Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simultaneous Equations: M N N M
Uploaded by
HadibahHarunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simultaneous Equations: M N N M
Uploaded by
HadibahHarunCopyright:
Available Formats
18
SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS
1. Solve the following simultaneous equations:
2
4
1
= + m n , n m 4 12
2
=
2. Solve the simultaneous equations : 0 5 2 , 3 2 = + = + y xy y x
Give your answers correct to three decimal places.
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
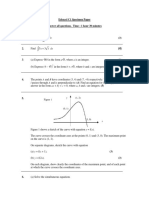
3. Sketch the graph of x y 2 cos 4 = for t 2 0 s s x .
By using the same axes, draw a suitable straight line to find the number of solutions to the
equation 3 2 cos 4 = x
x
t
for t 2 0 s s x . Hence state the number of solutions.
4. (a) Prove that x
x x
2 sin
cot tan
2
=
+
.
(b) (i) Sketch the graph of x y 2 sin = for
t s s x 0
.
(ii) Hence, using the same axes, sketch a suitable straight line to find the
number of solutions for the equation 0
2 cot tan
4
= +
+ t
x
x x
for
t s s x 0
.
State the number of solutions.
19
LINEAR LAW
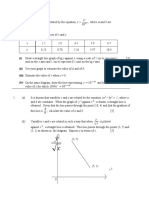
5. Use the graph paper to answer this question.
Table 5 shows the experimental values of two variables, x and y, that are related by the
equation abx ax y + =
2
, where a and b are constants .
x 1 2 3 4 5
y 5.0 18.4 39.5 69.2 106.9
Table 5
(a) Plot
x
y
against x, using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x - axis and 2 cm to 2 unit
on the
x
y
- axis . Hence, draw the line of best fit
(b) Use the graph in 5(a) to find the value of
(i) a,
(ii) b.
6 Use graph paper to answer this question.
Table 6 shows the values of two variables, x and y obtained from an experiment. Variables
x and y are related by the equation
k
x h y ) 1 ( + = , where h and k are constants.
x 1 2 3 4 5 6
y 5 6.5 7.8 8.9 10 10.9
Table 6
(a) Based on table 2, construct a table for the values of log
10
y and log
10
( x +1)
(b) Plot log
10
y against log
10
( x +1) by using a scale of 2 cm to 0.1 unit on both axes.
Hence, draw the line of best fit.
(c) Use the graph in 6 (b) to find the value of
(i) h
(ii) k .
20
INTEGRATION
7. Diagram 7 shows part of the curve y = 4 x
2
which passes through point A (1, 3 ).
(a) Find the equation of normal to the curve at the point A.
(b) Find the area of the shaded region.
(c) The shaded region is revolved through 360
0
about y -axis.
Find the volume generated, in terms of t .
Diagram 7
O
y
x
y = 4 x
2
A (1, 3)
y = 3
21
8. Diagram 8 shows the curve 3
2
+ = x y intersects the straight line AC at point B.
It is given that the equation of straight line AC is y + x = 9 and the gradient of the curve
at point B is 4.
Find
(a) the value of k,
(b) the area of the shaded region P,
(c) the volume of revolution, in terms of t , when the shaded region Q is rotated
through 360
o
about the x axis .
9. (a) In a study conducted on a group of graduates, it is found that 75% of them
succeeded in gaining employment after graduation.
(i) If 15 graduates are chosen at random, find the probability that there are at
least 13 graduates employed after graduation.
(ii) If the standard deviation of the employment of the graduates is 10.2,
calculate the number of graduates who participated in this study.
(b) The mass of 2500 students of Excellent College is normally distributed with
mean 58 kg and standard deviation 15 kg .
Calculate
y
Diagram 8
A
O
P
C
x
k
B
Q
3
2
+ = x y
9 = + x y
22
(i) the number of students whose mass is more than 85 kg,
(ii) the value of w, given that 10% of the students have a mass of
less than w kg.
