Professional Documents
Culture Documents
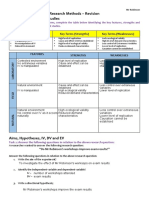
IB Psychology Option: Abnormal - Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Noor MohsinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IB Psychology Option: Abnormal - Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Noor MohsinCopyright:
Available Formats
Q. 1 normality and abnormality 1. Jahoda (1958) 6 normal characteristics a. Efficient self-perception b. Realistic self-esteem c. Control of behvaiour d.
d. True perception of world e. Sustain relationships f. Productivity Most people would be abnormal! Normality depends on culture and society! 2. Szasz (1962) some disorders are diseases, others only problems in living. Behaving strangely is not a symptom. 3. Rosenhan (1973) test reliability of diagnosis. 8 ppl gain admission to 12 dif. psychiatric hospitals, hearing voices. 7 submitted as schizophrenia. 7-52 days to get out. Normal person get faulty diagnosed. 4. Roenhan (1973) told hospital that 41 pseudo were coming, all were real patients. Only 19 suspected to be fake! Be mistaken for healthy or sick patients. Not possible to distinguish between normal and abnormal/ sane and insane in psychiatric hospitals. Lack of scientific evidence. Diagnosis of classification system are unreliable. Criticism once admitted, every behavior is seen as abnormal. What about powerlessness and depersonalization? (cuckoos nest!!).
Q. 2 validity and reliability DSM-IV-TR (1952) includes 5 axes in which the diagnose finding is carried out. Axis 1: Main Diagnose Axis 2: Development, personality disorder, perception and response to the world. Axis 3: medical status Physical problems are relevant for the mental disorder.
Axis 4: Social situation, unemployment, family situation etc. Axis 5: overall assessment of individuals functions. Reliability 1. Beck (1962) found that agreement between two psychiatrists on 153 diagnoses was only 54%!!!!! 2. Lipton and Simmons (1985) 131 patients in hospital, diagnosed them. Originally 89 diagnoses of schizophrenia only 16 got this now. Originally 15 mood disorders now 50! Being misdiagnosed cause mood disorder to develop. Validity 1. Rosenhan (1973) test reliability of diagnosis. 8 ppl gain admission to 12 dif. psychiatric hospitals, hearing voices. 7 submitted as schizophrenia. 7-52 days to get out. Normal person get faulty diagnosed. 2. Roenhan (1973) told hospital that 41 pseudo were coming, all were real patients. Only 19 suspected to be fake! Be mistaken for healthy or sick patients.
Q. 7 & 8 biomedical, individual and group approach to treatment of one disorder Biomedical biological factors associated with disease, drugs used to restore malfunction. Serotonin not available in synaptic gap depression. SSRI prevent reuptake. Effectiveness of drugs are limited unless used with other treatment.
1. Kirsch (1998) 2000 patients take Prozac (prevent reuptake of serotonin, increase it), only 25% more effective than placebos, same effect as other drugs. 2. Kirsch (2008) reviews 47 clinical trials on effectiveness of antidepressants. Medical treatment and placebo same effect. Depressed patients improve without medicines. 3. Bluementhal (1999) exercise and SSRI same effect on treatment in elderly ppl. 4. Elkin (1989) 280 patients, randomly assigned to drug therapy, ITP, CBT or other. Control group given placebo pill. 50% recovered in all groups, except 29% in placebo. No difference in effectiveness of CBT, ITP and drug, doesnt matter which treatment is given. Individual CBT - replace negative thoughts with positive to remove depression (Beck 60). Find positive ways to interpret life-events, do activities that used to reward. 1. Rush (1997) cognitive therapy treats patients with depression2. Elkin (1989) 280 patients, randomly assigned to drug therapy, ITP, CBT or other. Control group given placebo pill. 50% recovered in all groups, except 29% in placebo. No difference in effectiveness of CBT, ITP and drug, doesnt matter which treatment is given. 3. Riggs (2007) effectiveness of CBT with placebo or SSRI. 126 teenagers, 13-19 yrs, depressed and addicted to drugs. Treated for 4 months. 67% of CBT+placebo and 76% of CBT+SSRI. Treatment was almost as effective with placebo too, no difference. Group belonging, share and discuss with others. Meet others who have improved, be more optimistic about recovery. 1. McDermut (2000) effectiveness of group therapy. 48 studies examined 43 reduced depression signs, 9 no difference between group and IT, 8 more effective with CBT than group. 2. Hyun (2005) shelter for teenagers runaways. Two groups one with CBT and one without any therapy. CBT extremely more effective to relieve depression symptoms. 3. Toseland (1986) 74 studies group therapy much more effective than individual. 4. Traux (2001) CBT not effective for all, since many major-depressed patients are not considered. Dissatisfaction with group is major reason to drop-outs.
