Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WBCSD-IEA CementRoadmap Centre Spread Actual Size
Uploaded by
Charlie DeanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WBCSD-IEA CementRoadmap Centre Spread Actual Size
Uploaded by
Charlie DeanCopyright:
Available Formats
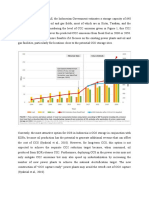
Cement roadmap targets
3
This timeline is based on a set of 38 technology papers developed by the European Cement Research Academy (ECRA) on behalf of CSI, and on IEA modeling and scenario analysis Targets for decrease in energy intensity, 2010-2050
4.0
Energy intensity (GJ / t clinker)
2010
2020
2030
2040
2050
Baseline emissions: 2.34 Gt
Opportunities for CO2 emissions reductions
The BLUE scenario examines the implications of a policy objective to halve global energy-related CO2 emissions in 2050 compared to todays level The outcomes implicit in the BLUE scenario are consistent with a global rise in temperatures of 2C to 3C, but only if the reduction in energy-related CO2 emissions is combined with deep cuts in other greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions A halving of global emissions will mean that the cement industry will need to reduce its current emissions by 18% by 2050
Cement sector CO2 emissions reductions below the baseline, low demand scenario, 2006-2050
2.5
2.33
Baseline high BLUE high
Direct emissions (Gt Co2)
2.22
20 Baseline low
Energy consumption (EJ)
Energy efficiency: 10% : 24% Alternative fuel use and other fuel switching Clinker substitution: 10%
40
Alternative fuel use (%)
37%
Cement to clinker ratio (%)
80 75 70 65 0
3.5 3.0 2.5 0 2010
3.6 3.4 3.2
30 25 20 15 10 5 0 23%
74%
73% 71%
1.88 Gt 12%
5% 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050
CO2 emissions reductions
Biomass and alternative fuels Electricity Oil Coal Natural gas 5 0 2006 2050 10
15
BLUE low
3.9
2.0
35
77%
2.20
100%
1.86
Carbon capture and storage (CCS): 56%
2020
2030
2040
2050
1.5
2010
2020
2030
2040
2050
Acronyms:
Cement to clinker ratio (%)
Targets for alternative fuel use, 2010-2050
40 35
Alternative fuel use (%)
2006
37%
Cement to clinker ratio (%)
2010
20
2015
Baseline high BLUE high 81% Baseline low BLUE low 79% 78%
2020
2025
2030
80 75
77% 73% 71%
Energy consumption (EJ)
30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 5% 12% 23%
74%
15 10
Energy 70 efficiency
65
R&D on fluidised bed technology
Alternative 0 fuel use and 2010 fuel switching Clinker substitution
Cement to clinker ratio (%)
R&D into new grinding equipment and additives 5
2020 2030 2040 2050 0
0 2010
Diffusion of BAT: phase out of wet kilns in OECD Electricity
2020 2030 2040
76% Biomass and alternative fuels Natural gas 2050 Oil
Diffusion of BAT: international standard for new kilns
Diffusion of BAT: phase out of wet kilns in non-OECD
Diffusion of BAT: global energy intensity 3.2-3.4 Gt / t clinker
Ongoing identification and classification of suitable Coal alternative fuels
2006 2050
BAT C.A. 2035 CCS CSI EJ ECRA GJ Gt IEA OECD R&D tCO2
Note: excludes CCS energy use and electricity
2006
Energy consumption (EJ)
15 10 5 0 2006
BLUE low
Targets for decrease in cement to clinker ratio, 2010-2050
80
Cement to clinker ratio (%)
Baseline low
0.5
Cement to clinker ratio: 73%
Cement to clinker ratio: 71%
20
Baseline high
BLUE high Biomass and alternative fuels Electricity Natural gas Oil Coal
Assess substitution material properties and evaluate regional availability
Baseline high BLUE high
2010
Develop international standards on blended cement use
Implement international standards on blended cement use
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
best available technology chemical absorption 2040 carbon capture and storage Cement Sustainability Initiative Exajoule European Cement Research Academy Gigajoule Gigatonne International Energy Agency Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development research and development tonne of CO2
BLUE emissions: 1.55 Gt
2045 2050
All of these technologies need to be applied together if the BLUE scenario targets are to be achieved no one option alone can yield the necessary emissions reductions
Diffusion of BAT: global energy intensity 3.1-3.2 Gt/t clinker
2040
2045
2050
Final energy consumption in the cement sector by scenario, 2006 and 2050
Baseline low
77% 74% 73% 71%
81% 20
Energy consumption (EJ)
79%
75 70 65 0 2010
BLUE low
78%
0
2020 2030 2040 2050
Carbon capture 0 10 and storage 2010 (CCS) 5
0
15
76%
R&D - oxyfueling, gas cleaning: 1st CCS pilot plant
Biomass and alternative fuels Electricity Natural gas Oil Coal
