Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Posses Ives Explained
Uploaded by
Cordy Lyman DixonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Posses Ives Explained
Uploaded by
Cordy Lyman DixonCopyright:
Available Formats
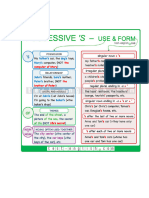
Possessive Nouns and Possessive Adjectives
The formation of possessive nouns and possessive adjectives is sometimes confusing to students. The reason for this is that many languages commonly use 'of' for this construction. Examples The color of his shirt NOT shirt's color The ball of his dog NOT his dog's ball In everyday English, however, we generally use possessive nouns and possessive adjectives rather than this 'of' form. Possessive Adjectives Possessive adjectives are used instead of possessive nouns when the reference is understood. For example: Tom is a dog lover. He takes his dog Spike everywhere! In this case, it is clear that 'his' refers to Tom because of the context. Possessive adjectives are always placed in front of the noun they modify. Here is a list of possessive adjectives: I - my dog You - your cat He - his book She - her car It - its color (NOT it's!) We - our dog You - your house They - their farm Examples That's my dog in the picture. Does you cat like tuna? He left his book in the car. That's her car over there. Its color is purple! Our dog is like a member of the family. Your house isn't far, is it? Their farm produces pumpkins. Possessive Nouns Possessive nouns also modify other nouns to indicate possession. Examples Peter's motorcycle The building's structure etc. Form the possessive pronoun by placing an apostrophe (') after the noun + s.
Peter -> Peter's motorcycle building -> building's structure When nouns end in 's' it can be difficult to know where to place the 's'. For nouns ending in 's', or to use the possessive with regular plurals, place the apostrophe directly after the 's'. Do not add another 's'. Parents -> parents' concern for their children Computers -> computers' manufacturer Notice that this construction can change the meaning from singular to plural. Examples The cat's favorite food is tuna. (one cat) The cats' favorite food is tuna. (more than one cat) Possessive Pronouns Use possessive pronouns to indicate possession when no noun is used. This is the case when the object of possession is understood from the context. Examples Whose book is that? It's mine. = It's my book. Is this your pen? No, it's hers. = It's her pen. In both cases, the possessive pronoun can be substituted for the possessive adjective because the object of possession is understood from the context. Here is a list of possessive pronouns. I - mine You - yours He - his She - hers We - ours You - yours They - theirs Is this your car? - No, that one over there is mine. Whose lunch is this? - It's yours. Whose house is it? - It's his. Do you know who this belongs to? - It's hers. This isn't her car. It's ours Whose picture is this? - It's yours. Who do those books belong to? - They're theirs. Finally, possessive nouns can also be used in the same manner as possessive pronouns. Examples Whose cell phone is that? - It's John's. Who do these computers belong to? - They're our parents'.
You might also like
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarFrom EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Possessive Pronouns and AdjectivesDocument3 pagesPossessive Pronouns and AdjectivesBogdan Si Alexa PaunNo ratings yet
- Possessives, Conditionals and Other Grammar TopicsDocument103 pagesPossessives, Conditionals and Other Grammar Topicspedro perezNo ratings yet
- POSESIVOSDocument8 pagesPOSESIVOSMaria Victoria SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns (Material de Apoyo)Document7 pagesPronouns (Material de Apoyo)FRANKLIN RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 The 8 Parts of Speech-1Document26 pagesWEEK 1 The 8 Parts of Speech-1Aya MeftiNo ratings yet
- Possessive PronounsDocument12 pagesPossessive PronounsJojj LimNo ratings yet
- Possessive PronounDocument5 pagesPossessive PronounAbdul HarisNo ratings yet
- What Is A Possessive NounDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Possessive NounKartika JayaNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument78 pagesBasic English GrammarPbNo ratings yet
- Unidad-1 Ingles Iniciacion 5%Document12 pagesUnidad-1 Ingles Iniciacion 5%KARINA MOSQUERANo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Possessive Pronoun and A Possessive AdjectiveDocument13 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Possessive Pronoun and A Possessive AdjectiveOJ RioNo ratings yet
