Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study (Case Pre)
Uploaded by
Denice Fayne Amid TahiyamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study (Case Pre)
Uploaded by
Denice Fayne Amid TahiyamCopyright:
Available Formats
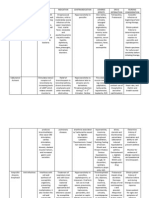
NAME OF DRUG Haloperidol
CLASSIFICATION
ACTIONS
INDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS Not all effects have been reported with haloperidol; however, because haloperidol has certain pharmacologic similarities to the phenothiazine class of antipsychotic drugs, all adverse effects associated with phenothiazine therapy should be kept in mind when haloperidol is used. >CNS: Drowsiness, insomnia, vertigo, headache, weakness, tremor, ataxia, slurring, cerebral edema, seizures, exacerbation of psychotic symptoms, extrapyramidal syndromes,pseudo parkinsonism; dystonias; akathisia, tardive
CONTRAINDICATIONS
>Antipsychotic >Dopaminogern ic blocker
>antipsychotics block postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the brain, depress the RAS, including those parts of the brain involved with wakefulness and emesis; chemically resembles the phenothiazines
>management of manifestations of psychotic disorders >control of tics and vocalizations in Tourette syndrome in adults and children > explosive hyperexcitability that cannot be attributed to immediate provovation >short-term treatment of hyperactive children with excessive motor activity, mood lability >Haloperidol decanoate: Prolonged parenteral therapy of chronic schizophrenia
>contraindicated with hypersensitivity to typical antipsychotics, coma or severe CNS depression, bone marrow depression, blood dyscrasia, circulatory collapse, subcortical brain damage, Parkinsons disease, liver damage, cerebral arteriosclerosis, coronary disease, severe hypotension or hypertension
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIE S >do not give children IM injection >do not use haloperidol deconoate for IV
dyskinesias, potentially irreversible (no known treatment)
NAME OF DRUG Aripiprazole
CLASSIFICATION >Atypical antipsychotic >Dopamine, serotonin agonist and antagonist >Psychotic drug
ACTIONS >acts as an agonist at dopamine and serotonin sites and antagonist at other serotonin receptor sites; this combination of actions is thought to be responsible for the drugs effectiveness in treating schizophrenia, though the mechanism of action is not understood
INDICATIONS >treatment of schizophrenia in patients 13 years and older >treatment of major depressive disorder as adjunct to antidepressant therapy >treatment and maintenance of acute manic and mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorders in patients 10 years and older >adjunct to lithium or valproate for acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorder in patients 10 years and older >treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, manic or mixed (injection)
ADVERSE EFFECTS >CNS: Headache, anxiety, insomnia, lightheadedness , somnolence, tremor, asthenia, tardive dyskinesia, blurred vision, seizures (potentially lifethreatening), akathisia, dizziness, restlessness
CONTRAINDICATION S >hypersensitivity to drug >use cautiously in cerebrovascular dse,HPN, seizure is disorder and suicidal ideation >high risk for aspiration pneumonia
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES >have patient place orally disintegrating tablet on time >allow to dissolve then swallow >protect patient from extremes, of heat >monitor blood pressure if overheating occurs
NAME OF DRUG Escitalopram Oxalate (Talobpram)
CLASSIFICATION >Antidepressant >SSRI
ACTIONS >potentiates serotonergic activity in the CNS by inhibiting reuptake of serotonin resulting in antidepressant effect with little effect on norepinephrine or dopamine; an isomer of citalopram
INDICATIONS >treatment of major depressive disorder >maintenance of patients with major depressive disorder >treatment of generalized anxiety disorder >maintenance treatment for major depressive disorder in patients 12-17 years
ADVERSE EFFECTS >CNS: Somnolence, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, complex sleep disorders, serotonin syndrome (with abrupt discontinuation)
CONTRAINDICATIONS >contraindicated with MAOI, pimozide use; with allergy to drug or to citalopram or any component of the drug
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES >encourage patient to continue use for 4-6 weeks directed to ensure adequate level to affect depression >give once a day in the morning or in the evening, may be taken with food if desired
NAME OF DRUG Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride
CLASSIFICATION >Antihistamine >Antimotionsickness drug >Antiparkinsonian >Cough suppressant >Sedativehypnotic
ADVERSE EFFECTS >interferes with >active and >CNS: histamine effects prophylactic Drowsiness, at histamine1- treatment of sedation, receptor sites; motion sickness dizziness, prevents but disturbed doesnt reverse coordination, histaminefatigue, mediated confusion, response restlessness, >possesses CNS excitation, depressant and nervousness, anticholinergic tremor, properties headache, blurred vision, diplopia
ACTIONS
INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES >hypersensitivity to >administer with drug food if GI upset >contraindicated with occurs allergy to >administer syrup antihistamine form if patient is unable to take tablets >monitor patient response and arrange for adjustment of dosage to lowest possible effective dose
NAME OF DRUG Biperiden
CLASSIFICATION >Antiparkinsonian
ACTIONS >anticholinergic activity in the CNS that is believed to help normalize the hypothesized in balance of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the basal ganglia in the brain of parkinsonian patient >reduces severity of rigidity and to lessen extent akinesia and tremor characterizing parkinsonism
INDICATIONS >in the therapy of parkinsonism/postce phalitic, arteriosclerotic, and idiopathic types >relief of symptoms of extrapyramidal disorder that accompany phenothiazine therapy
ADVERSE EFFECTS >CNS: Disorientation, confusion, memory loss, halllucination, psychosis, agitation, nervousness, delusion, delirium, paronia, euphoria, excitement, lightheadednes s, dizziness, depression, drowsiness, weakness, paresthesia, heaviness of the limbs
CONTRAINDICATIONS >contraindicated with hypersensitivity to benzotropine, glaucoma, especially angle-closure glaucoma, pyloric duodenal obstruction, stenosing peptic ulcers, hypertrophy of bladder, neck obstructions, myasthenia gravis
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES >decrease dosage or discontinue temporarily if dry mouth makes swallowing or speaking difficult >give with meals if GI upset occurs; give before meals to patient with dry mouth; give after meals if drooling or nausea occur >ensure that the patient voids just before receiving each dose of drug if urinary retention is the problem
You might also like
- Ivon Neil Adams Form IV RedactedDocument3 pagesIvon Neil Adams Form IV Redactedkc wildmoonNo ratings yet
- QRG-DC-004 Procedure and Regulation Governing The Requirements For CPWDocument56 pagesQRG-DC-004 Procedure and Regulation Governing The Requirements For CPWKarthi Keyan100% (2)
- Babok Framework Overview: BA Planning & MonitoringDocument1 pageBabok Framework Overview: BA Planning & MonitoringJuan100% (1)
- Psycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Dirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsDocument4 pagesDirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsMariuszNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDDocument5 pagesAdrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDKeon RicoNo ratings yet
- Dextroamphetamine SulfateDocument3 pagesDextroamphetamine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Anti-Bribery and Corruption PolicyDocument2 pagesAnti-Bribery and Corruption PolicyAJAY PatilNo ratings yet
- Edited Psyche DrugsDocument49 pagesEdited Psyche Drugsa_lavina02No ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Paracetamol OverdoseDocument1 pageGuidelines For The Management of Paracetamol Overdoseps_ares2No ratings yet
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Nammcesa 000008 PDFDocument197 pagesNammcesa 000008 PDFBasel Osama RaafatNo ratings yet
- Drug PresentationDocument32 pagesDrug PresentationManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Other Respiratory Medications DefindDocument4 pagesAsthma and Other Respiratory Medications DefindKiran ManojNo ratings yet
- Hotel Transportation and Discount Information Chart - February 2013Document29 pagesHotel Transportation and Discount Information Chart - February 2013scfp4091No ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinJAYMIE ROSE M. MANUELNo ratings yet
- MediclaimDocument3 pagesMediclaimPrajwal ShettyNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- General Anesthetics AbeerDocument45 pagesGeneral Anesthetics AbeerYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- ImipramineDocument1 pageImipramineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Mini RinDocument5 pagesMini Rinlovely_dyaNo ratings yet
- Frisium Knowledge ModuleDocument7 pagesFrisium Knowledge ModulesiddiqrehanNo ratings yet
- Saa6d107e 1CC S N 26540705 Up - Parts Book Do Motor GD655-5Document164 pagesSaa6d107e 1CC S N 26540705 Up - Parts Book Do Motor GD655-5kit101No ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument10 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Exceeding Sinfulness of Sin - Guy CaskeyDocument402 pagesThe Exceeding Sinfulness of Sin - Guy Caskeyclaroblanco100% (1)
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Leaflet Dosage High-Resolution-1Document4 pages2014 Leaflet Dosage High-Resolution-1Zarbakht AliNo ratings yet
- AMAZEO (Amisulpride)Document14 pagesAMAZEO (Amisulpride)Konark DinkarNo ratings yet
- 39207618Document6 pages39207618api-301074100% (1)
- Fluanxol Depot: Name of MedicineDocument11 pagesFluanxol Depot: Name of MedicineIvo_NichtNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants: HistoryDocument8 pagesAntidepressants: HistoryTejus Murthy A GNo ratings yet
- Psych DrugsDocument12 pagesPsych Drugsapi-3739910100% (1)
- Summary of Product Characteristics: PosologyDocument9 pagesSummary of Product Characteristics: Posologyddandan_2No ratings yet
- Midazolam FinalDocument2 pagesMidazolam FinalAhmad AbqariNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic AgentsDocument108 pagesAntipsychotic Agentspappu khan100% (2)
- ZoloftDocument26 pagesZoloftgofastjayNo ratings yet
