Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Sharmini ShankarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Sharmini ShankarCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R.
Buttigieg
Pg. 20
Topic 2 Organic Chemistry
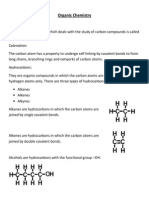
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds, which are found in living things or are derived from living things. The basis of these molecules is carbon chains or rings.
A Homologous series is a family of compounds. E.g. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, fatty acids. Members of a series have: 1. Same general molecular formula, each member differing from the next by CH2. 2. Similar chemical reactions 3. All possess the same functional group 4. Physical properties of members change gradually in the same direction along the series. e.g. melting points and boiling points and density rise as molecular mass increases. Alkanes (CnH2n+1) See GCSE pg. 175, C4U pg. 159 1. Alkanes are hydrocarbons. 2. They have only single bonds between carbon atoms. 3. b.p and m.p. and density increase with chain length i. C1 to C4 are gases at room temperature ii. C5 to C15 are liquids iii. C16 upwards are solids 4. They are volatile compared to ionic compounds. E.g. tar with RMM>500 melts on hot days While NaCl with RMM of 58.5 melts at 808oC 5. Alkanes are found in natural gas and crude oil. 6. Insoluble in water. 7. Soluble in organic solvents like benzene and tetrachloromethane (CCl4) 8. Very unreactive due to strong C-C and C-H bonds. 9. Do not react with metals, aqueous oxidising agents, acids or alkalis. 10. Burn. Combustion is very exothermic so used as fuels. CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Make sure you can draw Methane to decane structures
When there is little oxygen, C and CO form as well as CO2. CO is poisonous so a danger.
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 21
11. Alkanes react with halogens by substitution reactions.
This reaction is catalysed by light (U.V.) and is explosive in bright sunlight. The reaction is slower with bromine. Nothing happens with iodine.
12. Alkanes readily decompose when they are strongly heated, the higher members splitting more readily. This is the basis of cracking. Cracking helps to produce more petrol. High temperatures are used and a catalyst, finely divided aluminium oxide and silicon (IV) oxide speed up the reaction.
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 22
The products of crude oil, which are produced by a specific number of carbon atoms in a hydrogen chain at a particular temperature, are given in this table:
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 23
Answer the following: 1. Which one of the following compounds is not a hydrocarbon? C2H4 C6H12 C2H6O C7H16 C6H6 C10H22 C4H10 C40H82
2. Which one of the compounds below isnt an alkane?
3. Write down a use for each of the following alkanes a. methane: ______________________________________________________________________ b. propane: ______________________________________________________________________ c. octane: _______________________________________________________________________ 4. Write down the equations for burning of: a. methane: ______________________________________________________________________ b. propane: ______________________________________________________________________
Saturated Compounds contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. So alkanes are
saturated hydrocarbons. Compounds which have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms are said to be unsaturated. E.g. alkenes and alkynes. They are called saturated as more atoms can be added to the molecules. Isomers compounds which have the same molecular formula but a different structural formula. E.g. Butane Isobutane
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 24
ETHENE A colourless gas Insoluble in water. It has a faint sweet smell, About the same density as air Burns with a yellow flame (luminous flame) Decolourises bromine water and acidified potassium permanganate. Produced industrially by cracking heavier fractions from crude oil. Laboratory preparation of ethene
Ethene is produced by the dehydration of ethanol by hot, concentrated sulphuric acid. 100cm3 of concentrated sulphuric acid (excess is used) are mixed with 50cm3 of ethanol. This is done slowly and while cooling under running cold water as when the sulphuric acid is mixed with ethanol, a lot of heat is given out. Then some sand (acid washed) is placed in the flask so that the ethene forms on the sand and so avoid frothing. The contents are then heated on a sand-bath to about 180oC. The ethene given off is passed through sodium hydroxide solution to remove impurities (sulphur dioxide and carbon dioxide) and collected over water. The liquid darkens in the flask due to carbon formed by charring.