R&D - oxyfueling, gas cleaning: develop oxyfueling and chemical looping Demonstration: 2 chemical absorption demonstration plants Mitigation costs USD/tCO2 cement (post combustion/oxyfueling): 125/na
R&D - oxyfueling, gas cleaning: C.A. energy use to fall to 2.2 GJ/t Deployment: all large new kilns with CCS Demonstration: 3 oxyfuel demos, 3 chemical looping demos Mitigation costs USD/tCO2 cement (post combustion/oxyfueling): 100/60 Commercial use of membrane technology Deployment
Deployment: 50-70 cement kilns with CCS Mitigation costs USD/tCO2 cement (post combustion/oxyfueling): 100/50 Gt captured: 0.11-0.16 Gt; % CO2 captured: 10-12%
Deployment: 100-200 cement kilns with CCS
Deployment: 220-430 cement kilns with CCS Mitigation costs USD/tCO2 cement (post combustion/ oxyfueling): 75/40
2020
2030
2040
2050
2050
2006
2006 2050
2010
2015
2020
2025
2030
2035
2040
2045
Gt captured: 0.5-1.0 Gt ; % CO2 captured: 40-45%
2050
Note: all figures show global average
%)
Research and development (R&D)
Demonstration
Commercialisation
(EJ)
20
The application of CCS increases energy use and hence in the BLUE scenarios energy use rises compared to the Baseline scenarios
Production (Mt cement)
Key regional milestones
This roadmap aims to propose tangible policy recommendations for governments around the world and so is written with a broad, global view However, it acknowledges the wide differences between regions for many aspects of cement industry technology development and implementation. There are differences, for example, in alternative fuel availability, and in building standards enabling or preventing higher clinker substitution It is key that nationally appropriate policies should be developed to reinforce this roadmaps broad recommendations Canada and United States
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 12.4 8% 0.90 0 BLUE low demand 2030 11.4 21% 0.85 4.9 2050 12.3 37% 0.81 21.5 2015 12.2 9% 0.90 0 BLUE high demand 2030 11.3 22% 0.84 9.3 2050 14.2 38% 0.81 43.0
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Producti
2 000
Economies in transition Other developing Asia Latin America
2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050
5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
1 000
Regional cement production
2006 2015 2030 2050 low high low high low high
Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
0
4 000
2006 2006 2015
2015 2030 2030 2050 2050
Other OECD Europe OECD Pacific China India
2006 2006 2015
2015 2030 2030 2050 2050
2006
Africa and Middle East
3 000
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement) Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement) Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt)
2015 19.4 13% 0.77 0
2030 29.9 23% 0.73 23.7
2050 47.4 33% 0.71 99.8
2015 19.6 15% 0.77 0
2030 33.6 27% 0.72 28.8
2050 60.1 35% 0.72 173.1
300 200 100 0
300 200 100 0 2006 2015 2030 2050
300 200 100
300 200 100 2030 2050
2006 300 300
200 200 100 100
300 200 100
2015 high low
2030300 300
300
2050 low high
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
India
BLUE low demand
BLUE high demand
This map and figures show estimated cement production for the years 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050, and regional breakdown of forecast production under BLUE high and low demand scenarios Between 2006 and 2050, cement production is projected to grow by 0.8-1.2% per year, reaching between 3,700 megatonnes (Mt) and 4,400 Mt in 2050. This represents a 43-72% increase compared to production in 2006
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip Union 25 ex ea European commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Regional cement production:
400 2006 2015 2030 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050 2050
2 000
Economies in transition Other developing Asia
Canada and United States
400
OECD Pacific European Union 25
400 400
1 000
Latin America
0 0 Regional cement production: 2006 2015 2030 2006 2015 2050 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050
0 0 0 Regional cement production: 2006 2006 2015 2030 2050 2006 2015 2015 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2030 2030 2050 2050
European Union 25
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 15.5 17% 0.76 0
BLUE low demand 2030 13.3 28% 0.73 4.3 2050 13.7 39% 0.69 20.7 2015 16.5 18% 0.76 0
BLUE high demand 2030 15.7 30% 0.72 9.4 2050 19.0 40% 0.71 69.8
Other developing Asia
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 24.7 11% 0.78 0
Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu Latin AmericaEconomies in transition Other OECD Europefugiat nulla pariatur.
