Professional Documents
Culture Documents
32 Major Pressure Points
Uploaded by
Salvador BuenaguaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
32 Major Pressure Points
Uploaded by
Salvador BuenaguaCopyright:
Available Formats
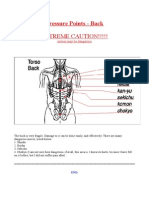
32 major pressure points
1. Coronal structure: the top of the head toward forehead, known as the soft spot on babies. it is the space between skull bones covered by membrane that closes in 18 months but the coronal structure is weaker than rest of skull. Beneath that is the sensory portion and optic cavity. 2. Trigeminal nerve and frontal bone: just below centermost point of forehead on the outside of skull so when struck could result in jarring cerebral hemisphere, concussion, unconsciousness, impaired vision, paralysis, and with maximum force death by brain hemmorage. 3. Temple and Fosa Temporalis: Bonetip of sphenoid recessed part on each side of head horizontal to top of ear. trigeminal nerve runs through temple and also meningeal artery. 4. Eyes: Sensitive to even the slightest touch. Held in facia bulbi (soft membrane) and eye muscles. Easy to pop out. If a blow reached the vitreous body (center of eye) the eyeball would collapse. 5. Ears: Air is easily trapped into eardrum causing it to burst. 6. Mastoid: behind earlobes where skull meets neck. 7. Septal Cartilage: this is the nose. 8. Anterior Nasal Spine: Beneath nose above lips. where two lines run from nose to top lip. direct hit sends shock to pons causing dizziness. could also cause damage to maxilla bone holding gums and teeth causing excessive bleeding. 9. Temporomandibular Joint: joint that holds jaw in place. connects skull in front of ear. 10. Tip of mandible: jaw bone and very end of chin. sends shock sensor to cerebellum causing unconsciousness. (this is the spot that boxers aim for with upper cuts to cause a quick KO) 11. Sternocleidomastoid region: Frontal neck behind ear down clavicle bones beneath that is the jugular vein and cartoid artery which supplies blood to heart and brain. Very sensitive. 12. Anterior Neck Region: Windpipe or throat, center portion of neck. 13. Brachial PLexus and Trapezius muscle: base of neck to shoulders. 14. Suprasternal notch: Between the collarbones. Blow could dislodge collarbones from sternum. 15. Clavicle: supports shoulders. a simple break could immobilize, serious break could puncture lungs, heart, aorta, vena cava, and/or trachea. 16. Heart: forceful strike could cause the heart to skip beats and collapse ceasing movement of oxygen around the body causing death.
17. Kidneys: Firm strike generates a lot of pain and internal bleeding could result in death. 18. Shoulder Socket: where the humurus and scaptula meet at ball and socket joint. 19. Elbow: Breaks easily causing extreme pain and immobility. 20. Carpals, Metacarpals, and Phalanges: these are the fingers and parts of the hand connecting fingers to wrist. 21. Petalla: Knee cap, also breaks easily causing extreme pain and immobility. 22. Tarsals, Metatarsals: these are the toes and parts of the foot connecting toes to ankle. 23. Thoracic cage: rib cage. forceful strike or stamp could cause rib cage to collapse and puncture lungs or heart. 24. Floating ribs: these ribs are not connected to the sternum and break fairly easily. Could pierce liver or spleen resulting in rapid bleeding causing death. 25. Vertebral column: spinal cord. Strong strike could break vertebrae and could snap spinal cord resulting in full or partial paralysis. 26. Diaphragm: solar plexus at the base of sternum. regulates the intake of oxygen. damage could result in inability to breathe causing unconsciousness or death. 27. Testes: male genitalia. even the slightest strike could cause extreme pain, immobility, and maybe unconsciousness. 28. Coccyx: the tailbone. forceful strike causes extreme pain and immobility. 29. Armpit: strike could cause extreme pain and immobility, but not often accessible. 30. Posterior Cutaneous: nerves found in back of upper leg. pinch could cause sharp pain and reflex action. 31. Liver: on right side of body extending to left side at a point. botoom right is unprotected by ribs. liver is saturated in blood and damage could result in rapid blood loss due to internal bleeding leading to death. 32. Spleen: on left side of body, smaller than liver, but completely protected by ribs. also saturated in blood and causes rapid blood loss due to internal bleeding causing death.