10. (a) X is a discrete random variable such that X ~ B (n, p). Given that the mean and
the variance are 24 and 6 respectively. Find
(i) the value of p and n,
(ii) P(X 20).
(b) The masses of papaya harvested from a papaya orchard has a normal distribution
with a mean of 750 g and a standard deviation of 80 g.
.
(i) If a papaya is chosen at random from that orchard, calculate the probability that
its mass is in between 720 g and 770 g.
(ii) In a particular day, 2000 papayas were plucked from the orchard. Estimate the
number of papayas with mass between 720 g and 770 g.
(Round up your answer to the nearest integer)
23
VECTORS
11. Diagram 11 shows a triangle OPQ. E is a point at PQ where PE : EQ = 1 : 2 and F is the
midpoint of OQ. The line OE intersects with PF at point G. Given OP = x 3 and
OQ = y 6 .
(a) Express in terms of x and / or y
(i)
OF ,
(ii)
OE .
(b) (i) Given
= PF h PG , state
OG in terms of x h, and y .
(ii) Given
= OE k OG , state
OG in terms of x k, and y .
(c) With using both
OG from (b), find the value of h and k
P
G
O
E
Q
Diagram 11
F
24
12 Diagram 12 shows two triangles, OAB and OMW . Point M lies on AO. Line AB and
line MW intersect at point T .
It is given that OM =
3
1
OA , AT = AB
4
3
,
~
12a OA =
and
~
4b OB =
(a) Express in terms of
~
a and
~
b
(i)
AT
,
(ii)
MT
.
(b) Given that MW = h MT and OB k OW = where h and k are constants.
Find the value of h and of k.
Diagram 12
W
O
M
A T
B
25
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
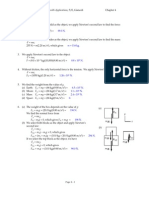
13. Diagram 13 shows a quadrilateral PQRS.
Diagram 13
Calculate,
(a) the length of QS,
(b) QPS Z ,
(c) the area of the quadrilateral PQRS,
(d) the perpendicular distance from Q to PS.
14 Diagram 14 shows a quadrilateral PQRSand PQR Z is acute.
S
12 cm
8 cm
58
o
128
o
7.5 cm
P
Q
R
P
Q
R
S
10.2 cm
15.3 cm
8.7 cm
11.6 cm
o
42
Diagram 14
26
(a) Calculate
(i) PQR Z ,
(ii) PSR Z ,
(iii) the area , cm
2
, of quadrilateral PQRS.
(b) Another triangle ' ' ' R Q P has the same measurements as triangle PQR, that is,
= ' ' R P 15.3 cm, = ' ' R Q 11.6 cm and
o
R P Q 42 ' ' ' = Z , but it is different in shape
to triangle PQR.
(i) Sketch the triangle ' ' ' R Q P ,
(ii) State the size of ' ' ' R Q P .
INDEX NUMBER
15.. Table 15 shows the prices and the price indices with the weightage for three
components, A, B and C respectively.
Component
Prices/(RM)
Price index for the year 2007
based on the year 2005
Weightage
2005 2007
A 27.00 29.70 x 7
B y 42.00 125 4
C 17.50 z 130 5
Table 15
(a) Find the value of x, y and z.
(b) Calculate the composite index for all the components in 2007 based on
the year 2005.
(c) The three components are used to make P. P is sold at the price RM210
in the year 2005, find the selling price of P in the year 2007
(d) The cost of making P is expected to increase by 70% from the year 2007 to the
year 2010. Find the expected composite index for the year 2010 based on the
year 2005.
27
16 Table 16 shows the price indices and weightage of usage of four items K, L, M and N,
which are the main ingredients in the production of a type of cake.
Item
Price index for the year 2005 based on the year 2003
Weightage
K
190 4
L
120 2
M
x 3
N
220 5
Table 16
(a) Calculate
(i) the price of L in the year 2003 if its price in the year 2005 is RM 24,
(ii) the price index of K in the year 2005 based on the year 2001 if its price index
in the year 2003 based on the year 2001 is 120.