C2H5OH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) C2H5OH - H2O
C2H5HSO4 (aq) + H2O (l) C2H4
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 25
JL Annual 2006 - Section 1
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 26
Properties of Alkenes (taking ethene as example)
1. More reactive than alkanes due to unstable Carbon-Carbon double bond. 2. Undergo addition reactions due to their double bond. a. With Hydrogen A nickel catalyst at 150oC. Called Sabatiers Reaction Used in hardening oils to make margerine Oils are solidified by reacting them with hydrogen. increases they solidify. This is also called a hydrogenation reaction as hydrogen is added. As their RMM
Ethene
Hydrogen
Ethane
b. With water - e.g. Ethene
With water ethanol is formed. This is the industrial preparation of ethanol. Takes place at 300oC, 60 atm and over a catalysts of phosphoric acid.
Ethene
water
ethanol
3. Ethene is oxidised with acidified or alkaline potassium permanganate
C2H4 + H2O + [O]
CH2OH. CH2OH
Ethan-1,2-diol is used as a coolant in aircraft engines, an antifreeze solution for motor car radiators and in the production of terylene.
4. Ethene burns. C2H4 (g) + 3 O2 (g)
2 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 27
5. Ethene can undergo polymerisation. This happens when molecules of ethene add on to each other to form giant molecules of poly-ethene or polythene. Polythene is a white solid. High temperatures and pressure are needed and a catalyst (trace of oxygen)
6. Ethene is used: to make plastics (polythene, terylene, polystyrene, PVC), ethanol (in methylated spirits), and 1,2-dibromoethane (an important additive in petrol).
JL2006 annual
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 28
Alkynes
These are hydrocarbons which have a triple bond between 2 of the carbon atoms.
Physical properties 1. They are insoluble in water. 2. They are quite soluble in the usual organic solvents of low polarity (e.g. ligroin, ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, etc.). 3. They are less dense than water. 4. Their boiling points show the usual increase with increasing carbon number. 5. They are very nearly the same as the boiling points of alkanes or alkenes with the same carbon skeletons. Chemical properties They burn in air to produce carbon dioxide and water . The ethynes are highly dangerously explosives when mixed with air or oxygen.
They undergo addition reactions.
Naming alkynes
Number of Carbons Ethyne
Chemical formula
Structural formula
Propyne
Butyne
The alkynes are said to be unsaturated because of the existence of a multiple bond in the molecule. The general structure of the alkyne series of hydrocarbons is CnH2n-2.
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 29
1. Copy and complete the following on the HW copybook.
Hydrocarbons are compounds containing the elements _______________ and ______________. If they are saturated, the atoms of carbons are bound together by _________________ bonds. On the other hand, unsaturated hydrocarbons include at least one _______________ or _______________ bond. One example of unsaturated hydrocarbons is _________________. This compound burns in a plentiful supply of air to produce ________________________ and _________________. It also reacts with bromine water changing the colour of the solution from _________________ to _________________. (5 marks) 2. The statements below describe the chemistry of carbon and some of its compounds. Write brief notes to show that you understand the meaning of these statements with particular reference to the underlined terms.
