Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Managing acute pain related to biliary obstruction and inflammation
Uploaded by
Ashraf QutmoshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Managing acute pain related to biliary obstruction and inflammation
Uploaded by
Ashraf QutmoshCopyright:
Available Formats
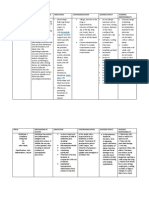
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: acute Pain, related to Biological injuring agents: obstruction/ductal spasm, inflammatory process, tissue ischemia/necrosis Desired
Outcomes\goals Report pain is relieved/controlled. Demonstrate use of relaxation skills and diversional activities as indicated for individual situation. Nursing Interventions Observe and document location, severity (0 10 scale), and character of pain (e.g., steady, intermittent, colicky). Rationale Assists in differentiating cause of pain, and provides information about disease progression/resolution, development of complications, and effectiveness of interventions. Note response to medication, and report to physician if pain is not being relieved. Promote bedrest, allowing patient to assume position of comfort. Use soft/cotton linens; calamine lotion, oil bath; cool/moist compresses as indicated. Control environmental temperature. Encourage use of relaxation techniques, e.g., guided imagery, visualization, deep-breathing exercises. Provide diversional activities. Make time to listen to and maintain frequent contact with patient. Maintain NPO status, insert/maintain NG suction as indicated. Administer medications as indicated:Anticholinergics, e.g., atropine, propantheline (Pro-Banth-ne); Sedatives, e.g., phenobarbital; Helpful in alleviating anxiety and refocusing attention, which can relieve pain. Removes gastric secretions that stimulate release of cholecystokinin and gallbladdercontractions. Relieves reflex spasm/smooth muscle contraction and assists with pain management.Promotes rest and relaxes smooth muscle, relieving pain. Severe pain not relieved by routine measures may indicate developing complications/need for further intervention. Bedrest in low-Fowlers position reduces intraabdominal pressure; however, patient will naturally assume least painful position. Reduces irritation/dryness of the skin and itching sensation. Cool surroundings aid in minimizing dermal discomfort. Promotes rest, redirects attention, may enhance coping.
Given to reduce severe pain. Morphine is used Narcotics, e.g., meperidine hydrochloride (Demerol), morphine sulfate; with caution because it may increase spasms of the sphincter of Oddi, although nitroglycerin may be given to reduce morphine-induced spasms if they occur.
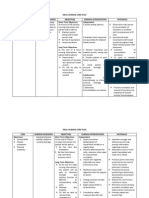
Monoctanoin (Moctanin);
This medication may be used after a cholecystectomy for retained stones or for newly formed large stones in the bile duct. It is a lengthy treatment (13 wk) and is administered via a nasal-biliary tube. A cholangiogram is done periodically to monitor stone dissolution.
Relieves ductal spasm. Smooth muscle relaxants, e.g., papaverine (Pavabid), nitroglycerin, amyl nitrite;
Chenodeoxycholic acid (Chenix), ursodeoxycholic acid (Urso, Actigall);
These natural bile acids decrease cholesterol synthesis, dissolving gallstones. Success of this treatment depends on the number and size of gallstones (preferably three or fewer stones smaller than 20 min in diameter) floating in a functioning gallbladder.
Antibiotics.
To treat infectious process, reducing inflammation.
