf Euro 2 NKR 55excelmin338No ratings yet
- L Series Position ControllerDocument2 pagesL Series Position ControllerKaiser Iqbal100% (1)
- Pirus 1 DTCDocument870 pagesPirus 1 DTCjahangir khan100% (1)
- Proposal Automatic Carwashing in PakistanDocument16 pagesProposal Automatic Carwashing in PakistanMuhammad Azhar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Solution To Aerody Mock Exam 2014 (HolyDocument23 pagesSolution To Aerody Mock Exam 2014 (HolyReem RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ME231 Solid Mechanics Spring 2023 SyllabusDocument3 pagesME231 Solid Mechanics Spring 2023 Syllabus김수민No ratings yet
- Failure Elimination Made Simple 1688417692Document10 pagesFailure Elimination Made Simple 1688417692samba fayeNo ratings yet
- BCM Manual PDFDocument19 pagesBCM Manual PDFSuthari AmbikaNo ratings yet
- Audi A4 Quattro 3.0 Liter 6-Cyl. 5V Fuel Injection & IgnitionDocument259 pagesAudi A4 Quattro 3.0 Liter 6-Cyl. 5V Fuel Injection & IgnitionNPNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument30 pagesIntroductionbhanuka2009No ratings yet
- Open Ended LAB: Name: Ayyan AhmadDocument7 pagesOpen Ended LAB: Name: Ayyan AhmadMaheenNo ratings yet
- QW 482Document2 pagesQW 482Ramu NallathambiNo ratings yet
- DADF-B1 K1 PC Ir400-330Document51 pagesDADF-B1 K1 PC Ir400-330Julio CésarNo ratings yet
- CURTIS Ks50 Series PARTSDocument89 pagesCURTIS Ks50 Series PARTSrobertNo ratings yet
- 00 Hvac CalcDocument52 pages00 Hvac CalcjosebolisNo ratings yet
- Blowdown Drum LNGDocument121 pagesBlowdown Drum LNGsswahyudi100% (1)
- Lifting Operation Plan ExampleDocument5 pagesLifting Operation Plan ExampleAhmad Sutrisna100% (1)
- Cool Pack DescriptionDocument4 pagesCool Pack DescriptionMayuri KothawadeNo ratings yet
- Cds Dino Vam 13.375in. 72lb-Ft p110 API Drift 12.191in. 87.5%Document1 pageCds Dino Vam 13.375in. 72lb-Ft p110 API Drift 12.191in. 87.5%secanggang.scgdNo ratings yet
- Motori Asicroni MonofaseDocument3 pagesMotori Asicroni MonofasegianlucaNo ratings yet
- Report: Pneumatic UTMDocument14 pagesReport: Pneumatic UTMadibah ismail50% (2)
- Brosur Katalog Valve Flange Fitting Elbow Reducer Tee JakartaDocument13 pagesBrosur Katalog Valve Flange Fitting Elbow Reducer Tee JakartaAlvindo Catur SentosaNo ratings yet
- 4.heater TreaterDocument53 pages4.heater TreaterMohamed Elabbasy100% (1)
- BIM ProfileDocument6 pagesBIM ProfilekurniaNo ratings yet
- Sumber: Smith. Introduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 6th EditionDocument6 pagesSumber: Smith. Introduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 6th EditionDhea AliviaNo ratings yet
- Al-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMDocument8 pagesAl-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMMarija MusaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic design and flight performance of RLV-TDDocument16 pagesAerodynamic design and flight performance of RLV-TDbalasubramanian.sNo ratings yet