- Plurals Me Gusta Se LlamaDocument13 pagesPlurals Me Gusta Se Llamaapi-262025495No ratings yet
- Summary ExpDocument7 pagesSummary ExpAndrea100% (1)
- Possessive S UPDSDocument27 pagesPossessive S UPDSPablo PazNo ratings yet
- Possessive PronounsDocument17 pagesPossessive PronounsCarlos TatosNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives and Pronouns Senor Jordan Version of The LessonDocument133 pagesPossessive Adjectives and Pronouns Senor Jordan Version of The Lessonapi-247236673No ratings yet
- English Grammar (WWW - Qmaths.in)Document169 pagesEnglish Grammar (WWW - Qmaths.in)aayushcooolzNo ratings yet
- English 103 - AssignmentDocument6 pagesEnglish 103 - Assignmentleyymejido04No ratings yet
- PronounDocument117 pagesPronounmorpheus23No ratings yet
- Possessive Pronouns: Mine Yours His Hers Ours Yours TheirsDocument9 pagesPossessive Pronouns: Mine Yours His Hers Ours Yours TheirsledracNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pronouns Examples: Get It Now, It's FreeDocument3 pagesPossessive Pronouns Examples: Get It Now, It's FreeSam YanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GomezDocument25 pagesParts of Speech GomezsingcosweindinglasaNo ratings yet
- POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES AND PRONOUNS PLUS MORE INTERESTING MATERIALS - NumberedDocument83 pagesPOSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES AND PRONOUNS PLUS MORE INTERESTING MATERIALS - NumberedMelanie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument6 pagesCountable and Uncountable NounsOrellana Mary BonillaNo ratings yet
- Nouns and PronounsDocument2 pagesNouns and PronounsErmie SoleroNo ratings yet
- Grammar Assignment 4Document7 pagesGrammar Assignment 4shara santosNo ratings yet
- Possession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)Document10 pagesPossession (John's Car, A Friend of Mine)CarlosAbelFuentesRiveraNo ratings yet
- Proper PossessivesDocument15 pagesProper PossessivesgrammarwitchNo ratings yet
- Nouns That Don't Show Quantity Are Normally Used Without A or An. TheDocument17 pagesNouns That Don't Show Quantity Are Normally Used Without A or An. Theselvia anggrainiNo ratings yet
- Noun PhrasesDocument13 pagesNoun PhrasesLegends FunanzaNo ratings yet
- Possesive CaseDocument15 pagesPossesive Caseananeva.nastena999No ratings yet
- Pronouns and Possessive AdjectivesDocument14 pagesPronouns and Possessive AdjectivesIlinca DamianNo ratings yet
- Possessive PronounsDocument13 pagesPossessive PronounsOumaima BenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Darun Najah Ramadhan Short CourseDocument20 pagesChapter 1 - Darun Najah Ramadhan Short CourseMunir MaverickNo ratings yet
- Accusative CaseDocument24 pagesAccusative Caseromance.man333No ratings yet
- Pronouns and Possessive AdjectivesDocument9 pagesPronouns and Possessive AdjectivesSolange PluaNo ratings yet
- GRAMMARBOOKDocument87 pagesGRAMMARBOOKOscar SerranoNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument37 pagesParts of SpeechMuhammad Umar NaheedNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Parts of SpeechDocument53 pages1.1 Parts of Speechrani priyanka GsitsNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives in EnglishDocument4 pagesPossessive Adjectives in Englishissra allammyNo ratings yet
- Nouns PresentationDocument44 pagesNouns PresentationIvan Jr100% (1)
- Possessive AdjectivesDocument2 pagesPossessive AdjectivesRaquel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Possessive Case - Genitive Case: 1. Singular NounsDocument7 pagesPossessive Case - Genitive Case: 1. Singular NounsRadu IonelNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns: Singular PluralDocument17 pagesPersonal Pronouns: Singular PluralAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Masculine and Feminine NounsDocument12 pagesMasculine and Feminine Nounspsycho_psychoNo ratings yet
- A1 GrammarDocument26 pagesA1 GrammarEmilgsNo ratings yet
- Noun As Modifiers: English For Public Health Handout 9Document6 pagesNoun As Modifiers: English For Public Health Handout 9tiarapuspita06No ratings yet
- Possessive PronounsDocument15 pagesPossessive PronounsPamela GregorioNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument8 pagesInglesjuanNo ratings yet
- Leccion 1y 2Document25 pagesLeccion 1y 2NaTalia CuAscotaNo ratings yet