You might also like
- Discharge Planning for Amputation RecoveryDocument4 pagesDischarge Planning for Amputation Recoveryalynnavictoria100% (4)
- Trigeminal NeuragliaDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NeuragliabryanboytenNo ratings yet
- OBcarestudyDocument9 pagesOBcarestudyJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasNo ratings yet
- BURN PAIN - Pain Management Made Incredibly EasyDocument2 pagesBURN PAIN - Pain Management Made Incredibly EasySakura Kimono100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute PainDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute PainAJ Tuban Compelio100% (1)
- NCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisDocument9 pagesNCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisJavie100% (7)
- Nursing Care for Nephrolithiasis and DiabetesDocument22 pagesNursing Care for Nephrolithiasis and DiabetesNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiNo ratings yet
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Impaired Bone Tissue Perfusion Related To ContinuationDocument5 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS: Impaired Bone Tissue Perfusion Related To ContinuationmasterlouieNo ratings yet
- Burn ManagementDocument7 pagesBurn Managementalinaziyad3No ratings yet
- PYOMYOSITISDocument12 pagesPYOMYOSITISJeg B. Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- Inguinal HerniaDocument40 pagesInguinal HerniaShaf AbubakarNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain Rhea FinalDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain Rhea FinalSolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPFaustino LicudNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis: Free Nursing LecturesDocument9 pagesCholecystitis With Cholelithiasis: Free Nursing LecturesKath CacatianNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Cholecystitis: Narciso A. CañibanDocument10 pagesMedical Management of Cholecystitis: Narciso A. Cañibanalexandrajane2007No ratings yet
- PYOMYOSITISDocument12 pagesPYOMYOSITISPaolo VillaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP - Acute PainRene John Francisco0% (1)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisEnzo DyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDiolan Novero BagorioNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care PAIN and Constipation ManagementDocument5 pagesPalliative Care PAIN and Constipation ManagementLeyla MajundaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Diclofenac KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Diclofenac KCarl Julienne Masangcay100% (1)
- Multiple MyelomaDocument2 pagesMultiple MyelomaKolin JandocNo ratings yet
- ThyroidectomyDocument11 pagesThyroidectomySherina W. EddingNo ratings yet
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP AppendicitisSHAMUS DANINo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPbabycheska08No ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesDexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseDocument10 pagesNCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseJavie100% (3)
- Dipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc. College of NursingDocument16 pagesDipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc. College of NursingTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesAcute Pain Nursing DiagnosisAngelo Cuaresma0% (1)
- NCP Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNCP Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Painphvega06No ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument3 pagesAbdominal PainReiciel Joy Gombio100% (2)
- Nursing Management of PatientDocument32 pagesNursing Management of PatientNoky KiaNo ratings yet
- NCP7Document2 pagesNCP7Jenny Rose JustoNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3jsalise_1No ratings yet
- NCP and DrugsDocument13 pagesNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangNo ratings yet
- Iec PainDocument2 pagesIec PainTheresa LagmayNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument6 pagesAcute Pain NCPPesky Pescante-MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholelitiasisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of CholelitiasisJASMINENICHOLE �GALAPONNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Appendicitis PatientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Appendicitis PatientMargarita PaureneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CholecystitisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For CholecystitisEemyaj Jaymee88% (8)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionRene John Francisco90% (10)
- Section 03 Concepts of Family MedicineDocument2 pagesSection 03 Concepts of Family MedicineNikey LimNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument4 pagesNursingSittie Hidaya MaiNo ratings yet
- NCP FractureDocument3 pagesNCP FractureVanessa Paguirigan0% (1)
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentKevin KroytNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)From EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)No ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)From EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)No ratings yet
- Holistic Approach to Relieve Neck Pain, Back, and Shoulder Pain: An Effective Method for Pain ReductionFrom EverandHolistic Approach to Relieve Neck Pain, Back, and Shoulder Pain: An Effective Method for Pain ReductionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Breakthrough Back Pain Healing and Relief Plan: The book that unlocked the secrets of back pain care, sciatica pain relief naturally via diet, exercises & understanding the mind-body connectionFrom EverandThe Breakthrough Back Pain Healing and Relief Plan: The book that unlocked the secrets of back pain care, sciatica pain relief naturally via diet, exercises & understanding the mind-body connectionNo ratings yet
