Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Respiratory Failure
Uploaded by
Paolo Luis MontenegroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Respiratory Failure
Uploaded by
Paolo Luis MontenegroCopyright:
Available Formats
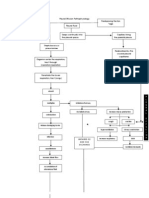
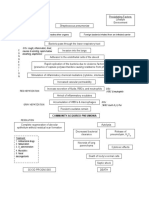
Acute Respiratory Failure is characterized by acute lung inflammation and
diffuse alveolocapillary injury with non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
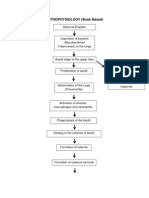
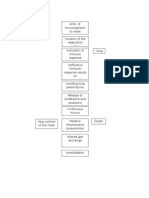
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
ALVEOLAR OR PULMONARY CAPILLARY WALL INJURY
Increased capillary permeability
Cell Damage
Fluid protein leaks into alveoli and interstitial tissue
PULMONARY EDEMA
DECREASED SURFACTANT PRODUCTION
Decreased compliance, labored inspiration
RESPIRATORY INSUFFIECIENCY
Decreased Oxygen Exchange Hypoxemia Decreased Lung volume Atelectasis
RESPIRATORY FAILURE
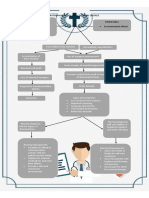
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT: Diagnostic Test ABG analysis CXR ECG Pulse oximetry CBC Serum electrolytes Pulmonary artery catheterization Treatment and drugs: Cautious oxygen therapy (nasal prongs or Venturi mask) If Respiratory Acidosis persist, Mechanical ventilation with an Edotracheal is attached or Tracheostomy Antibiotics Bronchodilators Corticosteroids If cor pulmonale and cardiac output decreased administer Inotropic agents, vasopresors, and diuretics may ordered
NURSING MANAGEMENT: Orient the patient to the treatment unit to prevent anxiety To reverse hypoxemia, administer oxygen as ordered Maintain patent airway Monitor BP, RR and PR Place patient in semi-fowlers position
You might also like
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument20 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeAngel Cauilan100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument29 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurePurnima ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- IX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesIX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsCandace AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- SLE Risk Factors and ComplicationsDocument5 pagesSLE Risk Factors and Complicationsjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Contributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumoniaDocument2 pagesContributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumoniabilliam123No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Patho PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology SARSDocument4 pagesPathophysiology SARSStephanie Joy Escala71% (7)
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy Case StudyDocument29 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathy Case Studydvalitz100% (2)
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural Effusionarvinian01100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Community Acquired Pneumoniajordan aguilar67% (3)
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument22 pagesAspiration PneumoniaAya AlamsjahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 pagesArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- Pathophysiology and Management of COPDDocument6 pagesPathophysiology and Management of COPDNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Munity Acquired Pneumonia PathoDocument1 pageMunity Acquired Pneumonia PathoJohanna Elaine Tandoc100% (1)
- BFCDocument8 pagesBFCIrene GunongNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument2 pagesLung CancerCarla Mae Guillermo Navarro50% (2)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyJoann67% (3)
- Pathophysiology ARDSDocument1 pagePathophysiology ARDSRoderick Agbuya100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument8 pagesAbruptio PlacentaNutz TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Document1 pagePathophysiology - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Jewel YapNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis Airborne InfectionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Tuberculosis Airborne InfectionRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Myesthenia GravisDocument3 pagesMyesthenia GravisJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- ARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyDocument3 pagesARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyJorie Roco100% (1)
- Asthma PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAsthma PathophysiologyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchial Asthma PathophysiologyElisa Kerr100% (2)
- Cap PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCap PathophysiologyNoriel Henricks Acuna100% (3)
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Status EpilepticusDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Status EpilepticusKysha Ruth SevillaNo ratings yet
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- PP - Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 pagePP - Community-Acquired Pneumonialpetallo100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Pleural Effusion Case StudyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Case Studyjanice ianNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisShirlyn100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentcrisolandNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimers DiseaseJaysellePuguonTabijeNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument24 pagesARDSMuhammad NurmanNo ratings yet
- Emed - Pulmonary EmergenciesDocument13 pagesEmed - Pulmonary EmergenciesPrincess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Emed - Pulmonary EmergenciesDocument13 pagesEmed - Pulmonary EmergenciesPrincess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument22 pagesRespiratory Failure: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementreynoldNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument43 pagesAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Pediatric Respiratory Failure: Signs and SymptomsDocument23 pagesPediatric Respiratory Failure: Signs and SymptomsAjp Ryuzaki CaesarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Moderator - Asso Prof DR Arun Kumar Presentor - DR Kannan GDocument39 pagesPulmonary Edema: Moderator - Asso Prof DR Arun Kumar Presentor - DR Kannan GGrace JasminNo ratings yet
- Acute RFDocument7 pagesAcute RFLoren SangalangNo ratings yet