- Abstract and Concrete NounDocument4 pagesAbstract and Concrete Nounralph allan bibatNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar: Parts of SpeechInfotainment and Entertainment Videos & MoviesNo ratings yet
- Determiners 1Document17 pagesDeterminers 1Rashi SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Qué Debo SaberDocument14 pagesQué Debo SaberMaria Angelica Moreno O.100% (1)
- DeterminersDocument7 pagesDeterminerskhushiali301No ratings yet
- Pronouns and PossesivesDocument35 pagesPronouns and PossesivesAlfredo AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Inglés I Mg. Nancy León Pereyra Showing Possession: Possessive Adjectives and PronounsDocument6 pagesInglés I Mg. Nancy León Pereyra Showing Possession: Possessive Adjectives and PronounsMiguel Ipanaque SilvaNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns: Forms of "To Be"Document7 pagesPersonal Pronouns: Forms of "To Be"David EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Contrasting of English and Vietnamese Addressing FormsDocument19 pagesContrasting of English and Vietnamese Addressing Formsxuxunguyen100% (2)
- Samoan Language PDFDocument200 pagesSamoan Language PDFAlif Arienzo Wirakusumah100% (1)
- Noun, Pro Noun, AdjectiveDocument19 pagesNoun, Pro Noun, AdjectiveConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- BI 31 Greek ExegesisDocument10 pagesBI 31 Greek ExegesisRed FernanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document102 pagesExercise 4Yana Ruseva SlavovaNo ratings yet
- A Typological Description of Modern Mandarin ChineseDocument20 pagesA Typological Description of Modern Mandarin ChineseLamnguyentai100% (1)
- Present Simple 'Teachers'Document28 pagesPresent Simple 'Teachers'abdelgoui rymNo ratings yet
- S Aho S Aho Language: Lit.: ADocument4 pagesS Aho S Aho Language: Lit.: AahahaNo ratings yet
- Grammar 111Document33 pagesGrammar 111Suntithvibol Sem100% (1)
- Unit One 2023Document12 pagesUnit One 2023alijalalkalel2018No ratings yet
- Minus 365 Mistakes Per YearDocument196 pagesMinus 365 Mistakes Per Yearngocnga19nn202No ratings yet
- Talking About Language Stie 1Document8 pagesTalking About Language Stie 1Melynda Novita DewiNo ratings yet
- Arindam Chakrabarty (2011) Troubles With A Second Self The Problem of Other Minds in 11th Century Indian and 20th Century Western Philosophy PDFDocument13 pagesArindam Chakrabarty (2011) Troubles With A Second Self The Problem of Other Minds in 11th Century Indian and 20th Century Western Philosophy PDFAmitranjan BasuNo ratings yet
- Morphological Composition 2. Morphological Characteristics 3. Patterns of Combinability 4. Syntactic Functions 5. Substantivized NumeralsDocument6 pagesMorphological Composition 2. Morphological Characteristics 3. Patterns of Combinability 4. Syntactic Functions 5. Substantivized NumeralsМария АрнаутNo ratings yet
- 10 Subject-Verb Agreement SimplifiedDocument29 pages10 Subject-Verb Agreement SimplifiedIola Faith Cena ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Acet ReviewDocument5 pagesAcet Reviewmary100% (1)
- Polish Simplified GrammarDocument70 pagesPolish Simplified GrammarWilliam Acevedo100% (4)
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument22 pagesCountable and Uncountable Nounsmarialecortez100% (1)
- Unit 7 - DeterminersDocument27 pagesUnit 7 - Determinersano.sstoreNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense: Nathan/17 Sekar/8 Jovita/10 JJ/11 Class of 7.1 Stella Maris BSDDocument12 pagesSimple Present Tense: Nathan/17 Sekar/8 Jovita/10 JJ/11 Class of 7.1 Stella Maris BSDarnoldNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument59 pagesEnglish GrammarductaiutcNo ratings yet
- Spanish Subject PronounsDocument2 pagesSpanish Subject PronounsBetsy100% (1)
- ELPT - Intensive CourseDocument41 pagesELPT - Intensive CourseYuan faiha100% (1)
- DuroosBook1 @piousfactsDocument5 pagesDuroosBook1 @piousfactsSpy ninjaNo ratings yet
- Countable Nouns: These Shoes Look Old NowDocument6 pagesCountable Nouns: These Shoes Look Old NowTaseco TumocoNo ratings yet
- Analysis Od Words From Gothic BibleDocument10 pagesAnalysis Od Words From Gothic BibleОксана ШаловилоNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structure: Parts of SpeechDocument34 pagesSentence Structure: Parts of SpeechChiera FayeNo ratings yet
- English Glossary of Grammar TermsDocument73 pagesEnglish Glossary of Grammar TermsArash Karimi100% (1)
- Aap-77 Eda V1 eDocument74 pagesAap-77 Eda V1 eNicoleta NiţăNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument10 pagesPronounsMisty Rose FernandoNo ratings yet