Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Balance Skeletal Traction
Uploaded by
Lourdes PinedaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Balance Skeletal Traction
Uploaded by
Lourdes PinedaCopyright:
Available Formats
Balance Skeletal Traction (BST) Traction Traction is used to manage fractures in an effort torealign broken bones; it is most often
used as atemporary measure when operative fixation is notavailable for a period of time. Traction can either be applied through the skin (skintraction) or through pins inserted into bones (skeletaltraction) Skin traction is generally less desirable due to the factthat skin can be injured when pressure is applied for extend periods of time. Skin traction called Buck'straction - is commonly used in patients who have ahip fracture Skeletal traction does have the disadvantage of complications associated with pin insertion, andinfections can come from the sites of pin insertion Balance Skeletal Traction (BST) Purpose: To maintain the anatomical position of the fractured bone
Skeletal traction requires an invasive procedure inwhich pins, screws, or wires are surgically installedfor use in longer term traction requiring heavier weights. Weights used in skeletal traction generally range from2540 lbs (1118 kg) Other forms of skeletal traction are tibia pin traction,for fractures of the pelvis, hip, or femur; andoverhead arm traction, used in certain upper armfractures. Cervical traction is used when the neck vertebrae are fractured. Materials needed: 1) Thomas Splint placement of the thigh2)Pearson Attachment placement of the leg3)Steinmans holder 4)Steinmans pin5)Traction weighta.10% of the Body weight b.Inside of the suspension rope6)Supension weighta.50% of the traction weight7)Rest Splint8)3 ropes:a.Thigh rope the shortest b.Suspension rope the longestc.Traction rope9)Slings & pins10)Foot board The Thomas splint - (half ring) is applied in various ways: with the ring fitted posteriorlyagainst the ischium or anteriorly in the groin. The thigh rests in a canvas or bandage-stripsling with the popliteal space left free. The leather ring should not be wrapped or padded.If kept smooth, dry, and polished, the leather of the ring isdesigned to rest against theskin and resist moistureThe
Pearson attachment - is attached by clamps to the Thomas splint at knee level. Acanvas or bandage-strip sling supports the lower leg and provides the desired degree of knee flexion. A footplate is attached to the distal end of the Pearson attachment to support the foot in a neutral position. The heel should be left free
Thomas Splint - The traction is in line with the long axis of the femoral shaft and is maintained by the rope, pulley, and weights attached to the skeletal tractor, which is fitted onto the wire or pin. Counter traction and balanced suspension are provided by the ropes, pulleys, andweights attached to the Pearson attachment. When all is operational, the thigh and Thomas splint will be suspended at about a 45 angle with the bed and the lower leg andPearson attachment will be suspended horizontal to the mattress. The patient may sit up,turn toward the traction side, and raise his hips above the bed by means of the trapeze and still maintain the line of traction Application of Traction 1.Verify Doctors order 2.Inform the patient about the need & purpose of the procedure 3.preparation a.Identify the different parts of orthopaedic bed b.Assemble the neede equipments i.Thomas Splint ii.Pearson Attachment1 Rest SplintSteinman Holder Steinman Pin
You might also like
- A Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1Document25 pagesA Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1JM UncianoNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument5 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusPeterzen ManaigNo ratings yet
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDocument3 pagesPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Braces Ortho..Document16 pagesBraces Ortho..karendelarosa062770% (1)
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Document2 pagesRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDocument7 pagesIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease): A Case PresentationDocument16 pagesThromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease): A Case PresentationYan VencerNo ratings yet
- 2019 Focus Charting FDARDocument15 pages2019 Focus Charting FDARGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Khaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionDocument4 pagesKhaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Im Case Study 04Document49 pagesIm Case Study 04Shaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Casestudy Pott's DiseaseDocument36 pagesCasestudy Pott's DiseaseyasiraNo ratings yet
- Cast and TractionsDocument7 pagesCast and TractionsMerlene Sarmiento SalungaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhoidectomy Case StudyDocument19 pagesHemorrhoidectomy Case StudyJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Application Balanced Skeletal TractionDocument6 pagesApplication Balanced Skeletal TractionLorenz ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument2 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveDocument5 pagesOrthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Self Task For English Lesson Part 2THDocument1 pageSelf Task For English Lesson Part 2THistiningrum0% (1)
- ClubfootDocument9 pagesClubfootLorebell100% (5)
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- 1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationDocument19 pages1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Casts and Molds AssignmentDocument3 pagesCasts and Molds AssignmentKimberlee Ced Garcia NoolNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Appendectomy Procedure DetailsDocument11 pagesExploratory Appendectomy Procedure DetailsJessica Christine Datuin GustiloNo ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- Cu 3 Week 3Document3 pagesCu 3 Week 3Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for post-surgical gastric cancer patientDocument2 pagesNursing care plan for post-surgical gastric cancer patientkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument5 pagesCongenital Hip DislocationMonica Aguirre QuilangNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Document34 pagesOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PreoperativeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Preoperativekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Splints and Casts Indications and MethodsDocument9 pagesSplints and Casts Indications and MethodsJay GaneshNo ratings yet