(b) The composite index of the cost of cake production for the year 2005 based on the year
2003 is 165.
Calculate
(i) the value of x,
(ii) the price of a cake in the year 2003 if the corresponding price in the year 2005 is
RM 32.50.
28
LINEAR PROGRAMMING
17. A whole sale company plans to sell cakes and biscuits in packets. Every packet A
contains 100 pieces of cakes and 80 pieces of biscuits. Whereas every packet B contains
60 pieces of cakes and 120 pieces of biscuits. To gain profit, the company has to fulfill
the following conditions:
I: Cakes being sold must not exceed 6600 pieces.
II: Biscuits being sold must not less than 4800 pieces.
III: The total number of packet B must be at least 2 times of the total number of
packet A.
(a) If x and y represent packet A and packet B respectively, state three inequalities other
than x> 0 and y>0, that satisfy all the above conditions.
(b) By using a scale of 2 cm to 10 units on both axes, draw and shade the region R that
satisfies the conditions above.
(c) Based on your graph, answer the following questions:
(i) Find the range of the number of packet B that is sold if the number of packet
A being sold is 15.
(ii) For each packet A and packet B being sold, the company will make a profit of
RM 50 and RM 25 respectively. Calculate the maximum profit that the
company will gain.
18. A Mathematics Club intends to sell two types of souvenirs , type P and type Q. The
Mathematics Club sells x units of souvenirs of type P and y units of souvenirs of type
Q,based on the following constraints:
I: The total number of souvenirs to be sold is not more than 150.
II: The number of souvenirs of type Q is at least half the number of souvenirs of type P
.
III: The number of souvenirs of type Q exceeds the number of souvenirs of type P by
at most 80.
(a) Write three inequalities , other than x > 0 and y > 0, which satisfy all the above
constraints.
29
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 20 souvenirs on both axes, construct and shade the region R
which satisfies all the above constraints.
(c) Use the graph constructed in 15 (b), to find
(i) the maximum number of souvenirs of type P sold if 50 souvenirs of type Q
are sold.
(ii) the maximum profit obtained if the profit from the sale of one souvenir of type
P is RM3 and the profit from the sale of one souvenir of type Q is RM5.
END OF MODULE
You might also like
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- SPM 2010 Paper 2Document3 pagesSPM 2010 Paper 2kysimNo ratings yet
- Negeri Sembilan 2010 P2Document5 pagesNegeri Sembilan 2010 P2kysimNo ratings yet
- F5 Am (CLB 2020-08)Document3 pagesF5 Am (CLB 2020-08)wickeromg12No ratings yet
- Edexcel C1 Specimen Paper Answer All Questions. Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument3 pagesEdexcel C1 Specimen Paper Answer All Questions. Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Novdec 2018 C-MathsDocument5 pagesNovdec 2018 C-MathsPreciousNo ratings yet
- O Level Mathematics Practice 2019Document10 pagesO Level Mathematics Practice 2019Atukunda EdwinNo ratings yet
- C4 Solomon J Question PaperDocument4 pagesC4 Solomon J Question PaperSachitra WijethungaNo ratings yet
- Pastpaper DoubtsDocument34 pagesPastpaper DoubtsArishaNo ratings yet
- PA CombinedDocument9 pagesPA CombinedumbfkamaldeenNo ratings yet
- QP G11 MathematicsDocument10 pagesQP G11 Mathematicsmourees karanNo ratings yet
- Higher Maths Prelim 2004Document17 pagesHigher Maths Prelim 2004StephenMcINo ratings yet
- Linear Law QuestionDocument13 pagesLinear Law QuestionFardeena DaniaNo ratings yet
- Cssa of NSW Cssa of NSW Cssa of NSWDocument5 pagesCssa of NSW Cssa of NSW Cssa of NSWTuan Brendan HoangNo ratings yet
- Test 5Document2 pagesTest 5hNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision Test2Document4 pagesIGCSE Revision Test2yslnjuNo ratings yet
