Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Rib
Uploaded by
yachiru121Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Rib
Uploaded by
yachiru121Copyright:
Available Formats
www.1aim.
net
Anatomy Tables - Bones of the Thorax
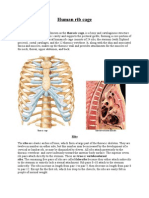
Bone rib Structure Description the bone forming the lateral thoracic wall Notes 12 pairs; several types are described: typical or "true" ribs, "false" ribs, "floating" ribs; all three types of ribs have many features in common: head, neck, tubercle, angle, body, costal groove it articulates with demifacets of two adjacent vertebral bodies the neck of the rib is located between the head and the tubercle
head neck
posteromedial end of the rib the constricted region lateral to the head of the rib
tubercle
a projection it articulates with the located transverse process of a vertebra posteroinferior and lateral to the neck of the rib the shaft of the rib the marked angulation of the body located just lateral to the tubercle the groove on the inner surface of the inferior border of the body of the rib the body is the longest part of a typical rib the angle of the rib is its most posterior part
body angle
costal groove
it accommodates the intercostal neurovascular bundle; the costal groove provides a protective function for the intercostal neurovascular bundle, true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of a costal
ribs 1-7
"true" ribs - those which attach
directly to the sternum rib 1 the most cephalic rib
cartilage and a true synovial joint it is the broadest, shortest and widest of the ribs; the scalene tubercle marks its superior surface and is an elevation between grooves for the subclavian vein & artery; the scalene tubercle is the attachment site of the scalenus anterior m. it articulates via a costal cartilage with the sternum at the level of the sternal angle; its superior surface is roughened by the attachments of the scalene mm. they articulate via costal cartilages with the costal cartilage of rib 7 the anterior ends of these ribs do not articulate with the sternum or the costal cartilage of the rib above; their costal cartilages are short and end in the muscle of the posterolateral abdominal wall
rib 2
the rib attached to the 1st and 2nd thoracic vertebrae
rib 8-10
"false" ribs
rib 1112
"floating" ribs
sternum
the broad flat bone it is formed by three parts: forming the manubrium, body, xiphoid anterior thoracic process wall manubrium jugular (suprasternal) notch clavicular notch the superior part of manubrium means "handle", as the sternum in the handle of a sword a notch on the superior border of the manubrium a notch on the superolateral border of the manubrium it is located between the clavicular notches which articulate with the sternal ends of the clavicles it articulate with the sternal end of the clavicle
sternal angle
the junction of the manubrium and body of the sternum the middle part of the sternum
it is an anterior projection located at the level of the costal cartilage of rib 2; an important landmark for internal thoracic anatomy it articulates with the manubrium superiorly and the xiphoid process inferiorly; laterally it articulates with the costal cartilages of ribs 2-7 xiphoid means "sword shaped"; it is variable in size, shape & ossification; it articulates with the body of the sternum superiorly
body
xiphoid process
the inferior part of the sternum
You might also like
- Spaces.: TH TH TH THDocument4 pagesSpaces.: TH TH TH THbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Thoracic CageDocument46 pagesThoracic CageEmtnan MuntiNo ratings yet
- The Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsDocument2 pagesThe Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsAn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021Document7 pagesHuman Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021AlexanderNo ratings yet
- College of Human Sciences & Psychology Department: ClavicleDocument17 pagesCollege of Human Sciences & Psychology Department: ClavicleJohn Patrick LagmayNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageDocument23 pagesANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageArianna RomanoNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانDocument9 pagesالمحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Thoracic Wall.Document54 pagesOrientation of Thoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cage Thoracic InletDocument40 pagesThoracic Cage Thoracic InletERIAS TENYWANo ratings yet
- 03 Bones Thorax HandoutDocument3 pages03 Bones Thorax HandoutÇağlaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Back RegionDocument9 pagesBones of The Back Regionyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones of the Back and Upper Limbscapulait is the longest border of the scapula; it is a site of attachmentfor the serratus anterior mDocument38 pagesBones of the Back and Upper Limbscapulait is the longest border of the scapula; it is a site of attachmentfor the serratus anterior mshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The CVS: ThoraxDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The CVS: ThoraxNayerShammaaNo ratings yet
- The Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryDocument7 pagesThe Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryAndreeaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The The RegionDocument51 pagesBones of The The RegionjazzyNo ratings yet
