Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nota Kimia
Uploaded by
Muhammad IzzuddinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nota Kimia
Uploaded by
Muhammad IzzuddinCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 12 : OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
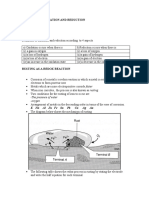
REDOX REACTION Definition of oxidation and reduction according to 4 aspects a) Oxidation occurs when there is (i) a gain in oxygen (ii)a loss of hydrogen (iii)a loss of electron (iv)an increase in the oxidation state RUSTING AS A REDOX REACTION Corrosion of a metal is a redox reaction in which a metal is oxidized by losing electrons to form positive ions Metals which are more electropositive corrode faster When iron corrodes , the process is also known as rusting. Two conditions for the rusting of iron to occur are -The presence of water -oxygen Arrangement of metals in the descending order in terms of the ease of corrosion. K Na Al Zn Fe Sn Pb Cu Ag Au The diagram below shows the mechanism of rusting b)Reduction occurs when there is (i) a loss of oxygen (ii)a gain of hydrogen (iii)a gain of electron (iv)a decrease in the oxidation state
The following table shows the redox process in rusting by stating the electrode and write the half equation for each terminal
Terminal A B
Electrode Anode Cathode
Half-equation FeFe2+ + 2eO2 + 2H2O + 4e- 4OH-
Overall redox equation in rusting : 2Fe(aq) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) Fe(OH) 2(s) Name for the rust : Iron(III) oxide Chemical Formula for the rust : Fe2O3.xH2O, where x varies Three main ways to prevent rusting -by using protective coating -by forming alloys -by using sacrificial metal Three metals that can be used in sacrificial protection for an underground iron pipe -magnesium -aluminium -zinc A reagent that is usually used to detect the presence of iron (II) ion in a laboratory experiment. -Potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) solution THE REACTIVITY SERIES OF METALS AND ITS APPLICATION In the reactivity series, metals are arranged in the order of their reactivity with oxygen The metal at the top of the series is the most reactive. They burn more vigorously and most quickly in oxygen. The more reactive the metal is the more powerful it is as a reducing agent. K Na Mg Al Very Reactive Unreactive Reactivity Decreases Zn Fe Sn Pb Cu Hg Ag Au
Very
When metal X is heated with an oxide of metal Y , metal X will displace metal Y from its oxide if metal X is more reactive than metal Y X + metal Y oxide of X + Y Reactivity Decreases K Na Mg Al C Very Reactive Very Unreactive Zn H Fe Sn Pb Cu Hg Ag Au
If metal remove oxygen from carbon dioxide , the metal is more reactive than carbon
metal + carbon dioxide metal oxide + carbon If hydrogen is more reactive than the metal oxide , the metal oxide, the metal oxide will be reduced to metal hydrogen + metal oxide metal + carbon dioxide Two application of the reactivity series -to predict the possibility of reactions involving metals -to predict the method of metal extraction from its ore.
You might also like
- Chapter 12 Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Redox Reactions Explainedayu_isa85No ratings yet
- Metals Extraction 2Document9 pagesMetals Extraction 2sujana hossainNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Metals Extraction and PropertiesDocument21 pagesMetals Extraction and PropertiesMuhammad UzairNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument10 pagesReactivity SeriesZeedan MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument9 pagesThe Reactivity Series of MetalsTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesDocument14 pagesClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- The Reactivity Series NotesDocument8 pagesThe Reactivity Series NotesTHEVINESHNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesMustafa Khan100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedDocument15 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedCyber Atharv100% (1)
- METALSDocument12 pagesMETALSjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesAzeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening EtcDocument25 pagesCSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening Etcdela2100% (2)
- MetalsDocument7 pagesMetalsritesh kavuruNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument11 pagesMetalsZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: Metals Physical PropertiesDocument10 pagesMetallurgy: Metals Physical PropertiespbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Metals & Non MetalsDocument47 pagesChapter 3 - Metals & Non MetalsRoberto PerisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes LearnITDocument16 pagesChemical Changes LearnITIoana IonNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Document10 pages10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Rishu KaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Metals and Non MetalsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Metals and Non Metalskush96122No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-metalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non-metalsmonkey.luffy.kenNo ratings yet
- Mainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineDocument14 pagesMainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineOrderPlace AccountNo ratings yet
- C13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesDocument39 pagesC13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- Displacement Reactions-Power PointDocument10 pagesDisplacement Reactions-Power PointMuyatwa LiksNo ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesDiyaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals: The Reactivity Series of Metalseugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy 2024Document13 pagesMetallurgy 2024pokeninjazxNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non Metalsbhumika motiyaniNo ratings yet
- Notes_Metals ad Non-Metals_C-XDocument8 pagesNotes_Metals ad Non-Metals_C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument27 pagesThe Reactivity Series of Metals118latelyNo ratings yet
- Metals-and-Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals-and-Non-Metalskebepef613No ratings yet
- The Disintegration of An Engineered Material Into Its Constituent AtomsDocument41 pagesThe Disintegration of An Engineered Material Into Its Constituent Atomsanudeep009No ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 31 OCT CLASS 10 CHEM Chapter-3 NCERT SOLUTIONSDocument13 pages31 OCT CLASS 10 CHEM Chapter-3 NCERT SOLUTIONSgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes ChecklistDocument6 pagesChemical Changes ChecklistJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- D 4-4-chemical-changes-trilogyDocument5 pagesD 4-4-chemical-changes-trilogyishikagajjar123No ratings yet
- DownloadedDocument12 pagesDownloadedAniket shuklaNo ratings yet
- New Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockDocument19 pagesNew Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockAnamikaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes: In-Text Questions Set 1 Page Number 40Document13 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes: In-Text Questions Set 1 Page Number 40Shrihari UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Intermediate 2 Unit 3 (C)Document23 pagesCorrosion: Intermediate 2 Unit 3 (C)Om DhandeNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical ChangesDocument6 pages4.4 Chemical Changesdynamiccosmic7No ratings yet
- Metals IGCSE NotesDocument27 pagesMetals IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Ualikhan. ADocument20 pagesUalikhan. AZhansaya KairatbekkyzyNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series-DisplacementDocument16 pagesReactivity Series-Displacementmeganekokun kawaiiNo ratings yet
- Chap4 - Reactivity of MineralDocument124 pagesChap4 - Reactivity of MineralYeLynTanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Eng - ChemistryDocument32 pagesModule 3 Eng - Chemistrypythondef2000No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pagesChapter - 3: Metals and Non MetalsBharat SavajiyaniNo ratings yet
- Iron Part 2 - Redox PotentialDocument41 pagesIron Part 2 - Redox PotentialHiểu Lam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFKaran Pratap67% (3)
- Metals OlevleDocument9 pagesMetals OlevleaayannisarNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)