Q.9 eclectic approaches Using several treatments to treat a disorder. 1. Elkin (1989) 280 patients, randomly assigned to drug therapy, ITP, CBT or other. Control group given placebo pill. 50% recovered in all groups, except 29% in placebo. No difference in effectiveness of CBT, ITP and drug, doesnt matter which treatment is given. The two therapies less effective than drugs, more effective than placebo. 2. Riggs (2007) effectiveness of CBT with placebo or SSRI. 126 teenagers, 13-19 yrs, depressed and addicted to drugs. Treated for 4 months. 67% of CBT+placebo and 76% of CBT+SSRI. Treatment was almost as effective with placebo too, no difference. Q. 10 etiology and therapeutic approach Etiology is the origins of a disorder. (Link theories and causes to treatments CBT is used because its shown that depression is due to negative thinking.)
You might also like
- Biological Approach to Behaviour SAQsDocument14 pagesBiological Approach to Behaviour SAQsMyra JainNo ratings yet
- Biological Approach John CraneDocument108 pagesBiological Approach John CranePedro Mauricio Pineda LópezNo ratings yet
- Higgins IB Psychology Syllabus ScheduleDocument4 pagesHiggins IB Psychology Syllabus SchedulejacquelineyipNo ratings yet
- New IB Psychology IA GuideDocument16 pagesNew IB Psychology IA GuideYeşim Eylül ÇimenciNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology Paper 3Document83 pagesIB Psychology Paper 3Caroline LeeNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - Revision Lab, Field and Natural StudiesDocument10 pagesResearch Methods - Revision Lab, Field and Natural StudiesSupriyaa Chordia50% (2)
- IB Psychology HL Biological LOADocument11 pagesIB Psychology HL Biological LOAgfore3No ratings yet
- IB Psychology: Sociocultural Level of AnalysisDocument10 pagesIB Psychology: Sociocultural Level of AnalysisLily DeckardNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology ERQsDocument15 pagesIB Psychology ERQsMichelle Karam LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Ib Psychology UnitsDocument28 pagesIb Psychology Unitsapi-3255807630% (1)
- Biological Levels of AnalysisDocument12 pagesBiological Levels of AnalysisCheezy HeadNo ratings yet
- 04 IB Psych Developmental Psych Topic Essays SAMPLEDocument6 pages04 IB Psych Developmental Psych Topic Essays SAMPLEMyraNo ratings yet
- Biological Approach to BehaviourDocument9 pagesBiological Approach to BehaviourVasuNo ratings yet
- Biological Approaches To Psychology - Unit 1 - Brain and BehaviourDocument12 pagesBiological Approaches To Psychology - Unit 1 - Brain and Behaviourleher shah100% (1)
- Psych HL Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesPsych HL Exam ReviewisraraniNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology Abnormal and Human Relationships Options Studies SheetDocument13 pagesIB Psychology Abnormal and Human Relationships Options Studies SheetNaomiGrahamNo ratings yet
- Ib Psych Lesson Plan Week 20 f19 YlDocument2 pagesIb Psych Lesson Plan Week 20 f19 Ylapi-280368667No ratings yet
- Experiments For IB Psychology SLDocument23 pagesExperiments For IB Psychology SLHilda HiongNo ratings yet
- Ib Psychology Course Syllabus 2014-15Document6 pagesIb Psychology Course Syllabus 2014-15api-255249178No ratings yet
- Hormones Study GuideDocument4 pagesHormones Study GuideSebastien Berka100% (1)
- Lingua House Level Placement TestDocument5 pagesLingua House Level Placement TestBalanean TatianaNo ratings yet
- IB SL Psychology Brief Revision NotesDocument30 pagesIB SL Psychology Brief Revision NotesSeoyoung KimNo ratings yet
- Psychology 2019 IB HL NotesDocument85 pagesPsychology 2019 IB HL NotesCawin KumarNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology: Study Guide For The Psychology of Human RelationshipsDocument7 pagesIB Psychology: Study Guide For The Psychology of Human RelationshipsaishahcholmondeleyNo ratings yet
- Psychology Assignment APFCC Ha He HO IV DV Ethnics On Internet Addition Article.Document2 pagesPsychology Assignment APFCC Ha He HO IV DV Ethnics On Internet Addition Article.chl23No ratings yet
- Research Methods 1Document46 pagesResearch Methods 1Cawin Kumar100% (1)