- 02 Appendicular SkeletonDocument40 pages02 Appendicular SkeletonkalyanNo ratings yet
- Sternum, Joints Muscles of The Thoracic WallDocument21 pagesSternum, Joints Muscles of The Thoracic WallEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic WallDocument46 pagesThoracic WallJavin BissoondyalNo ratings yet
- CLAVICLE BONEDocument4 pagesCLAVICLE BONEpari59084No ratings yet
- Stelios - Joints and LigamentsDocument16 pagesStelios - Joints and LigamentsAdbhut YadavNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraDocument76 pagesThoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraEsdras DountioNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument388 pagesBooksMayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- 4 Rib CageDocument20 pages4 Rib Cagenoor.komalNo ratings yet
- The Thorax and Chest WallDocument15 pagesThe Thorax and Chest WallVIRESH VNo ratings yet
- Front View (Anterior) Back View (Posterior)Document9 pagesFront View (Anterior) Back View (Posterior)Merlin'z CabillasNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument211 pagesAnatomyIshimwe TheotimeNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbDocument25 pagesANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbArianna RomanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument8 pagesSkeletalJeanina BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- BSC 702 Gross Anatomy Lecture Notes: Thorax, Abdomen and PelvisDocument144 pagesBSC 702 Gross Anatomy Lecture Notes: Thorax, Abdomen and PelvislavanyaNo ratings yet
- Thorax MooreDocument8 pagesThorax MooreivanajanealexisNo ratings yet
- Thorax Part 1Document56 pagesThorax Part 1idrimuha333No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic WallDocument27 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic WallSamuel Pola Karta Sembiring100% (1)
- Upper Limb SummaryDocument19 pagesUpper Limb SummaryPremangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocument3 pagesPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1st AssignmentDocument11 pagesAnatomy 1st Assignmenthasnain ahmedNo ratings yet
- Human Rib CageDocument3 pagesHuman Rib CageAmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Spinal CordDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Spinal CordAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- LowerLimbExam NurDocument108 pagesLowerLimbExam Nuralina nguynNo ratings yet
- Clavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyDocument24 pagesClavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyBishal Chauhan100% (1)
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Inferior Thoracic ApertureDocument7 pagesThoracic Outlet Syndrome Inferior Thoracic ApertureerilarchiNo ratings yet
- Exp 12 PDFDocument16 pagesExp 12 PDFKath BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument31 pagesUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)Document43 pagesPrepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument17 pagesUpper LimbPapadoveNo ratings yet
- Jointsofthorax 180527203532Document14 pagesJointsofthorax 180527203532Lina AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument6 pagesAppendicular SkeletonJohn Snow1No ratings yet
- The anatomy and features of thoracic vertebraeDocument32 pagesThe anatomy and features of thoracic vertebraeAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Larynx Anatomy and Functions GuideDocument49 pagesLarynx Anatomy and Functions GuideenoNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document138 pagesWeek 4Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocument14 pagesBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument25 pagesLower LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Structure of The SkeletonDocument21 pagesStructure of The SkeletonlindaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cage Components and JointsDocument30 pagesThoracic Cage Components and JointsSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ShoulderDocument61 pagesAnatomy of The ShoulderChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- Vertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaDocument39 pagesVertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaT CNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Anatomy 1Document6 pagesUpper Limb Anatomy 1shahab shamsiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology ReviewDocument47 pagesBacteriology ReviewDeti ParidlahNo ratings yet
- Assess Notes Nursing AssessmentDocument206 pagesAssess Notes Nursing Assessmenttostc100% (7)
- Anatomy Lower Extr ReviewDocument12 pagesAnatomy Lower Extr Reviewabuzeid5No ratings yet
- Anatomy Abdomin ReviewDocument24 pagesAnatomy Abdomin Reviewmooni2009No ratings yet
- API Review Muscles f2009Document1 pageAPI Review Muscles f2009yachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy Thorax ReviewDocument18 pagesAnatomy Thorax Reviewyachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study GuideDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study Guideyachiru121No ratings yet
- AP Review NotesDocument15 pagesAP Review Notesyachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy Pelvis ReviewDocument20 pagesAnatomy Pelvis Reviewyachiru121No ratings yet
- Anatomy Head ReviewDocument34 pagesAnatomy Head ReviewJordan BrooksNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Levels and Planes ReviewDocument3 pagesAnatomy Levels and Planes Revieware4erNo ratings yet