- Hardware Ortho.Document35 pagesHardware Ortho.karendelarosa06277100% (2)
- Pott's Disease Night SweatsDocument22 pagesPott's Disease Night SweatsjesuitkrisNo ratings yet
- Types of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDocument3 pagesTypes of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDoyTanNo ratings yet
- Cell Ab ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCell Ab ActivitiesJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Cast and TractionsDocument3 pagesCast and TractionsMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionCharry de VeraNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma Due To Surgical Procedure Done (Thoracentesis)Document6 pagesAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma Due To Surgical Procedure Done (Thoracentesis)Jasmine Ruth ValdezNo ratings yet
- Causes and Symptoms of Scoliosis: Understanding Spinal CurvatureDocument1 pageCauses and Symptoms of Scoliosis: Understanding Spinal Curvaturebwester2222No ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINDocument4 pagesDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDanielle Patricia Valencia OtedaNo ratings yet
- TahbsoDocument4 pagesTahbsomichZ_13No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain PatientDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain PatientAnni BarbaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 - NCPDocument3 pagesNCM 114 - NCPReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis, PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOsteomyelitis, Pathophysiology4kscribdNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKenneth ManalangNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fever, Pain, Weakness, Loss of AppetiteDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fever, Pain, Weakness, Loss of AppetiteNoemi GarciaNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease NCP .. JustificationDocument8 pagesPotts Disease NCP .. JustificationMicah SalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageMaintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing Interventionsjanine marie oraizNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument3 pagesMannitolAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Traction TechniquesDocument22 pagesLower Extremity Traction TechniquesJo-Anne Karen SerdeñaNo ratings yet
- LilianDocument5 pagesLilianLilian Laureto SabinesNo ratings yet
- Types of Traction An CareDocument1 pageTypes of Traction An CarePrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Types of Traction An CareDocument1 pageTypes of Traction An CarePrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Its Principles-PE3Document2 pagesExercise and Its Principles-PE3Nica EstoperesNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioner TroubleshootingDocument6 pagesAir Conditioner TroubleshootingMeetoo SharvamNo ratings yet
- Massage ExchangeDocument1 pageMassage Exchangeanon-411215No ratings yet
- 209Document4 pages209Nezer VergaraNo ratings yet
- Codex: Adeptus Mechanicus: Updates & ErrataDocument2 pagesCodex: Adeptus Mechanicus: Updates & ErrataLouis De salaberryNo ratings yet
- Automotive TransmissionDocument10 pagesAutomotive TransmissionvpadayhagNo ratings yet
- Paeroa A&PDocument19 pagesPaeroa A&PchaseandcrewNo ratings yet
- Packmaster & Gorehounds Character SheetDocument6 pagesPackmaster & Gorehounds Character SheetColin ZachauNo ratings yet
- The Seeker v4 Nº1 (October 2002)Document4 pagesThe Seeker v4 Nº1 (October 2002)rumtariNo ratings yet
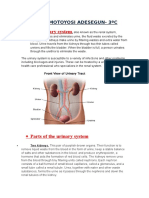
- The Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesThe Urinary Systemade100% (1)
- XJF 151 PartsDocument4 pagesXJF 151 PartsMahmoud Mohamed100% (1)
- Eevee Traits and EvolutionsDocument4 pagesEevee Traits and EvolutionsErica FieldNo ratings yet
- Hammer ThrowDocument49 pagesHammer ThrowAnonymous O7NI8R3gFA0% (1)
- PeriodisationDocument17 pagesPeriodisationBobNo ratings yet
- Lyric JLO Im Into YouDocument13 pagesLyric JLO Im Into YouNidya CuaranNo ratings yet
- TotalEnergies BWF World Championships 2022 Seeding ListDocument3 pagesTotalEnergies BWF World Championships 2022 Seeding ListnikeNo ratings yet
- Section Thru 'B-B' Section Thru 'A-A': A3 B3 C3 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5Document1 pageSection Thru 'B-B' Section Thru 'A-A': A3 B3 C3 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5Brian Carl PongaoNo ratings yet
- Notes PeDocument3 pagesNotes PeNyasha ChekeraNo ratings yet
- Spiro Omr SheetDocument2 pagesSpiro Omr Sheetsmart prabhuNo ratings yet
- Laois Connecting Ireland Maps and Network TableDocument3 pagesLaois Connecting Ireland Maps and Network TableJohn HayesNo ratings yet
- Euro Truck Simulator 2 Crash LogDocument622 pagesEuro Truck Simulator 2 Crash LogAndo Bayu C. HutapeaNo ratings yet
- PE 4 Mod 1 21-22Document25 pagesPE 4 Mod 1 21-22JULLIE CARMELLE H. CHATTONo ratings yet
- Gallagher J. - The Trompowsky - Everyman Chess 1998Document146 pagesGallagher J. - The Trompowsky - Everyman Chess 1998andrevsantos2008No ratings yet
- Target ShooterDocument60 pagesTarget Shooterdevildgog100% (1)
- Module Six Wellness PlanDocument12 pagesModule Six Wellness PlanConnor GayNo ratings yet
- GRUNDFOS INSTRUCTIONS MULTIlift M/MD AND MOGDocument7 pagesGRUNDFOS INSTRUCTIONS MULTIlift M/MD AND MOGParveez HusnooNo ratings yet
- MICU Early Mobility ROM GuideDocument21 pagesMICU Early Mobility ROM GuideAkkipero123No ratings yet
- Terminal Tractor SpecificationDocument4 pagesTerminal Tractor Specification徐磊No ratings yet
- Fundamental RhythmDocument27 pagesFundamental RhythmJohn Luis MolanoNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion ComponentsDocument24 pagesProjectile Motion ComponentsRHEAMAE GALLEGONo ratings yet