- Drug DilantinDocument1 pageDrug DilantinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument31 pagesAnxiolytic Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- Effexor/Effexor XR (Venlafaxine) : General InformationDocument5 pagesEffexor/Effexor XR (Venlafaxine) : General InformationAchmad HariyantoNo ratings yet
- Daptomycin (Cubicin)Document1 pageDaptomycin (Cubicin)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Amitriptyline PDFDocument3 pagesAmitriptyline PDFscribdseewalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form TJDocument4 pagesDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Sedative - HypnoticsDocument60 pagesSedative - HypnoticsNurul AinNo ratings yet
- IsoprenalineDocument2 pagesIsoprenalineImmanuel Victor GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- CKDDocument54 pagesCKDAnonymous UHnQSkxLBDNo ratings yet
- Wellbutrin SR Pi MG PDFDocument37 pagesWellbutrin SR Pi MG PDFAlfyGototronNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilizing Drugs-Daga, JaDocument19 pagesMood Stabilizing Drugs-Daga, JaJoel Andrew Java DagaNo ratings yet
- Xylocard PiDocument11 pagesXylocard PiRamakant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- Mechanism of Action of QuetiapineDocument4 pagesMechanism of Action of QuetiapineThoha AlbaarNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyBien EstrellaNo ratings yet
- TrihexyphenidylDocument7 pagesTrihexyphenidylfachsyarNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics, Sedative & Hypnotic DrugsDocument22 pagesAnxiolytics, Sedative & Hypnotic DrugsPh Hany MohamedNo ratings yet
- EzetimibeDocument3 pagesEzetimibeapi-3797941No ratings yet
- SH CP 17 Zuclopenthixol Acetate GuidelinesxDocument8 pagesSH CP 17 Zuclopenthixol Acetate Guidelinesxlight002No ratings yet
- Need Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryDocument8 pagesNeed Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyArdy PadamadaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Communication in Older AdultsDocument1 pageBarriers To Communication in Older AdultsLegendXNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram of StrokeMaricar K. BrionesNo ratings yet
- نسخة 264889196 Tramadol Drug StudyDocument1 pageنسخة 264889196 Tramadol Drug StudyMeteab AlzhiryNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument3 pagesVancomycinAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Drug Study: ER DrugsDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ER Drugsmaeca101No ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument4 pagesOlanzapineJaica Jane BunadoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Hypertensive 2Document49 pagesAnti-Hypertensive 2pushpaNo ratings yet
- Brief Psychotic DisorderDocument3 pagesBrief Psychotic Disorderapi-3712326No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Pharmacology of Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesChapter 14 - Pharmacology of Psychotropic MedicationsmysNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report KapilDocument66 pagesThesis Report Kapilkapilsharma2686100% (1)
- Maxs AdultDocument1 pageMaxs Adultclark lopezNo ratings yet
- Pentacon Six-02Document28 pagesPentacon Six-02Melissa Moreira TYNo ratings yet
- BURNS GeneralDocument59 pagesBURNS GeneralValluri MukeshNo ratings yet
- Bio1 11 - 12 Q1 0501 FDDocument23 pagesBio1 11 - 12 Q1 0501 FDIsabelle SchollardNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentGlennford Loreto SuyatNo ratings yet
- Julie Trimarco: A Licensed Speech-Language PathologistDocument5 pagesJulie Trimarco: A Licensed Speech-Language PathologistJulie TrimarcoNo ratings yet
- Powador 7700 - 7900 8600 - 9600: OriginalDocument52 pagesPowador 7700 - 7900 8600 - 9600: Originalashraf-84No ratings yet
- LapasiDocument3 pagesLapasiWenny MellanoNo ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. ISO 9001-2015 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMDocument17 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. ISO 9001-2015 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMAGM S&M-CMNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets & Institutions: Lecture Notes #3Document90 pagesFinancial Markets & Institutions: Lecture Notes #3Joan MaduNo ratings yet
- Period of Intuitive NursingDocument4 pagesPeriod of Intuitive NursingJhey-ar Toledo100% (1)
- Secondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Document15 pagesSecondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Menon HariNo ratings yet
- NFPA 25 2011 Sprinkler Inspection TableDocument2 pagesNFPA 25 2011 Sprinkler Inspection TableHermes VacaNo ratings yet
- MLT IMLT Content Guideline 6-14Document4 pagesMLT IMLT Content Guideline 6-14Arif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Seachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetDocument10 pagesSeachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetJorge Restrepo HernandezNo ratings yet
- MN - 2019 01 29Document28 pagesMN - 2019 01 29mooraboolNo ratings yet
- Unit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A ProfitDocument4 pagesUnit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A Profitkarupukamal100% (2)
- Cough: A Rapid Expulsion of Air FromDocument2 pagesCough: A Rapid Expulsion of Air FromaubyangNo ratings yet