3. This question concerns the laboratory preparation of ethene and its properties.
a) Ethene can be prepared in the laboratory by dehydration of ethanol. Explain this statement, including essential conditions and an equation for the reaction. (A diagram is not required). (6 marks)
b) Ethene undergoes a number of addition reactions such as halogenation, hydration and hydrogenation. For each of these addition reactions, (i) name the substance that adds on the ethene, (ii) give an equation for the reaction. (9 marks) c) Ethene burns with a smoky flame. Give a reason for this observation and write an equation for the reaction. (3 marks) d) Give two uses of ethene. (2 marks)
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 30
Alcohols (see Chemistry for You pg. 178 182, GCSE pg. 203)
These contain the OH group. The OH group hydroxyl group does not form hydroxide ions in solution. Alcohols are NOT alkaline. Naming alcohols Number of Carbons Methanol Chemical formula Structural formula
Ethanol
Propanol
Alcoholic drinks contain ethanol. Thats what makes them alcoholic. So beer, wine and whisky all contain ethanol. If alcohol is taken in excess it: Slows down our reactions Makes us overconfident Damages the liver Is addictive Laboratory Preparation of Ethanol - by fermentation Sugar is dissolved in water. Some yeast is added. The mixture is put in a conical flask. A delivery tube leads to a test-tube containing calcium hydroxide solution (lime-water). The flask is left in a warm place for several days. The contents in the flask begin to froth. A gas is given out. When it is bubbled through the calcium hydroxide solution, this turns milky, indicating it is carbon dioxide. C12H22O11 (s) + H2O (l) sugar C6H12O6 (aq) 2 C6H12O6 (aq) glucose
2 C2H5OH (aq) + 2 CO2 (g)
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 31
These two reactions happen through the action of yeast. After several days the contents are found to contain between 5 and 10% ethanol. Pure ethanol can be obtained by fractional distillation. Ethanol can be tested by burning as it burns easily with a pale yellow flame. Industrial Preparation of Ethanol Ethene is reacted with steam to form ethanol.
o
C2H4 (g) + H2O (l)
C2H5OH (aq)
Temp: 300 C Pressure: 65 atm Catalyst: Phosphoric Acid Properties of Ethanol 1. Miscible with water 2. Colourless liquid (b.p. 78oC) 3. Very good solvent for molecular substances 4. Burns very easily with a pale yellow flame C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) 2 C2H5OH (l) + Na (s) is ionic: C2H5O- Na+ 6. Ethanol reacts with phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5 C2H5OH (l) + PCl5 (l) C2H5Cl (g) + POCl3 (l) + HCl (g) It is a vigorous reaction in which steamy fumes of hydrogen chloride are formed. 7. Ethanol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid that acts as a dehydrating agent. a. If it is in excess at a temperature of 180oC C2H5OH - H2O 2 molecules of ethanol. 2 C2H5OH - H2O C2H5OC2H5 ethoxyethanoate C2H4 b. If it is in excess at a temperature of 145oC only 1 molecule of water is extracted from 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l) 2 C2H5ONa (aq) + H2 (g)
5. Ethanol reacts with sodium. Hydrogen gas is given off.
If the excess ethanol is evaporated, sodium ethoxide is obtained as a white solid. Sodium ethoxide
Work these out on your copybook - Chemistry For You Pg. 185 numbers 1, 2 Pg. 254 numbers 11, 14, 15; Pg. 255 numbers 16, 19
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 32
8. Ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid to form an ESTER C2H5OH (l) + CH3COOH (l) CH3COOC2H5 (l) + H2O (l)
To make an ester, we use: 4 cm3 of ethanol 2 cm2 ethanoic acid, some concentrated sulphuric acid some antibumping granules. The contents are heated under reflux in a water bath for 25 minutes, then poured in a brine solution. Oily drops are seen on the surface smelling of pear drops. This is the ester ethyl ethanoate. 9. Ethanol can be oxidised to ethanoic acid, if we use acidified potassium dichromate as an oxidising agent. The ethanol is oxidised to ethanoic acid. C2H5OH (l) + 2 [O] The orange potassium dichromate turns to green. The experiment is performed in the following way: Mix ethanol with acidified potassium dichromate. Heat under reflux for 15 minutes. Fractionally distillate the contents to obtain ethanoic acid. Wine goes sour as the ethanol in it is oxidised to ethanoic acid (vinegar). The oxidation is catalysed by enzymes in the wine, using oxygen from the air Esters have a pleasant fruity smell. They are found in fruit, flowers and are used in perfumes. Fats are complex esters. CH3COOH (l) + H2O (l)
See GCSE Chemistry, page 208, 209 pg. 208 no. 2 Work out Pg. 276 no. 76 Pg. 277 no. 78, 80
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 33
Number of Carbons 1
Alkanes
Alkenes
Alkynes
Organic Acids
An organic compound is an acid if it has the COOH group. This COOH is called a carboxyl group. Acid Ethanoic acid Chemical formula Chemical Structure
Propanoic Acid.