You might also like
- HandbookDocument31 pagesHandbookMiguelin666No ratings yet
- Head and Neck Anatomy MnemonicsDocument4 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy MnemonicsBianca81% (16)
- The Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisDocument190 pagesThe Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisTomas De Wael100% (2)
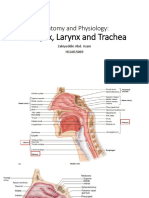
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Pharynx-Larynx-TracheaDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Pharynx-Larynx-TracheaZacky Abdoel AzamNo ratings yet
- Vital TargetsDocument6 pagesVital TargetsSurendra Singh Rathore Pokarna100% (1)
- Martial Arts - Pressure Points - Dragon's TouchDocument6 pagesMartial Arts - Pressure Points - Dragon's Touchrewer23No ratings yet
- Martial Arts Pressure PointsDocument6 pagesMartial Arts Pressure Pointsbella0% (1)
- Relaxed Breath Retention Yi Swallows ChiDocument9 pagesRelaxed Breath Retention Yi Swallows ChiWinston MahNo ratings yet
- Mat ExercisesDocument22 pagesMat ExercisesLuis ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Boxing TechniqueDocument3 pagesBoxing TechniquePatriot Haryo Trenggono100% (1)
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDocument40 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Dragon's Touch (Exerpt) - Hei Long - Paladin Press PDFDocument6 pagesDragon's Touch (Exerpt) - Hei Long - Paladin Press PDFbizasephiroth100% (2)
- Bhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFDocument675 pagesBhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFPrince Trambadiya100% (1)
- Bones of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and Clinical CorrelationsDocument27 pagesBones of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and Clinical CorrelationsFoday H Kalokoh100% (1)
- Working Out at HomeDocument3 pagesWorking Out at HomeNemrac NemracNo ratings yet
- On The Value of Yiquan - by Master Han JingchenDocument6 pagesOn The Value of Yiquan - by Master Han JingchenLiew Yetmeng100% (1)
- Dragons Touch - Weaknesses of HumanDocument6 pagesDragons Touch - Weaknesses of Humanprakharmishra902No ratings yet
- ARNISDocument12 pagesARNISJhane MarieNo ratings yet
- Dim Mak and Acupuncture: Understanding the Medical Reasons Behind this Martial ArtDocument6 pagesDim Mak and Acupuncture: Understanding the Medical Reasons Behind this Martial ArtIoan NeacsuNo ratings yet
- How To Stop Yourself SnoringDocument3 pagesHow To Stop Yourself SnoringAzmi MohamadNo ratings yet
- To Work DummyDocument11 pagesTo Work DummyaldraNo ratings yet
- Aikido - Pressure Points Martial ArtsDocument3 pagesAikido - Pressure Points Martial Artsyura100% (1)
- Chapter Nine Attack Using SoundDocument3 pagesChapter Nine Attack Using SoundNour Ben Messaoud100% (2)
- Mouth, Throat, Nose, and Sinuses Assessment ChinnyDocument6 pagesMouth, Throat, Nose, and Sinuses Assessment ChinnyXing-Jin Romero0% (1)
- Cranial Neuropathies Guide: Electrodiagnosis and ManagementDocument74 pagesCranial Neuropathies Guide: Electrodiagnosis and ManagementKevin Woodard100% (1)
- Scapula - Elevation and DepressionDocument16 pagesScapula - Elevation and DepressiondulexNo ratings yet
- Deadly Pressure Points GuideDocument34 pagesDeadly Pressure Points Guidemixmanmax100% (1)
- PressurePoints PDFDocument27 pagesPressurePoints PDFMeier CraginNo ratings yet
- Sectioning Hair is Important for Balanced HaircutsDocument6 pagesSectioning Hair is Important for Balanced HaircutsJay Mark PahapayNo ratings yet
- Self-Massage GuideDocument21 pagesSelf-Massage GuideSvitic NataliaNo ratings yet
- 6 Step Qigong BlueprintDocument3 pages6 Step Qigong BlueprintManish SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Master Series Sound and Colour PDFDocument6 pagesThe Master Series Sound and Colour PDFAMIT KUMAR PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Military - Pressure PointsDocument27 pagesMilitary - Pressure PointssujeetpaiNo ratings yet
- 10 Theses On Hsing I ChuanDocument19 pages10 Theses On Hsing I ChuanCasey Palmer Taska100% (3)
- (Ebook - Martial-Arts) Pressure Points - Military Hand To Hand Combat GuideDocument8 pages(Ebook - Martial-Arts) Pressure Points - Military Hand To Hand Combat GuideHotaru6No ratings yet
- CrossBite Lecture Dr. Hadeel AdelDocument10 pagesCrossBite Lecture Dr. Hadeel Adelعمار سعدNo ratings yet
- What Is The Position of The Arm With An Erb's Palsy?: Hide Related Topic DetailsDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Position of The Arm With An Erb's Palsy?: Hide Related Topic DetailsOmar Nayef TaaniNo ratings yet
- Medium-Range Combatives Vital TargetsDocument27 pagesMedium-Range Combatives Vital TargetsAïn' FidyNo ratings yet
- Kyusho Jutsu Black Belt Self Study: Module 2: Top 10 Pressure PointsDocument8 pagesKyusho Jutsu Black Belt Self Study: Module 2: Top 10 Pressure PointsCosmin RaduNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument5 pagesOphthalmologyGudapati Surendranadhchowdhary100% (1)
- Standard Points of Acupuncture For Kyusho ApplicationsDocument18 pagesStandard Points of Acupuncture For Kyusho ApplicationsAndriela LemosNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgical EmergenciesDocument25 pagesNeurosurgical EmergenciesFarah Wahidah Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- Arnett - Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning - Part 2 PDFDocument17 pagesArnett - Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning - Part 2 PDFdeep100% (1)