Production (Mt cement) Production (Mt cement) Production (Mt cement) 400 300 200 100 0 400 300 200 100 0 2050 2006 400 300 200 100 0 2030 2006 2015 2050
BLUE low demand 2030 35.1 21% 0.72 21.4 2050 51.2 34% 0.70 100.2 2015 26.3 15% 0.78 0
BLUE high demand 2030 39.4 28% 0.72 21.0 2050 64.5 35% 0.73 150.6
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
Other OECD Europe
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 2.7 19% 0.82 0
BLUE low demand 2030 3.3 30% 0.80 1.7 2050 3.9 39% 0.80 5.5 2015 2.9 21% 0.78 0
BLUE high demand 2030 3.9 30% 0.72 4.6 2050 5.4 40% 0.73 3.7
Economies in transition
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 14.7 14% 0.77 0
SOURCE Regional cement production: 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050
Production (Mt cement)
BLUE low demand 2030 12.7 22% 0.74 1.5 2050 10.8 35% 0.72 12.9 2015 17.9 7% 0.77 0
BLUE high demand 5000
4000 3000 2000 1000 0
15.2 16% 0.74 4.1
16.2 37% 0.72 19.0
Alternative fuel shares presented exclude the additional energy requirement for CCS The CO2 storage figures presented here are based on capture potentials. Additional analysis is needed to verify the storage potential in different regions
2006 Post-2030 global cement 200 200 production will be fuelled by strong 100 100 demand growth in India and other 0 0 2006 2015 2030 2050 developing Asian countries, and in Africa and the Middle East
2015
2030
2050
2006 2015 200 100 0 2006
2030
2050
2006
2015
2030
2015
2030
2050
2006
2015
2030
2050
high demand scenario low demand scenario
high demand scenario
Production (Mt cement)
2030
2050
Cement consumption in China, which currently accounts forOther OECD Europe just Economies in transition under half of total production, is 400 400 expected to peak between 2015 300 300 and 2030, as per capita cement European Union 25 Canada and United States 200 OECD Pacific 200 consumption declines towards 400 100 100 more 400 developed country levels 400
300 300 300
The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply official endorsement or acceptance by the IEA or WBCSD.
2006
2015
2030
2050
2015
2030
2050
OECD Pacific
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 9.7 12% 0.83 0
BLUE low demand 2030 8.2 23% 0.77 4.0 2050 7.5 35% 0.72 15.8 2015 10.3 13% 0.82 0
BLUE high demand 2030 9.5 24% 0.76 7.2 2050 10.7 35% 0.72 38.2
Latin America
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 14.5 16% 0.73 0
BLUE low demand 2030 18.4 25% 0.71 9.7 2050 26.4 39% 0.70 49.7 2015 14.4 16% 0.73 0
BLUE high demand 2030 18.5 25% 2050 32.7 40%
Regional cement production: 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050
Production (Mt cement)
Global cement production: 2006, 2015, 2030 and 2050
5 000 high demand scenario low demand scenario 4 000 Canada and United States European Union 25 Other OECD Europe OECD Pacific China India Economies in transition Other developing Asia Latin America Africa and Middle East 0
Regional cement production: 2006, 0.71 2030 and 2050 2015, 0.72