Properties 1. These acids are weak acids. i.e. they are not fully dissociated in solution. CH3COOH (aq) CH3COO- (aq) + H+ (aq)
2. When pure they are not acidic, since it is in water that they break up into ions. 3. Ethanoic acid is a weak electrolyte. Like all acids, it reacts with metals, alkalis and carbonates. 2 CH3COOH (aq) + Ca (s) CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) 2 CH3COOH (aq) + Na2CO3 (s) (CH3COO)2 (aq) + H2 (g) CH3COONa (aq) + H2O (g) 2CH3COONa (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (g)
Laboratory preparation of ethanoic Acid see previous page oxidation of ethanol
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 34
Synthetic Polymers
These can be either addition or condensation polymers.
Addition Polymers Polystyrene poly(phenyl ethene)
Perspex
Note: The above are addition polymers. Units are added together as the monomers are unsaturated. The polymer than gives a saturated product.
Condensation Polymers Nylon
Terylene
Note: i. Formation of the above polymers requires two types of monomer molecules, each with two reactive groups. ii. Each time a bond is formed, a small molecule such as water is removed.
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 35
Answer the following questions: 1. The following represent two monomers, which react together to form a polymer. H2N - NH2 COOH - COOH
a. Name the type of polymerisation ______________________________ b. What is the substance lost during polymerisation ________________________ c. Draw a diagram to show the structure of the polymer formed from, at least three monomers.
d. Give the name of one example of this type of polymer. ______________________ e. Another type of polymer, poly(chloroethene), is formed by the polymerisation of chloroethene. The following diagram represents part of the poly(chloroethene chain). - CH2 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH | | | | Cl Cl Cl Cl Draw a diagram to represent a single molecule of chloroethane
JL Annual 2001 Past paper questions related to organic chemistry 2
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg
Pg. 36
JL Annual 2002 Past paper questions related to organic chemistry 3
JL Annual 2001 Past paper questions related to organic chemistry 4
You might also like
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDocument23 pagesChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundMudzaffar Shah100% (3)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon TerminologyDocument16 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon Terminologyakusabrina2012No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - ThermochemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 13 - ThermochemistryvaogerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 ExperimentDocument15 pagesChemistry Paper 3 ExperimentTan Yi Ning100% (3)
- Short Note Chemistry Forn 5-Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument16 pagesShort Note Chemistry Forn 5-Chapter 2 Carbon Compoundssalamah_sabri100% (10)
- Chemistry Form 5Document3 pagesChemistry Form 5alliey75% (8)
- WAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Document35 pagesWAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Safwan MazlanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compound SPM ExerciseDocument6 pagesCarbon Compound SPM ExerciseAnuar NasriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersDocument12 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersOrkid Fazz89% (9)
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9Nadira AtiqahNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2Document11 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2kslpeter87No ratings yet
- Carbon Compound SPM Form 5Document12 pagesCarbon Compound SPM Form 5Azie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Past Year Questions AnalysisDocument36 pagesThermochemistry Past Year Questions AnalysisdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument80 pagesSPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsManisha Sekaran MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument25 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDocument22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL METALS & ALLOYSDocument3 pagesINDUSTRIAL METALS & ALLOYSChloeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Document2 pagesChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 NotesDocument10 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 NotesPrakash VeenPunk100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 3 Oxidation and Reduction 2014Document97 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 3 Oxidation and Reduction 2014Cheah Foo Kit33% (3)
- Chapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Document5 pagesChapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Revision SheetsDocument26 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Revision SheetsPanagiotis ScordisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Document9 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Science Notes Form 4Document15 pagesScience Notes Form 4Raychel Leong100% (2)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Document15 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Helene_mbbt100% (9)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Document24 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9dinda syi100% (18)
- SPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS: CHEMICAL BONDING PAPER 2Document11 pagesSPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS: CHEMICAL BONDING PAPER 2Luna LatisyaNo ratings yet
- Mas SPM 2012Document218 pagesMas SPM 2012fizzykolaNo ratings yet
- Technique To Answer Biology Paper 3Document6 pagesTechnique To Answer Biology Paper 3李友志100% (1)
- Exercise On Chemical Composition of The CellDocument7 pagesExercise On Chemical Composition of The CellNorliyana Ali100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionDocument23 pagesChemistry Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionAbdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 RevisionDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 RevisionAyu YunusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Document5 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds (Good)Document6 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds (Good)Everest Lim Yong KeanNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument15 pagesBlood Circulation and Transportqas1727No ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 2Document38 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2Azie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble TeacherDocument24 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble Teacherangie0812No ratings yet
- Short Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumerDocument4 pagesShort Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 5 Chemical For Consumersalamah_sabri100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Understanding States of Matter and Chemical BondingDocument46 pagesUnderstanding States of Matter and Chemical Bondingsaz14No ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Tingkatan, 5 Rate of Reaction ExerciseDocument7 pagesSPM Kimia Tingkatan, 5 Rate of Reaction Exerciseryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Biology SPM 2020 Model Answers For Predicted QuestionsDocument30 pagesBiology SPM 2020 Model Answers For Predicted Questionskumarantuition100% (1)
- Form 4 Science Chapter 2: Body Coordination (38Document13 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 2: Body Coordination (38Cheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Kbat Kimia SPMDocument9 pagesKbat Kimia SPMZanariah Binti Lihat67% (6)
- Paper 6 Chemistry General NotesDocument5 pagesPaper 6 Chemistry General NotesMiran El-MaghrabiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 5 Form 5 KSSMDocument81 pagesChemistry Chapter 5 Form 5 KSSMnoorsuriatiNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Document151 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Cikgu Faizal100% (15)
- 17.5 To 17.8 Organic Chemistry Notes-2Document7 pages17.5 To 17.8 Organic Chemistry Notes-2ahmedNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Basics: Hydrocarbons, Alcohols & AcidsDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basics: Hydrocarbons, Alcohols & AcidsEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryNivas KaruppananNo ratings yet
- Igcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesDocument9 pagesIgcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesJamiu Yusuf AsukuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Organic Chemistry ConceptsDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Organic Chemistry ConceptsYoviNo ratings yet
- SS2_HydroCarbonDocument35 pagesSS2_HydroCarbonnou242320058No ratings yet