- 4 Tips For A 7 in IB PsychologyDocument1 page4 Tips For A 7 in IB PsychologyMatthewsocksNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology HL SyllabusDocument4 pagesIB Psychology HL SyllabusSathya ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Psychology of RelationshipsDocument15 pagesPsychology of RelationshipsDanitza Laurente100% (1)
- Paper 1 Study Guide For IB PsychologyDocument24 pagesPaper 1 Study Guide For IB PsychologyIsabelle Fellay100% (4)
- Cognitive Psychology IBDocument198 pagesCognitive Psychology IBSrnt YyoNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology Example IADocument18 pagesIB Psychology Example IALucy Han100% (1)
- Ib Psych Lesson Plan Week 12 f19 YlDocument2 pagesIb Psych Lesson Plan Week 12 f19 Ylapi-280368667No ratings yet
- APFCC Studies For Cognitive PsychologyDocument3 pagesAPFCC Studies For Cognitive PsychologyAshley SeoNo ratings yet
- Bloa Erq Ib 1 5-14Document2 pagesBloa Erq Ib 1 5-14api-233994581No ratings yet
- Essay Question Explain The Role That Culture Plays in The Formation of RelationshipsDocument2 pagesEssay Question Explain The Role That Culture Plays in The Formation of Relationshipschl23100% (1)
- 2018 Summer Reading Assignment For IB Psychology IDocument5 pages2018 Summer Reading Assignment For IB Psychology ICsmittysNo ratings yet
- TOK Natural Science SchemeDocument10 pagesTOK Natural Science SchemeSimon100% (3)
- EssaysampleTo What Extent Do Cognitive and Biological Factors Interact in EmotionDocument6 pagesEssaysampleTo What Extent Do Cognitive and Biological Factors Interact in Emotionchl23100% (2)
- Ib Psychology Revision EbookDocument142 pagesIb Psychology Revision Ebookapi-188978784No ratings yet
- IB Psychology Revision EbookDocument142 pagesIB Psychology Revision EbookStarryz1221c100% (3)
- Evaluate Schema Theory With Reference To Research StudiesDocument24 pagesEvaluate Schema Theory With Reference To Research StudiesMinahil FatimaNo ratings yet
- BLOA Study Guide - IB PschologyDocument6 pagesBLOA Study Guide - IB PschologyMatthewsocksNo ratings yet
- Ib Psych Command TermsDocument2 pagesIb Psych Command Termsloveis102050% (2)
- IB Psychology - Stereotype FormationDocument2 pagesIB Psychology - Stereotype FormationNoor Mohsin100% (2)
- AQA A-Level Psychology PYA5: Cultural Bias in Psychological ResearchDocument9 pagesAQA A-Level Psychology PYA5: Cultural Bias in Psychological ResearchStephan Amaranath100% (2)
- Methods in Studying PsychologyDocument35 pagesMethods in Studying Psychologyvlabrague6426No ratings yet
- Psychology Paper 1 HL MarkschemeDocument13 pagesPsychology Paper 1 HL MarkschemeTaehyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Ib Psychology - Perfect Saq Examination AnswersDocument7 pagesIb Psychology - Perfect Saq Examination Answerszeelaf sirajNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology Biological NotesDocument2 pagesIB Psychology Biological NotesSara Bhalla0% (1)
- Biological-Approach-Key-Terms IB PsychologyDocument2 pagesBiological-Approach-Key-Terms IB PsychologySupriyaa ChordiaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Processes PaperDocument46 pagesCognitive Processes PapertriptirathoreNo ratings yet
- Biological Approach SampleDocument37 pagesBiological Approach SamplesofiaNo ratings yet
- Essay Plan TOKDocument3 pagesEssay Plan TOKSimran Toor0% (3)
- IB Psychology IA ChecklistDocument3 pagesIB Psychology IA Checklisthikari1796100% (1)
- Evaluate Social Identity Theory, Making Reference To Relevant StudiesDocument2 pagesEvaluate Social Identity Theory, Making Reference To Relevant Studieschl2367% (3)
- Ib Psych Lesson Plan Week 21 f19 YlDocument2 pagesIb Psych Lesson Plan Week 21 f19 Ylapi-280368667No ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Psychology PYA4: Endogenous Pacemakers and Exogenous ZeitgebersDocument16 pagesAQA A-Level Psychology PYA4: Endogenous Pacemakers and Exogenous ZeitgebersStephan Amaranath100% (5)