- A P1 Review Test 4Document1 pageA P1 Review Test 4yachiru121No ratings yet
- First Aid ManualDocument225 pagesFirst Aid ManualHugo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Lower LimbDocument15 pagesBones of The Lower Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones of The Pelvis and PerineumDocument6 pagesBones of The Pelvis and Perineumyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones of The Back RegionDocument9 pagesBones of The Back Regionyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocument14 pagesBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones of The Abdominal RegionDocument7 pagesBones of The Abdominal Regionyachiru121No ratings yet
- Bones and Cartilages of The Head and NeckDocument27 pagesBones and Cartilages of The Head and Neckyachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. GironDocument56 pagesDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. Gironyachiru121No ratings yet
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Where Are We Now, K in K To 12Document21 pagesDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Where Are We Now, K in K To 12yachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - Assessment in Kinder Mam VioletaDocument54 pagesDEPED 2012 - Assessment in Kinder Mam Violetayachiru121No ratings yet
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB RationaleDocument30 pagesDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB Rationaleyachiru121100% (3)
- DEPED 2012 - Classroom DR VillanezaDocument17 pagesDEPED 2012 - Classroom DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- HandbookDocument53 pagesHandbookyachiru121No ratings yet
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR VillanezaDocument32 pagesDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012Document38 pagesDEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012yachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012Document44 pagesDEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012yachiru121No ratings yet
- 9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument6 pages9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Positioning Presentation-VertebraeDocument156 pagesPositioning Presentation-Vertebraeron reteracionNo ratings yet
- Vertebral ColumnDocument138 pagesVertebral ColumnAl-ajim Hadjili50% (2)
- Anatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Document24 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument6 pagesAnaphyrhona esteibarNo ratings yet
- The Vertebal Column.Document259 pagesThe Vertebal Column.Jo Hn VengzNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDocument4 pagesAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNo ratings yet
- 265 269 BradicJDocument22 pages265 269 BradicJNaida BaNo ratings yet
- Body of The VertebraDocument3 pagesBody of The VertebraCristina-Andreea RebegeaNo ratings yet
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocument3 pagesPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Back PPT AauDocument44 pages1 - Back PPT Aauahmed mohammedNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFDocument156 pagesManual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFEliMihaela100% (2)
- All About The SpineDocument3 pagesAll About The SpineSapoCacoNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8Th Edition Bontrager Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8Th Edition Bontrager Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdecagrambarrymfh100% (6)
- Anatomy of VertebraeDocument63 pagesAnatomy of VertebraeMeylisa GresiaNo ratings yet
- Lap6 CT Usg Radio 6 - 2017Document118 pagesLap6 CT Usg Radio 6 - 2017irwanNo ratings yet
- Erector Spinae Muscles: Spinalis Thoracis, Spinalis Cervicis and Spinalis CapitisDocument21 pagesErector Spinae Muscles: Spinalis Thoracis, Spinalis Cervicis and Spinalis CapitisNeil Dolendo100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDocument60 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Laporan Bu Tri FEBRUARI Newww YG LAINNAPDocument25 pagesLaporan Bu Tri FEBRUARI Newww YG LAINNAPDita Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton Study Guide from Jessenius Faculty of MedicineDocument108 pagesAxial Skeleton Study Guide from Jessenius Faculty of MedicineTheFTWPandaNo ratings yet
- Complete SlidesDocument355 pagesComplete Slidesnimra khaliqNo ratings yet
- Columna Vertebralis Structure and FeaturesDocument20 pagesColumna Vertebralis Structure and FeaturesnadiaryNo ratings yet
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- Annotated diagrams of the mechanics of the human vertebral columnDocument245 pagesAnnotated diagrams of the mechanics of the human vertebral columnVTZIOTZIAS90% (10)
- Pengumuman LPDPDocument4 pagesPengumuman LPDPMuhammad DzulfikarNo ratings yet
- Bio 230 Axial Skeleton Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesBio 230 Axial Skeleton Lecture NotesDenise MathreNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine AnatomyDocument14 pagesCervical Spine Anatomylala_girl100% (1)
- Anatomical structures of the vertebral column and thoraxDocument156 pagesAnatomical structures of the vertebral column and thoraxTea mjavanadzeNo ratings yet
- 08.16.16 Skeletal AxialDocument83 pages08.16.16 Skeletal AxialCindy GazoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Vertebral ColumnDocument5 pagesAnatomy - Vertebral ColumnArmelda Elda MuhollariNo ratings yet