- Quiz: Form 4 Revision: FX X GFX X G FX X GX Abx GF GF X X XDocument4 pagesQuiz: Form 4 Revision: FX X GFX X G FX X GX Abx GF GF X X XsewcinNo ratings yet
- First 3 Non Calculator, Next 7 Calculator: Diagram Not To ScaleDocument4 pagesFirst 3 Non Calculator, Next 7 Calculator: Diagram Not To ScaleV NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Plane Coordinate GeometryDocument30 pagesModule 3 Plane Coordinate GeometryjeanNo ratings yet
- 25.1.2020 Maths TenDocument2 pages25.1.2020 Maths TenYe Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- EC1sh ADocument4 pagesEC1sh Ashah143No ratings yet
- As Cham 2002Document4 pagesAs Cham 2002Yon Seo YooNo ratings yet
- Form IV Mathematics SeriesDocument12 pagesForm IV Mathematics SeriesEmmanuel R. Siwila100% (1)
- Solomon G QP - C1 Edexcel PDFDocument4 pagesSolomon G QP - C1 Edexcel PDFkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Solomon G QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon G QP - C1 EdexcelMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Practice Set 12Document6 pagesAdd Maths Practice Set 12Athanaseus ShazamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Questions (TheoryDocument4 pagesMathematics Questions (TheoryAbdulbaasit IN CRYPTONo ratings yet
- 1st SPM TRIAL F5Document9 pages1st SPM TRIAL F5Justin NgoNo ratings yet
- S.6 Math 1Document3 pagesS.6 Math 1Ahebwa DaliousNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 AM - 2022 EYE Revision - TopicalDocument6 pagesSec 3 AM - 2022 EYE Revision - TopicalTeo Yen Teng Phoebe (Cchms)No ratings yet
- MBABAZI RODNEY Principal Maths PDFDocument6 pagesMBABAZI RODNEY Principal Maths PDFMbabazi RodneyNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiaryshah143No ratings yet
- Tarea 5Document2 pagesTarea 5Edgar Ernesto Granados BetancourtNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledEremu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Prediction Paper 2 Summer 2023Document37 pagesPrediction Paper 2 Summer 2023PANo ratings yet
- Wakissha Mock 1 2016Document3 pagesWakissha Mock 1 2016Kwomu JosephNo ratings yet
- Revise 3Document88 pagesRevise 3Aisha QasimNo ratings yet
- C4 Parametric Equations 1 QPDocument4 pagesC4 Parametric Equations 1 QPLouie BalouieNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Math - EnglishDocument13 pages2019 - Math - EnglishAhmad Abed Al FattahNo ratings yet
- PureMaths1978 Pastpaper P2Document3 pagesPureMaths1978 Pastpaper P2wltfNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1khatua.deb87No ratings yet
- DHS H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesDHS H2 2021 Prelim P1猪猪侠No ratings yet
- PureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2Document4 pagesPureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2wltfNo ratings yet
- P1Document5 pagesP1MohPlaysNo ratings yet
- 1406 C4 June 2014 OkDocument8 pages1406 C4 June 2014 Okkostas kNo ratings yet
- Test1 (Revision)Document47 pagesTest1 (Revision)hehey321No ratings yet
- 2023 Consolidation of Year 12 Work For Year 13Document8 pages2023 Consolidation of Year 12 Work For Year 13isobelhandleyNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C4: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiarySachitra WijethungaNo ratings yet
- Linear LawDocument4 pagesLinear LawJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Difficult Add MathDocument5 pagesDifficult Add MathAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- HCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoDocument7 pagesHCI 2023 H2 Maths PromoMarcus LinNo ratings yet
- St. Konrad Integrated Vocational School P. O Box 946, Kabale-Uganda S.4 MathematicsDocument3 pagesSt. Konrad Integrated Vocational School P. O Box 946, Kabale-Uganda S.4 MathematicsTumusiime osagyefo Johnbosco AdyeeriNo ratings yet