11.8 73.3 Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed
Other OECD Europe
Production (Mt cement) 400 300 200 100 0 2006 2015 2030 2050
Economies in transition
300 200 100 0
Latin America
Production (Mt cement) 400 300 200 100 0 2006 2015 2030 2050
China
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 118.2 8% 0.72 0
BLUE low demand 2030 66.1 20% 0.69 25.0 2050 53.3 36% 0.68 82.0 2015 118.8 8% 0.71 0
BLUE high demand 2030 85.6 14% 0.69 40.3 2050 76.9 34% 0.70 236.8
Africa and Middle East
Technologies Energy use (Mtoe) Share of alternative fuel use Clinker to cement ratio CO2 captured (Mt) 2015 25.5 11% 0.82 0
Production (Mt cement)
do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
3 000 400
BLUE low demand 2030 30.5 22% 0.77 8.4 2050 47.0 33% 0.74 97.1
Production (Mt cement)
low
high
low
high
low
high
Production (Mt cement)
Production (Mt cement)
2050
400
400
Production (Mt cement)
2006 2006
2015 2015
2030
2050 2030
Production (Mt cement)
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis 2015 nostrud exercitation ullamco 2030 2050 laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea 26.4 commodo consequat. Duis aute 35.3 68.0 irure dolor in reprehenderit in 14% voluptate velit esse35% dolore 25% cillum eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
BLUE high demand
2 000
1 000
180 160 140 120 10 0 80 60 40 20 0
180 160 140 120 10 0 80 60 40 20 0
Canada and United States Other OECD Europe Other OECD Europe
400 400 400
OECD Pacific in transition Africa and Middle East Economies Economies in transition
400 400 400
low
200 200 200
high
00
100 100 100 0 high demand scenario 2050 2050 2006 2015 2015 2030 2030 2030 2050 2006 2006 2015 low demand scenario
5 000 2050
China and United States Canada
European Union 25
1 800
Production (Mt cement)
4 000
Other OECD Europe OECD Pacific
1 600 China
3 000
India 2 000
1 400
Economies in transition Other developing Asia
1 000
Latin America Africa and Middle East
1 200
2006 low
2015 high low
2030 high low
2050 high
1 000
Latin America
400 300 200 100
800
600
400
180 160 140 120 10 0 80 60 40 20 0
Latin Latin Am
400 300 200 100 0 300 200 100
400
0 2006
high d
low de
200
India
800
low demand scenario
2006
2015
2030
2050
600
Production (Mt cement)
400
200
2006
2015
2030
2050
Africa & Middle East
800
Other developing Asia
800
600
European Union 25
400 300 200 100 0
Canada and United States
400 300
600
OECD Pacific
400 300 200 100 0 2006 2015 2030 2050
high demand scenario low demand scenario
0.81
0.76
0.76
21.5
158.7
DO NG KI M D ItE S
European Union 25
Production (Mt cement) 400 300
O W D RL CA S tE tA
200
Canada and United States
Production (Mt cement)
2006 2015 2030
200 200 100
OECD Pacific
Production (Mt cement) 400 300 200 100 0 2006
Global cement production 2006 (total 100%)
A BR 2% L ZI A A AD IN AN C CH % 1% 47 FR 1% CE AN RM GE 1% AN Y A DI IN 6% LY ItA 2% N PA JA 3% M E 2% CO XI S RU 2% SIA
400 2050 300 200 100 0
2006
2015
2030
2050
0 0 2006 2006 20152015 2030 2030 2050 2050
RI AF D H ItE Ut SO UN 5% 1% 0.