- Holistic Pain Relief: How to ease muscles, joints and other painful conditionsFrom EverandHolistic Pain Relief: How to ease muscles, joints and other painful conditionsNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain (Neuralgia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNeuropathic Pain (Neuralgia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Healing Hands: A Treatise on First-Aid Equine AcupressureFrom EverandHealing Hands: A Treatise on First-Aid Equine AcupressureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- A Simple Guide to Neuralgia and Related Nerve DisordersFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Neuralgia and Related Nerve DisordersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Therapeutic Presence and Polyvagal Theory 2014 PDFDocument15 pagesTherapeutic Presence and Polyvagal Theory 2014 PDFGonzalo D AlessandroNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology (IJRPB) Vol-1 Issue-2Document126 pagesIndian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology (IJRPB) Vol-1 Issue-2Debjit BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Braverman 2007 PMS and Dysphoric DisorderDocument10 pagesBraverman 2007 PMS and Dysphoric DisorderCarolina GómezNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Visual and Radiographic Changes in Teeth Subjected To High Temperatures: A Forensic StudyDocument6 pagesAssessment of The Visual and Radiographic Changes in Teeth Subjected To High Temperatures: A Forensic StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Ielts Reading Test 17Document8 pagesIelts Reading Test 17Trương Thuận KiệtNo ratings yet
- The Roles and Characteristics of The Physical Therapist NotesDocument3 pagesThe Roles and Characteristics of The Physical Therapist NotesEowyn Wayne dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Banana - Recommendations For Maintaining Postharvest Quality - Postharvest Technology Center - UC Davis PDFDocument3 pagesBanana - Recommendations For Maintaining Postharvest Quality - Postharvest Technology Center - UC Davis PDFFernando SanchezNo ratings yet
- First Middle East Experience WDocument8 pagesFirst Middle East Experience WAsmat BurhanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illnes1Document5 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illnes1Ryan VocalanNo ratings yet
- Bordeline Personality DisorderDocument6 pagesBordeline Personality DisorderWilliam Donato Rodriguez PacahualaNo ratings yet
- FIGHTING BACK: Canadian Cancer Society, Ontario Division - Impact Report 2009-2010Document32 pagesFIGHTING BACK: Canadian Cancer Society, Ontario Division - Impact Report 2009-2010canadiancancersocietyNo ratings yet
- Eight Simple Steps PDFDocument26 pagesEight Simple Steps PDFbuiqn100% (1)
- Gases Toxicos Irritantes PDFDocument6 pagesGases Toxicos Irritantes PDFLUIS ANDRES JUAREZ CALLENo ratings yet
- Case Presentation BronchiectasisDocument61 pagesCase Presentation BronchiectasisUzair Muhd100% (6)
- Hodgkin LymphomaDocument4 pagesHodgkin LymphomaMinelle Sanchez InsoNo ratings yet
- Adlerian Therapy Written ReportDocument3 pagesAdlerian Therapy Written ReportEl Jhonna Duyag-MamaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation Power PointDocument29 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation Power PointsameerarswNo ratings yet
- Sexual IntercourseDocument26 pagesSexual Intercoursenathan100% (2)
- Beldner 2020Document10 pagesBeldner 2020Salsabila HMNo ratings yet
- KINE 2115 Chapter 8 Cardiovascular Disease Fall 2014Document22 pagesKINE 2115 Chapter 8 Cardiovascular Disease Fall 2014Juan VargasNo ratings yet
- The Aetiology and Management of Atrophic RhinitisDocument11 pagesThe Aetiology and Management of Atrophic Rhinitisanoop_aiims1No ratings yet
- Product Catalogue DCMDocument12 pagesProduct Catalogue DCMShree Kumar100% (1)
- Dharam Pani Pandey, Dr. Uday Shankar Sharma, Dr. Ram Babu. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) Improve Functional Independence in Critically Ill PatientsDocument8 pagesDharam Pani Pandey, Dr. Uday Shankar Sharma, Dr. Ram Babu. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) Improve Functional Independence in Critically Ill PatientsDr. Krishna N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Orange Peel MSDSDocument4 pagesOrange Peel MSDSarvind kaushikNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Excipients-Boolket For Pharmacy StudentsDocument33 pagesPharmaceutical Excipients-Boolket For Pharmacy StudentsRaja Bhai89% (9)
- Assessment and Treatment of Adolescent Sexual Offenders Implications of Recent Research On Generalist Versus Specialist Explanations PDFDocument7 pagesAssessment and Treatment of Adolescent Sexual Offenders Implications of Recent Research On Generalist Versus Specialist Explanations PDFjlbermudezcNo ratings yet
- Eye Exercises For Healthy Eye: September 2015Document3 pagesEye Exercises For Healthy Eye: September 2015spiridon_andrei2011No ratings yet
- Narrative TherapyDocument11 pagesNarrative TherapyCamila Orellana100% (1)
- Article - Importance of Fruits, Nuts, and Vegetables in Human Nutrition and HealthDocument3 pagesArticle - Importance of Fruits, Nuts, and Vegetables in Human Nutrition and HealthAlena JosephNo ratings yet
- Implant Supported Overdenture: Presented By:-Dr. Anuja Gunjal 19/01/18Document93 pagesImplant Supported Overdenture: Presented By:-Dr. Anuja Gunjal 19/01/18Instrument SeparationNo ratings yet