- 2014 PureDocument20 pages2014 PuremiryanamhNo ratings yet
- A B A+ B A B: Class - 9 Pre - Final Exam Mathematics Section - ADocument4 pagesA B A+ B A B: Class - 9 Pre - Final Exam Mathematics Section - ASubhajit RoyNo ratings yet
- 2001 CE A Math - NSSDocument5 pages2001 CE A Math - NSSConstance SinNo ratings yet
- AS Pure Practice Paper M7Document8 pagesAS Pure Practice Paper M7junksNo ratings yet
- ALEVEL Math Pepr 2 Set 11Document2 pagesALEVEL Math Pepr 2 Set 11Maama PhionaNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C2: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C2: GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiary007salmanNo ratings yet
- Betty Blue Eyes Kotta PDFDocument306 pagesBetty Blue Eyes Kotta PDFCsóka Anita83% (6)
- Scriptcase MacrosDocument6 pagesScriptcase MacrosMeliana WangNo ratings yet
- EASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanesDocument120 pagesEASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanessnorrigNo ratings yet
- PURL Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesPURL Questions and AnswersSHAHAN VS100% (5)
- 10 TazmahalDocument12 pages10 TazmahalSifat E Noor SahibaNo ratings yet
- The Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsDocument6 pagesThe Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsEight AlykNo ratings yet
- 2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFDocument10 pages2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFammarNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 - Motion and Force - DynamicsDocument24 pagesChapter 04 - Motion and Force - DynamicsMohamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Orchid Group of Companies Company ProfileDocument3 pagesOrchid Group of Companies Company ProfileAngelica Nicole TamayoNo ratings yet
- Productstock 2021-01-18 (Produk Laku & Belum KinwatchDocument32 pagesProductstock 2021-01-18 (Produk Laku & Belum KinwatchKin WatchNo ratings yet
- CS 2400 - 2500 BrochureDocument8 pagesCS 2400 - 2500 BrochureOo Kenx OoNo ratings yet
- 4148-Article Text-14752-1-10-20211029Document7 pages4148-Article Text-14752-1-10-20211029Daffa AzkaNo ratings yet
- Cultures of The West A History, Volume 1 To 1750 3rd PDFDocument720 pagesCultures of The West A History, Volume 1 To 1750 3rd PDFtonnyNo ratings yet
- Smartpilot s1 s1g Service ManualDocument30 pagesSmartpilot s1 s1g Service Manualmalte winbaldNo ratings yet
- Definite NessDocument398 pagesDefinite NessKbraNo ratings yet
- Case Study-BPPVDocument97 pagesCase Study-BPPVArbie Jacinto83% (6)
- WCDMA19 Prfile Descriptions W19P8 08A APPRDocument254 pagesWCDMA19 Prfile Descriptions W19P8 08A APPRoaguilar83No ratings yet
- Tes - 29 October 2021 UserUploadNetDocument120 pagesTes - 29 October 2021 UserUploadNetTran Nhat QuangNo ratings yet
- CV (Martin A Johnson)Document7 pagesCV (Martin A Johnson)kganesanNo ratings yet
- Javascript PrefiDocument66 pagesJavascript Prefiguendelyn omegaNo ratings yet
- Semi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksDocument75 pagesSemi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksPei Cheng WuNo ratings yet
- 10 Day Penniman Chart - Literacy NarrativesDocument5 pages10 Day Penniman Chart - Literacy Narrativesapi-502300054No ratings yet
- Wincam TornoDocument3 pagesWincam Tornocaballerillo100% (1)
- Case AnalyzerDocument19 pagesCase AnalyzeranuragNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemDung Nguyễn Thị MỹNo ratings yet
- Installation ManualDocument16 pagesInstallation ManualJosé Manuel García MartínNo ratings yet
- Manual de Caja Eaton Fuller ET20113Document22 pagesManual de Caja Eaton Fuller ET20113Juan Gomez100% (3)
- Social and Professional Issues Pf2Document4 pagesSocial and Professional Issues Pf2DominicOrtegaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument15 pagesSeminar ReportNipesh MAHARJANNo ratings yet