UN 4%
F tO ES 5% 200R 7. 2
100 0 2006 2015 2030 2050
2006
2015
2030
2050
2015
2030
2050
180 160 140 120 10 0 80
You might also like
- Trace Elements - Sample Prep ProtocolDocument3 pagesTrace Elements - Sample Prep ProtocolCharlie DeanNo ratings yet
- XRD SlideDocument1 pageXRD SlideCharlie DeanNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical DataDocument1 pageThermochemical DataEsteban Alvarez AguilarNo ratings yet
- Measurements of The Quality of Cement Produced From Looped LimestoneDocument30 pagesMeasurements of The Quality of Cement Produced From Looped LimestoneCharlie Dean100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- European Wholesale Gas MarketDocument37 pagesEuropean Wholesale Gas Marketandreea negrescuNo ratings yet
- Coalinformation PDFDocument566 pagesCoalinformation PDFgiselechavesNo ratings yet
- First Launch Asia CCUS NetworkDocument6 pagesFirst Launch Asia CCUS NetworkEconomic Research Institute for ASEAN and East AsiaNo ratings yet
- National Energy Policy 2018 FinalDocument193 pagesNational Energy Policy 2018 FinalEdwin KhundiNo ratings yet
- Natural GasDocument660 pagesNatural Gasrichardsena100% (2)
- GuarDocument16 pagesGuarAn Đinh Thị ThúyNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Trasnport System GIZDocument88 pagesEnergy Efficiency Trasnport System GIZVarun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- SG Annual Report 2021 CEO Interview Green TransitionDocument46 pagesSG Annual Report 2021 CEO Interview Green Transitionbogdan darcaciuNo ratings yet
- (Harrie Knoef) Handbook Biomass Gasification PDFDocument12 pages(Harrie Knoef) Handbook Biomass Gasification PDFdfiorilloNo ratings yet
- 07 Global Scenarios For Biofuels Impacts and Implications 01Document16 pages07 Global Scenarios For Biofuels Impacts and Implications 01Vaibhav NagoriNo ratings yet
- BS Delhi English 15-06-2023Document18 pagesBS Delhi English 15-06-2023Shreya SinhaNo ratings yet
- (2017) International Energy Agency - World Energy Outlook 2017Document782 pages(2017) International Energy Agency - World Energy Outlook 2017Pedro César VieiraNo ratings yet
- Digital Oil Field (DOF)Document2 pagesDigital Oil Field (DOF)Vibhav Prasad MathurNo ratings yet
- 040329EE04P2Document188 pages040329EE04P2sharathNo ratings yet
- EnergyProviderDeliveredEnergyEfficiency WEBDocument145 pagesEnergyProviderDeliveredEnergyEfficiency WEBPeter ChristensenNo ratings yet
- (RenewX Special) SQ - India Feb-Mar Issue 2023Document68 pages(RenewX Special) SQ - India Feb-Mar Issue 2023Kumaresh RameshNo ratings yet
- Energy Fuel Report Avalara Tax Changes 2023Document15 pagesEnergy Fuel Report Avalara Tax Changes 2023aramsaranNo ratings yet
- Abn Amro August 12th 2016Document15 pagesAbn Amro August 12th 2016ethan100% (1)
- Valuing Wind Farm Assets April 2016Document26 pagesValuing Wind Farm Assets April 2016Dallas DragonNo ratings yet
- Carbon Emission and Tax - Singapore Case (2013)Document23 pagesCarbon Emission and Tax - Singapore Case (2013)Toh Mun HengNo ratings yet
- A Review and Comparative Evaluation of Thermochemical Water SplittingDocument17 pagesA Review and Comparative Evaluation of Thermochemical Water SplittingHEGEL JOHAN RINCON LAURENSNo ratings yet
- Fostering Effective Energy Transition 2022 Edition: Insight Report M A Y 2 0 2 2Document57 pagesFostering Effective Energy Transition 2022 Edition: Insight Report M A Y 2 0 2 2Griselda Meza GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Coal and The Commonwealth WebDocument192 pagesCoal and The Commonwealth WebAndrei LeuNo ratings yet
- NorthStar Kick Off - MasterDocument78 pagesNorthStar Kick Off - MasterDavid AryanNo ratings yet
- Post Covid 19 Market TrendsDocument40 pagesPost Covid 19 Market TrendsKaran Ojha100% (1)
- Zulfiqar Ali MS ThesisDocument136 pagesZulfiqar Ali MS ThesisKamran AhmedNo ratings yet
- CCS and Carbon Capture and Utilization For IndonesiaDocument3 pagesCCS and Carbon Capture and Utilization For IndonesiaFairuz AthallahNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Strategic Management - ChevronDocument66 pagesCase Study - Strategic Management - ChevronThanos PitatzisNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: F. Manzano-Agugliaro, A. Alcayde, F.G. Montoya, A. Zapata-Sierra, C. GilDocument10 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: F. Manzano-Agugliaro, A. Alcayde, F.G. Montoya, A. Zapata-Sierra, C. GilAztec MayanNo ratings yet
- CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion OverviewDocument14 pagesCO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion OverviewFitria Wahyu KurniawatiNo ratings yet