- ALCOHOLS_summary_21 02 2024Document7 pagesALCOHOLS_summary_21 02 2024Chantal EttaNo ratings yet
- Ogranic Chemistry (FULL NOTES) - 1Document11 pagesOgranic Chemistry (FULL NOTES) - 1Ali NyallNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkenesDocument5 pagesReactions of AlkenesJâmãçy BräthwåítèNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSC Full Notes BEST NOTESDocument83 pagesChemistry HSC Full Notes BEST NOTESiloverabows100% (5)
- IVAN Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesIVAN Organic ChemistryYoviNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Mod 1 AlkenesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Mod 1 AlkeneskerisweetNo ratings yet
- BREF Glass Manufacturing Industry enDocument323 pagesBREF Glass Manufacturing Industry enAleINo ratings yet
- Richard P Feynman-Surely Youre Joking MR Feynman v5Document3 pagesRichard P Feynman-Surely Youre Joking MR Feynman v5Anonymous Nayak0% (1)
- Seeing NPR Material From The Mechanic Point of ViewDocument14 pagesSeeing NPR Material From The Mechanic Point of View施元No ratings yet
- Thesis EliseCamilleChevallier Welding Plastic Strain PDFDocument211 pagesThesis EliseCamilleChevallier Welding Plastic Strain PDFHui DaiNo ratings yet
- The Separation and Examination of Stickies: Standard Practice ForDocument5 pagesThe Separation and Examination of Stickies: Standard Practice Forjamaljamal20No ratings yet
- Building Construction 2. Masonry: Civil Engineering Materials and ConstructionDocument55 pagesBuilding Construction 2. Masonry: Civil Engineering Materials and ConstructionGautam ChandraNo ratings yet
- 20 Things You Can Do With Graphene: ApplicationsDocument4 pages20 Things You Can Do With Graphene: ApplicationsEmilio Lecaros BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Sds Sodium HydroxideDocument11 pagesSds Sodium HydroxideusenuyaNo ratings yet
- Choice of Specifications and Design Codes For Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument12 pagesChoice of Specifications and Design Codes For Duplex Stainless SteelsRonald Leyva GiraldoNo ratings yet
- TDS Byk-024 enDocument2 pagesTDS Byk-024 enHiroshi PhanNo ratings yet
- Exel International Group IncDocument56 pagesExel International Group InccristopherNo ratings yet
- Bag Filter CalculationDocument2 pagesBag Filter Calculationjenifferrayen71% (7)
- Compaction RegisterDocument73 pagesCompaction Registersuraj ChinttuNo ratings yet
- Making Magnesium Sulfate CrystalsDocument2 pagesMaking Magnesium Sulfate CrystalsHector CabezasNo ratings yet
- Wire Reinforcement InstituteDocument6 pagesWire Reinforcement InstituteVu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Davies Epoxy Enamel Coating GuideDocument2 pagesDavies Epoxy Enamel Coating GuideStanley Saavedra100% (1)
- 05 PDFDocument491 pages05 PDFNatasha Mgt JoharNo ratings yet
- 10 PackedColumnDesignDocument68 pages10 PackedColumnDesignMy best Of bestNo ratings yet
- Tankguard StorageDocument5 pagesTankguard StorageBiju_PottayilNo ratings yet
- Geotechnics With GeosyntheticsDocument24 pagesGeotechnics With GeosyntheticsAnonymous VeDNBhNo ratings yet
- Resistance Wire: Properties of Major AlloysDocument2 pagesResistance Wire: Properties of Major Alloysyasir127No ratings yet
- The Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFDocument4 pagesThe Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFLBNo ratings yet
- How Biomechanics Can Affect The Endodontic Treated Teeth and Their Restorative ProceduresDocument15 pagesHow Biomechanics Can Affect The Endodontic Treated Teeth and Their Restorative ProceduresEdward AbadiaNo ratings yet
- Cement Technology: ReclaimerDocument17 pagesCement Technology: ReclaimerYana Damayanti100% (1)
- Mod 2 BA PhysicsDocument412 pagesMod 2 BA PhysicsBenitoKameloNo ratings yet
- DivyaDocument10 pagesDivyadivya0103No ratings yet
- Elektroenerģētikas TehnoloģijasDocument6 pagesElektroenerģētikas TehnoloģijasMihails LarionovsNo ratings yet
- Paroc Extra: Product DatasheetDocument2 pagesParoc Extra: Product Datasheetturkertalayman1660No ratings yet
- Georgia Department of Public Health Environmental Health SectionDocument8 pagesGeorgia Department of Public Health Environmental Health Sectionjclark13010No ratings yet
- Hooke's Law: The Extension Is Directly Proportional To The Stretching Force (Load)Document2 pagesHooke's Law: The Extension Is Directly Proportional To The Stretching Force (Load)Shalini KulshresthaNo ratings yet