- Structural Preservation Rhinoplasty: A Hybrid ApproachDocument16 pagesStructural Preservation Rhinoplasty: A Hybrid ApproachAdRiaNa JuLIetH LoZaDa PaTiÑo100% (1)
- Pressure Points - BackDocument1 pagePressure Points - BackJoãoTorresNo ratings yet
- Bujinjutsu NinjutsuDocument3 pagesBujinjutsu NinjutsuDan AndrewNo ratings yet
- Karate TechniquesDocument12 pagesKarate TechniquesveljaNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Acupressure Points To Treat Cold, Flu and FeverDocument16 pagesTop 5 Acupressure Points To Treat Cold, Flu and Feverdlpurpos0% (1)
- Wudang Sword 13 MovesDocument2 pagesWudang Sword 13 MovesUrban DaoistNo ratings yet
- StancesDocument8 pagesStancesMohammed SalmiNo ratings yet
- Bodyweight/Martial Arts Exercises GuideDocument36 pagesBodyweight/Martial Arts Exercises GuideaakritichNo ratings yet
- A Study of Taiji Push-Hands TechniquesDocument7 pagesA Study of Taiji Push-Hands TechniqueseberalejandroNo ratings yet
- Chin Na Grading ListDocument2 pagesChin Na Grading ListRonaldo BriantNo ratings yet
- Ana 211 The Brachial PlexusDocument10 pagesAna 211 The Brachial PlexusAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton Chapter 7Document6 pagesThe Skeleton Chapter 7rheamii18No ratings yet
- Human Spinal Cord Picture C1 To S5 VertebraDocument3 pagesHuman Spinal Cord Picture C1 To S5 Vertebraajjju02No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 14 NotesRhianon Annie McDowellNo ratings yet
- MSK SummaryDocument5 pagesMSK SummaryRahla KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology EditedDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology EditedAya BantuasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument62 pagesSkeletal SystemAlyza AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LMRP 2019Document32 pagesAnatomy LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review Block 1Document32 pagesAnatomy Review Block 1ngNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Forum BackDoneDocument3 pagesAnatomy Forum BackDoneMedShareNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument94 pagesAnatomypshahNo ratings yet
- meningesDocument27 pagesmeningesSefrinmi AyodejiNo ratings yet
- L1-Bones of Upper LimbDocument25 pagesL1-Bones of Upper LimbYakshender AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes SummaryDocument16 pagesBlue Boxes Summaryridin007No ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus Nerve Injury GuideDocument11 pagesBrachial Plexus Nerve Injury GuidecpNo ratings yet
- Ent PPT On Pharyngeal AbscessDocument20 pagesEnt PPT On Pharyngeal AbscessDocwocNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss: Dr. Timothy GacaniDocument21 pagesHearing Loss: Dr. Timothy GacaniGladys MainaNo ratings yet
- Oral Radio Lec 4 FinalDocument11 pagesOral Radio Lec 4 FinalPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal AnatomyDocument38 pagesLaryngeal AnatomyDevender OncogeekNo ratings yet
- Outer Ear Infection (Swimmer's Ear)Document2 pagesOuter Ear Infection (Swimmer's Ear)ScraaaaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Occlusion JipsDocument7 pagesConcepts of Occlusion JipsDRPRIYA007No ratings yet
- Evolve Resources For Illustrated Anatomy of The Head and Neck 5Th Edition Fehrenbach Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesEvolve Resources For Illustrated Anatomy of The Head and Neck 5Th Edition Fehrenbach Test Bank Full Chapter PDFRyanFernandezqxzkc100% (10)
- Tracheostomy Care: PhysiologyDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care: PhysiologyrajirajeshNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Consideration in Oral Implant SurgeryDocument27 pagesAnatomical Consideration in Oral Implant SurgeryMaryam Zanjir50% (4)
- Classsification of RPDDocument37 pagesClasssification of RPDdranandmds100% (2)
- GROUP E - Gingival Stripping in RPDDocument14 pagesGROUP E - Gingival Stripping in RPDmaisarah100% (1)
- AnemiaDocument9 pagesAnemiaManjeevNo ratings yet
- Gradenigos Syndrome A ReviewDocument5 pagesGradenigos Syndrome A ReviewPaola SanchezNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Trauma Le Fort 2Document120 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma Le Fort 2Irene UdarbeNo ratings yet
- Role of Tympanometry in Otosclerosis With A Proposal of New Classification For Type 'As' CurveDocument3 pagesRole of Tympanometry in Otosclerosis With A Proposal of New Classification For Type 'As' CurveHarshit AmbeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral CavityDocument9 pagesLecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral Cavitykasonde bowaNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Preadolecent Management by GowthamDocument53 pagesClass 3 Preadolecent Management by GowthamAbirami scientistNo ratings yet
- Report (Chap 10)Document81 pagesReport (Chap 10)Field StudyNo ratings yet
- Corticospinal Tract - Pyramidal TractDocument52 pagesCorticospinal Tract - Pyramidal TractdrgokuNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Occlusion Variation of Single PosterDocument6 pagesAnalyzing The Occlusion Variation of Single PosterDilara IngecNo ratings yet