- 007Document3 pages007Ed RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Health Psychology: Biopsychosocial Model and Research MethodsDocument42 pagesIntroduction to Health Psychology: Biopsychosocial Model and Research MethodssherrybrarNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology - Stereotype FormationDocument2 pagesIB Psychology - Stereotype FormationNoor Mohsin100% (2)
- IB Psychology - Discuss Validity and Reliability of Diagnosis Q 4Document2 pagesIB Psychology - Discuss Validity and Reliability of Diagnosis Q 4Noor Mohsin50% (2)
- IB Psychology - Social Identity TheoryDocument2 pagesIB Psychology - Social Identity TheoryNoor Mohsin50% (2)
- IB Psychology - Paper 3 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesIB Psychology - Paper 3 Revision NotesNoor Mohsin86% (7)
- IB Psychology - Dicuss Factors Influencing ConformityDocument2 pagesIB Psychology - Dicuss Factors Influencing ConformityNoor Mohsin100% (4)
- IB Psych Biological Level - Revision NotesDocument2 pagesIB Psych Biological Level - Revision NotesNoor MohsinNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology Sociocultual Level - Revision NotesDocument3 pagesIB Psychology Sociocultual Level - Revision NotesNoor Mohsin0% (1)
- Assessment in Southeast AsiaDocument17 pagesAssessment in Southeast AsiathuckhuyaNo ratings yet
- Teaching TrigonometryDocument20 pagesTeaching Trigonometryapi-21940065No ratings yet
- Litz Wire Termination GuideDocument5 pagesLitz Wire Termination GuideBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Transformer InsulationDocument14 pagesTransformer InsulationcjtagayloNo ratings yet
- Canterburytales-No Fear PrologueDocument10 pagesCanterburytales-No Fear Prologueapi-261452312No ratings yet
- Electronics Foundations - Basic CircuitsDocument20 pagesElectronics Foundations - Basic Circuitsccorp0089No ratings yet
- Prodelin 1385Document33 pagesProdelin 1385bebebrenda100% (1)
- OTGNNDocument13 pagesOTGNNAnh Vuong TuanNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Whole NumberDocument22 pagesTopic1 Whole NumberDayang Siti AishahNo ratings yet
- What Are Universities ForDocument19 pagesWhat Are Universities ForBikash Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- EMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotDocument13 pagesEMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotWei ShingNo ratings yet
- AD 251 - Equivalent Uniform Moment Factor, M (Italic)Document1 pageAD 251 - Equivalent Uniform Moment Factor, M (Italic)symon ellimacNo ratings yet
- IntuitionDocument10 pagesIntuitionmailsonNo ratings yet
- User Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaDocument15 pagesUser Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaGael OmgbaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2maxamed0% (1)
- New Japa Retreat NotebookDocument48 pagesNew Japa Retreat NotebookRob ElingsNo ratings yet
- 04 LimeDocument32 pages04 LimeGoogle user100% (1)
- Department of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityRica Tano50% (2)
- Nataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaDocument8 pagesNataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaSiva Krishna100% (1)
- Moment Influence Line LabsheetDocument12 pagesMoment Influence Line LabsheetZAXNo ratings yet
- Historical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentDocument5 pagesHistorical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentMark Saldie RoncesvallesNo ratings yet
- Magnets Catalog 2001Document20 pagesMagnets Catalog 2001geckx100% (2)
- Comparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksDocument9 pagesComparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksIkbal HardiyantoNo ratings yet
- Statement Bank MBBDocument11 pagesStatement Bank MBBminyak bidara01No ratings yet
- Symasym BBDocument37 pagesSymasym BBChandraRizkyNo ratings yet
- Health Information SystemDocument11 pagesHealth Information SystemVineeta Jose100% (1)
- Strata KT Office OpportunityDocument41 pagesStrata KT Office OpportunitySanskar SurekaNo ratings yet
- Project Report VajDocument15 pagesProject Report VajTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Nursing Care GuideDocument12 pagesIntraoperative Nursing Care GuideDarlyn AmplayoNo ratings yet
- CE ProblemDocument5 pagesCE ProblemJho FNo ratings yet